Windows下的高精度定时器实现及精确时刻获取
2013-11-17 20:20
375 查看
通讯、VOIP、视频等领域的很多核心技术对时间精度的要求非常高,比如数据采集、时间同步、媒体流平滑控制、拥塞算法等等,很多技术都是以毫秒为单位来进行计算和控制的。但是Windows设计之初并不是以实时系统为目标的,所以Windows系统的时间精度一直不高,实际最小单位是15ms左右,导致的结果就是所有Windows的时间、线程相关的操作都无法以1ms来实现精确控制。
受影响的操作包括Sleep、GetTickCount、_ftime等等。比如你调用Sleep(2),期待2ms之后线程自动唤醒,但是实际结果可能是15ms甚至2x ms的时候才会唤醒,对于简单应用来说影响不大,但是对于精度要求非常高的系统来说,这样的问题就是非常致命的了。
代码思路如下:
1、高精度定时器。使用Singleton模式挂起请求Sleep的线程并统一管理,后台使用Windows MultiMedia SDK的定期回调函数不断检测并回复到时的线程,超时时间与当前时间采用QueryPerformanceCounter/QueryPerformanceFrequency的高精度计时,确保整体功能可靠性。
2、精确时刻获取。由于可以获取到毫秒级别的_ftime与GetTickCount都受到Windows系统时间精度影响,最小单位只有15ms,所以需要借助QueryPerformanceCounter/QueryPerformanceFrequency进行准确计时。代码首先根据_ftime获取起始时刻的精确刻度,然后根据差量计算当前的精确时刻。
代码中的Singleton模式可以找到很多实现,因此本文不进行详述
代码(VS2005 c++编译)
1、高精度定时器
[c-sharp]
view plaincopy
#pragma once
#include <Windows.h>
#include <list>
#include <akumaslab/system/singleton.hpp>
namespace akumaslab{
namespace time{
using std::list;
class PreciseTimerProvider
{
struct WaitedHandle{
HANDLE threadHandle;
LONGLONG elapsed;//超时时间
} ;
typedef list< WaitedHandle > handle_list_type;
typedef akumaslab::system::Singleton< PreciseTimerProvider > timer_type;
public:
PreciseTimerProvider(void):highResolutionAvailable(false), timerID(0)
{
InitializeCriticalSection(&critical);
static LARGE_INTEGER systemFrequency;
if(0 != QueryPerformanceFrequency(&systemFrequency))
{
timeBeginPeriod(callbackInterval);
highResolutionAvailable = true;
countPerMilliSecond = systemFrequency.QuadPart/1000;
timerID = timeSetEvent(callbackInterval, 0, &PreciseTimerProvider::TimerFunc, NULL, TIME_PERIODIC);
}
}
//挂起当前线程
//@milliSecond:超时时间,单位:毫秒
bool suspendCurrentThread(int milliSecond)
{
if(milliSecond <= 0)return false;
if (!highResolutionAvailable)return false;
HANDLE currentThreadHandle = GetCurrentThread();
HANDLE currentProcessHandle = GetCurrentProcess();
HANDLE realThreadHandle(0);
DuplicateHandle(currentProcessHandle, currentThreadHandle, currentProcessHandle, &realThreadHandle, 0, FALSE, DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS);
WaitedHandle item;
item.threadHandle = realThreadHandle;
LARGE_INTEGER now;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&now);
now.QuadPart += milliSecond * countPerMilliSecond;
item.elapsed = now.QuadPart;
EnterCriticalSection(&critical);
waitList.push_back(item);
LeaveCriticalSection(&critical);
//挂起线程
SuspendThread(realThreadHandle);
CloseHandle(realThreadHandle);
return true;
}
//恢复超时线程
void resumeTimeoutThread()
{
if (!highResolutionAvailable)return;
LARGE_INTEGER now;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&now);
EnterCriticalSection(&critical);
for (handle_list_type::iterator ir = waitList.begin(); ir != waitList.end(); )
{
WaitedHandle& waited = *ir;
if (now.QuadPart >= waited.elapsed)
{
ResumeThread(waited.threadHandle);
ir = waitList.erase(ir);
continue;
}
ir++;
}
LeaveCriticalSection(&critical);
}
~PreciseTimerProvider(){
if (0 != timerID)
{
timeKillEvent(timerID);
timerID = 0;
timeEndPeriod(callbackInterval);
}
DeleteCriticalSection(&critical);
}
private:
static void CALLBACK TimerFunc(UINT uID, UINT uMsg, DWORD dwUser, DWORD dw1, DWORD dw2)
{
static bool initialed = false;
if (!initialed)
{
if (initialWorkThread())
{
initialed = true;
}
else{
return;
}
}
timer_type::getRef().resumeTimeoutThread();
}
//调整定时器工作线程优先级
static bool initialWorkThread()
{
HANDLE realProcessHandle = OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, _getpid());
if (NULL == realProcessHandle)
{
return false;
}
if (0 == SetPriorityClass(realProcessHandle, REALTIME_PRIORITY_CLASS))
{
CloseHandle(realProcessHandle);
return false;
}
HANDLE currentThreadHandle = GetCurrentThread();
HANDLE currentProcessHandle = GetCurrentProcess();
HANDLE realThreadHandle(0);
DuplicateHandle(currentProcessHandle, currentThreadHandle, currentProcessHandle, &realThreadHandle, 0, FALSE, DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS);
SetThreadPriority(realThreadHandle, THREAD_PRIORITY_TIME_CRITICAL);
//必须关闭复制句柄
CloseHandle(realThreadHandle);
CloseHandle(realProcessHandle);
return true;
}
private:
const static int callbackInterval = 1;
CRITICAL_SECTION critical;
MMRESULT timerID;
LONGLONG countPerMilliSecond;
bool highResolutionAvailable;
handle_list_type waitList;
};
class PreciseTimer
{
typedef akumaslab::system::Singleton< PreciseTimerProvider > timer_type;
public:
static bool wait(int milliSecond)
{
//static PreciseTimerProvider timer;
return timer_type::getRef().suspendCurrentThread(milliSecond);
}
};
}
}
DEMO
[cpp]
view plaincopy
int interval = 1;
int repeatCount = 50;
cout << getCurrentTime() << "test begin" << endl;
unit.reset();
for (int i = 0; i < repeatCount; i++)
{
akumaslab::time::PreciseTimer::wait(interval);
cout << getCurrentTime() << "/" << getNewTime() << " used " << unit.getPreciseElapsedTime() << " ms" << endl;
unit.reset();
}
2、精确时刻获取
[cpp]
view plaincopy
#pragma once
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <akumaslab/system/singleton.hpp>
namespace akumaslab{
namespace time{
struct HighResolutionTime
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
int hour;
int min;
int second;
int millisecond;
};
class CurrentTimeProvider
{
public:
CurrentTimeProvider():highResolutionAvailable(false), countPerMilliSecond(0), beginCount(0)
{
static LARGE_INTEGER systemFrequency;
if(0 != QueryPerformanceFrequency(&systemFrequency))
{
highResolutionAvailable = true;
countPerMilliSecond = systemFrequency.QuadPart/1000;
_timeb tb;
_ftime_s(&tb);
unsigned short currentMilli = tb.millitm;
LARGE_INTEGER now;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&now);
beginCount = now.QuadPart - (currentMilli*countPerMilliSecond);
}
};
bool getCurrentTime(HighResolutionTime& _time)
{
time_t tt;
::time(&tt);
tm now;
localtime_s(&now, &tt);
_time.year = now.tm_year + 1900;
_time.month = now.tm_mon + 1;
_time.day = now.tm_mday + 1;
_time.hour = now.tm_hour;
_time.min = now.tm_min;
_time.second = now.tm_sec;
if (!highResolutionAvailable)
{
_time.millisecond = 0;
}
else{
LARGE_INTEGER qfc;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&qfc);
_time.millisecond = (int)((qfc.QuadPart - beginCount)/countPerMilliSecond)%1000;
}
return true;
}
private:
bool highResolutionAvailable;
LONGLONG countPerMilliSecond;
LONGLONG beginCount;
};
class CurrentTime
{
public:
static bool get(HighResolutionTime& _time)
{
return akumaslab::system::Singleton< CurrentTimeProvider >::getRef().getCurrentTime(_time);
}
};
}
}
DEMO:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
HighResolutionTime time;
CurrentTime::get(time);
const int size = 20;
char buf[size] = {0};
_snprintf_s(buf, size, size, "%02d:%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%03d ", time.month, time.day, time.hour, time.min, time.second, time.millisecond);
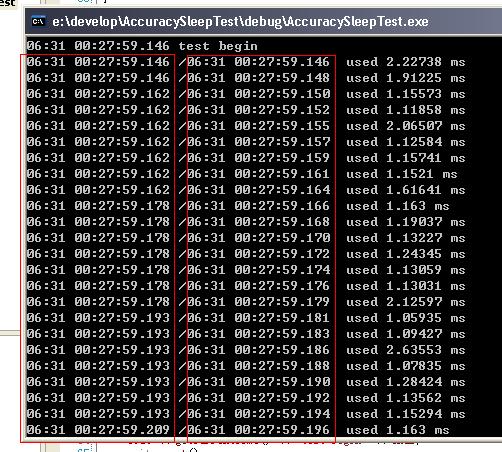
测试结果如下,下图是高精度计时器按1ms进行Sleep的结果,左侧为使用_ftime计时,右侧为使用精确时刻计时,总体来说,虽然无法达到100%可靠,但是相对原来的15ms已经有较大提升,期望Windows能够尽快提供真正的高精度时间管理技术
受影响的操作包括Sleep、GetTickCount、_ftime等等。比如你调用Sleep(2),期待2ms之后线程自动唤醒,但是实际结果可能是15ms甚至2x ms的时候才会唤醒,对于简单应用来说影响不大,但是对于精度要求非常高的系统来说,这样的问题就是非常致命的了。
代码思路如下:
1、高精度定时器。使用Singleton模式挂起请求Sleep的线程并统一管理,后台使用Windows MultiMedia SDK的定期回调函数不断检测并回复到时的线程,超时时间与当前时间采用QueryPerformanceCounter/QueryPerformanceFrequency的高精度计时,确保整体功能可靠性。
2、精确时刻获取。由于可以获取到毫秒级别的_ftime与GetTickCount都受到Windows系统时间精度影响,最小单位只有15ms,所以需要借助QueryPerformanceCounter/QueryPerformanceFrequency进行准确计时。代码首先根据_ftime获取起始时刻的精确刻度,然后根据差量计算当前的精确时刻。
代码中的Singleton模式可以找到很多实现,因此本文不进行详述
代码(VS2005 c++编译)
1、高精度定时器
[c-sharp]
view plaincopy
#pragma once
#include <Windows.h>
#include <list>
#include <akumaslab/system/singleton.hpp>
namespace akumaslab{
namespace time{
using std::list;
class PreciseTimerProvider
{
struct WaitedHandle{
HANDLE threadHandle;
LONGLONG elapsed;//超时时间
} ;
typedef list< WaitedHandle > handle_list_type;
typedef akumaslab::system::Singleton< PreciseTimerProvider > timer_type;
public:
PreciseTimerProvider(void):highResolutionAvailable(false), timerID(0)
{
InitializeCriticalSection(&critical);
static LARGE_INTEGER systemFrequency;
if(0 != QueryPerformanceFrequency(&systemFrequency))
{
timeBeginPeriod(callbackInterval);
highResolutionAvailable = true;
countPerMilliSecond = systemFrequency.QuadPart/1000;
timerID = timeSetEvent(callbackInterval, 0, &PreciseTimerProvider::TimerFunc, NULL, TIME_PERIODIC);
}
}
//挂起当前线程
//@milliSecond:超时时间,单位:毫秒
bool suspendCurrentThread(int milliSecond)
{
if(milliSecond <= 0)return false;
if (!highResolutionAvailable)return false;
HANDLE currentThreadHandle = GetCurrentThread();
HANDLE currentProcessHandle = GetCurrentProcess();
HANDLE realThreadHandle(0);
DuplicateHandle(currentProcessHandle, currentThreadHandle, currentProcessHandle, &realThreadHandle, 0, FALSE, DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS);
WaitedHandle item;
item.threadHandle = realThreadHandle;
LARGE_INTEGER now;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&now);
now.QuadPart += milliSecond * countPerMilliSecond;
item.elapsed = now.QuadPart;
EnterCriticalSection(&critical);
waitList.push_back(item);
LeaveCriticalSection(&critical);
//挂起线程
SuspendThread(realThreadHandle);
CloseHandle(realThreadHandle);
return true;
}
//恢复超时线程
void resumeTimeoutThread()
{
if (!highResolutionAvailable)return;
LARGE_INTEGER now;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&now);
EnterCriticalSection(&critical);
for (handle_list_type::iterator ir = waitList.begin(); ir != waitList.end(); )
{
WaitedHandle& waited = *ir;
if (now.QuadPart >= waited.elapsed)
{
ResumeThread(waited.threadHandle);
ir = waitList.erase(ir);
continue;
}
ir++;
}
LeaveCriticalSection(&critical);
}
~PreciseTimerProvider(){
if (0 != timerID)
{
timeKillEvent(timerID);
timerID = 0;
timeEndPeriod(callbackInterval);
}
DeleteCriticalSection(&critical);
}
private:
static void CALLBACK TimerFunc(UINT uID, UINT uMsg, DWORD dwUser, DWORD dw1, DWORD dw2)
{
static bool initialed = false;
if (!initialed)
{
if (initialWorkThread())
{
initialed = true;
}
else{
return;
}
}
timer_type::getRef().resumeTimeoutThread();
}
//调整定时器工作线程优先级
static bool initialWorkThread()
{
HANDLE realProcessHandle = OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, _getpid());
if (NULL == realProcessHandle)
{
return false;
}
if (0 == SetPriorityClass(realProcessHandle, REALTIME_PRIORITY_CLASS))
{
CloseHandle(realProcessHandle);
return false;
}
HANDLE currentThreadHandle = GetCurrentThread();
HANDLE currentProcessHandle = GetCurrentProcess();
HANDLE realThreadHandle(0);
DuplicateHandle(currentProcessHandle, currentThreadHandle, currentProcessHandle, &realThreadHandle, 0, FALSE, DUPLICATE_SAME_ACCESS);
SetThreadPriority(realThreadHandle, THREAD_PRIORITY_TIME_CRITICAL);
//必须关闭复制句柄
CloseHandle(realThreadHandle);
CloseHandle(realProcessHandle);
return true;
}
private:
const static int callbackInterval = 1;
CRITICAL_SECTION critical;
MMRESULT timerID;
LONGLONG countPerMilliSecond;
bool highResolutionAvailable;
handle_list_type waitList;
};
class PreciseTimer
{
typedef akumaslab::system::Singleton< PreciseTimerProvider > timer_type;
public:
static bool wait(int milliSecond)
{
//static PreciseTimerProvider timer;
return timer_type::getRef().suspendCurrentThread(milliSecond);
}
};
}
}
DEMO
[cpp]
view plaincopy
int interval = 1;
int repeatCount = 50;
cout << getCurrentTime() << "test begin" << endl;
unit.reset();
for (int i = 0; i < repeatCount; i++)
{
akumaslab::time::PreciseTimer::wait(interval);
cout << getCurrentTime() << "/" << getNewTime() << " used " << unit.getPreciseElapsedTime() << " ms" << endl;
unit.reset();
}
2、精确时刻获取
[cpp]
view plaincopy
#pragma once
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <akumaslab/system/singleton.hpp>
namespace akumaslab{
namespace time{
struct HighResolutionTime
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
int hour;
int min;
int second;
int millisecond;
};
class CurrentTimeProvider
{
public:
CurrentTimeProvider():highResolutionAvailable(false), countPerMilliSecond(0), beginCount(0)
{
static LARGE_INTEGER systemFrequency;
if(0 != QueryPerformanceFrequency(&systemFrequency))
{
highResolutionAvailable = true;
countPerMilliSecond = systemFrequency.QuadPart/1000;
_timeb tb;
_ftime_s(&tb);
unsigned short currentMilli = tb.millitm;
LARGE_INTEGER now;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&now);
beginCount = now.QuadPart - (currentMilli*countPerMilliSecond);
}
};
bool getCurrentTime(HighResolutionTime& _time)
{
time_t tt;
::time(&tt);
tm now;
localtime_s(&now, &tt);
_time.year = now.tm_year + 1900;
_time.month = now.tm_mon + 1;
_time.day = now.tm_mday + 1;
_time.hour = now.tm_hour;
_time.min = now.tm_min;
_time.second = now.tm_sec;
if (!highResolutionAvailable)
{
_time.millisecond = 0;
}
else{
LARGE_INTEGER qfc;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&qfc);
_time.millisecond = (int)((qfc.QuadPart - beginCount)/countPerMilliSecond)%1000;
}
return true;
}
private:
bool highResolutionAvailable;
LONGLONG countPerMilliSecond;
LONGLONG beginCount;
};
class CurrentTime
{
public:
static bool get(HighResolutionTime& _time)
{
return akumaslab::system::Singleton< CurrentTimeProvider >::getRef().getCurrentTime(_time);
}
};
}
}
DEMO:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
HighResolutionTime time;
CurrentTime::get(time);
const int size = 20;
char buf[size] = {0};
_snprintf_s(buf, size, size, "%02d:%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%03d ", time.month, time.day, time.hour, time.min, time.second, time.millisecond);
测试结果如下,下图是高精度计时器按1ms进行Sleep的结果,左侧为使用_ftime计时,右侧为使用精确时刻计时,总体来说,虽然无法达到100%可靠,但是相对原来的15ms已经有较大提升,期望Windows能够尽快提供真正的高精度时间管理技术

相关文章推荐
- Windows下的高精度定时器实现及精确时刻获取
- Windows下的高精度定时器实现及精确时刻获取
- Windows下的高精度定时器实现及精确时刻获取
- Windows下的高精度定时器实现及精确时刻获取
- Windows下的高精度定时器实现及精确时刻获取
- Windows高精度微秒级(并发)定时器实现
- 定时器:为 Windows 实现一个连续更新,高精度的时间供应器
- 定时器:为 Windows 实现一个连续更新,高精度的时间供应器
- linux下使用select实现精确定时器
- Linux时间子系统之六:高精度定时器(HRTIMER)的原理和实现
- JAVA分别实现Windows平台和Linux平台下的ip获取
- 使用linux内核hrtimer高精度定时器实现GPIO口模拟PWM,【原创】
- Windows C++ 获取文件夹大小(通过FindNextFile实现)
- 非实时系统精确定时器的实现
- 线程实现定时器(windows下C++版)
- Linux时间子系统之六:高精度定时器(HRTIMER)的原理和实现
- Windows下高精度定时器讨论
- linux下使用select实现精确定时器
- 不用定时器和汇编语言,只用C语言实现精确无误的延时
- Linux时间子系统之六:高精度定时器(HRTIMER)的原理和实现【转】
