OC-本地化操作(序列化,归档)
2014-01-23 15:44
218 查看
先介绍一个自定义类描述的方法description,一般情况下,一个自定义类我们在用%@输出的时候,给出的是一个内存地址,我们在该类的.m文件里重写description方法,来修改输出内容,呆会儿我们要用到这个方法来验证今天学习内容,所以先看一段代码熟悉一下:
Human.h:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Human : NSObject
{
int age;
NSString *name;
Human *child;
}
@property int age;
@property (copy)NSString *name;
@property (retain)Human *child;
@end
Human.m:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import "Human.h"
@implementation Human
@synthesize age;
@synthesize name;
@synthesize child;
//-(NSString *)description
//{
// NSString *des = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d,%@,%@",age,name,child];
// return des;
//}
@end
上面的重写描述被注释掉了,我们先看未修改前的输出:
main.m:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Human.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
Human *human1=[[Human alloc]init];
Human *human2=[[Human alloc]init];
human1.child=human2;
human1.name=@"holydancer";
human1.age=22;
NSLog(@"%@",human1);
}
return 0;
}
2012-03-20 08:47:32.980 category[304:403] <Human: 0x7ff2cb414380>
如果把human.m中的注释去掉的话输出结果如下:
2012-03-20 08:48:09.869 category[315:403] 22,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
很简单吧,这样就可以查看自己定义类的内容了,好了,下面就让我们来研究一下在objective-c中如何实现序列化。
在OC中,有四类对象是可以直接使用writeToFile方法将内容写入磁盘的,分别是NSString,NSArray,NSDictionary,NSData.看代码:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Human.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
NSData *data=[[NSData alloc]init];
NSString *string=[[NSString alloc]init];
NSArray *array=[[NSArray alloc]init];
NSDictionary *dictionary=[[NSDictionary alloc]init];
[data writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/text1.txt" atomically:YES];
[string writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/text2.txt" atomically:YES];
[array writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/text3.txt" atomically:YES];
[dictionary writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/text4.txt" atomically:YES];
//atomically参数是指是否将写入文件的内容开启保护机制,如果开启,会在复制时创建临时文件进行复制,以免写入失败破坏原始文件。安全,但是会消耗内存。
//上面的文件地址,如果不存在的话会自动生成。有的话会覆盖原有文件内容。
}
return 0;
}

以上四种是COCOA自带可以写入磁盘文件的类型,但是我们常常用到自定义类,可是里面并没有writeToFile方法,怎么办呢?这时NSData的作用就体现出来了,我们可以把任意自定义类转化成NSData格式即可,这个过程我们称之为编码,或者archive归档,需要将自定义类实现NSCoding协议并重写encodeWithCoder和initWithCoder两个方法,分别用以编码和反编码。然后在编码时会用NSCoder的子类NSKeyedArchiver和NSKeyedUnarchiver分别调用archivedDataWithRootObject和unarchiveObjectWithData来启动自定义类中重写的那两个方法,类似于回调。看代码:
Human.h:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Human : NSObject<NSCoding>
{
int age;
NSString *name;
Human *child;
}
@property int age;
@property (copy)NSString *name;
@property (retain)Human *child;
@end
Human.m:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import "Human.h"
@implementation Human
@synthesize age;
@synthesize name;
@synthesize child;
-(NSString *)description
{
NSString *des = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d,%@,%@",age,name,child];
return des;
}
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder//要一一对应
{
[aCoder encodeInt:age forKey:@"age"];
[aCoder encodeObject:name forKey:@"name"];
[aCoder encodeObject:child forKey:@"child"];
}
-(id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder//和上面对应
{
if (self=[super init]) {
self.age=[aDecoder decodeIntForKey:@"age"];
self.name=[aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"];
self.child=[aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"child"];
}
return self;
}
@end
main.m:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Human.h"
#import <Foundation/NSKeyedArchiver.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
Human *human1=[[Human alloc]init];
Human *human2=[[Human alloc]init];
human1.age=20;
human1.name=@"holydancer";
human1.child=human2;
//定义好自定义对象后使用NSCoding的子类调用archivedDataWithRootObject方法进行archive
NSData *data1=[NSKeyedArchiver archivedDataWithRootObject:human1];
//转成NSData类型后就可以写入本地磁盘了
[data1 writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/tmp.txt" atomically:YES];
//倒过来的话先读取磁盘文件
NSData *data2=[NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/tmp.txt"];
Human *human3=[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithData:data2];
NSLog(@"%@,%@",human1,human3);
}
return 0;
}
2012-03-20 10:10:29.871 category[458:403]
20,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
20,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
有的同学一直不太清楚NSKeyedArchiver和NSKeyedUnarchiver是什么,调用的又是什么方法,大家可以在头文件里找到这样的信息:
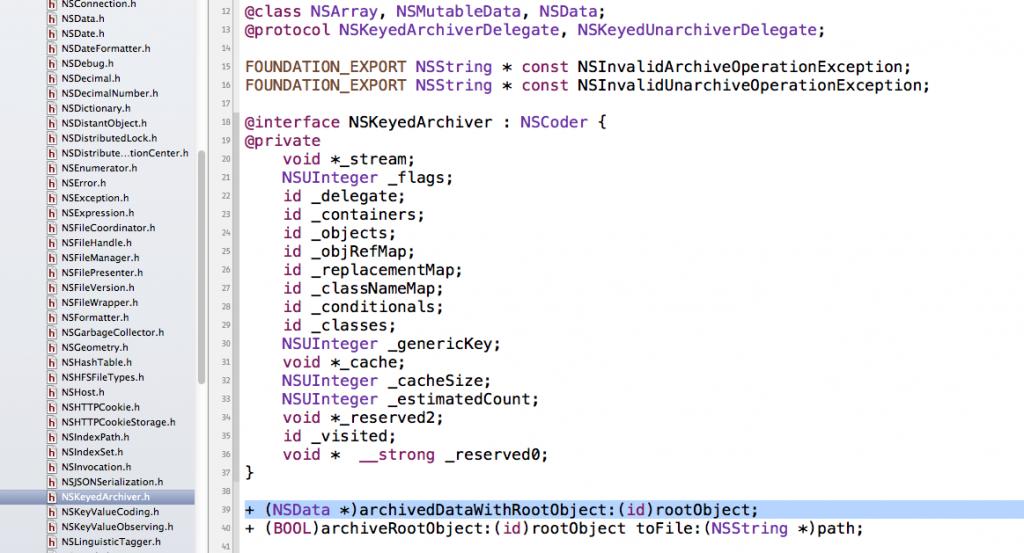
可以发现,NSKeyedArchiver是NSCoder的子类,而archivedDataWithRootObject是里面的一个类方法,这时我们看到archivedDataWithRootObject方法下在还有一个方法,不错,这个方法可以直接将自定义类写入本地磁盘,所以上在的代码我们还可以这样写:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Human.h"
#import <Foundation/NSKeyedArchiver.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
Human *human1=[[Human alloc]init];
Human *human2=[[Human alloc]init];
human1.age=20;
human1.name=@"holydancer";
human1.child=human2;
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:human1 toFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/tmp.txt"];//直接写入磁盘
Human *human3=[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/tmp.txt"];//从磁盘直接读取为id类型
NSLog(@"\n%@\n%@",human1,human3);
}
return 0;
}
2012-03-20 10:16:43.561 category[475:403]
20,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
20,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
最后,不得不说说cocoa中的方法命名,一个一个方法长得,虽然很人性化很好记,不过敲起来真是麻烦啊。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/holydancer/article/details/7371643
Human.h:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Human : NSObject
{
int age;
NSString *name;
Human *child;
}
@property int age;
@property (copy)NSString *name;
@property (retain)Human *child;
@end
Human.m:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import "Human.h"
@implementation Human
@synthesize age;
@synthesize name;
@synthesize child;
//-(NSString *)description
//{
// NSString *des = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d,%@,%@",age,name,child];
// return des;
//}
@end
上面的重写描述被注释掉了,我们先看未修改前的输出:
main.m:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Human.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
Human *human1=[[Human alloc]init];
Human *human2=[[Human alloc]init];
human1.child=human2;
human1.name=@"holydancer";
human1.age=22;
NSLog(@"%@",human1);
}
return 0;
}
2012-03-20 08:47:32.980 category[304:403] <Human: 0x7ff2cb414380>
如果把human.m中的注释去掉的话输出结果如下:
2012-03-20 08:48:09.869 category[315:403] 22,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
很简单吧,这样就可以查看自己定义类的内容了,好了,下面就让我们来研究一下在objective-c中如何实现序列化。
在OC中,有四类对象是可以直接使用writeToFile方法将内容写入磁盘的,分别是NSString,NSArray,NSDictionary,NSData.看代码:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Human.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
NSData *data=[[NSData alloc]init];
NSString *string=[[NSString alloc]init];
NSArray *array=[[NSArray alloc]init];
NSDictionary *dictionary=[[NSDictionary alloc]init];
[data writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/text1.txt" atomically:YES];
[string writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/text2.txt" atomically:YES];
[array writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/text3.txt" atomically:YES];
[dictionary writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/text4.txt" atomically:YES];
//atomically参数是指是否将写入文件的内容开启保护机制,如果开启,会在复制时创建临时文件进行复制,以免写入失败破坏原始文件。安全,但是会消耗内存。
//上面的文件地址,如果不存在的话会自动生成。有的话会覆盖原有文件内容。
}
return 0;
}

以上四种是COCOA自带可以写入磁盘文件的类型,但是我们常常用到自定义类,可是里面并没有writeToFile方法,怎么办呢?这时NSData的作用就体现出来了,我们可以把任意自定义类转化成NSData格式即可,这个过程我们称之为编码,或者archive归档,需要将自定义类实现NSCoding协议并重写encodeWithCoder和initWithCoder两个方法,分别用以编码和反编码。然后在编码时会用NSCoder的子类NSKeyedArchiver和NSKeyedUnarchiver分别调用archivedDataWithRootObject和unarchiveObjectWithData来启动自定义类中重写的那两个方法,类似于回调。看代码:
Human.h:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Human : NSObject<NSCoding>
{
int age;
NSString *name;
Human *child;
}
@property int age;
@property (copy)NSString *name;
@property (retain)Human *child;
@end
Human.m:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import "Human.h"
@implementation Human
@synthesize age;
@synthesize name;
@synthesize child;
-(NSString *)description
{
NSString *des = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d,%@,%@",age,name,child];
return des;
}
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder//要一一对应
{
[aCoder encodeInt:age forKey:@"age"];
[aCoder encodeObject:name forKey:@"name"];
[aCoder encodeObject:child forKey:@"child"];
}
-(id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder//和上面对应
{
if (self=[super init]) {
self.age=[aDecoder decodeIntForKey:@"age"];
self.name=[aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"];
self.child=[aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"child"];
}
return self;
}
@end
main.m:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Human.h"
#import <Foundation/NSKeyedArchiver.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
Human *human1=[[Human alloc]init];
Human *human2=[[Human alloc]init];
human1.age=20;
human1.name=@"holydancer";
human1.child=human2;
//定义好自定义对象后使用NSCoding的子类调用archivedDataWithRootObject方法进行archive
NSData *data1=[NSKeyedArchiver archivedDataWithRootObject:human1];
//转成NSData类型后就可以写入本地磁盘了
[data1 writeToFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/tmp.txt" atomically:YES];
//倒过来的话先读取磁盘文件
NSData *data2=[NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/tmp.txt"];
Human *human3=[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithData:data2];
NSLog(@"%@,%@",human1,human3);
}
return 0;
}
2012-03-20 10:10:29.871 category[458:403]
20,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
20,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
有的同学一直不太清楚NSKeyedArchiver和NSKeyedUnarchiver是什么,调用的又是什么方法,大家可以在头文件里找到这样的信息:

可以发现,NSKeyedArchiver是NSCoder的子类,而archivedDataWithRootObject是里面的一个类方法,这时我们看到archivedDataWithRootObject方法下在还有一个方法,不错,这个方法可以直接将自定义类写入本地磁盘,所以上在的代码我们还可以这样写:
[plain] view
plaincopy
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Human.h"
#import <Foundation/NSKeyedArchiver.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
@autoreleasepool {
Human *human1=[[Human alloc]init];
Human *human2=[[Human alloc]init];
human1.age=20;
human1.name=@"holydancer";
human1.child=human2;
[NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:human1 toFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/tmp.txt"];//直接写入磁盘
Human *human3=[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:@"/Users/holydancer/Desktop/tmp.txt"];//从磁盘直接读取为id类型
NSLog(@"\n%@\n%@",human1,human3);
}
return 0;
}
2012-03-20 10:16:43.561 category[475:403]
20,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
20,holydancer,0,(null),(null)
最后,不得不说说cocoa中的方法命名,一个一个方法长得,虽然很人性化很好记,不过敲起来真是麻烦啊。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/holydancer/article/details/7371643
相关文章推荐
- 老生长谈,使用spring发送mail
- Count and Say
- jetty Remember
- 《信息可视化的艺术:信息可视化在英国》
- springmvc拦截过滤静态资源的一种方法
- Spring MVC 框架搭建及详解
- mysql的binlog日志删除查询
- win7系统红警2怎么全屏?
- 软件设计是怎样炼成的(1)——什么是优秀的设计?
- php弹出对话框实现重定向代码
- win7上搭建hadoop开发环境
- ActiveMQ 远程监控JMX设置
- firebug调试
- JSON转换
- jQuery $.isNumeric vs. $.isNaN vs. isNaN
- 远程 不显示本地硬盘解决办法(高级版)
- 远程 不显示本地硬盘解决办法(高级版)
- Push Button Web Hosting
- 谷歌地图地理解析和反解析geocode.geocoder详解
- Shell 小技巧的问题 mysql -e ,字符串替换telnet命令检测
