VB.NET位运算之交换两个数字的效率分析
2011-11-09 16:38
155 查看
一、问题描述
近日,同事Kings给我看了一段奇怪的C#代码,鄙人对位运算了解甚少,初看之下懵了,还真不知道其功能,代码如下:
出于个人喜好,我习惯性的想到:那么这种通过位运算的方式进行数字交换的效率和普通交换方式的效率相比,孰高孰低呢?
还是测试。
二、问题剖析
先用C#语言来测试,代码如下:
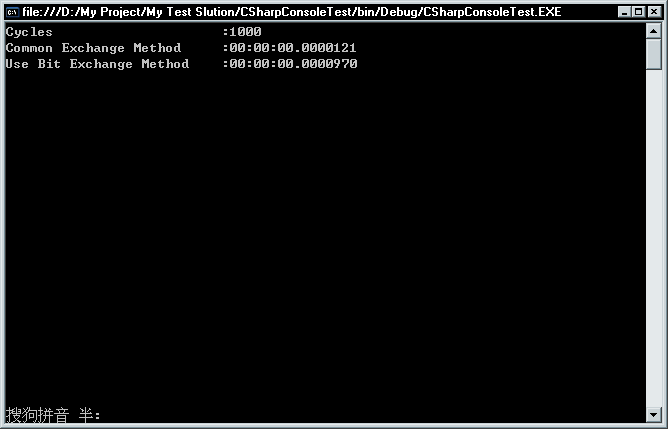
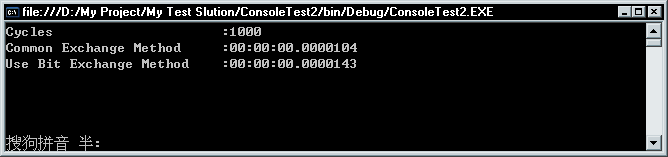
哎,C#位运算的效率怎么会这么低呐?
再看看VB的,不过我想效率应该也不怎么样,测试一下再说吧,代码如下:

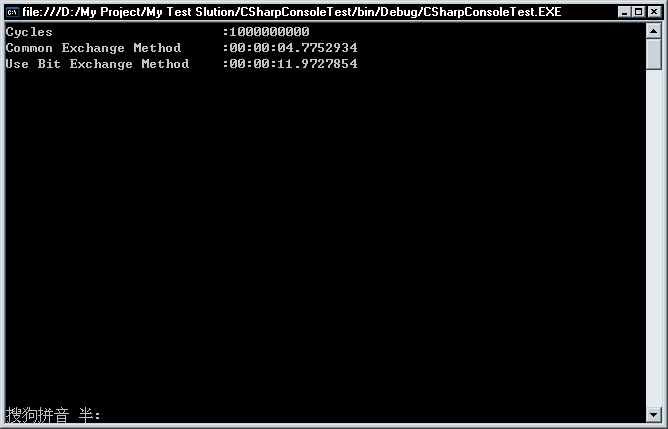
哦?VB中位运算的效率是还高于C#的!
但是不论是C#还是VB,在位运算的效率都要低于普通的交换方法。看来,这种位运算不仅难懂,而且效率不高(这里仅只.net平台的C#和VB)。
反汇编(以VB为例)显示结果无法复制文本,只好截图了:


一下是IL代码:
综上所述,交换两个数字还是使用中间变量吧。
另外,截图中的反汇编和IL代码还望有高手指点一二!
不知C/C++在位运算交换两个数字时的效率如何,还望高手指点一二!
近日,同事Kings给我看了一段奇怪的C#代码,鄙人对位运算了解甚少,初看之下懵了,还真不知道其功能,代码如下:
Int32 a=10,b=20; a=a^b; b=a^b; a=a^b;不过,我相信各位看客肯定都遇到过类似代码,对了,就是不用中间变量完成交换两个数字的功能。
出于个人喜好,我习惯性的想到:那么这种通过位运算的方式进行数字交换的效率和普通交换方式的效率相比,孰高孰低呢?
还是测试。
二、问题剖析
先用C#语言来测试,代码如下:
private void ExchangeMethodTest()
{
Int32 a = 10, b = 20;
Console.WriteLine(op_format, "Cycles", count);
Stopwatch sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (Int32 i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
Int32 temp = 0;
temp = b;
b = a;
a = temp;
}
Console.WriteLine(op_format, "Common Exchange Method", sw.Elapsed);
for (Int32 i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
}
Console.WriteLine(op_format, "Use Bit Exchange Method", sw.Elapsed);
}测试结果截图如下:

哎,C#位运算的效率怎么会这么低呐?
再看看VB的,不过我想效率应该也不怎么样,测试一下再说吧,代码如下:
Private Sub ExchangeMethodTest() Dim intA As Int32 = 10, intB As Int32 = 20 Dim sw As Stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew() For i As Int32 = 0 To count Dim j As Int32 j = intB intB = intA intA = j Next Console.WriteLine(op_format, "Common Exchange Method", sw.Elapsed) sw = Stopwatch.StartNew() For i As Int32 = 0 To count intA = intA Xor intB intB = intA Xor intB intA = intA Xor intB Next Console.WriteLine(op_format, "Use Bit Exchange Method", sw.Elapsed) End Sub运行结果如下截图:


哦?VB中位运算的效率是还高于C#的!
但是不论是C#还是VB,在位运算的效率都要低于普通的交换方法。看来,这种位运算不仅难懂,而且效率不高(这里仅只.net平台的C#和VB)。
反汇编(以VB为例)显示结果无法复制文本,只好截图了:


一下是IL代码:
.method private static void ExchangeMethodTest() cil managed
{
.maxstack 3
.locals init (
[0] int32 intA,
[1] int32 intB,
[2] class [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch sw,
[3] int32 i,
[4] int32 j,
[5] int32 V_5,
[6] int32 VB$CG$t_i4$S0)
L_0000: nop
L_0001: ldc.i4.s 10
L_0003: stloc.0
L_0004: ldc.i4.s 20
L_0006: stloc.1
L_0007: ldstr "{0,-27}:{1}"
L_000c: ldstr "Cycles"
L_0011: ldc.i4 0x3b9aca00
L_0016: box int32
L_001b: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string, object, object)
L_0020: nop
L_0021: call class [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::StartNew()
L_0026: stloc.2
L_0027: ldc.i4.0
L_0028: stloc.3
L_0029: ldloc.1
L_002a: stloc.s j
L_002c: ldloc.0
L_002d: stloc.1
L_002e: ldloc.s j
L_0030: stloc.0
L_0031: nop
L_0032: ldloc.3
L_0033: ldc.i4.1
L_0034: add.ovf
L_0035: stloc.3
L_0036: ldloc.3
L_0037: ldc.i4 0x3b9aca00
L_003c: stloc.s VB$CG$t_i4$S0
L_003e: ldloc.s VB$CG$t_i4$S0
L_0040: ble.s L_0029
L_0042: ldstr "{0,-27}:{1}"
L_0047: ldstr "Common Exchange Method"
L_004c: ldloc.2
L_004d: callvirt instance valuetype [mscorlib]System.TimeSpan [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::get_Elapsed()
L_0052: box [mscorlib]System.TimeSpan
L_0057: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string, object, object)
L_005c: nop
L_005d: call class [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::StartNew()
L_0062: stloc.2
L_0063: ldc.i4.0
L_0064: stloc.s V_5
L_0066: ldloc.0
L_0067: ldloc.1
L_0068: xor <---异或操作
L_0069: stloc.0
L_006a: ldloc.0
L_006b: ldloc.1
L_006c: xor <---异或操作
L_006d: stloc.1
L_006e: ldloc.0
L_006f: ldloc.1
L_0070: xor <---异或操作
L_0071: stloc.0
L_0072: nop
L_0073: ldloc.s V_5
L_0075: ldc.i4.1
L_0076: add.ovf
L_0077: stloc.s V_5
L_0079: ldloc.s V_5
L_007b: ldc.i4 0x3b9aca00
L_0080: stloc.s VB$CG$t_i4$S0
L_0082: ldloc.s VB$CG$t_i4$S0
L_0084: ble.s L_0066
L_0086: ldstr "{0,-27}:{1}"
L_008b: ldstr "Use Bit Exchange Method"
L_0090: ldloc.2
L_0091: callvirt instance valuetype [mscorlib]System.TimeSpan [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::get_Elapsed()
L_0096: box [mscorlib]System.TimeSpan
L_009b: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string, object, object)
L_00a0: nop
L_00a1: nop
L_00a2: ret
}三、总结综上所述,交换两个数字还是使用中间变量吧。
另外,截图中的反汇编和IL代码还望有高手指点一二!
不知C/C++在位运算交换两个数字时的效率如何,还望高手指点一二!
相关文章推荐
- 用异或运算实现两个数字的交换(装x)
- 不使用 临时变量交换两个变量的值(SWAP)【原理分析】
- mysql中提高Order by语句查询效率的两个思路分析
- 为什么异或运算可以实现两个整数的交换,而无需借助第3个临时变量
- 不建立临时变量 交换两个数字
- 交换两个值,不用临时变量(C位运算)
- 找出数组中两个只出现一次的数字;异或运算^的一个作用
- 程序设计中利用“按位异或”运算交换两个变量的值原理
- 交换两个变量的(六种)方法分析
- java交换两个数字位置
- C语言交换两个数字的三种做法
- 交换两个数字的两种方法
- loner_li 机试题 编写一个简单的计算器实现加减乘除:输入两个数字和一个运算符号,输出结果(注意容错性)
- 给定一个非负整数,你可以最多交换两个数字一次来获得最大值的数字。 返回您可以获得的最大值。
- 如何实现两个整数类型的数字交换
- java中把两个变量进行值交换,通过异或两次运算就能实现值互换。
- 用JAVA写一个函数交换两个数字
- Java--交换两个变量的值的三种方法:借助中间量交换,数值相加减交换,位移运算交换
- [2016/12/5]不用第三个变量交换两个数字
- Java里不用第三变量完成两个数字的交换
