Android Service生命周期及用法
2012-05-07 09:25
453 查看
首先我们要知道Service具体是干什么的,什么时候用到?以及它的生命周期等。
Service概念及用途:
Android中的服务,它与Activity不同,它是不能与用户交互的,不能自己启动的,运行在后台的程序,如果我们退出应用时,Service进程并没有结束,它仍然在后台运行,那 我们什么时候会用到Service呢?比如我们播放音乐的时候,有可能想边听音乐边干些其他事情,当我们退出播放音乐的应用,如果不用Service,我 们就听不到歌了,所以这时候就得用到Service了,又比如当我们一个应用的数据是通过网络获取的,不同时间(一段时间)的数据是不同的这时候我们可以 用Service在后台定时更新,而不用每打开应用的时候在去获取。
Service生命周期 :
Android Service的生命周期并不像Activity那么复杂,它只继承了onCreate(),onStart(),onDestroy()三个方法,当我们第一次启动Service时,先后调用了onCreate(),onStart()这两个方法,当停止Service时,则执行onDestroy()方法,这里需要注意的是,如果Service已经启动了,当我们再次启动Service时,不会在执行onCreate()方法,而是直接执行onStart()方法,具体的可以看下面的实例。
Service与Activity通信:
Service后端的数据最终还是要呈现在前端Activity之上的,因为启动Service时,系统会重新开启一个新的进程,这就涉及到不同进程间通信的问题了(AIDL)这一节我不作过多描述,当我们想获取启动的Service实例时,我们可以用到bindService和onBindService方法,它们分别执行了Service中IBinder()和onUnbind()方法。
为了让大家 更容易理解,我写了一个简单的Demo,大家可以模仿着我,一步一步的来。
第一步:新建一个Android工程,我这里命名为ServiceDemo.
第二步:修改main.xml代码,我这里增加了四个按钮,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/startservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="startService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="stopService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="bindService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="unbindService"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第三步:新建一个Service,命名为MyService.java代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.text.format.Time;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
//定义个一个Tag标签
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
//这里定义吧一个Binder类,用在onBind()有方法里,这样Activity那边可以获取到
private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start IBinder~~~");
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
//这里我写了一个获取当前时间的函数,不过没有格式化就先这么着吧
public String getSystemTime(){
Time t = new Time();
t.setToNow();
return t.toString();
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
MyService getService()
{
return MyService.this;
}
}
}
第四步:修改ServiceDemo.java,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ServiceDemo extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
private MyService mMyService;
private TextView mTextView;
private Button startServiceButton;
private Button stopServiceButton;
private Button bindServiceButton;
private Button unbindServiceButton;
private Context mContext;
//这里需要用到ServiceConnection在Context.bindService和context.unBindService()里用到
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
//当我bindService时,让TextView显示MyService里getSystemTime()方法的返回值
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mMyService = ((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
setupViews();
}
public void setupViews(){
mContext = ServiceDemo.this;
mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text);
startServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
stopServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
bindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
unbindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice);
startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
}
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(v == startServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.startService(i);
}else if(v == stopServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.stopService(i);
}else if(v == bindServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.bindService(i, mServiceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}else{
mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
}
}
}
第五步:修改AndroidManifest.xml代码(将我们新建的MyService注册进去如下代码第14行:)
[java] view
plaincopy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.tutor.servicedemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".ServiceDemo"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" android:exported="true"></service>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
</manifest>
第六步:执行上述工程,效果图如下:
点击startServie按钮时先后执行了Service中onCreate()->onStart()这两个方法,打开Logcat视窗效果如下图:

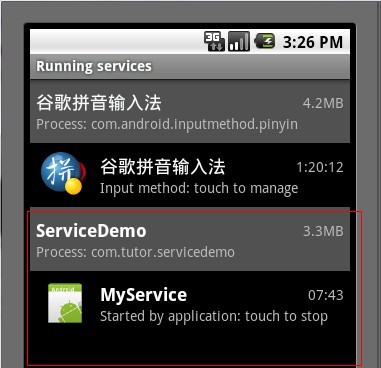
我们这时可以按HOME键进入Settings(设置)->Applications(应用)->Running Services(正在运行的服务)看一下我们新启动了一个服务,效果如下:
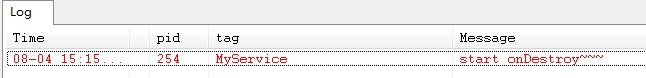
点击stopService按钮时,Service则执行了onDestroy()方法,效果图如下所示:
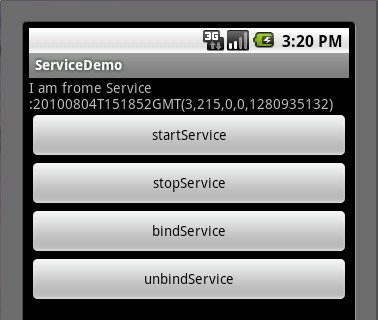
这时候我们再次点击startService按钮,然后点击bindService按钮(通常bindService都是bind已经启动的Service),我们看一下Service执行了IBinder()方法,以及TextView的值也有所变化了,如下两张图所示:

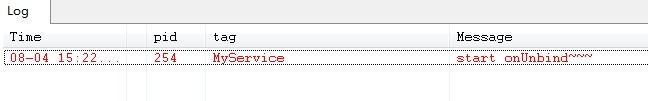
最后点击unbindService按钮,则Service执行了onUnbind()方法,如下图所示:
转载请标明出处 http://blog.csdn.net/shimiso
技术交流群:173711587
Service概念及用途:
Android中的服务,它与Activity不同,它是不能与用户交互的,不能自己启动的,运行在后台的程序,如果我们退出应用时,Service进程并没有结束,它仍然在后台运行,那 我们什么时候会用到Service呢?比如我们播放音乐的时候,有可能想边听音乐边干些其他事情,当我们退出播放音乐的应用,如果不用Service,我 们就听不到歌了,所以这时候就得用到Service了,又比如当我们一个应用的数据是通过网络获取的,不同时间(一段时间)的数据是不同的这时候我们可以 用Service在后台定时更新,而不用每打开应用的时候在去获取。
Service生命周期 :
Android Service的生命周期并不像Activity那么复杂,它只继承了onCreate(),onStart(),onDestroy()三个方法,当我们第一次启动Service时,先后调用了onCreate(),onStart()这两个方法,当停止Service时,则执行onDestroy()方法,这里需要注意的是,如果Service已经启动了,当我们再次启动Service时,不会在执行onCreate()方法,而是直接执行onStart()方法,具体的可以看下面的实例。
Service与Activity通信:
Service后端的数据最终还是要呈现在前端Activity之上的,因为启动Service时,系统会重新开启一个新的进程,这就涉及到不同进程间通信的问题了(AIDL)这一节我不作过多描述,当我们想获取启动的Service实例时,我们可以用到bindService和onBindService方法,它们分别执行了Service中IBinder()和onUnbind()方法。
为了让大家 更容易理解,我写了一个简单的Demo,大家可以模仿着我,一步一步的来。
第一步:新建一个Android工程,我这里命名为ServiceDemo.
第二步:修改main.xml代码,我这里增加了四个按钮,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/startservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="startService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="stopService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="bindService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="unbindService"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第三步:新建一个Service,命名为MyService.java代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.text.format.Time;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
//定义个一个Tag标签
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
//这里定义吧一个Binder类,用在onBind()有方法里,这样Activity那边可以获取到
private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start IBinder~~~");
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
//这里我写了一个获取当前时间的函数,不过没有格式化就先这么着吧
public String getSystemTime(){
Time t = new Time();
t.setToNow();
return t.toString();
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
MyService getService()
{
return MyService.this;
}
}
}
第四步:修改ServiceDemo.java,代码如下:
[java] view
plaincopy
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ServiceDemo extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
private MyService mMyService;
private TextView mTextView;
private Button startServiceButton;
private Button stopServiceButton;
private Button bindServiceButton;
private Button unbindServiceButton;
private Context mContext;
//这里需要用到ServiceConnection在Context.bindService和context.unBindService()里用到
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
//当我bindService时,让TextView显示MyService里getSystemTime()方法的返回值
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mMyService = ((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
setupViews();
}
public void setupViews(){
mContext = ServiceDemo.this;
mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text);
startServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
stopServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
bindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
unbindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice);
startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
}
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(v == startServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.startService(i);
}else if(v == stopServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.stopService(i);
}else if(v == bindServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.bindService(i, mServiceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}else{
mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
}
}
}
第五步:修改AndroidManifest.xml代码(将我们新建的MyService注册进去如下代码第14行:)
[java] view
plaincopy
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.tutor.servicedemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".ServiceDemo"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" android:exported="true"></service>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
</manifest>
第六步:执行上述工程,效果图如下:

点击startServie按钮时先后执行了Service中onCreate()->onStart()这两个方法,打开Logcat视窗效果如下图:

我们这时可以按HOME键进入Settings(设置)->Applications(应用)->Running Services(正在运行的服务)看一下我们新启动了一个服务,效果如下:

点击stopService按钮时,Service则执行了onDestroy()方法,效果图如下所示:

这时候我们再次点击startService按钮,然后点击bindService按钮(通常bindService都是bind已经启动的Service),我们看一下Service执行了IBinder()方法,以及TextView的值也有所变化了,如下两张图所示:


最后点击unbindService按钮,则Service执行了onUnbind()方法,如下图所示:

转载请标明出处 http://blog.csdn.net/shimiso
技术交流群:173711587
相关文章推荐
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- 【Android】 Android Service生命周期及用法
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法
- Android Service用法总结和生命周期详解
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法
- Android Service组件的生命周期及用法总结
- Android Service生命周期及用法
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android中service基本用法,生命周期2
- Android Service生命周期及用法!
- Android Service生命周期及用法
