ASP.NET 用户密码加密机制
2013-04-22 15:04
746 查看
ASP.NET 用户密码加密机制
2010-12-18 11:22:48| 分类:ASP.NET |字号 订阅
加Salt散列
我们知道,如果直接对密码进行散列,那么黑客(统称那些有能力窃取用户数据并企图得到用户密码的人)可以对一个已知密码进行散列,然后通过对比散列值得到某用户的密码。换句话说,虽然黑客不能取得某特定用户的密码,但他可以知道使用特定密码的用户有哪些。
加Salt可以一定程度上解决这一问题。所谓加Salt,就是加点“佐料”。其基本想法是这样的——当用户首次提供密码时(通常是注册时),由系统自动往这个密码里撒一些“佐料”,然后再散列。而当用户登录时,系统为用户提供的代码撒上同样的“佐料”,然后散列,再比较散列值,已确定密码是否正确。
这里的“佐料”被称作“Salt值”,这个值是由系统随机生成的,并且只有系统知道。这样,即便两个用户使用了同一个密码,由于系统为它们生成的salt值不同,他们的散列值也是不同的。即便黑客可以通过自己的密码和自己生成的散列值来找具有特定密码的用户,但这个几率太小了(密码和salt值都得和黑客使用的一样才行)。
下面详细介绍一下加Salt散列的过程。介绍之前先强调一点,前面说过,验证密码时要使用和最初散列密码时使用“相同的”佐料。所以Salt值是要存放在数据库里的。
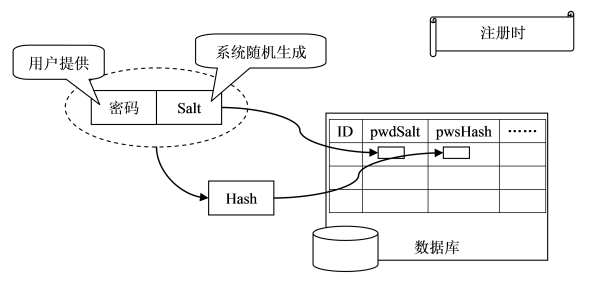
图1. 用户注册
如图1所示,注册时,
1)用户提供密码(以及其他用户信息);
2)系统为用户生成Salt值;
3)系统将Salt值和用户密码连接到一起;
4)对连接后的值进行散列,得到Hash值;
5)将Hash值和Salt值分别放到数据库中。
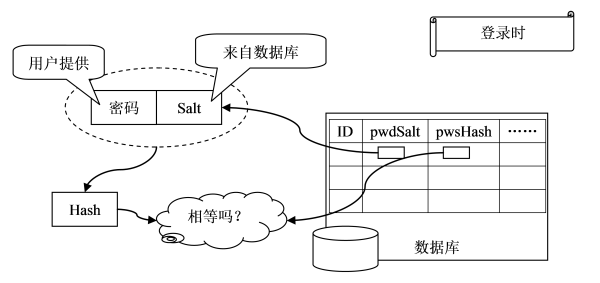
图2. 用户登录
如图2所示,登录时,
1)用户提供用户名和密码;
2)系统通过用户名找到与之对应的Hash值和Salt值;
3)系统将Salt值和用户提供的密码连接到一起;
4)对连接后的值进行散列,得到Hash'(注意有个“撇”);
5)比较Hash和Hash'是否相等,相等则表示密码正确,否则表示密码错误。
3 ASP.NET 2.0 Membership中的相关代码
(省略关于Membership的介绍若干字)
本文Anders Liu仅研究了SqlMembershipProvider,该类位于System.Web.dll,System.Web.Security命名空间中。
首先,要使用Membership,必须先用aspnet_regsql.exe命令来配置数据库,该工具会向现有数据库中添加一系列表和存储过程等,配置好的数据库中有一个表aspnet_Membership,就是用于存放用户帐户信息的。其中我们所关注的列有三个——Password、PasswordFormat和PasswordSalt。
Password存放的是密码的散列值,PasswordFormat存放用于散列密码所使用的算法,PasswordSalt就是系统生成的Salt值了。
注册时用到了该类的CreateUser方法,该方法主要代码如下:
public override MembershipUser CreateUser(string username, string password, string email, string passwordQuestion, string passwordAnswer, bool isApproved, object providerUserKey, out MembershipCreateStatus status)
{
string str3;
MembershipUser user;
if (!SecUtility.ValidateParameter(ref password, true, true, false, 0x80))
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidPassword;
return null;
}
// 生成salt值
string salt = base.GenerateSalt();
// 结合salt值对密码进行散列
string objValue = base.EncodePassword(password, (int) this._PasswordFormat, salt);
if (objValue.Length > 0x80)
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidPassword;
return null;
}
if (passwordAnswer != null)
{
passwordAnswer = passwordAnswer.Trim();
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(passwordAnswer))
{
if (passwordAnswer.Length > 0x80)
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidAnswer;
return null;
}
str3 = base.EncodePassword(passwordAnswer.ToLower(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture), (int) this._PasswordFormat, salt);
}
else
{
str3 = passwordAnswer;
}
if (!SecUtility.ValidateParameter(ref str3, this.RequiresQuestionAndAnswer, true, false, 0x80))
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidAnswer;
return null;
}
if (!SecUtility.ValidateParameter(ref username, true, true, true, 0x100))
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidUserName;
return null;
}
if (!SecUtility.ValidateParameter(ref email, this.RequiresUniqueEmail, this.RequiresUniqueEmail, false, 0x100))
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidEmail;
return null;
}
if (!SecUtility.ValidateParameter(ref passwordQuestion, this.RequiresQuestionAndAnswer, true, false, 0x100))
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidQuestion;
return null;
}
if ((providerUserKey != null) && !(providerUserKey is Guid))
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidProviderUserKey;
return null;
}
if (password.Length < this.MinRequiredPasswordLength)
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidPassword;
return null;
}
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < password.Length; i++)
{
if (!char.IsLetterOrDigit(password, i))
{
num++;
}
}
if (num < this.MinRequiredNonAlphanumericCharacters)
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidPassword;
return null;
}
if ((this.PasswordStrengthRegularExpression.Length > 0) && !Regex.IsMatch(password, this.PasswordStrengthRegularExpression))
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidPassword;
return null;
}
ValidatePasswordEventArgs e = new ValidatePasswordEventArgs(username, password, true);
this.OnValidatingPassword(e);
if (e.Cancel)
{
status = MembershipCreateStatus.InvalidPassword;
return null;
}
try
{
SqlConnectionHolder connection = null;
try
{
connection = SqlConnectionHelper.GetConnection(this._sqlConnectionString, true);
this.CheckSchemaVersion(connection.Connection);
DateTime time = this.RoundToSeconds(DateTime.UtcNow);
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand("dbo.aspnet_Membership_CreateUser", connection.Connection);
command.CommandTimeout = this.CommandTimeout;
command.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@ApplicationName", SqlDbType.NVarChar, this.ApplicationName));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@UserName", SqlDbType.NVarChar, username));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@Password", SqlDbType.NVarChar, objValue));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@PasswordSalt", SqlDbType.NVarChar, salt));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@Email", SqlDbType.NVarChar, email));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@PasswordQuestion", SqlDbType.NVarChar, passwordQuestion));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@PasswordAnswer", SqlDbType.NVarChar, str3));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@IsApproved", SqlDbType.Bit, isApproved));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@UniqueEmail", SqlDbType.Int, this.RequiresUniqueEmail ? 1 : 0));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@PasswordFormat", SqlDbType.Int, (int) this.PasswordFormat));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@CurrentTimeUtc", SqlDbType.DateTime, time));
SqlParameter parameter = this.CreateInputParam("@UserId", SqlDbType.UniqueIdentifier, providerUserKey);
parameter.Direction = ParameterDirection.InputOutput;
command.Parameters.Add(parameter);
parameter = new SqlParameter("@ReturnValue", SqlDbType.Int);
parameter.Direction = ParameterDirection.ReturnValue;
command.Parameters.Add(parameter);
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
int num3 = (parameter.Value != null) ? ((int) parameter.Value) : -1;
if ((num3 < 0) || (num3 > 11))
{
num3 = 11;
}
status = (MembershipCreateStatus) num3;
if (num3 != 0)
{
return null;
}
providerUserKey = new Guid(command.Parameters["@UserId"].Value.ToString());
time = time.ToLocalTime();
user = new MembershipUser(this.Name, username, providerUserKey, email, passwordQuestion, null, isApproved, false, time, time, time, time, new DateTime(0x6da, 1, 1));
}
finally
{
if (connection != null)
{
connection.Close();
connection = null;
}
}
}
catch
{
throw;
}
return user;
}
其中我们可以看到两个比较令人感兴趣的方法:GenerateSalt和EncodePassword。由于本文讨论的仅仅是密码的散列,而不是整个用户注册过程,所以这里只对这两个函数进行分析。
这两个方法来自于SqlMembershipProvider的父类,MembershipProvider。
GenerateSalt方法的代码比较简单:
internal string GenerateSalt()
{
byte[] data = new byte[0x10];
new RNGCryptoServiceProvider().GetBytes(data);
return Convert.ToBase64String(data);
}
但是要注意的是,在这种方法里Salt值的高度随机性是安全的保障,所以不能简单的使用Random来获取随机数,而应该使用更安全的方式。这里使用了RNGCryptoServiceProvider来生成随机数。
EncodePassword方法的代码也不难:
internal string EncodePassword(string pass, int passwordFormat, string salt)
{
if (passwordFormat == 0)
{
return pass;
}
// 将密码和salt值转换成字节形式并连接起来
byte[] bytes = Encoding.Unicode.GetBytes(pass);
byte[] src = Convert.FromBase64String(salt);
byte[] dst = new byte[src.Length + bytes.Length];
byte[] inArray = null;
Buffer.BlockCopy(src, 0, dst, 0, src.Length);
Buffer.BlockCopy(bytes, 0, dst, src.Length, bytes.Length);
// 选择算法,对连接后的值进行散列
if (passwordFormat == 1)
{
HashAlgorithm algorithm = HashAlgorithm.Create(Membership.HashAlgorithmType);
if ((algorithm == null) && Membership.IsHashAlgorithmFromMembershipConfig)
{
RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().Membership.ThrowHashAlgorithmException();
}
inArray = algorithm.ComputeHash(dst);
}
else
{
inArray = this.EncryptPassword(dst);
}
// 以字符串形式返回散列值
return Convert.ToBase64String(inArray);
}
这段代码的作用就是,首先将密码和salt值转换成字节数组(分别放到bytes和src数组中),然后拼接到一起(dst数组)。之后再根据Web.config中设置的加密算法,对这个拼接值进行散列,最后把散列值转换成字符串形式返回。
最后,用户登录时,将会使用SqlMembershipProvider的CheckPassword方法对密码进行检验。该方法有两种重载形式,最为完整的一种如下所示:
private bool CheckPassword(string username, string password, bool updateLastLoginActivityDate, bool failIfNotApproved, out string salt, out int passwordFormat)
{
SqlConnectionHolder connection = null;
string str; // 密码散列值
int num;
int num2;
int num3;
bool flag2;
DateTime time;
DateTime time2;
// 从数据库中拿到Hash和Salt
this.GetPasswordWithFormat(username, updateLastLoginActivityDate, out num, out str, out passwordFormat, out salt, out num2, out num3, out flag2, out time, out time2);
if (num != 0)
{
return false;
}
if (!flag2 && failIfNotApproved)
{
return false;
}
// 对用户刚刚输入的密码进行散列
string str2 = base.EncodePassword(password, passwordFormat, salt);
// 比较两个散列值,看密码是否相等
bool objValue = str.Equals(str2);
if ((objValue && (num2 == 0)) && (num3 == 0))
{
return true;
}
try
{
try
{
connection = SqlConnectionHelper.GetConnection(this._sqlConnectionString, true);
this.CheckSchemaVersion(connection.Connection);
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand("dbo.aspnet_Membership_UpdateUserInfo", connection.Connection);
DateTime utcNow = DateTime.UtcNow;
command.CommandTimeout = this.CommandTimeout;
command.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@ApplicationName", SqlDbType.NVarChar, this.ApplicationName));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@UserName", SqlDbType.NVarChar, username));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@IsPasswordCorrect", SqlDbType.Bit, objValue));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@UpdateLastLoginActivityDate", SqlDbType.Bit, updateLastLoginActivityDate));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@MaxInvalidPasswordAttempts", SqlDbType.Int, this.MaxInvalidPasswordAttempts));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@PasswordAttemptWindow", SqlDbType.Int, this.PasswordAttemptWindow));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@CurrentTimeUtc", SqlDbType.DateTime, utcNow));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@LastLoginDate", SqlDbType.DateTime, objValue ? utcNow : time));
command.Parameters.Add(this.CreateInputParam("@LastActivityDate", SqlDbType.DateTime, objValue ? utcNow : time2));
SqlParameter parameter = new SqlParameter("@ReturnValue", SqlDbType.Int);
parameter.Direction = ParameterDirection.ReturnValue;
command.Parameters.Add(parameter);
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
num = (parameter.Value != null) ? ((int) parameter.Value) : -1;
return objValue;
}
finally
{
if (connection != null)
{
connection.Close();
connection = null;
}
}
}
catch
{
throw;
}
return objValue;
}
这个代码首先通过GetPasswordWithFormat得到了Hash值(变量str)和Salt值(变量salt),然后对用户输入的密码(参数password)进行与注册时一样的散列(只是salt值使用了数据库中现存的值)得到散列值str2,之后通过对比str和str2,就知道密码正确与否了。
FormsAuthentication.HashPasswordForStoringInConfigFile(pd+salt,"SHA1");//直接加密
相关文章推荐
- 浅析ASP.NET 2.0的用户密码加密机制
- 浅析ASP.NET 2.0的用户密码加密机制
- 浅析ASP.NET 2.0的用户密码加密机制
- 浅析ASP.NET 2.0的用户密码加密机制
- 浅析ASP.NET 2.0的用户密码加密机制
- ASP.NET中怎么把Button的Accesskey设成回车键 用户输完密码后,按回车也能进入,
- ASP.NET中散列加密密码
- ASP.NET的页面加密机制【转】
- ASP.NET中利用JQuery AJAX修改用户密码
- asp.net系统增加用户登录后修改密码的功能
- Tailspin Spyworks指南第六讲:ASP.NET用户机制
- asp.net创建用户出现“密码最短长度为7,其中必须包含以下非字母数字字符:1“提示
- asp.net用户注册的与密码强度及验证的相关问题。对上一次详细叙述。
- Asp.Net使用加密cookie代替session验证用户登录状态 源码分享
- asp.net 密码加密 MD5 加密
- ASP.NET专题研究——用户登录、注册和发送密码
- ASP.NET的用户验证方法,及加密处理
- iis +asp.net 4 输入网提示用户和密码
- 4000 asp.net用户注册的与密码强度相关的问题。
- 重置ASP.NET membership加密后的密码
