opencv 笔记02Core_Scan
2013-04-09 23:26
225 查看
1. OpenCV提供了两个简便的可用于计时的函数 getTickCount() 和 getTickFrequency() 。第一个函数返回你的CPU自某个事件(如启动电脑)以来走过的时钟周期数,第二个函数返回你的CPU一秒钟所走的时钟周期数。这样,我们就能轻松地以秒为单位对某运算计时:
2. 图像矩阵的大小取决于我们所用的颜色模型,确切地说,取决于所用通道数。如果是灰度图像,矩阵就会像这样:

而对多通道图像来说,矩阵中的列会包含多个子列,其子列个数与通道数相等。例如,RGB颜色模型的矩阵:
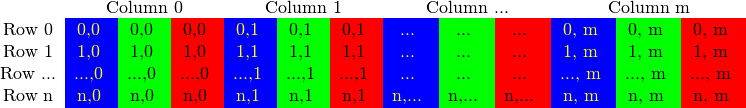
子列的通道顺序是反过来的:BGR而不是RGB。很多情况下,因为内存足够大,可实现连续存储,因此,图像中的各行就能一行一行地连接起来,形成一个长行。连续存储有助于提升图像扫描速度,我们可以使用 isContinuous() 来去判断矩阵是否是连续存储的.
另一种方法:使用data,data会从 Mat 中返回指向矩阵第一行第一列的指针。注意如果该指针为NULL则表明对象里面无输入
对于彩色图像中的一行,每列中有3个uchar元素,这可以被认为是一个小的包含uchar元素的vector,在OpenCV中用 Vec3b 来命名。如果要访问第n个子列,我们只需要简单的利用[]来操作就可以。OpenCV的迭代在扫描过一行中所有列后会自动跳至下一行
事实上这个方法并不推荐被用来进行图像扫描,它本来是被用于获取或更改图像中的随机元素。
为避免反复输入数据类型和at带来的麻烦和浪费的时间,OpenCV 提供了:basicstructures:Mat_ <id3> data
type. 它同样可以被用于获知矩阵的数据类型
在图像处理中,对于一个给定的值,将其替换成其他的值是一个很常见的操作
operationsOnArrays:LUT() <lut> ,一个包含于core
module的函数
I 是输入 J 是输出
结论:推荐LUT批量查改,Efficient、Iterator其次,On-The-Fly随即存储
double t = (double)getTickCount(); // 做点什么 ... t = ((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency(); cout << "Times passed in seconds: " << t << endl;
2. 图像矩阵的大小取决于我们所用的颜色模型,确切地说,取决于所用通道数。如果是灰度图像,矩阵就会像这样:

而对多通道图像来说,矩阵中的列会包含多个子列,其子列个数与通道数相等。例如,RGB颜色模型的矩阵:

子列的通道顺序是反过来的:BGR而不是RGB。很多情况下,因为内存足够大,可实现连续存储,因此,图像中的各行就能一行一行地连接起来,形成一个长行。连续存储有助于提升图像扫描速度,我们可以使用 isContinuous() 来去判断矩阵是否是连续存储的.
1.高效的方法 Efficient Way
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceC(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
int channels = I.channels();
int nRows = I.rows * channels;
int nCols = I.cols;
if (I.isContinuous())
{
nCols *= nRows;
nRows = 1;
}
int i,j;
uchar* p;
for( i = 0; i < nRows; ++i)
{
p = I.ptr<uchar>(i);
for ( j = 0; j < nCols; ++j)
{
p[j] = table[p[j]];
}
}
return I;
}另一种方法:使用data,data会从 Mat 中返回指向矩阵第一行第一列的指针。注意如果该指针为NULL则表明对象里面无输入
uchar* p = I.data; for( unsigned int i =0; i < ncol*nrows; ++i) *p++ = table[*p];
2.迭代
106c7
法 The iterator (safe) method
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceIterator(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
MatIterator_<uchar> it, end;
for( it = I.begin<uchar>(), end = I.end<uchar>(); it != end; ++it)
*it = table[*it];
break;
}
case 3:
{
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it, end;
for( it = I.begin<Vec3b>(), end = I.end<Vec3b>(); it != end; ++it)
{
(*it)[0] = table[(*it)[0]];
(*it)[1] = table[(*it)[1]];
(*it)[2] = table[(*it)[2]];
}
}
}
return I;
}对于彩色图像中的一行,每列中有3个uchar元素,这可以被认为是一个小的包含uchar元素的vector,在OpenCV中用 Vec3b 来命名。如果要访问第n个子列,我们只需要简单的利用[]来操作就可以。OpenCV的迭代在扫描过一行中所有列后会自动跳至下一行
3. 通过相关返回值的On-the-fly地址计算
事实上这个方法并不推荐被用来进行图像扫描,它本来是被用于获取或更改图像中的随机元素。Mat& ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
for( int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for( int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j )
I.at<uchar>(i,j) = table[I.at<uchar>(i,j)];
break;
}
case 3:
{
Mat_<Vec3b> _I = I;
for( int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for( int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j )
{
_I(i,j)[0] = table[_I(i,j)[0]];
_I(i,j)[1] = table[_I(i,j)[1]];
_I(i,j)[2] = table[_I(i,j)[2]];
}
I = _I;
break;
}
}
return I;
}为避免反复输入数据类型和at带来的麻烦和浪费的时间,OpenCV 提供了:basicstructures:Mat_ <id3> data
type. 它同样可以被用于获知矩阵的数据类型
4. 核心函数LUT(The Core Function)
在图像处理中,对于一个给定的值,将其替换成其他的值是一个很常见的操作operationsOnArrays:LUT() <lut> ,一个包含于core
module的函数
Mat lookUpTable(1, 256, CV_8U); uchar* p = lookUpTable.data; for( int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) p[i] = table[i];
LUT(I, lookUpTable, J);
I 是输入 J 是输出
性能表现
| Efficient Way | 79.4717 milliseconds |
| Iterator | 83.7201 milliseconds |
| On-The-Fly RA | 93.7878 milliseconds |
| LUT function | 32.5759 milliseconds |
相关文章推荐
- OpenCV学习笔记(四)——新版本的数据结构core
- OpenCV学习笔记(四)——新版本的数据结构core
- OpenCV学习笔记(四十八)——PCA算法实现core
- OpenCV学习笔记(二十一)——绘图函数core OpenCV学习笔记(二十二)——粒子滤波跟踪方法 OpenCV学习笔记(二十三)——OpenCV的GUI之凤凰涅槃Qt OpenCV学习笔记(二十
- OpenCV学习笔记 存取像素值操作汇总core
- opencv 笔记07Core_RND
- OpenCV学习笔记(四)——新版本的数据结构core
- OpenCv基础学习笔记之一[core_c.h]
- OpenCV2学习笔记02:MSVC2013搭建OpenCV开发环境
- OpenCV学习笔记(五十)——Algorithm类介绍(core)
- OpenCV学习笔记2 OpenCV核心模块与核心功能Core Module & Core Functionality(一)
- OpenCV学习笔记5 OpenCV核心模块与核心功能Core Module & Core Functionality(四)
- OpenCV学习笔记6 OpenCV核心模块与核心功能Core Module & Core Functionality(五)
- OpenCV学习笔记02--利用滚动条控制视频;高斯滤波处理图像。
- opencv笔记02-main函数使用
- OpenCV学习笔记3 OpenCV核心模块与核心功能Core Module & Core Functionality(二)
- 二、openCV学习笔记(The Core Functionality)
- OpenCV学习笔记(五十)——Algorithm类介绍(core)
- opencv_笔记_core_basic structures_1117
- OpenCV学习笔记二(scan images)
