Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
2013-12-08 02:38
411 查看
【转】Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
面对这么复杂一个Android显示系统,如何入手呢? 根据以前的经验,不管它有多么复杂,其功能不就是以下三步曲吗?
1)显示系统的创建及初始化
2)画图
3)销毁
哪我的分析就从显示系统的创建及初始化开始吧!由于小弟对Java没有什么研究兴趣,所有重点就分析Native部分。当然Native的入口就在android_view_Surface.cpp中,此文件主要包含以下两部分给Java层调用:
1)gSurfaceSessionMethods: 操作SurfaceSession的方法
2)gSurfaceMethods:操作Surface的方法
view plaincopy
static JNINativeMethod gSurfaceSessionMethods[] = {
{"init", "()V", (void*)SurfaceSession_init }, //创建SurfaceComposerClient
{"destroy", "()V", (void*)SurfaceSession_destroy }, //直接销毁SurfaceComposerClient
{"kill", "()V", (void*)SurfaceSession_kill },//先clear,再销毁SurfaceComposerClient
};
1)创建SurfaceComposerClient对象
2)调用SurfaceComposerClient::onFirstRef方法
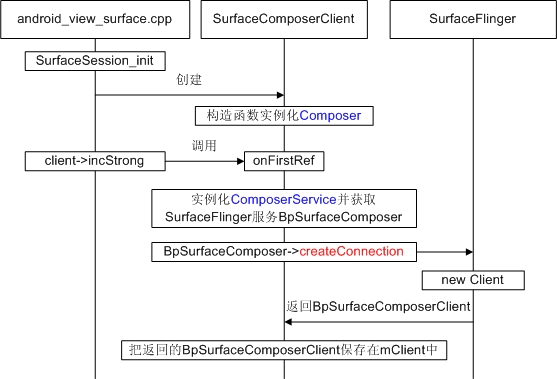
现在已经进入到SurfaceComposerClient的地盘,根据其名字含义,它应该是一个进行Surface合成的客户端,通过它发命令给SurfaceFlinger来进行需要的操作。其初始化流程如下图所示:
2.1.2.1 ComposerService(获取SurfaceFlinger服务)
一看到名字为Service,应该是用于从SurfaceFlinger中获取Service以建立连接关系<它是一个单实例,一个进程有且只有一个实例对象>,然后供后面进行相关的操作。其构造函数代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class ComposerService : public Singleton<ComposerService>
{
//实质为BpSurfaceComposer,通过它与SurfaceFlinger进行通信,
//BnSurfaceComposer是SurfaceFlinger基类中的一个
sp<ISurfaceComposer> mComposerService;
//实质为BpMemoryHeap,它在SurfaceFlinger中对应为管理一个4096字节的
//一个MemoryHeapBase对象,在SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun中创建
sp<IMemoryHeap> mServerCblkMemory;
//为MemoryHeapBase管理的内存在用户空间的基地址,通过mmap而来,
//具体见MemoryHeapBase::mapfd
surface_flinger_cblk_t volatile* mServerCblk;
ComposerService();
friend class Singleton<ComposerService>;
public:
static sp<ISurfaceComposer> getComposerService();
static surface_flinger_cblk_t const volatile * getControlBlock();
};
ComposerService::ComposerService()
: Singleton<ComposerService>() {
const String16 name("SurfaceFlinger");
//获取SurfaceFlinger服务,即BpSurfaceComposer对象
while (getService(name, &mComposerService) != NO_ERROR) {
usleep(250000);
}
//获取共享内存块
mServerCblkMemory = mComposerService->getCblk();
//获取共享内存块基地址
mServerCblk = static_cast<surface_flinger_cblk_t volatile *>(
mServerCblkMemory->getBase());
}
由此可见,ComposerService主要是获取SurfaceFlinger服务、获取在SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun中创建的共享内存块及其基地址。在Client中,谁要想与SurfaceFlinger通信,需要通过接口getComposerService来获取此BpSurfaceComposer。
此ComposerService是在调用ComposerService::getInstance时进行有且只有一个的实例化,因为前面讲过,它是一个单实例。
2.1.2.2 Composer
它也是一个单实例,管理并发送每个layer的ComposerState。其定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct ComposerState {
sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> client;
layer_state_t state;
status_t write(Parcel& output) const;
status_t read(const Parcel& input);
};
class Composer : public Singleton<Composer>
{
friend class Singleton<Composer>;
mutable Mutex mLock;
//SurfaceComposerClient+SurfaceID与一个ComposerState一一对应
SortedVector<ComposerState> mStates;
int mOrientation;//整个屏幕的方向
Composer() : Singleton<Composer>(),
mOrientation(ISurfaceComposer::eOrientationUnchanged) { }
//通过BpSurfaceComposer把mStates发送给SurfaceFlinger处理
void closeGlobalTransactionImpl();
//根据client和id从mStates中获取对应原ComposerState,从而获取对应的layer_state_t
layer_state_t* getLayerStateLocked(
4000
const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id);
public:
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的位置信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setPosition(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
float x, float y);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的Size信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setSize(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
uint32_t w, uint32_t h);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的z-order信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setLayer(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
int32_t z);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的flags信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setFlags(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
uint32_t flags, uint32_t mask);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的透明区域信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setTransparentRegionHint(
const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
const Region& transparentRegion);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的alpha信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setAlpha(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
float alpha);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的矩阵信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setMatrix(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
float dsdx, float dtdx, float dsdy, float dtdy);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的位置信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setFreezeTint(
const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
uint32_t tint);
//设置整个屏幕的方向
status_t setOrientation(int orientation);
//通过BpSurfaceComposer把mStates发送给SurfaceFlinger处理
static void closeGlobalTransaction() {
Composer::getInstance().closeGlobalTransactionImpl();
}
}
把上面的comments看完就明白了,Composer管理每个SurfaceComposerClient中的每一个Surface的状态,并记录在ComposerState的layer_state_t中,然后调用者可以调用其closeGlobalTransaction方法把这些mStates发送给SurfaceFlinger处理(处理函数为:SurfaceFlinger::setTransactionState)。
谁来调用它的方法设置层的属性及发送mStates呢? -----答案是由SurfaceComposerClient来调用。
2.1.2.3 SurfaceComposerClient
前面介绍的两个类一个用于获取SurfaceFlinger服务;一个 用于记录每个Layer的状态,且可按要求把这些CoposerState发送给SurfaceFlinger。这个类是不是来使用前面两个类提供的服务 呢? --答案是肯定的。其定义及详细注释如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
#define NUM_DISPLAY_MAX 4 //最多支持四个显示屏
struct display_cblk_t //每个显示屏的配置参数
{
uint16_t w;
uint16_t h;
uint8_t format;
uint8_t orientation;
uint8_t reserved[2];
float fps;
float density;
float xdpi;
float ydpi;
uint32_t pad[2];
};
//在SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun中创建的共享控制块
struct surface_flinger_cblk_t // 4KB max,管理系统中所有的显示屏
{
uint8_t connected; //每一个bit表示一个显示屏
uint8_t reserved[3];
uint32_t pad[7];
display_cblk_t displays[NUM_DISPLAY_MAX];
};
class SurfaceComposerClient : public RefBase
{
friend class Composer;
public:
//获取Composer实例,并保存在mComposer中
SurfaceComposerClient();
virtual ~SurfaceComposerClient();
//通过BpSurfaceComposerClient<mClient>创建Surface,
//同时通过ISurfaceComposerClient::surface_data_t返回SurfaceID.然后创建一个SurfaceControl
//并把返回的BpSurface和当前的SurfaceComposerClient保存在SurfaceControl中,
//然后返回此SurfaceControl
sp<SurfaceControl> createSurface(
const String8& name,// name of the surface
DisplayID display, // Display to create this surface on
uint32_t w, // width in pixel
uint32_t h, // height in pixel
PixelFormat format, // pixel-format desired
uint32_t flags = 0 // usage flags
);
// Composer parameters <合成参数>
//所有的合成参数必须在一个transaction中被修改,多个surface可在一个transaction中被更新,
//所有的变化在关闭transaction时被一次性提交(通过调用closeGlobalTransaction来提交所有变化)。
//什么都没有做
static void openGlobalTransaction();
//通过调用Composer::closeGlobalTransaction(),
// 把Composer中记录的ComposerState(即mStates)发送给SurfaceFlinger
static void closeGlobalTransaction();
//什么都没做
static status_t freezeDisplay(DisplayID dpy, uint32_t flags = 0);
//什么都没做
static status_t unfreezeDisplay(DisplayID dpy, uint32_t flags = 0);
//把新的显示方向保存在Composer实例中
static int setOrientation(DisplayID dpy, int orientation, uint32_t flags);
//从surface_flinger_cblk_t.connected中获取显示屏个数
static ssize_t getNumberOfDisplays();
//获取显示屏的信息
static status_t getDisplayInfo(DisplayID dpy, DisplayInfo* info);
static ssize_t getDisplayWidth(DisplayID dpy);
static ssize_t getDisplayHeight(DisplayID dpy);
static ssize_t getDisplayOrientation(DisplayID dpy);
//通过注册,当Binder异常退出时,可以获得通知
status_t linkToComposerDeath(const sp<IBinder::DeathRecipient>& recipient,
void* cookie = NULL, uint32_t flags = 0);
//Start####: 以下函数都是把相应的修改状态记录在Composer的mStates中
//调用Composer::setFlags来设置对应(client+id)的layer状态〈即ComposerState中的layer_state_t〉
status_t hide(SurfaceID id);
status_t show(SurfaceID id, int32_t layer = -1);
status_t freeze(SurfaceID id);
status_t unfreeze(SurfaceID id);
status_t setFlags(SurfaceID id, uint32_t flags, uint32_t mask);
//调用Composer::setTransparentRegionHint
status_t setTransparentRegionHint(SurfaceID id, const Region& transparent);
//调用Composer::setLayer
status_t setLayer(SurfaceID id, int32_t layer);
//调用Composer::setAlpha
status_t setAlpha(SurfaceID id, float alpha=1.0f);
//调用Composer::setFreezeTint
status_t setFreezeTint(SurfaceID id, uint32_t tint);
//调用Composer::setMatrix
status_t setMatrix(SurfaceID id, float dsdx, float dtdx, float dsdy, float dtdy);
//调用Composer::setPosition
status_t setPosition(SurfaceID id, float x, float y);
//调用Composer::setSize
status_t setSize(SurfaceID id, uint32_t w, uint32_t h);
//End####:
status_t destroySurface(SurfaceID sid);//通过BpSurfaceComposerClient销毁Surface
private:
//通过BpSurfaceComposer从SurfaceFlinger获取BpSurfaceComposerClient,
//并把它保存在mClient中
virtual void onFirstRef();
Composer& getComposer();
mutable Mutex mLock;
status_t mStatus;
//实质为BpSurfaceComposerClient,与SurfaceFlinger.cpp中的Client相对应
sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> mClient;
//Composer实例
Composer& mComposer;
}
其功能列表如下:
1)获取BpSurfaceComposerClient(即mClient),在onFirstRef中实现
2)通过BpSurfaceComposerClient(即mClient)创建和销毁Surface
3)通过Composer来记录Surface和显示屏状态变化,及在Composer中通过BpSurfaceComposer把状态变化发给SurfaceFlinger处理
至此,SurfaceComposerClient功能已经分析清楚。可是从这三个类中,我们已经看到三个 Bp(BpSurfaceComposer,BpSurfaceComposerClient和BpSurface)及三个对应的接口。下面总结一下,每 个接口的功能,在客户端由谁使用,在服务器端谁来实现。
2.1.2.4 Surface相关接口总结

[cpp]
view plaincopy
static JNINativeMethod gSurfaceMethods[] = {
{"nativeClassInit", "()V", (void*)nativeClassInit },
{"init", "(Landroid/view/SurfaceSession;ILjava/lang/String;IIIII)V", (void*)Surface_init },
{"init", "(Landroid/os/Parcel;)V", (void*)Surface_initParcel },
{"initFromSurfaceTexture", "(Landroid/graphics/SurfaceTexture;)V", (void*)Surface_initFromSurfaceTexture },
{"getIdentity", "()I", (void*)Surface_getIdentity },
{"destroy", "()V", (void*)Surface_destroy },
{"release", "()V", (void*)Surface_release },
{"copyFrom", "(Landroid/view/Surface;)V", (void*)Surface_copyFrom },
{"isValid", "()Z", (void*)Surface_isValid },
{"lockCanvasNative", "(Landroid/graphics/Rect;)Landroid/graphics/Canvas;", (void*)Surface_lockCanvas },
{"unlockCanvasAndPost", "(Landroid/graphics/Canvas;)V", (void*)Surface_unlockCanvasAndPost },
{"unlockCanvas", "(Landroid/graphics/Canvas;)V", (void*)Surface_unlockCanvas },
{"openTransaction", "()V", (void*)Surface_openTransaction },
{"closeTransaction", "()V", (void*)Surface_closeTransaction },
{"setOrientation", "(III)V", (void*)Surface_setOrientation },
{"freezeDisplay", "(I)V", (void*)Surface_freezeDisplay },
{"unfreezeDisplay", "(I)V", (void*)Surface_unfreezeDisplay },
{"screenshot", "(II)Landroid/graphics/Bitmap;", (void*)Surface_screenshotAll },
{"screenshot", "(IIII)Landroid/graphics/Bitmap;", (void*)Surface_screenshot },
{"setLayer", "(I)V", (void*)Surface_setLayer },
{"setPosition", "(FF)V",(void*)Surface_setPosition },
{"setSize", "(II)V",(void*)Surface_setSize },
{"hide", "()V", (void*)Surface_hide },
{"show", "()V", (void*)Surface_show },
{"freeze", "()V", (void*)Surface_freeze },
{"unfreeze", "()V", (void*)Surface_unfreeze },
{"setFlags", "(II)V",(void*)Surface_setFlags },
{"setTransparentRegionHint","(Landroid/graphics/Region;)V", (void*)Surface_setTransparentRegion },
{"setAlpha", "(F)V", (void*)Surface_setAlpha },
{"setMatrix", "(FFFF)V", (void*)Surface_setMatrix },
{"setFreezeTint", "(I)V", (void*)Surface_setFreezeTint },
{"readFromParcel", "(Landroid/os/Parcel;)V", (void*)Surface_readFromParcel },
{"writeToParcel", "(Landroid/os/Parcel;I)V", (void*)Surface_writeToParcel },
};
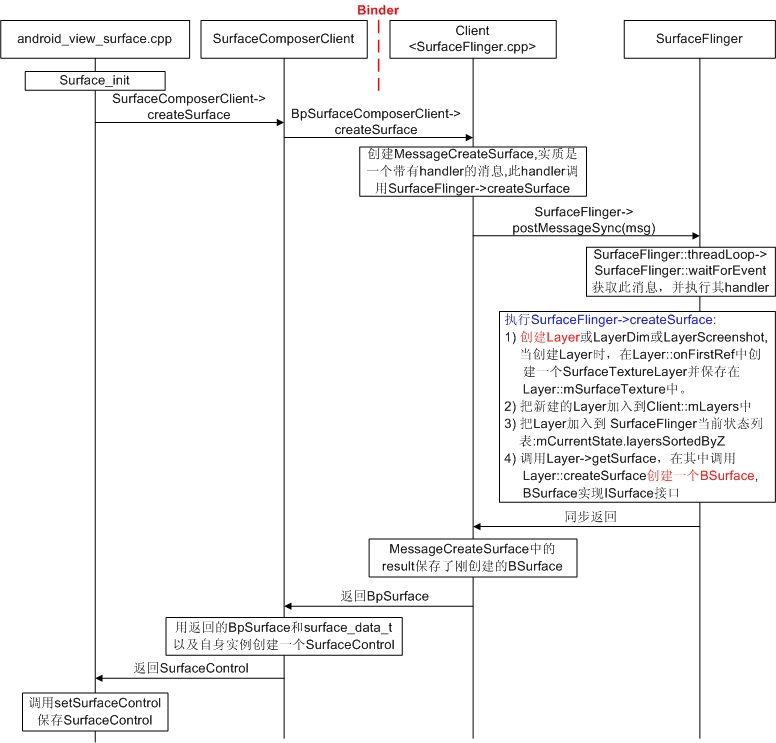
在SurfaceFlinger端创建BSurface,在客户端返回SurfaceControl,同时在SurfaceControl中拥有了BpSurface用于与BSurface交互。
其中token在SurfaceComposerClient的函数参数中,对应于SurfaceID。即在客户端,它就是SurfaceID。
token: 加入到Client::mLayers中的序号,在Client中单调递增,初始值为:1,一个Layer创建一个BSurface
identity: LayerBaseClient中的mIdentity,在所有的Layer中单调递增,初始值为:1
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct surface_data_t {
int32_t token; //加入到Client::mLayers中的序号,在Client中单调递增,初始值为:1
int32_t identity; //LayerBaseClient中的mIdentity,在所有的Layer中单调递增,初始值为:1
status_t readFromParcel(const Parcel& parcel);
status_t writeToParcel(Parcel* parcel) const;
};
2.2.1.2 创建真正的Surface
在Layer::createSurface中创建真正的BSurface,在SurfaceFlinger::createSurface中调用layer->getSurface时创建的。此BSurface定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
sp<ISurface> Layer::createSurface()
{
class BSurface : public BnSurface, public LayerCleaner {
wp<const Layer> mOwner;
virtual sp<ISurfaceTexture> getSurfaceTexture() const { //实现了ISurface的接口
sp<ISurfaceTexture> res;
sp<const Layer> that( mOwner.promote() );
if (that != NULL) {
res = that->mSurfaceTexture;
}
return res;
}
public:
BSurface(const sp<SurfaceFlinger>& flinger,
const sp<Layer>& layer)
: LayerCleaner(flinger, layer), mOwner(layer) { }
};
sp<ISurface> sur(new BSurface(mFlinger, this));
return sur;
}
在此BSurface中实现了ISurface的接口getSurfaceTexture,在此接口中返回 Layer::mSurfaceTexture(类型为:SurfaceTextureLayer,它才是真正操作内存的东东),此成员在 Layer::onFirstRef中创建,SurfaceTextureLayer是SurfaceTexture的派生类,代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
void Layer::onFirstRef()
{
LayerBaseClient::onFirstRef();
struct FrameQueuedListener : public SurfaceTexture::FrameAvailableListener {
FrameQueuedListener(Layer* layer) : mLayer(layer) { }
private:
wp<Layer> mLayer;
virtual void onFrameAvailable() {
sp<Layer> that(mLayer.promote());
if (that != 0) {
that->onFrameQueued();
}
}
};
mSurfaceTexture = new SurfaceTextureLayer(mTextureName, this); //创建Layer中的mSurfaceTexture
mSurfaceTexture->setFrameAvailableListener(new FrameQueuedListener(this));
mSurfaceTexture->setSynchronousMode(true);
mSurfaceTexture->setBufferCountServer(2);
}
2.2.1.3 不得不说的SurfaceControl
本来Surface_init调用SurfaceComposerClient::createSurface创建一个Surface,可却返回了一个SurfaceControl,下面看看SurfaceCotrol到底做了些什么,以及如何做的?
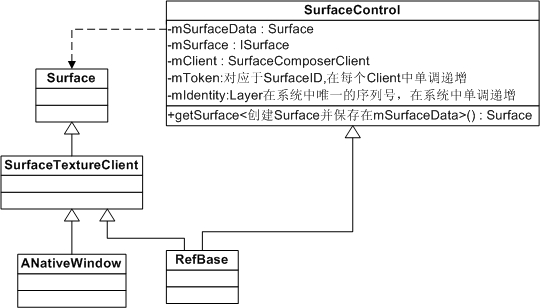
相关数据结构如下图所示:
SurfaceControl定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class SurfaceControl : public RefBase
{
public:
// release surface data from java
void clear();
//调用SurfaceComposerClient中对应方法,把对应信息保存在
//Composer的ComposerState中
status_t setLayer(int32_t layer);
status_t setPosition(int32_t x, int32_t y);
status_t setSize(uint32_t w, uint32_t h);
status_t hide();
status_t show(int32_t layer = -1);
status_t freeze();
status_t unfreeze();
status_t setFlags(uint32_t flags, uint32_t mask);
status_t setTransparentRegionHint(const Region& transparent);
status_t setAlpha(float alpha=1.0f);
status_t setMatrix(float dsdx, float dtdx, float dsdy, float dtdy);
status_t setFreezeTint(uint32_t tint);
//把SurfaceControl中的mSurface和mIdentity写入parcel
static status_t writeSurfaceToParcel(
const sp<SurfaceControl>& control, Parcel* parcel);
//以SurfaceControl为参数创建一个Surface返回,此Surface派生关系如下:
//class Surface : public SurfaceTextureClient
//class SurfaceTextureClient: public ANativeWindow, RefBase
//struct ANativeWindow
sp<Surface> getSurface() const;
private:
SurfaceControl(
const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client,
const sp<ISurface>& surface,
const ISurfaceComposerClient::surface_data_t& data);
~SurfaceControl();
void destroy();
sp<SurfaceComposerClient> mClient;
sp<ISurface> mSurface;
SurfaceID mToken; //对应SurfaceID,在Client中单调递增
uint32_t mIdentity; //Layer在系统中唯一的序列号,在系统中单调递增
mutable Mutex mLock;
mutable sp<Surface> mSurfaceData;
}
从其定义中可以看出,在getSurface中将有新花样,其它操作函数都是直接以mToken作为SurfaceID,直接调用 SurfaceComposerClient中对应方法。 经过这样一分析,SurfaceControl也没什么神秘的了。但它的getSurface 到有点神秘。
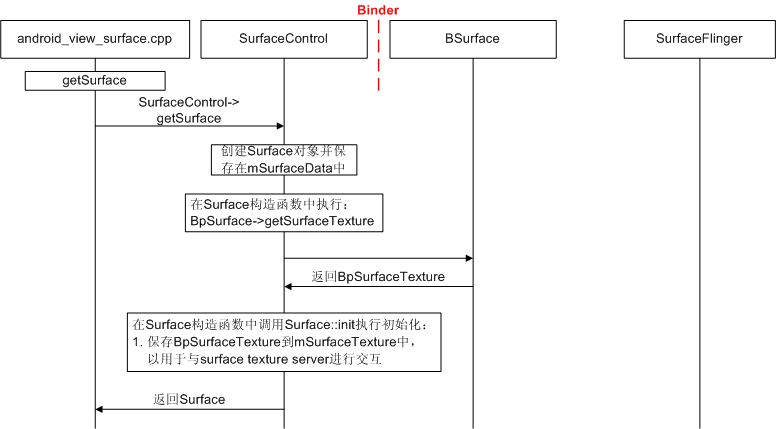
前面Surface初始化之后,就可以getSurface了。getSurface流程如下图所示:
有了Surface,且在Surface中又有了BpSurfaceTexture,下一步就操作GraphicBuffer了。
surface.lockCanvas->
lockCanvasNative(Java)->
(C++)Surface_lockCanvas<android_view_Surface.cpp>
surface.unlockCanvasAndPost(Java)->
(C++)Surface_unlockCanvasAndPost<android_view_Surface.cpp>
本章主要分析这两个函数到底做了些什么>
[cpp]
view plaincopy
typedef struct ANativeWindow_Buffer {
// The number of pixels that are show horizontally.
int32_t width;
// The number of pixels that are shown vertically.
int32_t height;
// The number of *pixels* that a line in the buffer takes in
// memory. This may be >= width.
int32_t stride;
// The format of the buffer. One of WINDOW_FORMAT_*
int32_t format;
// The actual bits.
void* bits; //显示内存基地址,通过服务器端fd通过flat_binder_object传给客户端, 然后客户端通过mmap获取。
// Do not touch.
uint32_t reserved[6];
} ANativeWindow_Buffer;
3.1.1.2 SurfaceInfo
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct SurfaceInfo {
uint32_t w;
uint32_t h;
uint32_t s;
uint32_t usage;
PixelFormat format;
void* bits;//显示内存基地址,通过服务器端fd通过flat_binder_object传给客户端, 然后客户端通过mmap获取。
uint32_t reserved[2];
};
3.1.1.3 二者对应关系
[cpp]
view plaincopy
SurfaceInfo* other;
ANativeWindow_Buffer outBuffer;
other->w = uint32_t(outBuffer.width);
other->h = uint32_t(outBuffer.height);
other->s = uint32_t(outBuffer.stride);
other->usage = GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_READ_OFTEN | GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_WRITE_OFTEN;
other->format = uint32_t(outBuffer.format);
other->bits = outBuffer.bits;
3.1.1.4 GraphicBuffer
在分析下面的流程时, 不得不对GraphicBuffer进行深入了解,特别是其Flattenable interface,这是实现画图buffer的关键。其相关定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
typedef struct native_handle
{
int version; /* sizeof(native_handle_t) */
int numFds; /* number of file-descriptors at &data[0] */
int numInts; /* number of ints at &data[numFds] */
int data[0]; /* numFds + numInts ints */
} native_handle_t;
typedef const native_handle_t* buffer_handle_t;
class GraphicBuffer
: public EGLNativeBase<
ANativeWindowBuffer,
GraphicBuffer,
LightRefBase<GraphicBuffer> >, public Flattenable
{
...
// Flattenable interface
size_t getFlattenedSize() const;
size_t getFdCount() const;
status_t flatten(void* buffer, size_t size,
int fds[], size_t count) const;
status_t unflatten(void const* buffer, size_t size,
int fds[], size_t count);
...
buffer_handle_t handle; //定义于基类ANativeWindowBuffer中
};
3.1.1.5 Flattenable interface
下面看看每个Flattenable interface是如何实现的:
3.1.1.5.1 getFlattenedSize
[cpp]
view plaincopy
size_t GraphicBuffer::getFlattenedSize() const {
return (8 + (handle ? handle->numInts : 0))*sizeof(int);
}
3.1.1.5.2 getFdCount
[cpp]
view plaincopy
size_t GraphicBuffer::getFdCount() const {
return handle ? handle->numFds : 0;
}
3.1.1.5.3 flatten
[cpp]
view plaincopy
status_t GraphicBuffer::flatten(void* buffer, size_t size,
int fds[], size_t count) const
{
size_t sizeNeeded = GraphicBuffer::getFlattenedSize();
if (size < sizeNeeded) return NO_MEMORY;
size_t fdCountNeeded = GraphicBuffer::getFdCount();
if (count < fdCountNeeded) return NO_MEMORY;
int* buf = static_cast<int*>(buffer);
buf[0] = 'GBFR';
buf[1] = width;
buf[2] = height;
buf[3] = stride;
buf[4] = format;
buf[5] = usage;
buf[6] = 0;
buf[7] = 0;
if (handle) {
buf[6] = handle->numFds;
buf[7] = handle->numInts;
native_handle_t const* const h = handle;
memcpy(fds, h->data, h->numFds*sizeof(int));
memcpy(&buf[8], h->data + h->numFds, h->numInts*sizeof(int));
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
把handle中的numFds拷贝到fds中,把handle中的numInts拷贝到buffer中。
3.1.1.5.4 unflatten
[cpp]
view plaincopy
status_t GraphicBuffer::unflatten(void const* buffer, size_t size,
int fds[], size_t count)
{
if (size < 8*sizeof(int)) return NO_MEMORY;
int const* buf = static_cast<int const*>(buffer);
if (buf[0] != 'GBFR') return BAD_TYPE;
const size_t numFds = buf[6];
const size_t numInts = buf[7];
const size_t sizeNeeded = (8 + numInts) * sizeof(int);
if (size < sizeNeeded) return NO_MEMORY;
size_t fdCountNeeded = 0;
if (count < fdCountNeeded) return NO_MEMORY;
if (handle) {
// free previous handle if any
free_handle();
}
if (numFds || numInts) {
width = buf[1];
height = buf[2];
stride = buf[3];
format = buf[4];
usage = buf[5];
native_handle* h = native_handle_create(numFds, numInts);
memcpy(h->data, fds, numFds*sizeof(int));
memcpy(h->data + numFds, &buf[8], numInts*sizeof(int));
handle = h;
} else {
width = height = stride = format = usage = 0;
handle = NULL;
}
mOwner = ownHandle;
if (handle != 0) {
mBufferMapper.registerBuffer(handle);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
把width,height,stride,format和usage保存到成员变量中,并创建一个native_handle,然后把numFds和 numInts拷贝到handle的data中。同时把此handle注册到mBufferMapper中,mBufferMapper的注册函数实现代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
status_t GraphicBufferMapper::registerBuffer(buffer_handle_t handle)
{
status_t err;
//gralloc_module_t const *mAllocMod;是一个硬件抽象层实现。通过hw_get_module(GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module)方式获取
err = mAllocMod->registerBuffer(mAllocMod, handle);
LOGW_IF(err, "registerBuffer(%p) failed %d (%s)",
handle, err, strerror(-err));
return err;
}
[cpp]
view plaincopy
GraphicBufferMapper::GraphicBufferMapper()
: mAllocMod(0)
{
hw_module_t const* module;
int err = hw_get_module(GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module);
LOGE_IF(err, "FATAL: can't find the %s module", GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID);
if (err == 0) {
mAllocMod = (gralloc_module_t const *)module;
}
}
3.1.1.5.4 GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID实例
对于GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,以hardware/msm7k/libgralloc/gralloc.cpp为例进行分 析。其registerBuffer实现函数:gralloc_register_buffer(hardware/msm7k/libgralloc /mapper.cpp),其相关代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
int gralloc_register_buffer(gralloc_module_t const* module,
buffer_handle_t handle)
{
if (private_handle_t::validate(handle) < 0)
return -EINVAL;
// if this handle was created in this process, then we keep it as is.
int err = 0;
private_handle_t* hnd = (private_handle_t*)handle;
if (hnd->pid != getpid()) {
hnd->base = NULL;
if (!(hnd->flags & private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_GPU)) {
void *vaddr;
err = gralloc_map(module, handle, &vaddr);
}
}
return err;
}
static int gralloc_map(gralloc_module_t const* module,
buffer_handle_t handle,
void** vaddr)
{
private_handle_t* hnd = (private_handle_t*)handle;
if (!(hnd->flags & private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_FRAMEBUFFER)) {
size_t size = hnd->size;
#if PMEM_HACK
size += hnd->offset;
#endif
void* mappedAddress = mmap(0, size,
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, hnd->fd, 0);
if (mappedAddress == MAP_FAILED) {
LOGE("Could not mmap handle %p, fd=%d (%s)",
handle, hnd->fd, strerror(errno));
hnd->base = 0;
return -errno;
}
hnd->base = intptr_t(mappedAddress) + hnd->offset;
//LOGD("gralloc_map() succeeded fd=%d, off=%d, size=%d, vaddr=%p",
// hnd->fd, hnd->offset, hnd->size, mappedAddress);
}
*vaddr = (void*)hnd->base;
return 0;
}
从gralloc_map可以看出,这个registerBuffer主要做了一件事:
1)根据handle中传过来的fd和size进行mmap映射(把kernel中的内存映射到用户空间),映射之后的地址再加上hnd->offset便获得hnd->base供后面使用。
从这里可以初步看出,这个图形buffer数据并不是真正的从client传递到server,而是在lock是从server把fd传递给client,由客户端进行mmap,然后进行使用。关于这个是怎么实现的,后面将详细分析其实现过程。
对于如何从native_handle转换为private_handle_t,且在private_handle_t中可以获取fd和offset? 看一下其数据结构和flatten的实现方式就可以得知:
native_handle:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
typedef struct native_handle
{
int version; /* sizeof(native_handle_t) */
int numFds; /* number of file-descriptors at &data[0] */
int numInts; /* number of ints at &data[numFds] */
int data[0]; /* numFds + numInts ints */
} native_handle_t;
这个data[0]是关键,虽然分配了哪么多buffer,但实质上native_handle只占了3个int.其它的数据由包含它的数据结构来解析。
private_handle_t:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct private_handle_t {
native_handle_t nativeHandle;
#endif
enum {
PRIV_FLAGS_FRAMEBUFFER = 0x00000001,
PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM = 0x00000002,
PRIV_FLAGS_USES_GPU = 0x00000004,
};
// file-descriptors
int fd;
// ints
int magic;
int flags;
int size;
int offset;
int gpu_fd; // stored as an int, b/c we don't want it marshalled
// FIXME: the attributes below should be out-of-line
int base;
int map_offset;
int pid;
#ifdef __cplusplus
static const int sNumInts = 8; //numInts在这儿明确指定
static const int sNumFds = 1; //numFds在这儿明确指定
static const int sMagic = 'gmsm';
private_handle_t(int fd, int size, int flags) :
fd(fd), magic(sMagic), flags(flags), size(size), offset(0),
base(0), pid(getpid())
{
version = sizeof(native_handle);
numInts = sNumInts;
numFds = sNumFds;
}
~private_handle_t() {
magic = 0;
}
static int validate(const native_handle* h) {
const private_handle_t* hnd = (const private_handle_t*)h;
if (!h || h->version != sizeof(native_handle) ||
h->numInts != sNumInts || h->numFds != sNumFds ||
hnd->magic != sMagic)
{
LOGE("invalid gralloc handle (at %p)", h);
return -EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
#endif
}
功能:Surface_lockCanvas获取显示buffer在本进程用户空间的地址,并据此创建一个SkBitmap给Java使用。
关键技术:BINDER_TYPE_FD类型的Binder、mmap、gralloc硬件抽象层
[cpp]
view plaincopy
const sp<GraphicBuffer>& buffer(mSlots[buf].mGraphicBuffer);
if ((buffer == NULL) ||
(uint32_t(buffer->width) != w) ||
(uint32_t(buffer->height) != h) ||
(uint32_t(buffer->format) != format) ||
((uint32_t(buffer->usage) & usage) != usage))
{
usage |= GraphicBuffer::USAGE_HW_TEXTURE;
status_t error;
sp<GraphicBuffer> graphicBuffer( //创建GraphicBuffer
mGraphicBufferAlloc->createGraphicBuffer(
w, h, format, usage, &error));
if (graphicBuffer == 0) {
ST_LOGE("dequeueBuffer: SurfaceComposer::createGraphicBuffer "
"failed");
return error;
}
if (updateFormat) {
mPixelFormat = format;
}
mSlots[buf].mGraphicBuffer = graphicBuffer;
mSlots[buf].mRequestBufferCalled = false;
if (mSlots[buf].mEglImage != EGL_NO_IMAGE_KHR) {
eglDestroyImageKHR(mSlots[buf].mEglDisplay, mSlots[buf].mEglImage);
mSlots[buf].mEglImage = EGL_NO_IMAGE_KHR;
mSlots[buf].mEglDisplay = EGL_NO_DISPLAY;
}
returnFlags |= ISurfaceTexture::BUFFER_NEEDS_REALLOCATION;
}
mGraphicBufferAlloc也是通过调用BpSurfaceComposer->createGraphicBufferAlloc而获取,它对应的服务器为SufaceFlinger中的GraphicBufferAlloc。
mGraphicBufferAlloc实质为一个BpGraphicBufferAlloc,它真正创建GraphicBuffer的代码位于GraphicBufferAlloc::createGraphicBuffer中。代码关键调用流程如下:
new GraphicBuffer(w, h, format, usage)->
initSize(w, h, reqFormat, reqUsage)->
GraphicBufferAllocator::get()->
allocator.alloc(w, h, format, reqUsage, &handle, &stride)->
返回handle,此handle为ANativeWindowBuffer成员,类型为native_handle。
GraphicBufferAllocator::alloc->
mAllocDev->alloc->
mAllocDev类型为alloc_device_t,它通过gralloc_open向
GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID获取,根据上面的实例msm7k,
它最终执行gralloc_device_open而获取gralloc_context_t.device.common,
alloc的实现函数为gralloc_alloc.
gralloc_alloc->
gralloc_alloc_buffer->
1)获取GPU内存(调用SimpleBestFitAllocator::allocate进行分配)
2)fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDONLY)获取fd
3)根据fd、size和flags创建private_handle_t,其相关代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
private_handle_t* hnd = new private_handle_t(fd, size, flags);
if (base == NULL) {...
}
} else {
private_module_t* m = reinterpret_cast<private_module_t*>(
dev->common.module);
hnd->offset = offset;
hnd->base = int(base)+offset;
hnd->gpu_fd = gpu_fd;
hnd->map_offset = m->fb_map_offset;
*pHandle = hnd;
}
出处:http://blog.csdn.net/myarrow/article/details/7180561
1. 简介
网上已经有很多兄弟对Android的显示系统做了深入解剖,很是佩服。可最近小弟在研究Android4.0时发现出入比较大,也许是Android4.0的修改比较多吧!因为小弟没有看Android4.0以前的代码。面对这么复杂一个Android显示系统,如何入手呢? 根据以前的经验,不管它有多么复杂,其功能不就是以下三步曲吗?
1)显示系统的创建及初始化
2)画图
3)销毁
哪我的分析就从显示系统的创建及初始化开始吧!由于小弟对Java没有什么研究兴趣,所有重点就分析Native部分。当然Native的入口就在android_view_Surface.cpp中,此文件主要包含以下两部分给Java层调用:
1)gSurfaceSessionMethods: 操作SurfaceSession的方法
2)gSurfaceMethods:操作Surface的方法
2. android_view_Surface.cpp
2.1 SurfaceSession操作方法
[cpp]view plaincopy
static JNINativeMethod gSurfaceSessionMethods[] = {
{"init", "()V", (void*)SurfaceSession_init }, //创建SurfaceComposerClient
{"destroy", "()V", (void*)SurfaceSession_destroy }, //直接销毁SurfaceComposerClient
{"kill", "()V", (void*)SurfaceSession_kill },//先clear,再销毁SurfaceComposerClient
};
2.1.1 SurfaceSession_init
其功能如下:1)创建SurfaceComposerClient对象
2)调用SurfaceComposerClient::onFirstRef方法
现在已经进入到SurfaceComposerClient的地盘,根据其名字含义,它应该是一个进行Surface合成的客户端,通过它发命令给SurfaceFlinger来进行需要的操作。其初始化流程如下图所示:

2.1.2 SurfaceComposerClient.cpp中的宝贝
为了方便后面的理解,先看看SurfaceComposerClient中有些什么宝贝来完成这个任务。在其中定义了如下几个类:2.1.2.1 ComposerService(获取SurfaceFlinger服务)
一看到名字为Service,应该是用于从SurfaceFlinger中获取Service以建立连接关系<它是一个单实例,一个进程有且只有一个实例对象>,然后供后面进行相关的操作。其构造函数代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class ComposerService : public Singleton<ComposerService>
{
//实质为BpSurfaceComposer,通过它与SurfaceFlinger进行通信,
//BnSurfaceComposer是SurfaceFlinger基类中的一个
sp<ISurfaceComposer> mComposerService;
//实质为BpMemoryHeap,它在SurfaceFlinger中对应为管理一个4096字节的
//一个MemoryHeapBase对象,在SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun中创建
sp<IMemoryHeap> mServerCblkMemory;
//为MemoryHeapBase管理的内存在用户空间的基地址,通过mmap而来,
//具体见MemoryHeapBase::mapfd
surface_flinger_cblk_t volatile* mServerCblk;
ComposerService();
friend class Singleton<ComposerService>;
public:
static sp<ISurfaceComposer> getComposerService();
static surface_flinger_cblk_t const volatile * getControlBlock();
};
ComposerService::ComposerService()
: Singleton<ComposerService>() {
const String16 name("SurfaceFlinger");
//获取SurfaceFlinger服务,即BpSurfaceComposer对象
while (getService(name, &mComposerService) != NO_ERROR) {
usleep(250000);
}
//获取共享内存块
mServerCblkMemory = mComposerService->getCblk();
//获取共享内存块基地址
mServerCblk = static_cast<surface_flinger_cblk_t volatile *>(
mServerCblkMemory->getBase());
}
由此可见,ComposerService主要是获取SurfaceFlinger服务、获取在SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun中创建的共享内存块及其基地址。在Client中,谁要想与SurfaceFlinger通信,需要通过接口getComposerService来获取此BpSurfaceComposer。
此ComposerService是在调用ComposerService::getInstance时进行有且只有一个的实例化,因为前面讲过,它是一个单实例。
2.1.2.2 Composer
它也是一个单实例,管理并发送每个layer的ComposerState。其定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct ComposerState {
sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> client;
layer_state_t state;
status_t write(Parcel& output) const;
status_t read(const Parcel& input);
};
class Composer : public Singleton<Composer>
{
friend class Singleton<Composer>;
mutable Mutex mLock;
//SurfaceComposerClient+SurfaceID与一个ComposerState一一对应
SortedVector<ComposerState> mStates;
int mOrientation;//整个屏幕的方向
Composer() : Singleton<Composer>(),
mOrientation(ISurfaceComposer::eOrientationUnchanged) { }
//通过BpSurfaceComposer把mStates发送给SurfaceFlinger处理
void closeGlobalTransactionImpl();
//根据client和id从mStates中获取对应原ComposerState,从而获取对应的layer_state_t
layer_state_t* getLayerStateLocked(
4000
const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id);
public:
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的位置信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setPosition(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
float x, float y);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的Size信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setSize(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
uint32_t w, uint32_t h);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的z-order信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setLayer(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
int32_t z);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的flags信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setFlags(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
uint32_t flags, uint32_t mask);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的透明区域信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setTransparentRegionHint(
const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
const Region& transparentRegion);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的alpha信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setAlpha(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
float alpha);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的矩阵信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setMatrix(const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
float dsdx, float dtdx, float dsdy, float dtdy);
//设置与client和id对应的layer_state_t中的位置信息,并保存在mStates中
status_t setFreezeTint(
const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client, SurfaceID id,
uint32_t tint);
//设置整个屏幕的方向
status_t setOrientation(int orientation);
//通过BpSurfaceComposer把mStates发送给SurfaceFlinger处理
static void closeGlobalTransaction() {
Composer::getInstance().closeGlobalTransactionImpl();
}
}
把上面的comments看完就明白了,Composer管理每个SurfaceComposerClient中的每一个Surface的状态,并记录在ComposerState的layer_state_t中,然后调用者可以调用其closeGlobalTransaction方法把这些mStates发送给SurfaceFlinger处理(处理函数为:SurfaceFlinger::setTransactionState)。
谁来调用它的方法设置层的属性及发送mStates呢? -----答案是由SurfaceComposerClient来调用。
2.1.2.3 SurfaceComposerClient
前面介绍的两个类一个用于获取SurfaceFlinger服务;一个 用于记录每个Layer的状态,且可按要求把这些CoposerState发送给SurfaceFlinger。这个类是不是来使用前面两个类提供的服务 呢? --答案是肯定的。其定义及详细注释如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
#define NUM_DISPLAY_MAX 4 //最多支持四个显示屏
struct display_cblk_t //每个显示屏的配置参数
{
uint16_t w;
uint16_t h;
uint8_t format;
uint8_t orientation;
uint8_t reserved[2];
float fps;
float density;
float xdpi;
float ydpi;
uint32_t pad[2];
};
//在SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun中创建的共享控制块
struct surface_flinger_cblk_t // 4KB max,管理系统中所有的显示屏
{
uint8_t connected; //每一个bit表示一个显示屏
uint8_t reserved[3];
uint32_t pad[7];
display_cblk_t displays[NUM_DISPLAY_MAX];
};
class SurfaceComposerClient : public RefBase
{
friend class Composer;
public:
//获取Composer实例,并保存在mComposer中
SurfaceComposerClient();
virtual ~SurfaceComposerClient();
//通过BpSurfaceComposerClient<mClient>创建Surface,
//同时通过ISurfaceComposerClient::surface_data_t返回SurfaceID.然后创建一个SurfaceControl
//并把返回的BpSurface和当前的SurfaceComposerClient保存在SurfaceControl中,
//然后返回此SurfaceControl
sp<SurfaceControl> createSurface(
const String8& name,// name of the surface
DisplayID display, // Display to create this surface on
uint32_t w, // width in pixel
uint32_t h, // height in pixel
PixelFormat format, // pixel-format desired
uint32_t flags = 0 // usage flags
);
// Composer parameters <合成参数>
//所有的合成参数必须在一个transaction中被修改,多个surface可在一个transaction中被更新,
//所有的变化在关闭transaction时被一次性提交(通过调用closeGlobalTransaction来提交所有变化)。
//什么都没有做
static void openGlobalTransaction();
//通过调用Composer::closeGlobalTransaction(),
// 把Composer中记录的ComposerState(即mStates)发送给SurfaceFlinger
static void closeGlobalTransaction();
//什么都没做
static status_t freezeDisplay(DisplayID dpy, uint32_t flags = 0);
//什么都没做
static status_t unfreezeDisplay(DisplayID dpy, uint32_t flags = 0);
//把新的显示方向保存在Composer实例中
static int setOrientation(DisplayID dpy, int orientation, uint32_t flags);
//从surface_flinger_cblk_t.connected中获取显示屏个数
static ssize_t getNumberOfDisplays();
//获取显示屏的信息
static status_t getDisplayInfo(DisplayID dpy, DisplayInfo* info);
static ssize_t getDisplayWidth(DisplayID dpy);
static ssize_t getDisplayHeight(DisplayID dpy);
static ssize_t getDisplayOrientation(DisplayID dpy);
//通过注册,当Binder异常退出时,可以获得通知
status_t linkToComposerDeath(const sp<IBinder::DeathRecipient>& recipient,
void* cookie = NULL, uint32_t flags = 0);
//Start####: 以下函数都是把相应的修改状态记录在Composer的mStates中
//调用Composer::setFlags来设置对应(client+id)的layer状态〈即ComposerState中的layer_state_t〉
status_t hide(SurfaceID id);
status_t show(SurfaceID id, int32_t layer = -1);
status_t freeze(SurfaceID id);
status_t unfreeze(SurfaceID id);
status_t setFlags(SurfaceID id, uint32_t flags, uint32_t mask);
//调用Composer::setTransparentRegionHint
status_t setTransparentRegionHint(SurfaceID id, const Region& transparent);
//调用Composer::setLayer
status_t setLayer(SurfaceID id, int32_t layer);
//调用Composer::setAlpha
status_t setAlpha(SurfaceID id, float alpha=1.0f);
//调用Composer::setFreezeTint
status_t setFreezeTint(SurfaceID id, uint32_t tint);
//调用Composer::setMatrix
status_t setMatrix(SurfaceID id, float dsdx, float dtdx, float dsdy, float dtdy);
//调用Composer::setPosition
status_t setPosition(SurfaceID id, float x, float y);
//调用Composer::setSize
status_t setSize(SurfaceID id, uint32_t w, uint32_t h);
//End####:
status_t destroySurface(SurfaceID sid);//通过BpSurfaceComposerClient销毁Surface
private:
//通过BpSurfaceComposer从SurfaceFlinger获取BpSurfaceComposerClient,
//并把它保存在mClient中
virtual void onFirstRef();
Composer& getComposer();
mutable Mutex mLock;
status_t mStatus;
//实质为BpSurfaceComposerClient,与SurfaceFlinger.cpp中的Client相对应
sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> mClient;
//Composer实例
Composer& mComposer;
}
其功能列表如下:
1)获取BpSurfaceComposerClient(即mClient),在onFirstRef中实现
2)通过BpSurfaceComposerClient(即mClient)创建和销毁Surface
3)通过Composer来记录Surface和显示屏状态变化,及在Composer中通过BpSurfaceComposer把状态变化发给SurfaceFlinger处理
至此,SurfaceComposerClient功能已经分析清楚。可是从这三个类中,我们已经看到三个 Bp(BpSurfaceComposer,BpSurfaceComposerClient和BpSurface)及三个对应的接口。下面总结一下,每 个接口的功能,在客户端由谁使用,在服务器端谁来实现。
2.1.2.4 Surface相关接口总结

2.2 Surface操作
其相关接口如下:[cpp]
view plaincopy
static JNINativeMethod gSurfaceMethods[] = {
{"nativeClassInit", "()V", (void*)nativeClassInit },
{"init", "(Landroid/view/SurfaceSession;ILjava/lang/String;IIIII)V", (void*)Surface_init },
{"init", "(Landroid/os/Parcel;)V", (void*)Surface_initParcel },
{"initFromSurfaceTexture", "(Landroid/graphics/SurfaceTexture;)V", (void*)Surface_initFromSurfaceTexture },
{"getIdentity", "()I", (void*)Surface_getIdentity },
{"destroy", "()V", (void*)Surface_destroy },
{"release", "()V", (void*)Surface_release },
{"copyFrom", "(Landroid/view/Surface;)V", (void*)Surface_copyFrom },
{"isValid", "()Z", (void*)Surface_isValid },
{"lockCanvasNative", "(Landroid/graphics/Rect;)Landroid/graphics/Canvas;", (void*)Surface_lockCanvas },
{"unlockCanvasAndPost", "(Landroid/graphics/Canvas;)V", (void*)Surface_unlockCanvasAndPost },
{"unlockCanvas", "(Landroid/graphics/Canvas;)V", (void*)Surface_unlockCanvas },
{"openTransaction", "()V", (void*)Surface_openTransaction },
{"closeTransaction", "()V", (void*)Surface_closeTransaction },
{"setOrientation", "(III)V", (void*)Surface_setOrientation },
{"freezeDisplay", "(I)V", (void*)Surface_freezeDisplay },
{"unfreezeDisplay", "(I)V", (void*)Surface_unfreezeDisplay },
{"screenshot", "(II)Landroid/graphics/Bitmap;", (void*)Surface_screenshotAll },
{"screenshot", "(IIII)Landroid/graphics/Bitmap;", (void*)Surface_screenshot },
{"setLayer", "(I)V", (void*)Surface_setLayer },
{"setPosition", "(FF)V",(void*)Surface_setPosition },
{"setSize", "(II)V",(void*)Surface_setSize },
{"hide", "()V", (void*)Surface_hide },
{"show", "()V", (void*)Surface_show },
{"freeze", "()V", (void*)Surface_freeze },
{"unfreeze", "()V", (void*)Surface_unfreeze },
{"setFlags", "(II)V",(void*)Surface_setFlags },
{"setTransparentRegionHint","(Landroid/graphics/Region;)V", (void*)Surface_setTransparentRegion },
{"setAlpha", "(F)V", (void*)Surface_setAlpha },
{"setMatrix", "(FFFF)V", (void*)Surface_setMatrix },
{"setFreezeTint", "(I)V", (void*)Surface_setFreezeTint },
{"readFromParcel", "(Landroid/os/Parcel;)V", (void*)Surface_readFromParcel },
{"writeToParcel", "(Landroid/os/Parcel;I)V", (void*)Surface_writeToParcel },
};
2.2.1 Surface_init调用流程
在SurfaceFlinger端创建BSurface,在客户端返回SurfaceControl,同时在SurfaceControl中拥有了BpSurface用于与BSurface交互。
2.2.1.1 调用流程分析
BpSurfaceComposerClient->createSurface返回BpSurface。且通过参数返回ISurfaceComposerClient::surface_data_t,其定义如下:其中token在SurfaceComposerClient的函数参数中,对应于SurfaceID。即在客户端,它就是SurfaceID。
token: 加入到Client::mLayers中的序号,在Client中单调递增,初始值为:1,一个Layer创建一个BSurface
identity: LayerBaseClient中的mIdentity,在所有的Layer中单调递增,初始值为:1
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct surface_data_t {
int32_t token; //加入到Client::mLayers中的序号,在Client中单调递增,初始值为:1
int32_t identity; //LayerBaseClient中的mIdentity,在所有的Layer中单调递增,初始值为:1
status_t readFromParcel(const Parcel& parcel);
status_t writeToParcel(Parcel* parcel) const;
};
2.2.1.2 创建真正的Surface
在Layer::createSurface中创建真正的BSurface,在SurfaceFlinger::createSurface中调用layer->getSurface时创建的。此BSurface定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
sp<ISurface> Layer::createSurface()
{
class BSurface : public BnSurface, public LayerCleaner {
wp<const Layer> mOwner;
virtual sp<ISurfaceTexture> getSurfaceTexture() const { //实现了ISurface的接口
sp<ISurfaceTexture> res;
sp<const Layer> that( mOwner.promote() );
if (that != NULL) {
res = that->mSurfaceTexture;
}
return res;
}
public:
BSurface(const sp<SurfaceFlinger>& flinger,
const sp<Layer>& layer)
: LayerCleaner(flinger, layer), mOwner(layer) { }
};
sp<ISurface> sur(new BSurface(mFlinger, this));
return sur;
}
在此BSurface中实现了ISurface的接口getSurfaceTexture,在此接口中返回 Layer::mSurfaceTexture(类型为:SurfaceTextureLayer,它才是真正操作内存的东东),此成员在 Layer::onFirstRef中创建,SurfaceTextureLayer是SurfaceTexture的派生类,代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
void Layer::onFirstRef()
{
LayerBaseClient::onFirstRef();
struct FrameQueuedListener : public SurfaceTexture::FrameAvailableListener {
FrameQueuedListener(Layer* layer) : mLayer(layer) { }
private:
wp<Layer> mLayer;
virtual void onFrameAvailable() {
sp<Layer> that(mLayer.promote());
if (that != 0) {
that->onFrameQueued();
}
}
};
mSurfaceTexture = new SurfaceTextureLayer(mTextureName, this); //创建Layer中的mSurfaceTexture
mSurfaceTexture->setFrameAvailableListener(new FrameQueuedListener(this));
mSurfaceTexture->setSynchronousMode(true);
mSurfaceTexture->setBufferCountServer(2);
}
2.2.1.3 不得不说的SurfaceControl
本来Surface_init调用SurfaceComposerClient::createSurface创建一个Surface,可却返回了一个SurfaceControl,下面看看SurfaceCotrol到底做了些什么,以及如何做的?
相关数据结构如下图所示:

SurfaceControl定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class SurfaceControl : public RefBase
{
public:
// release surface data from java
void clear();
//调用SurfaceComposerClient中对应方法,把对应信息保存在
//Composer的ComposerState中
status_t setLayer(int32_t layer);
status_t setPosition(int32_t x, int32_t y);
status_t setSize(uint32_t w, uint32_t h);
status_t hide();
status_t show(int32_t layer = -1);
status_t freeze();
status_t unfreeze();
status_t setFlags(uint32_t flags, uint32_t mask);
status_t setTransparentRegionHint(const Region& transparent);
status_t setAlpha(float alpha=1.0f);
status_t setMatrix(float dsdx, float dtdx, float dsdy, float dtdy);
status_t setFreezeTint(uint32_t tint);
//把SurfaceControl中的mSurface和mIdentity写入parcel
static status_t writeSurfaceToParcel(
const sp<SurfaceControl>& control, Parcel* parcel);
//以SurfaceControl为参数创建一个Surface返回,此Surface派生关系如下:
//class Surface : public SurfaceTextureClient
//class SurfaceTextureClient: public ANativeWindow, RefBase
//struct ANativeWindow
sp<Surface> getSurface() const;
private:
SurfaceControl(
const sp<SurfaceComposerClient>& client,
const sp<ISurface>& surface,
const ISurfaceComposerClient::surface_data_t& data);
~SurfaceControl();
void destroy();
sp<SurfaceComposerClient> mClient;
sp<ISurface> mSurface;
SurfaceID mToken; //对应SurfaceID,在Client中单调递增
uint32_t mIdentity; //Layer在系统中唯一的序列号,在系统中单调递增
mutable Mutex mLock;
mutable sp<Surface> mSurfaceData;
}
从其定义中可以看出,在getSurface中将有新花样,其它操作函数都是直接以mToken作为SurfaceID,直接调用 SurfaceComposerClient中对应方法。 经过这样一分析,SurfaceControl也没什么神秘的了。但它的getSurface 到有点神秘。
2.2.2 getSurface流程
getSurface在客户端返回Surface(派生于SurfaceTextureClient),并在Surface的mSurfaceTexture域中保存了BpSurfaceTexture。前面Surface初始化之后,就可以getSurface了。getSurface流程如下图所示:

有了Surface,且在Surface中又有了BpSurfaceTexture,下一步就操作GraphicBuffer了。
3. 画图流程
对于画图流程,可以从ViewRootImpl(ViewRootImpl.java)的draw函数看起,在画图之间,它要调用java层的surface.lockCanvas,画完图之后调用surface.unlockCanvasAndPost来提交显示。surface.lockCanvas->
lockCanvasNative(Java)->
(C++)Surface_lockCanvas<android_view_Surface.cpp>
surface.unlockCanvasAndPost(Java)->
(C++)Surface_unlockCanvasAndPost<android_view_Surface.cpp>
本章主要分析这两个函数到底做了些什么>
3.1 Surface_lockCanvas
Android图形系统中一个重要的概念是surface。View及其子类(如TextView, Button)要画在surface上。每个surface创建一个Canvas对象(但属性时常改变),用来管理view在surface上的绘图操 作,如画点画线。每个canvas对象对应一个bitmap,存储画在surface上的内容。3.1.1 相关数据结构定义
3.1.1.1 ANativeWindow_Buffer[cpp]
view plaincopy
typedef struct ANativeWindow_Buffer {
// The number of pixels that are show horizontally.
int32_t width;
// The number of pixels that are shown vertically.
int32_t height;
// The number of *pixels* that a line in the buffer takes in
// memory. This may be >= width.
int32_t stride;
// The format of the buffer. One of WINDOW_FORMAT_*
int32_t format;
// The actual bits.
void* bits; //显示内存基地址,通过服务器端fd通过flat_binder_object传给客户端, 然后客户端通过mmap获取。
// Do not touch.
uint32_t reserved[6];
} ANativeWindow_Buffer;
3.1.1.2 SurfaceInfo
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct SurfaceInfo {
uint32_t w;
uint32_t h;
uint32_t s;
uint32_t usage;
PixelFormat format;
void* bits;//显示内存基地址,通过服务器端fd通过flat_binder_object传给客户端, 然后客户端通过mmap获取。
uint32_t reserved[2];
};
3.1.1.3 二者对应关系
[cpp]
view plaincopy
SurfaceInfo* other;
ANativeWindow_Buffer outBuffer;
other->w = uint32_t(outBuffer.width);
other->h = uint32_t(outBuffer.height);
other->s = uint32_t(outBuffer.stride);
other->usage = GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_READ_OFTEN | GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_WRITE_OFTEN;
other->format = uint32_t(outBuffer.format);
other->bits = outBuffer.bits;
3.1.1.4 GraphicBuffer
在分析下面的流程时, 不得不对GraphicBuffer进行深入了解,特别是其Flattenable interface,这是实现画图buffer的关键。其相关定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
typedef struct native_handle
{
int version; /* sizeof(native_handle_t) */
int numFds; /* number of file-descriptors at &data[0] */
int numInts; /* number of ints at &data[numFds] */
int data[0]; /* numFds + numInts ints */
} native_handle_t;
typedef const native_handle_t* buffer_handle_t;
class GraphicBuffer
: public EGLNativeBase<
ANativeWindowBuffer,
GraphicBuffer,
LightRefBase<GraphicBuffer> >, public Flattenable
{
...
// Flattenable interface
size_t getFlattenedSize() const;
size_t getFdCount() const;
status_t flatten(void* buffer, size_t size,
int fds[], size_t count) const;
status_t unflatten(void const* buffer, size_t size,
int fds[], size_t count);
...
buffer_handle_t handle; //定义于基类ANativeWindowBuffer中
};
3.1.1.5 Flattenable interface
下面看看每个Flattenable interface是如何实现的:
3.1.1.5.1 getFlattenedSize
[cpp]
view plaincopy
size_t GraphicBuffer::getFlattenedSize() const {
return (8 + (handle ? handle->numInts : 0))*sizeof(int);
}
3.1.1.5.2 getFdCount
[cpp]
view plaincopy
size_t GraphicBuffer::getFdCount() const {
return handle ? handle->numFds : 0;
}
3.1.1.5.3 flatten
[cpp]
view plaincopy
status_t GraphicBuffer::flatten(void* buffer, size_t size,
int fds[], size_t count) const
{
size_t sizeNeeded = GraphicBuffer::getFlattenedSize();
if (size < sizeNeeded) return NO_MEMORY;
size_t fdCountNeeded = GraphicBuffer::getFdCount();
if (count < fdCountNeeded) return NO_MEMORY;
int* buf = static_cast<int*>(buffer);
buf[0] = 'GBFR';
buf[1] = width;
buf[2] = height;
buf[3] = stride;
buf[4] = format;
buf[5] = usage;
buf[6] = 0;
buf[7] = 0;
if (handle) {
buf[6] = handle->numFds;
buf[7] = handle->numInts;
native_handle_t const* const h = handle;
memcpy(fds, h->data, h->numFds*sizeof(int));
memcpy(&buf[8], h->data + h->numFds, h->numInts*sizeof(int));
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
把handle中的numFds拷贝到fds中,把handle中的numInts拷贝到buffer中。
3.1.1.5.4 unflatten
[cpp]
view plaincopy
status_t GraphicBuffer::unflatten(void const* buffer, size_t size,
int fds[], size_t count)
{
if (size < 8*sizeof(int)) return NO_MEMORY;
int const* buf = static_cast<int const*>(buffer);
if (buf[0] != 'GBFR') return BAD_TYPE;
const size_t numFds = buf[6];
const size_t numInts = buf[7];
const size_t sizeNeeded = (8 + numInts) * sizeof(int);
if (size < sizeNeeded) return NO_MEMORY;
size_t fdCountNeeded = 0;
if (count < fdCountNeeded) return NO_MEMORY;
if (handle) {
// free previous handle if any
free_handle();
}
if (numFds || numInts) {
width = buf[1];
height = buf[2];
stride = buf[3];
format = buf[4];
usage = buf[5];
native_handle* h = native_handle_create(numFds, numInts);
memcpy(h->data, fds, numFds*sizeof(int));
memcpy(h->data + numFds, &buf[8], numInts*sizeof(int));
handle = h;
} else {
width = height = stride = format = usage = 0;
handle = NULL;
}
mOwner = ownHandle;
if (handle != 0) {
mBufferMapper.registerBuffer(handle);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
把width,height,stride,format和usage保存到成员变量中,并创建一个native_handle,然后把numFds和 numInts拷贝到handle的data中。同时把此handle注册到mBufferMapper中,mBufferMapper的注册函数实现代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
status_t GraphicBufferMapper::registerBuffer(buffer_handle_t handle)
{
status_t err;
//gralloc_module_t const *mAllocMod;是一个硬件抽象层实现。通过hw_get_module(GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module)方式获取
err = mAllocMod->registerBuffer(mAllocMod, handle);
LOGW_IF(err, "registerBuffer(%p) failed %d (%s)",
handle, err, strerror(-err));
return err;
}
[cpp]
view plaincopy
GraphicBufferMapper::GraphicBufferMapper()
: mAllocMod(0)
{
hw_module_t const* module;
int err = hw_get_module(GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module);
LOGE_IF(err, "FATAL: can't find the %s module", GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID);
if (err == 0) {
mAllocMod = (gralloc_module_t const *)module;
}
}
3.1.1.5.4 GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID实例
对于GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,以hardware/msm7k/libgralloc/gralloc.cpp为例进行分 析。其registerBuffer实现函数:gralloc_register_buffer(hardware/msm7k/libgralloc /mapper.cpp),其相关代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
int gralloc_register_buffer(gralloc_module_t const* module,
buffer_handle_t handle)
{
if (private_handle_t::validate(handle) < 0)
return -EINVAL;
// if this handle was created in this process, then we keep it as is.
int err = 0;
private_handle_t* hnd = (private_handle_t*)handle;
if (hnd->pid != getpid()) {
hnd->base = NULL;
if (!(hnd->flags & private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_GPU)) {
void *vaddr;
err = gralloc_map(module, handle, &vaddr);
}
}
return err;
}
static int gralloc_map(gralloc_module_t const* module,
buffer_handle_t handle,
void** vaddr)
{
private_handle_t* hnd = (private_handle_t*)handle;
if (!(hnd->flags & private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_FRAMEBUFFER)) {
size_t size = hnd->size;
#if PMEM_HACK
size += hnd->offset;
#endif
void* mappedAddress = mmap(0, size,
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, hnd->fd, 0);
if (mappedAddress == MAP_FAILED) {
LOGE("Could not mmap handle %p, fd=%d (%s)",
handle, hnd->fd, strerror(errno));
hnd->base = 0;
return -errno;
}
hnd->base = intptr_t(mappedAddress) + hnd->offset;
//LOGD("gralloc_map() succeeded fd=%d, off=%d, size=%d, vaddr=%p",
// hnd->fd, hnd->offset, hnd->size, mappedAddress);
}
*vaddr = (void*)hnd->base;
return 0;
}
从gralloc_map可以看出,这个registerBuffer主要做了一件事:
1)根据handle中传过来的fd和size进行mmap映射(把kernel中的内存映射到用户空间),映射之后的地址再加上hnd->offset便获得hnd->base供后面使用。
从这里可以初步看出,这个图形buffer数据并不是真正的从client传递到server,而是在lock是从server把fd传递给client,由客户端进行mmap,然后进行使用。关于这个是怎么实现的,后面将详细分析其实现过程。
对于如何从native_handle转换为private_handle_t,且在private_handle_t中可以获取fd和offset? 看一下其数据结构和flatten的实现方式就可以得知:
native_handle:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
typedef struct native_handle
{
int version; /* sizeof(native_handle_t) */
int numFds; /* number of file-descriptors at &data[0] */
int numInts; /* number of ints at &data[numFds] */
int data[0]; /* numFds + numInts ints */
} native_handle_t;
这个data[0]是关键,虽然分配了哪么多buffer,但实质上native_handle只占了3个int.其它的数据由包含它的数据结构来解析。
private_handle_t:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct private_handle_t {
native_handle_t nativeHandle;
#endif
enum {
PRIV_FLAGS_FRAMEBUFFER = 0x00000001,
PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM = 0x00000002,
PRIV_FLAGS_USES_GPU = 0x00000004,
};
// file-descriptors
int fd;
// ints
int magic;
int flags;
int size;
int offset;
int gpu_fd; // stored as an int, b/c we don't want it marshalled
// FIXME: the attributes below should be out-of-line
int base;
int map_offset;
int pid;
#ifdef __cplusplus
static const int sNumInts = 8; //numInts在这儿明确指定
static const int sNumFds = 1; //numFds在这儿明确指定
static const int sMagic = 'gmsm';
private_handle_t(int fd, int size, int flags) :
fd(fd), magic(sMagic), flags(flags), size(size), offset(0),
base(0), pid(getpid())
{
version = sizeof(native_handle);
numInts = sNumInts;
numFds = sNumFds;
}
~private_handle_t() {
magic = 0;
}
static int validate(const native_handle* h) {
const private_handle_t* hnd = (const private_handle_t*)h;
if (!h || h->version != sizeof(native_handle) ||
h->numInts != sNumInts || h->numFds != sNumFds ||
hnd->magic != sMagic)
{
LOGE("invalid gralloc handle (at %p)", h);
return -EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
#endif
}
3.1.2 Surface_lockCanvas执行流程
查看高清大图

3.1.3 Surface_lockCanvas总结
功能:Surface_lockCanvas获取显示buffer在本进程用户空间的地址,并据此创建一个SkBitmap给Java使用。关键技术:BINDER_TYPE_FD类型的Binder、mmap、gralloc硬件抽象层
3.1.4 SurfaceTexture::dequeueBuffer如何创建GraphicBuffer
相关代码如下:[cpp]
view plaincopy
const sp<GraphicBuffer>& buffer(mSlots[buf].mGraphicBuffer);
if ((buffer == NULL) ||
(uint32_t(buffer->width) != w) ||
(uint32_t(buffer->height) != h) ||
(uint32_t(buffer->format) != format) ||
((uint32_t(buffer->usage) & usage) != usage))
{
usage |= GraphicBuffer::USAGE_HW_TEXTURE;
status_t error;
sp<GraphicBuffer> graphicBuffer( //创建GraphicBuffer
mGraphicBufferAlloc->createGraphicBuffer(
w, h, format, usage, &error));
if (graphicBuffer == 0) {
ST_LOGE("dequeueBuffer: SurfaceComposer::createGraphicBuffer "
"failed");
return error;
}
if (updateFormat) {
mPixelFormat = format;
}
mSlots[buf].mGraphicBuffer = graphicBuffer;
mSlots[buf].mRequestBufferCalled = false;
if (mSlots[buf].mEglImage != EGL_NO_IMAGE_KHR) {
eglDestroyImageKHR(mSlots[buf].mEglDisplay, mSlots[buf].mEglImage);
mSlots[buf].mEglImage = EGL_NO_IMAGE_KHR;
mSlots[buf].mEglDisplay = EGL_NO_DISPLAY;
}
returnFlags |= ISurfaceTexture::BUFFER_NEEDS_REALLOCATION;
}
mGraphicBufferAlloc也是通过调用BpSurfaceComposer->createGraphicBufferAlloc而获取,它对应的服务器为SufaceFlinger中的GraphicBufferAlloc。
mGraphicBufferAlloc实质为一个BpGraphicBufferAlloc,它真正创建GraphicBuffer的代码位于GraphicBufferAlloc::createGraphicBuffer中。代码关键调用流程如下:
new GraphicBuffer(w, h, format, usage)->
initSize(w, h, reqFormat, reqUsage)->
GraphicBufferAllocator::get()->
allocator.alloc(w, h, format, reqUsage, &handle, &stride)->
返回handle,此handle为ANativeWindowBuffer成员,类型为native_handle。
GraphicBufferAllocator::alloc->
mAllocDev->alloc->
mAllocDev类型为alloc_device_t,它通过gralloc_open向
GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID获取,根据上面的实例msm7k,
它最终执行gralloc_device_open而获取gralloc_context_t.device.common,
alloc的实现函数为gralloc_alloc.
gralloc_alloc->
gralloc_alloc_buffer->
1)获取GPU内存(调用SimpleBestFitAllocator::allocate进行分配)
2)fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDONLY)获取fd
3)根据fd、size和flags创建private_handle_t,其相关代码如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
private_handle_t* hnd = new private_handle_t(fd, size, flags);
if (base == NULL) {...
}
} else {
private_module_t* m = reinterpret_cast<private_module_t*>(
dev->common.module);
hnd->offset = offset;
hnd->base = int(base)+offset;
hnd->gpu_fd = gpu_fd;
hnd->map_offset = m->fb_map_offset;
*pHandle = hnd;
}
3.2 Surface_unlockCanvasAndPost
相关文章推荐
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android 4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- Android 4.0.3 显示系统深入理解
- 深入理解Android消息处理系统——Looper、Handler、Thread(转)
- 深入理解:Android 编译系统
- 深入理解Android消息处理系统——Looper、Handler、Thread
- 深入理解 Android 卷I - 第8章 深入理解Surface系统
- 深入理解:Android 编译系统
- 深入理解Android消息处理系统——Looper、Handler、Thread
