[ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的WCF分层结构示例Step by Step —— 02 Model的建立
2011-03-09 23:56
726 查看
业务逻辑的建立是如下:
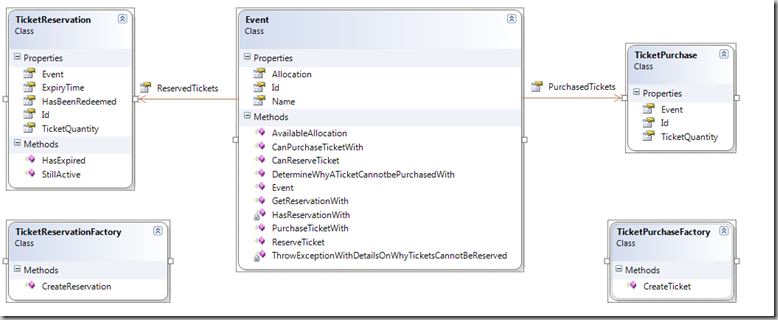
书中是用的业务逻辑层使用的模型为domain model,即实体Event为核心抽象为一个类,而其订票Reservation和买票Purchase这个两个行为也定义为两个类。
1. 在solution的Service文件夹下建立一个project名为ASPPatterns.Chap6.EventTickets.Model。
2. 建立TicketPurchase类,其内容为:

书中是用的业务逻辑层使用的模型为domain model,即实体Event为核心抽象为一个类,而其订票Reservation和买票Purchase这个两个行为也定义为两个类。
1. 在solution的Service文件夹下建立一个project名为ASPPatterns.Chap6.EventTickets.Model。
2. 建立TicketPurchase类,其内容为:
public class TicketPurchase
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public Event Event { get; set; }
public int TicketQuantity { get; set; }
}
可见这里TicketPurchase这个行为抽象出来的类与其数据库表中的Field是对应的。
3. 建立TicketReservation类:{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public Event Event { get; set; }
public int TicketQuantity { get; set; }
}
可见这里TicketPurchase这个行为抽象出来的类与其数据库表中的Field是对应的。
public class TicketReservation
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public Event Event { get; set; }
public DateTime ExpiryTime { get; set; }
public int TicketQuantity { get; set; }
public bool HasBeenRedeemed { get; set; }
public bool HasExpired()
{
return DateTime.Now > ExpiryTime;
}
public bool StillActive()
{
return !HasBeenRedeemed && !HasExpired();
}
}
可见对于Reservation的行为,除了有数据库表中field对应的Property以外,还对纯粹涉及property的两个行为进行了定义,即对ExpiryTime的判定,以及对是否Redeem了的判定。
4. 建立Event类。{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public Event Event { get; set; }
public DateTime ExpiryTime { get; set; }
public int TicketQuantity { get; set; }
public bool HasBeenRedeemed { get; set; }
public bool HasExpired()
{
return DateTime.Now > ExpiryTime;
}
public bool StillActive()
{
return !HasBeenRedeemed && !HasExpired();
}
}
可见对于Reservation的行为,除了有数据库表中field对应的Property以外,还对纯粹涉及property的两个行为进行了定义,即对ExpiryTime的判定,以及对是否Redeem了的判定。
public class Event
{
{
public Event()
{
ReservedTickets = new List<TicketReservation>();
PurchasedTickets = new List<TicketPurchase>();
}
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Allocation { get; set; }
public List<TicketReservation> ReservedTickets { get; set; }
public List<TicketPurchase> PurchasedTickets { get; set; }
public int AvailableAllocation()
{
int salesAndReservations = 0;
PurchasedTickets.ForEach(t => salesAndReservations += t.TicketQuantity);
ReservedTickets.FindAll(r => r.StillActive()).ForEach(r => salesAndReservations += r.TicketQuantity);
return Allocation - salesAndReservations;
}
public bool CanPurchaseTicketWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (HasReservationWith(reservationId))
return GetReservationWith(reservationId).StillActive();
return false;
}
public TicketPurchase PurchaseTicketWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (!CanPurchaseTicketWith(reservationId))
throw new ApplicationException(DetermineWhyATicketCannotbePurchasedWith(reservationId));
TicketReservation reservation = GetReservationWith(reservationId);
TicketPurchase ticket = TicketPurchaseFactory.CreateTicket(this, reservation.TicketQuantity);
reservation.HasBeenRedeemed = true;
PurchasedTickets.Add(ticket);
return ticket;
}
public TicketReservation GetReservationWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (!HasReservationWith(reservationId))
throw new ApplicationException(String.Format("No reservation ticket with matching id of '{0}'", reservationId.ToString()));
return ReservedTickets.FirstOrDefault(t => t.Id == reservationId);
}
private bool HasReservationWith(Guid reservationId)
{
return ReservedTickets.Exists(t => t.Id == reservationId);
}
public string DetermineWhyATicketCannotbePurchasedWith(Guid reservationId)
{
string reservationIssue = "";
if (HasReservationWith(reservationId))
{
TicketReservation reservation = GetReservationWith(reservationId);
if (reservation.HasExpired())
reservationIssue = String.Format("Ticket reservation '{0}' has expired", reservationId.ToString());
else if (reservation.HasBeenRedeemed )
reservationIssue = String.Format("Ticket reservation '{0}' has already been redeemed", reservationId.ToString());
}
else
reservationIssue = String.Format("There is no ticket reservation with the Id '{0}'", reservationId.ToString());
return reservationIssue;
}
private void ThrowExceptionWithDetailsOnWhyTicketsCannotBeReserved()
{
throw new ApplicationException("There are no tickets available to reserve.");
}
public bool CanReserveTicket(int qty)
{
return AvailableAllocation() >= qty;
}
public TicketReservation ReserveTicket(int tktQty)
{
if (!CanReserveTicket(tktQty))
ThrowExceptionWithDetailsOnWhyTicketsCannotBeReserved();
TicketReservation reservation = TicketReservationFactory.CreateReservation(this, tktQty);
ReservedTickets.Add(reservation);
return reservation;
}
}
这里我们可以发现这个类包含两个List的Field,其元素类型为TicketPurchase和TicketReservation,这样对于一个Event的类,它的行为,即Purchase和Reservation的记录将会保存在这个对象实体的元素里面。这种典型的通过Entity来包含其Behavior的结构,就是Domain Model。
5. 建立TicketPurchaseFactory类:{
ReservedTickets = new List<TicketReservation>();
PurchasedTickets = new List<TicketPurchase>();
}
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Allocation { get; set; }
public List<TicketReservation> ReservedTickets { get; set; }
public List<TicketPurchase> PurchasedTickets { get; set; }
public int AvailableAllocation()
{
int salesAndReservations = 0;
PurchasedTickets.ForEach(t => salesAndReservations += t.TicketQuantity);
ReservedTickets.FindAll(r => r.StillActive()).ForEach(r => salesAndReservations += r.TicketQuantity);
return Allocation - salesAndReservations;
}
public bool CanPurchaseTicketWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (HasReservationWith(reservationId))
return GetReservationWith(reservationId).StillActive();
return false;
}
public TicketPurchase PurchaseTicketWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (!CanPurchaseTicketWith(reservationId))
throw new ApplicationException(DetermineWhyATicketCannotbePurchasedWith(reservationId));
TicketReservation reservation = GetReservationWith(reservationId);
TicketPurchase ticket = TicketPurchaseFactory.CreateTicket(this, reservation.TicketQuantity);
reservation.HasBeenRedeemed = true;
PurchasedTickets.Add(ticket);
return ticket;
}
public TicketReservation GetReservationWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (!HasReservationWith(reservationId))
throw new ApplicationException(String.Format("No reservation ticket with matching id of '{0}'", reservationId.ToString()));
return ReservedTickets.FirstOrDefault(t => t.Id == reservationId);
}
private bool HasReservationWith(Guid reservationId)
{
return ReservedTickets.Exists(t => t.Id == reservationId);
}
public string DetermineWhyATicketCannotbePurchasedWith(Guid reservationId)
{
string reservationIssue = "";
if (HasReservationWith(reservationId))
{
TicketReservation reservation = GetReservationWith(reservationId);
if (reservation.HasExpired())
reservationIssue = String.Format("Ticket reservation '{0}' has expired", reservationId.ToString());
else if (reservation.HasBeenRedeemed )
reservationIssue = String.Format("Ticket reservation '{0}' has already been redeemed", reservationId.ToString());
}
else
reservationIssue = String.Format("There is no ticket reservation with the Id '{0}'", reservationId.ToString());
return reservationIssue;
}
private void ThrowExceptionWithDetailsOnWhyTicketsCannotBeReserved()
{
throw new ApplicationException("There are no tickets available to reserve.");
}
public bool CanReserveTicket(int qty)
{
return AvailableAllocation() >= qty;
}
public TicketReservation ReserveTicket(int tktQty)
{
if (!CanReserveTicket(tktQty))
ThrowExceptionWithDetailsOnWhyTicketsCannotBeReserved();
TicketReservation reservation = TicketReservationFactory.CreateReservation(this, tktQty);
ReservedTickets.Add(reservation);
return reservation;
}
}
这里我们可以发现这个类包含两个List的Field,其元素类型为TicketPurchase和TicketReservation,这样对于一个Event的类,它的行为,即Purchase和Reservation的记录将会保存在这个对象实体的元素里面。这种典型的通过Entity来包含其Behavior的结构,就是Domain Model。
public class TicketPurchaseFactory
{
public static TicketPurchase CreateTicket(Event Event, int tktQty)
{
TicketPurchase ticket = new TicketPurchase();
ticket.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
ticket.Event = Event;
ticket.TicketQuantity = tktQty;
return ticket;
}
}
6. 建立TicketReservationFactory类:{
public static TicketPurchase CreateTicket(Event Event, int tktQty)
{
TicketPurchase ticket = new TicketPurchase();
ticket.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
ticket.Event = Event;
ticket.TicketQuantity = tktQty;
return ticket;
}
}
public class TicketReservationFactory
{
public static TicketReservation CreateReservation(Event Event, int tktQty)
{
TicketReservation reservation = new TicketReservation();
reservation.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
reservation.Event = Event;
reservation.ExpiryTime = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(1);
reservation.TicketQuantity = tktQty;
return reservation;
}
}
7. 建立Repository层的接口:{
public static TicketReservation CreateReservation(Event Event, int tktQty)
{
TicketReservation reservation = new TicketReservation();
reservation.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
reservation.Event = Event;
reservation.ExpiryTime = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(1);
reservation.TicketQuantity = tktQty;
return reservation;
}
}
public interface IEventRepository
{
Event FindBy(Guid id);
void Save(Event eventEntity);
}
可见Repository层的结构非常简单,即提供两种功能,一是对数据的查询,二是数据的保存。数据的查询通过事件的ID进行,而数据的保存通过传递进去Event的对象实现。
{
Event FindBy(Guid id);
void Save(Event eventEntity);
}
可见Repository层的结构非常简单,即提供两种功能,一是对数据的查询,二是数据的保存。数据的查询通过事件的ID进行,而数据的保存通过传递进去Event的对象实现。
相关文章推荐
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的分层结构示例Step by Step —— 02 业务逻辑层
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的分层结构示例Step by Step —— 01 准备工作
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的分层结构示例Step by Step —— 05 表现层
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的分层结构示例Step by Step —— 06 用户界面层
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的WCF分层结构示例Step by Step —— 04 DataContract
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的WCF分层结构示例Step by Step —— 03 数据访问层
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的WCF分层结构示例Step by Step —— 01 准备工作
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的分层结构示例Step by Step —— 03 服务层
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的WCF分层结构示例Step by Step —— 05 Contracts
- [ASP.NET 设计模式] 用Visual Studio2010搭建一个简单的分层结构示例Step by Step —— 04 数据访问层
- 一个简单的ASP.NET WebForm "Model Binder"
- 【翻译】使用ASP.NET MVC 和LINQ建立一个简单的博客 - Part 3
- ASP.NET和Ajax应用一个超级实用的设计模式---享元模式
- 【翻译】使用ASP.NET MVC 和LINQ建立一个简单的博客 - Part 2
- 经验技巧分享--ASP.NET和Ajax应用一个超级实用的设计模式---享元模式
- 使用ArcGIS Server和ASP.net建立一个简单的网站
- asp.net 设计模式文摘
- ASP_NET设计模式
- 自己动手搭建 Redis 环境,并建立一个 .NET HelloWorld 程序测试(转)
- 通过ASP.NET Web API + JQuery创建一个简单的Web应用
