linux系统编程之文件与I/O(五):文件的内核结构file和dup实现重定向
2013-05-14 16:51
597 查看
一、打开文件内核数据结构
1、一个进程打开两个文件
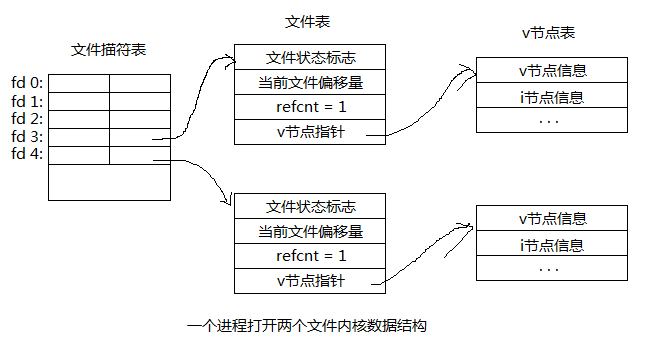
文件状态标志:读、写、追加、同步、非阻塞等
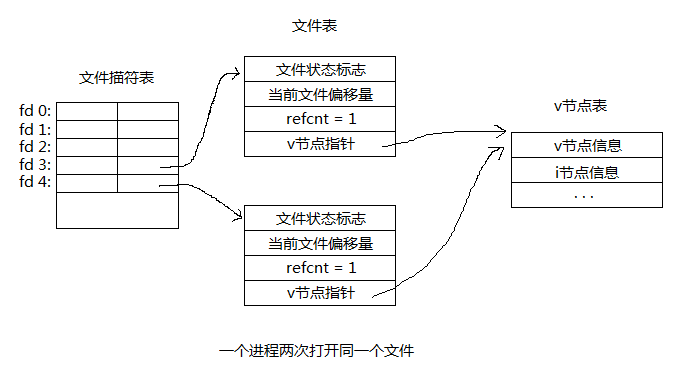
2、一个进程两次打开同一文件
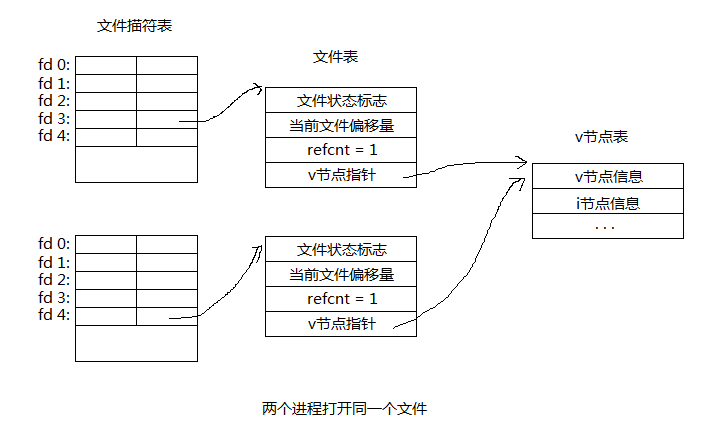
3、两个进程打开同一文件
示例程序:
C++ Code
假设test.txt文件的内容是 ABCDEhello
测试如下:
simba@ubuntu:~/Documents/code/linux_programming/APUE/File_IO$ ./file_share
buf1=ABCDE
buf2=ABCDE
buf1=AAAAA
test.txt文件内容变成 ABCDEAAAAA
分析:由上图分析可知,一个进程两次打开同一文件,文件表是不共享的,即各有自己的文件偏移量和打开文件标志,所以两次read不同的fd都是从头开始读取,但V节点表是共享的,在fd2写入(同个文件表的read和write是共享偏移的)更改了inode指向的硬盘数据块,再次read fd1得到的也是更改后的值。
二、I/O重定向
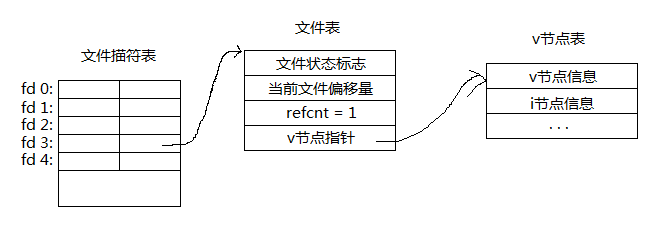
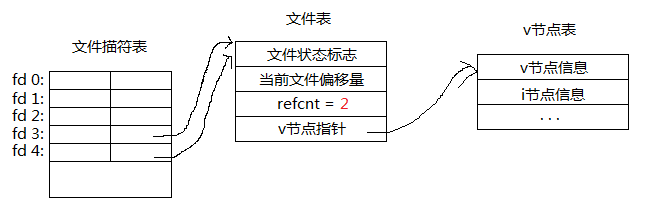
当我们执行了dup(3)之后,系统选择一个空闲的文件描述符即4,这样就有两个文件描述符指向同个文件表,所以引用计数为2。利用dup等函数可以进行重定向的步骤是先close输入输出文件描述符,然后执行dup(fd), 这样输入输出文件描述符也指向fd指向的文件,这样就实现了重定向。此外dup2, fcntl 函数也可以实现,其实不使用这些函数,而直接close(0/1/2)完再open也可以实现。如下使用cat命令实现复制文件的功能:
C++ Code
现在标准输入是文件Makefile,标准输出是文件test.txt ,将当前进程替换成cat,则cat会从标准输入读而后输出到标准输出,即完成了copy的功能。
dup/fcntl 函数示例程序如下:
C++ Code
参考:《APUE》
1、一个进程打开两个文件

文件状态标志:读、写、追加、同步、非阻塞等
2、一个进程两次打开同一文件

3、两个进程打开同一文件

示例程序:
C++ Code
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 | /************************************************************************* > File Name: file_share.c > Author: Simba > Mail: dameng34@163.com > Created Time: Sat 23 Feb 2013 02:34:02 PM CST ************************************************************************/ #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<errno.h> #include<string.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) \ do { \ perror(m); \ exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \ } while(0) int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int fd1, fd2; char buf1[1024] = {0}; char buf2[1024] = {0}; /* 进程控制块PCB * struct task { * ... * struct files_struct *files; * } * 同一个进程两次打开同一个文件,一个进程拥有的一个文件描述符表其中一个fd索引对应的指针指向一个 * 文件表(包括文件状态(读写追加同步非阻塞等),当前文件偏移量, * 文件引用次数(当有两个fd指向同个文件表时引用计数为2,见dup,也可用于重定向), * 文件操作指针, V节点指针等)不共享, * V节点表(包括V节点信息(struct stat), i节点信息等)共享 */ /* 两个进程打开同一个文件的情况与上类同*/ fd1 = open("test.txt", O_RDONLY); if (fd1 == -1) ERR_EXIT("open error"); read(fd1, buf1, 5); printf("buf1=%s\n", buf1); fd2 = open("test.txt", O_RDWR); if (fd2 == -1) ERR_EXIT("open error"); read(fd2, buf2, 5); printf("buf2=%s\n", buf2); write(fd2, "AAAAA", 5); memset(buf1, 0, sizeof(buf1)); read(fd1, buf1, 5); printf("buf1=%s\n", buf1); close(fd1); close(fd2); return 0; } |
测试如下:
simba@ubuntu:~/Documents/code/linux_programming/APUE/File_IO$ ./file_share
buf1=ABCDE
buf2=ABCDE
buf1=AAAAA
test.txt文件内容变成 ABCDEAAAAA
分析:由上图分析可知,一个进程两次打开同一文件,文件表是不共享的,即各有自己的文件偏移量和打开文件标志,所以两次read不同的fd都是从头开始读取,但V节点表是共享的,在fd2写入(同个文件表的read和write是共享偏移的)更改了inode指向的硬盘数据块,再次read fd1得到的也是更改后的值。
二、I/O重定向


当我们执行了dup(3)之后,系统选择一个空闲的文件描述符即4,这样就有两个文件描述符指向同个文件表,所以引用计数为2。利用dup等函数可以进行重定向的步骤是先close输入输出文件描述符,然后执行dup(fd), 这样输入输出文件描述符也指向fd指向的文件,这样就实现了重定向。此外dup2, fcntl 函数也可以实现,其实不使用这些函数,而直接close(0/1/2)完再open也可以实现。如下使用cat命令实现复制文件的功能:
C++ Code
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | /************************************************************************* > File Name: process_.c > Author: Simba > Mail: dameng34@163.com > Created Time: Sat 23 Feb 2013 02:34:02 PM CST ************************************************************************/ #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<errno.h> #include<string.h> #include<signal.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) \ do { \ perror(m); \ exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \ } while(0) int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { close(0); open("Makefile", O_RDONLY); close(1); open("test.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664); execlp("cat", "cat", NULL); return 0; } |
dup/fcntl 函数示例程序如下:
C++ Code
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | /************************************************************************* > File Name: file_dup.c > Author: Simba > Mail: dameng34@163.com > Created Time: Sat 23 Feb 2013 02:34:02 PM CST ************************************************************************/ #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<fcntl.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<errno.h> #include<string.h> #define ERR_EXIT(m) \ do { \ perror(m); \ exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \ } while(0) /* dup dup2 fcntl */ int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int fd; fd = open("test2.txt", O_WRONLY); if (fd == -1) ERR_EXIT("open error"); /* close(1); dup(fd); */ // dup2(fd, 1); close(1); if (fcntl(fd, F_DUPFD, 0) < 0) //从0开始搜索可用的fd ERR_EXIT("fcntl error"); printf("hello\n"); // 输出重定向到test2.txt return 0; } |
相关文章推荐
- linux系统编程之文件与I/O(五):文件的内核结构file和dup实现重定向
- 文件的内核结构file和dup实现重定向
- linux sudo 重定向,实现只有系统管理员才有权限操作的文件中写入信息
- 【Linux系统编程】Linux 可执行文件结构与进程结构
- Linux文件系统层次结构(译自Linux Filesystem Hierarchy)
- 文件进程linux系统编程之文件与I/O(五):打开文件的内核结构file和重定向
- (转)linux sudo 重定向,实现只有系统管理员才有权限操作的文件中写入信息
- Linux下C编程-----IO/文件操作 模拟linux ls程序显示文件系统树形结构(2)
- linux内核文件IO的系统调用实现分析(open)
- linux应用编程笔记(5)系统调用文件编程方法实现文件复制
- linux 2.6.11内核文件IO的系统调用实现分析(read,write)(转载)
- Linux 内核编程之文件系统(二)
- 【Linux 内核】文件系统(结构篇)
- linux系统之_虚拟文件系统的内核实现前世今生
- Linux 内核编程之文件系统(一)
- Linux 文件系统层次结构标准简介(Filesystem Hierarchy Standard)
- Linux序列文件(seq_file)接口的内核实现
- Linux 内核编程之文件系统 VFS中的目录项对象和文件对象 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-02/32127p2.htm
- Linux 内核文件系统关键数据结构
- Linux下的C语言编程——系统调用read和write函数实现文件拷贝
