二叉查找树
2012-07-06 14:51
162 查看
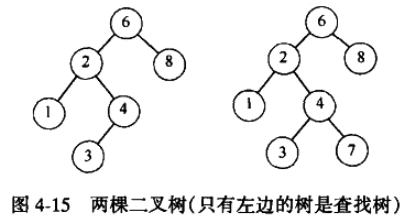
使二叉树成为二叉查找树的性质是,对于树中的每个节点 X ,它的左子树中所有项的值小于 X 中的值,而它右子树中所有项的值大于 X 中的值。
注意,这意味着该树所有的元素可以用某种一致的方式排序。
首先定义一个节点类:
contains 方法
findMin 方法和 findMax 方法
递归方法实现:
insert 方法
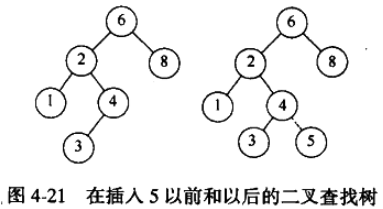
为了将 X 插入到数 T 中,你可以像用 contains 那样沿着树查找。如果找到 X ,则什么也不用做(或做一些“更新”)。否则将 X 插入到遍历的路径上的最后一点上。
remove 方法
如果节点是一片树叶,那么它可以被立即删除;
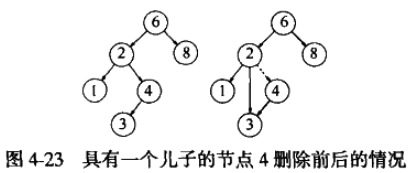
如果节点有一个儿子,则该节点可以在其父节点调整自己的链绕过该节点后被删除;
如果处理具有两个儿子的节点。一般的删除策略是用其右子树的最小的数据代替该节点的数据并递归地删除那个节点(现在它是空的)。因为右子树中的最小的节点不可能有左儿子,所以第二次 remove 要容易。

如果删除的次数不多,通常使用的策略是懒惰删除:当一个元素要被删除时,它仍留在树中,而只是被标记为删除。这特别是在有重复项时很常用,因为此时记录出现频率数的域可以减 1 。如果树中的实际节点数和“被删除”的节点数相同,那么树的深度预计只是上升一个小的常数,因此,存在一个与懒惰删除相关的非常小的时间损耗。再有,如果被删除的项重新插入的,那么分配一个新单元的开销就避免了。
完整代码:
注意,这意味着该树所有的元素可以用某种一致的方式排序。

首先定义一个节点类:
private static class BinaryNode<T>{
T element;
BinaryNode<T> left;
BinaryNode<T> right;
public BinaryNode( T element ) {
this( element, null, null );
}
public BinaryNode(T element, BinaryNode<T> left, BinaryNode<T> right) {
this.element = element;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}contains 方法
public boolean contains( T x ){
return contains( x, root );
}
private boolean contains( T x, BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t == null )
return false;
int compareResult = x.compareTo( t.element );
if( compareResult < 0 ){
return contains( x, t.left );
}
else if( compareResult > 0 ){
return contains( x, t.right );
}
else{
return true;
}
}findMin 方法和 findMax 方法
递归方法实现:
public T findMin(){
if( isEmpty() )
throw new UnderflowException();
return findMin( root ).element;
}
/**
* 递归的方法
* @param t
* @return
*
* Date :2012-7-6
* Author :GongQiang
*/
private BinaryNode<T> findMin( BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t == null ){
return null;
}
else if( t.left == null ){
return t;
}
return findMin( t.left );
}非递归方法实现:public T findMax(){
if( isEmpty() )
throw new UnderflowException();
return findMax( root ).element;
}
/**
* 循环迭代
* @param t
* @return
*
* Date :2012-7-6
* Author :GongQiang
*/
private BinaryNode<T> findMax( BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t!= null ){
while( t.right != null )
t = t.right;
}
return t;
}insert 方法
为了将 X 插入到数 T 中,你可以像用 contains 那样沿着树查找。如果找到 X ,则什么也不用做(或做一些“更新”)。否则将 X 插入到遍历的路径上的最后一点上。

public void insert( T x ){
root = insert( x, root );
}
private BinaryNode<T> insert( T x, BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t == null )
return new BinaryNode<T>( x, null, null );
int compareResult = x.compareTo( t.element );
if( compareResult < 0 ){
t.left = insert( x, t.left );
}
else if( compareResult > 0 ){
t.right = insert( x, t.right );
}
else{
; // 重复,不做任何操作
}
return t;
}remove 方法
如果节点是一片树叶,那么它可以被立即删除;
如果节点有一个儿子,则该节点可以在其父节点调整自己的链绕过该节点后被删除;

如果处理具有两个儿子的节点。一般的删除策略是用其右子树的最小的数据代替该节点的数据并递归地删除那个节点(现在它是空的)。因为右子树中的最小的节点不可能有左儿子,所以第二次 remove 要容易。

public void remove( T x ){
root = remove( x, root );
}
private BinaryNode<T> remove( T x, BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t == null )
return t; // Item not found; do nothing
int compareResult = x.compareTo( t.element );
if( compareResult < 0 ){
t.left = remove( x, t.left );
}
else if( compareResult > 0 ){
t.right = remove( x, t.right );
}
else if( t.left != null && t.right != null ){ // Two children
t.element = findMin( t.right ).element;
t.right = remove( t.element, t.right );
}
else{
t = ( t.left != null )? t.left : t.right;
}
return t;
}如果删除的次数不多,通常使用的策略是懒惰删除:当一个元素要被删除时,它仍留在树中,而只是被标记为删除。这特别是在有重复项时很常用,因为此时记录出现频率数的域可以减 1 。如果树中的实际节点数和“被删除”的节点数相同,那么树的深度预计只是上升一个小的常数,因此,存在一个与懒惰删除相关的非常小的时间损耗。再有,如果被删除的项重新插入的,那么分配一个新单元的开销就避免了。
完整代码:
public class BinarySearchTree<T extends Comparable<? super T>> {
private static class BinaryNode<T>{
T element;
BinaryNode<T> left;
BinaryNode<T> right;
public BinaryNode( T element ) {
this( element, null, null );
}
public BinaryNode(T element, BinaryNode<T> left, BinaryNode<T> right) {
this.element = element;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
private BinaryNode<T> root;
public BinarySearchTree() {
root = null;
}
public void makeEmpty(){
root = null;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return root == null;
}
public boolean contains( T x ){
return contains( x, root );
}
private boolean contains( T x, BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t == null )
return false;
int compareResult = x.compareTo( t.element );
if( compareResult < 0 ){
return contains( x, t.left );
}
else if( compareResult > 0 ){
return contains( x, t.right );
}
else{
return true;
}
}
public T findMin(){
if( isEmpty() )
throw new UnderflowException();
return findMin( root ).element;
}
/**
* 递归的方法
* @param t
* @return
*
* Date :2012-7-6
* Author :GongQiang
*/
private BinaryNode<T> findMin( BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t == null ){
return null;
}
else if( t.left == null ){
return t;
}
return findMin( t.left );
}
public T findMax(){
if( isEmpty() )
throw new UnderflowException();
return findMax( root ).element;
}
/**
* 循环迭代
* @param t
* @return
*
* Date :2012-7-6
* Author :GongQiang
*/
private BinaryNode<T> findMax( BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t!= null ){
while( t.right != null )
t = t.right;
}
return t;
}
public void insert( T x ){
root = insert( x, root );
}
private BinaryNode<T> insert( T x, BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t == null )
return new BinaryNode<T>( x, null, null );
int compareResult = x.compareTo( t.element );
if( compareResult < 0 ){
t.left = insert( x, t.left );
}
else if( compareResult > 0 ){
t.right = insert( x, t.right );
}
else{
; // 重复,不做任何操作
}
return t;
}
public void remove( T x ){
root = remove( x, root );
}
private BinaryNode<T> remove( T x, BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t == null )
return t; // Item not found; do nothing
int compareResult = x.compareTo( t.element );
if( compareResult < 0 ){
t.left = remove( x, t.left );
}
else if( compareResult > 0 ){
t.right = remove( x, t.right );
}
else if( t.left != null && t.right != null ){ // Two children
t.element = findMin( t.right ).element;
t.right = remove( t.element, t.right );
}
else{
t = ( t.left != null )? t.left : t.right;
}
return t;
}
public void printTree(){
//前序输出
printTree( root );
}
private void printTree( BinaryNode<T> t ){
if( t != null ){
printTree( t.left );
System.out.println( t.element );
printTree( t.right );
}
}
}
class UnderflowException extends RuntimeException{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
相关文章推荐
- erl_tree-通用二叉查找树 gb_tree
- [数据结构]二叉查找树 简单实现
- 二叉搜索树(二叉排序树,二叉查找树,二叉检索树)的查找,插入,删除
- 二叉查找树的实现
- 二叉查找树
- 二叉查找树
- C语言实现二叉查找树(BST)的基本操作
- bzoj 1564 [NOI2009]二叉查找树(树形DP)
- 检查一颗二叉树是否是二叉查找树
- 链表——有序链表化为平衡二叉查找树
- lintcode ----在二叉查找树中插入节点
- hdu 5444 继续二叉查找树
- 二叉查找树(一)之 C语言的实现
- 二叉查找树的基本操作实现
- 二叉查找树查找指定排名元素的算法
- 二叉查找树 _ 二叉排序树 _ 二叉搜索树_C++
- 二叉查找树(一)
- BST-二叉查找树
- 数据结构进阶(四)二叉排序树(二叉查找树)
- 每日一省之——使用递归法实现二叉查找树(BST),API齐全
