Copy List with Random Pointer 复制有随机指针的链表@LeetCode
2013-11-22 10:34
435 查看
1 先画好图
2 注意可能形成环的情况,因此必须拆成3个循环来做
代码是按照 http://www.cnblogs.com/lautsie/p/3259724.html 的图来写的
一个单链表,其中除了next指针外,还有一个random指针,指向链表中的任意某个元素。如何复制这样一个链表呢?通过next来复制一条链是很容易的,问题的难点在于如何恰当地设置新链表中的random指针。
很容易想到使用Hash表的做法,先依次遍历原链表,每经过一个节点X,开辟一个新节点Y,然后(key=X的地址,value=Y的地址)存入哈希表。第二次再遍历原链表,根据拓扑结构设置新的链表。需要O(n)的空间,时间也是O(n)。如果不使用额外的空间,那么要想在旧链表和新链表的对应节点之间建立联系。就要利用链表中多余的指针。
O(n)复杂度,O(1)空间。如图所示,扫描两边即可。需要复制的链表:

如图所示,ABCD是原来的链表,A’B’C’D’是复制的链表,第一遍扫描顺序复制next指针,把ABCD的next分别指向A’B’C’D’,将A’的next指针指向B,B’的next指针指向C,依次类推:

复制random指针: A’->random=A->random->next恢复:A->next=A’->next;A’->next=A’->next->next;
再来一张示例图:
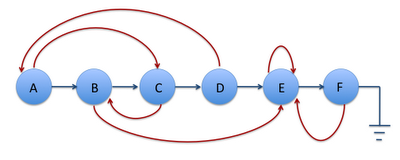
http://www.cnblogs.com/reynold-lei/p/3362614.html
package Level4;
import Utility.RandomListNode;
/**
* Copy List with Random Pointer
*
* A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random
* pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
*
* Return a deep copy of the list.
*
*/
public class S138 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RandomListNode head = new RandomListNode(1);
RandomListNode n2 = new RandomListNode(2);
RandomListNode n3 = new RandomListNode(3);
RandomListNode n4 = new RandomListNode(4);
head.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
head.random = n3;
n2.random = n4;
RandomListNode ret = copyRandomList(head);
while(ret != null){
System.out.println(ret.label);
ret = ret.next;
}
}
public static RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
RandomListNode cur = head;
RandomListNode copyHead = null;
RandomListNode copyCur = null;
// 形成图1
while(cur != null){
copyCur = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
if(copyHead == null){
copyHead = copyCur;
}
copyCur.next = cur.next;
cur.next = copyCur;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 形成图2
// 注意此处必须要分成两个while loop而不能合并。
// 如果合并,则在两对random指针互相形成环时会出错!
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
cur.next.random = cur.random!=null ? cur.random.next : null; // 设置copy节点的random指针
cur = cur.next.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
copyCur = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next; // 恢复cur节点的next指针
copyCur.next = cur.next!=null ? cur.next.next : null; // 设置copy节点的next指针
cur = cur.next;
}
return copyHead;
}
}
记住图和三个步骤,然后细心
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* class RandomListNode {
* int label;
* RandomListNode next, random;
* RandomListNode(int x) { this.label = x; }
* };
*/
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
RandomListNode copyHead = null;
RandomListNode copyCur = null;
RandomListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
copyCur = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
if(copyHead == null) {
copyHead = copyCur;
}
copyCur.next = cur.next;
cur.next = copyCur;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
cur = head;
copyCur = copyHead;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null) {
copyCur.random = cur.random.next;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
if(copyCur.next != null) {
copyCur = copyCur.next.next;
}
}
cur = head;
copyCur = copyHead;
while(cur != null) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
if(copyCur.next != null) {
copyCur.next = copyCur.next.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
copyCur = copyCur.next;
}
return copyHead;
}
}
2 注意可能形成环的情况,因此必须拆成3个循环来做
代码是按照 http://www.cnblogs.com/lautsie/p/3259724.html 的图来写的
一个单链表,其中除了next指针外,还有一个random指针,指向链表中的任意某个元素。如何复制这样一个链表呢?通过next来复制一条链是很容易的,问题的难点在于如何恰当地设置新链表中的random指针。
很容易想到使用Hash表的做法,先依次遍历原链表,每经过一个节点X,开辟一个新节点Y,然后(key=X的地址,value=Y的地址)存入哈希表。第二次再遍历原链表,根据拓扑结构设置新的链表。需要O(n)的空间,时间也是O(n)。如果不使用额外的空间,那么要想在旧链表和新链表的对应节点之间建立联系。就要利用链表中多余的指针。
O(n)复杂度,O(1)空间。如图所示,扫描两边即可。需要复制的链表:

如图所示,ABCD是原来的链表,A’B’C’D’是复制的链表,第一遍扫描顺序复制next指针,把ABCD的next分别指向A’B’C’D’,将A’的next指针指向B,B’的next指针指向C,依次类推:

复制random指针: A’->random=A->random->next恢复:A->next=A’->next;A’->next=A’->next->next;
再来一张示例图:

http://www.cnblogs.com/reynold-lei/p/3362614.html
package Level4;
import Utility.RandomListNode;
/**
* Copy List with Random Pointer
*
* A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random
* pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
*
* Return a deep copy of the list.
*
*/
public class S138 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RandomListNode head = new RandomListNode(1);
RandomListNode n2 = new RandomListNode(2);
RandomListNode n3 = new RandomListNode(3);
RandomListNode n4 = new RandomListNode(4);
head.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
head.random = n3;
n2.random = n4;
RandomListNode ret = copyRandomList(head);
while(ret != null){
System.out.println(ret.label);
ret = ret.next;
}
}
public static RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
RandomListNode cur = head;
RandomListNode copyHead = null;
RandomListNode copyCur = null;
// 形成图1
while(cur != null){
copyCur = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
if(copyHead == null){
copyHead = copyCur;
}
copyCur.next = cur.next;
cur.next = copyCur;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 形成图2
// 注意此处必须要分成两个while loop而不能合并。
// 如果合并,则在两对random指针互相形成环时会出错!
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
cur.next.random = cur.random!=null ? cur.random.next : null; // 设置copy节点的random指针
cur = cur.next.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
copyCur = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next; // 恢复cur节点的next指针
copyCur.next = cur.next!=null ? cur.next.next : null; // 设置copy节点的next指针
cur = cur.next;
}
return copyHead;
}
}
记住图和三个步骤,然后细心
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* class RandomListNode {
* int label;
* RandomListNode next, random;
* RandomListNode(int x) { this.label = x; }
* };
*/
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
RandomListNode copyHead = null;
RandomListNode copyCur = null;
RandomListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
copyCur = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
if(copyHead == null) {
copyHead = copyCur;
}
copyCur.next = cur.next;
cur.next = copyCur;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
cur = head;
copyCur = copyHead;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null) {
copyCur.random = cur.random.next;
}
cur = cur.next.next;
if(copyCur.next != null) {
copyCur = copyCur.next.next;
}
}
cur = head;
copyCur = copyHead;
while(cur != null) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
if(copyCur.next != null) {
copyCur.next = copyCur.next.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
copyCur = copyCur.next;
}
return copyHead;
}
}
相关文章推荐
- LeetCode138 Copy List with Random Pointer(深度复制带有随机指针的链表) Java题解
- 【LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现】【143-Copy List with Random Pointer(有随机指针的链表复制)】
- (不会)[LeetCode] Copy List with Random Pointer 拷贝带有随机指针的链表
- [LeetCode]—Copy List with Random Pointer 深度复制带“任意指针”的链表
- LeetCode之复制有random指针的链表Copy List with Random Pointer
- LeetCode | Copy List with Random Pointer(赋值带有随机指针的链表)
- 【LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现】【138-Copy List with Random Pointer(拷贝有随机指针的单链表)】
- [LintCode] 复制带随机指针的链表 Copy List with Random Pointer
- Copy List with Random Pointer复制带有随机指针的链表
- LeetCode OJ 之 Copy List with Random Pointer(复制含有随机指针的链表)
- Copy List with Random Pointer(复制有随机指针的链表)
- [LeetCode] Copy List with Random Pointer 拷贝带有随机指针的链表
- [Leetcode] Copy list with random pointer 对带有任意指针的链表深度拷贝
- [LeetCode]Copy List with Random Pointer &Clone Graph 复杂链表的复制&图的复制
- [LeetCode]Copy List with Random Pointer &Clone Graph 复杂链表的复制&图的复制
- 附有随机结点指针的链表的深度拷贝 Copy List with Random Pointer
- LeetCode OJ:Copy List with Random Pointer(复制存在随机链接的链表)
- Leetcode Copy List with Random Pointer 拷贝链表
- leetcode---copy-list-with-random-pointer---链表
- LeetCode(Copy List with Random Pointer) 复杂链表的深拷贝
