【亲测】Activity中的 ConfigChanges 属性以及横竖屏切换时候 Activity 的生命周期
2011-04-17 16:00
666 查看
一、Activity 的 ConfigChanges 属性
官方解释: 通过设置这个属性可以使Activity捕捉设备状态变化,以下是可以被识别的内容:
CONFIG_FONT_SCALE
CONFIG_MCC
CONFIG_MNC
CONFIG_LOCALE
CONFIG_TOUCHSCREEN
CONFIG_KEYBOARD
CONFIG_NAVIGATION
CONFIG_ORIENTATION
设置方法:将下列字段用“|”符号分隔开,例如:“locale|navigation|orientation”
Value
Description “mcc“
The IMSI mobile country code (MCC) has changed — that is, a SIM hasbeen detected and updated the MCC.移动国家号码,由三位数字组成,每个国家都有自己独立的MCC,可以识别手机用户所属国家。 “mnc“
The IMSI mobile network code (MNC) has changed — that is, a SIM hasbeen detected and updated the MNC.移动网号,在一个国家或者地区中,用于区分手机用户的服务商。 “locale“
The locale has changed — for example, the user has selected a new language that text should be displayed in.用户所在地区发生变化。 “touchscreen“
The touchscreen has changed. (This should never normally happen.) “keyboard“
The keyboard type has changed — for example, the user has plugged in an external keyboard.键盘模式发生变化,例如:用户接入外部键盘输入。 “keyboardHidden“
The keyboard accessibility has changed — for example, the user has slid the keyboard out to expose it.用户打开手机硬件键盘 “navigation“
The navigation type has changed. (This should never normally happen.) “orientation“
The screen orientation has changed — that is, the user has rotated the device.设备旋转,横向显示和竖向显示模式切换。 “fontScale“
The font scaling factor has changed — that is, the user has selected a new global font size.全局字体大小缩放发生改变 项目的AndroidManifest.xml文件配置方法:
二、横竖屏切换时候 Activity 的生命周期
测试代码:
Activity属性配置:
在 Android 2.2 模拟器上测试结果为:
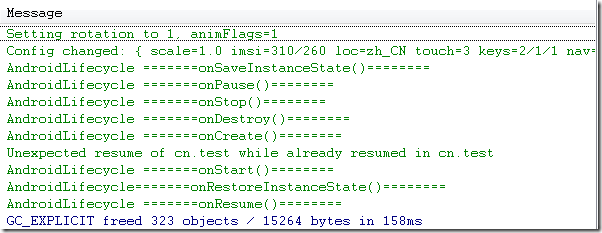
1、不设置Activity的android:configChanges时:
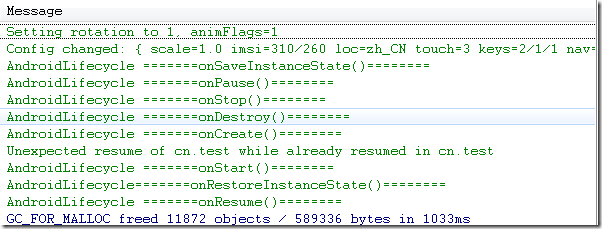
Simulator_切换到横屏
Simulator_切换到竖屏
模拟器这种情况切屏会重新调用各个生命周期,切横屏时会生命周期执行一次,切竖屏时生命周期会执行两次,且横竖屏onConfigurationChanged未被调用。但是在HTC DESIRE HD(G10) 这款手机上测试结果为:生命周期都只执行一次,且横竖屏onConfigurationChanged未被调用。
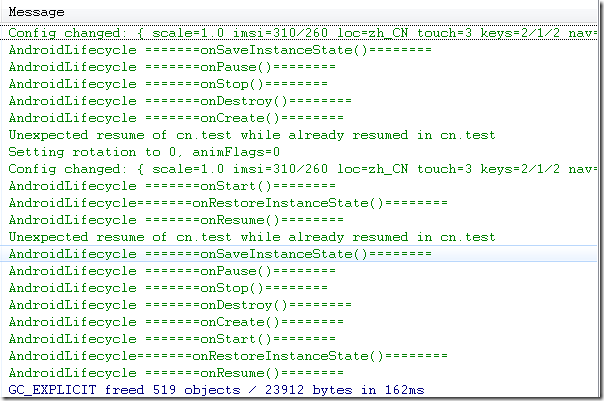
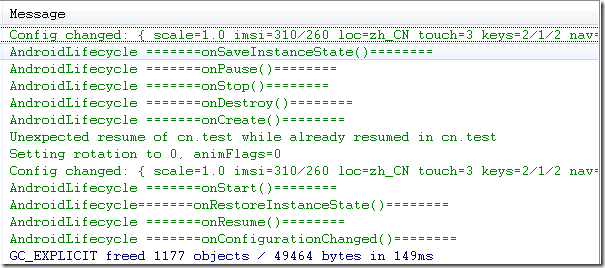
2、设置Activity的android:configChanges="orientation"时:
Simulator_orientation_切换到横屏
Simulator_orientation_切换到竖屏
模拟器这种情况切屏还是会重新调用各个生命周期,切横屏onConfigurationChanged未执行、竖屏时onConfigurationChanged执行1次。但是在HTC DESIRE HD(G10) 这款手机上测试结果为:生命周期未发生变化,且横竖屏onConfigurationChanged都只执行一次。
3、设置Activity的android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden"时:
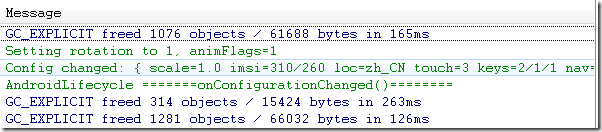
Simulator_orientation_keyboardHidden_切换到横屏
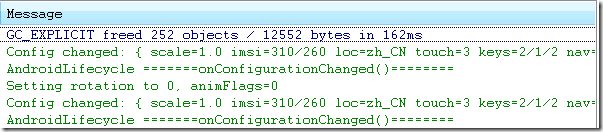
Simulator_orientation_keyboardHidden_切换到竖屏
模拟器这种情况切屏不会重新调用各个生命周期,切横屏时onConfigurationChanged会执行1次,切竖屏时onConfigurationChanged方法调用2次。 但是在HTC DESIRE HD(G10) 这款手机上测试结果为:横竖屏onConfigurationChanged都只执行一次。
结论:可以看出在G10这款真机上测试的结果比模拟器更加合理。
官方解释: 通过设置这个属性可以使Activity捕捉设备状态变化,以下是可以被识别的内容:
CONFIG_FONT_SCALE
CONFIG_MCC
CONFIG_MNC
CONFIG_LOCALE
CONFIG_TOUCHSCREEN
CONFIG_KEYBOARD
CONFIG_NAVIGATION
CONFIG_ORIENTATION
设置方法:将下列字段用“|”符号分隔开,例如:“locale|navigation|orientation”
Value
Description “mcc“
The IMSI mobile country code (MCC) has changed — that is, a SIM hasbeen detected and updated the MCC.移动国家号码,由三位数字组成,每个国家都有自己独立的MCC,可以识别手机用户所属国家。 “mnc“
The IMSI mobile network code (MNC) has changed — that is, a SIM hasbeen detected and updated the MNC.移动网号,在一个国家或者地区中,用于区分手机用户的服务商。 “locale“
The locale has changed — for example, the user has selected a new language that text should be displayed in.用户所在地区发生变化。 “touchscreen“
The touchscreen has changed. (This should never normally happen.) “keyboard“
The keyboard type has changed — for example, the user has plugged in an external keyboard.键盘模式发生变化,例如:用户接入外部键盘输入。 “keyboardHidden“
The keyboard accessibility has changed — for example, the user has slid the keyboard out to expose it.用户打开手机硬件键盘 “navigation“
The navigation type has changed. (This should never normally happen.) “orientation“
The screen orientation has changed — that is, the user has rotated the device.设备旋转,横向显示和竖向显示模式切换。 “fontScale“
The font scaling factor has changed — that is, the user has selected a new global font size.全局字体大小缩放发生改变 项目的AndroidManifest.xml文件配置方法:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.androidres.ConfigChangedTesting" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0.0"> <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"> <activity android:name=".ConfigChangedTesting" android:label="@string/app_name" android:configChanges="keyboardHidden|orientation"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
二、横竖屏切换时候 Activity 的生命周期
测试代码:
public class AndroidLifecycle extends Activity {
private String TAG = "AndroidLifecycle";
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onCreate()========");
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
@Override
protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onSaveInstanceState()========");
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Bundle outState) {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle=======onRestoreInstanceState()========");
super.onRestoreInstanceState(outState);
}
@Override
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onConfigurationChanged()========");
super.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
}
// Called after onCreate — or after onRestart when the activity had been
// stopped, but is now again being displayed to the user. It will be
// followed by onResume
protected void onStart() {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onStart()========");
super.onStart();
}
// Called after onRestoreInstanceState, onRestart, or onPause, for your
// activity to start interacting with the user
protected void onResume() {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onResume()========");
super.onResume();
}
// Called as part of the activity lifecycle when an activity is going into
// the background, but has not (yet) been killed
protected void onPause() {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onPause()========");
super.onPause();
}
// Called when you are no longer visible to the user. You will next receive
// either onRestart, onDestroy, or nothing, depending on later user
// activity.
protected void onStop() {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onStop()========");
super.onStop();
}
// Perform any final cleanup before an activity is destroyed
protected void onDestroy() {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onDestroy()========");
super.onDestroy();
}
// Called after onStop when the current activity is being re-displayed to
// the user (the user has navigated back to it). It will be followed by
// onStart and then onResume
protected void onRestart() {
Log.i(TAG,"AndroidLifecycle =======onRestart()========");
super.onRestart();
}
}Activity属性配置:
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"> <activity android:name=".AndroidLifecycle" android:label="@string/app_name" android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application>
在 Android 2.2 模拟器上测试结果为:
1、不设置Activity的android:configChanges时:

Simulator_切换到横屏

Simulator_切换到竖屏
模拟器这种情况切屏会重新调用各个生命周期,切横屏时会生命周期执行一次,切竖屏时生命周期会执行两次,且横竖屏onConfigurationChanged未被调用。但是在HTC DESIRE HD(G10) 这款手机上测试结果为:生命周期都只执行一次,且横竖屏onConfigurationChanged未被调用。
2、设置Activity的android:configChanges="orientation"时:

Simulator_orientation_切换到横屏

Simulator_orientation_切换到竖屏
模拟器这种情况切屏还是会重新调用各个生命周期,切横屏onConfigurationChanged未执行、竖屏时onConfigurationChanged执行1次。但是在HTC DESIRE HD(G10) 这款手机上测试结果为:生命周期未发生变化,且横竖屏onConfigurationChanged都只执行一次。
3、设置Activity的android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden"时:

Simulator_orientation_keyboardHidden_切换到横屏

Simulator_orientation_keyboardHidden_切换到竖屏
模拟器这种情况切屏不会重新调用各个生命周期,切横屏时onConfigurationChanged会执行1次,切竖屏时onConfigurationChanged方法调用2次。 但是在HTC DESIRE HD(G10) 这款手机上测试结果为:横竖屏onConfigurationChanged都只执行一次。
结论:可以看出在G10这款真机上测试的结果比模拟器更加合理。
相关文章推荐
- 横竖屏切换时候activity的生命周期 android:configChanges
- 横竖屏切换时候activity的生命周期 android:configChanges
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期变化
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- android横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- Android--横竖屏切换时候activity的生命周期
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期的总结
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 深入学习横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期 2015-06-16 00:38 13人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
- android横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 深入学习横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- Activity生命周期,关于锁屏,横竖屏切换以及页面切换
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 浅析:横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
- 横竖屏切换时候Activity的生命周期
