设计模式学习之路——Strategy 策略模式
2010-06-10 21:19
711 查看
1. 意图
定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来, 并且使它们可相互替换。本模式使得算法可独立于使用它的客户而变化。2. 动机
在软件构建过程中,某些对象使用的算法可能多种多样,经常改变,如果将这些算法都编码到对象中,将会使对象变得异常复杂;而且有时候支持不使用的算法也是一个性能负担。如何在运行时根据需要透明地更改对象的算法?将算法与对象本身解耦,从而避免上述问题?
如果一个程序需要一种特定的服务或功能,而且该程序有多种实现该功能的方式,此时适合于使用策略模式。程序可根据运算效率或用户选项在这些算法之间选择。程序中可以有任意数量的策略,可以添加策略,也可以在任何时候修改策略。
3. 结构
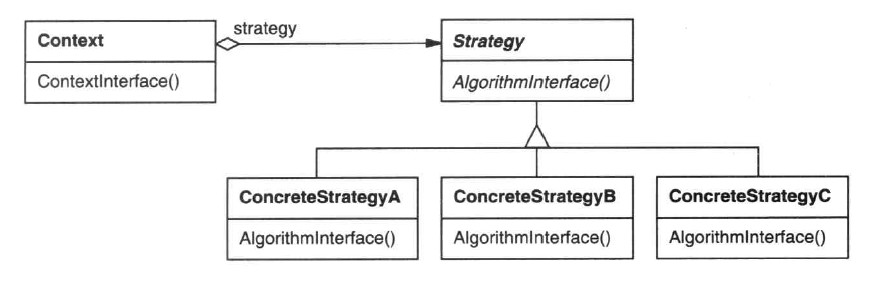
4. 代码实现
类关系图如下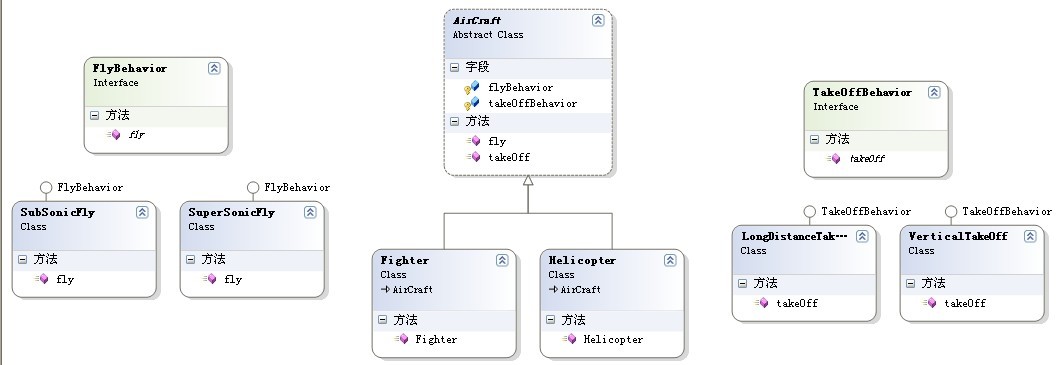
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace Strategy
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Helicopter h = new Helicopter();
Console.WriteLine("");
Fighter f = new Fighter();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public interface FlyBehavior
{
void fly();
}
public class SuperSonicFly : FlyBehavior
{
public void fly()
{
Console.WriteLine("超音速飞行!");
}
}
public class SubSonicFly : FlyBehavior
{
public void fly()
{
Console.WriteLine("亚音速飞行!");
}
}
public interface TakeOffBehavior
{
void takeOff();
}
public class VerticalTakeOff : TakeOffBehavior
{
public void takeOff()
{
Console.WriteLine("垂直起飞!");
}
}
public class LongDistanceTakeOff : TakeOffBehavior
{
public void takeOff()
{
Console.WriteLine("长距离起飞!");
}
}
public abstract class AirCraft
{
protected FlyBehavior flyBehavior;
protected TakeOffBehavior takeOffBehavior;
public void fly()
{
flyBehavior.fly();
}
public void takeOff()
{
takeOffBehavior.takeOff();
}
}
public class Helicopter : AirCraft
{
public Helicopter()
{
flyBehavior = new SubSonicFly();
takeOffBehavior = new VerticalTakeOff();
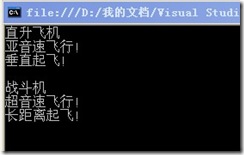
Console.WriteLine("直升飞机");
fly();
takeOff();
}
}
public class Fighter : AirCraft
{
public Fighter()
{
flyBehavior = new SuperSonicFly();
takeOffBehavior = new LongDistanceTakeOff();
Console.WriteLine("战斗机");
fly();
takeOff();
}
}
}
5. .NET体系架构中的Strategy模式
using System;
using System.Collections;
public class SamplesArrayList {
public class myReverserClass : IComparer {
// Calls CaseInsensitiveComparer.Compare with the parameters reversed.
int IComparer.Compare( Object x, Object y ) {
return( (new CaseInsensitiveComparer()).Compare( y, x ) );
}
}
public static void Main() {
// Creates and initializes a new ArrayList.
ArrayList myAL = new ArrayList();
myAL.Add( "The" );
myAL.Add( "quick" );
myAL.Add( "brown" );
myAL.Add( "fox" );
myAL.Add( "jumps" );
myAL.Add( "over" );
myAL.Add( "the" );
myAL.Add( "lazy" );
myAL.Add( "dog" );
// Displays the values of the ArrayList.
Console.WriteLine( "The ArrayList initially contains the following values:" );
PrintIndexAndValues( myAL );
// Sorts the values of the ArrayList using the default comparer.
myAL.Sort();
Console.WriteLine( "After sorting with the default comparer:" );
PrintIndexAndValues( myAL );
// Sorts the values of the ArrayList using the reverse case-insensitive comparer.
IComparer myComparer = new myReverserClass();
myAL.Sort( myComparer );
Console.WriteLine( "After sorting with the reverse case-insensitive comparer:" );
PrintIndexAndValues( myAL );
}
public static void PrintIndexAndValues( IEnumerable myList ) {
int i = 0;
foreach ( Object obj in myList )
Console.WriteLine( "\t[{0}]:\t{1}", i++, obj );
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
/*
This code produces the following output.
The ArrayList initially contains the following values:
[0]: The
[1]: quick
[2]: brown
[3]: fox
[4]: jumps
[5]: over
[6]: the
[7]: lazy
[8]: dog
After sorting with the default comparer:
[0]: brown
[1]: dog
[2]: fox
[3]: jumps
[4]: lazy
[5]: over
[6]: quick
[7]: the
[8]: The
After sorting with the reverse case-insensitive comparer:
[0]: the
[1]: The
[2]: quick
[3]: over
[4]: lazy
[5]: jumps
[6]: fox
[7]: dog
[8]: brown
*/6 Strategy模式的几个要点
1. Strategy及其子类为组件提供了一系列可重用的算法,从而可以使得类型在运行时方便地根据需要在各个算法之间进行切换。所谓封装算法,支持算法的变化。2. Strategy模式提供了用条件判断语句以外的另一种选择,消除条件判断语句,就是在解耦合。含有许多条件判断语句的代码通常都需要Strategy模式。
3. 与State类似,如果Strategy对象没有实例变量,那么各个上下文可以共享同一个Strategy对象,从而节省对象开销。
相关文章推荐
- 设计模式学习1——策略模式(Strategy)
- 设计模式学习系列十四:策略模式(Strategy)
- 设计模式学习笔记--Strategy 策略模式
- 设计模式学习之路-----策略模式
- 设计模式深入学习--Strategy 策略模式(行为型模式)
- 设计模式学习之一策略模式(Strategy)——从鸭子的设计说起
- 学习设计模式之旅 / 策略模式 (Strategy) 推荐
- Strategy策略模式 ---设计模式学习
- 【设计模式学习笔记二十二】【行为模式】【策略模式(Strategy)】
- 我的模式之路一:策略模式(Strategy)学习
- 学习php设计模式 php实现策略模式(strategy)
- 【设计模式】学习笔记1:策略模式(Strategy)
- 设计模式学习之路-策略模式
- java 设计模式学习笔记十五 strategy 策略设计模式
- 设计模式学习之路——策略模式
- 设计模式学习笔记--策略(Strategy)模式
- 步步为营 .NET 设计模式学习笔记 三、Strategy(策略模式)
- java 设计模式学习笔记十五 strategy 策略设计模式
- 步步为营 .NET 设计模式学习笔记 三、Strategy(策略模式)
- 学习php设计模式 php实现策略模式(strategy)
