nhibernate性能之二级缓存篇
2008-03-30 19:26
363 查看
1.学习目标
通过进一步学习nhibernate,了解二级缓存在nhiernate中的工作机制以及使用方法
2.开发环境和必要准备
开发环境为:windows 2003,Visual studio .Net 2005,Sql server 2005 developer edition
必要准备:学习前五篇nhibernate学习系列Nhibernate学习之起步篇-1 ,Nhibernate学习起步之many-to-one篇 ,Nhibernate学习之many-to-many篇 ,nhibernate学习之三级联(Ternary Associations)篇 ,Nhibernate学习之性能改善1
3.学前分析
在买电脑的时候,我们经常会看CPU的配置,其中衡量CPU性能的一项指标为二级缓存-Level 2 Cache,二级缓存越大,CPU性能越高。这是为什么,大家知道CPU的处理速度非常快,比在内存(memory)中的操作快上很多倍,这样在系统运行的时候,势必会造成一定的瓶颈效应,在内存和CPU之间加上一块处理速度在内存和处理器之间的介质-高速缓存,可以起到平衡的作用,每次CPU都试图先从高速缓存中读取数据,如果没有的话,再去内存中读取,一般CPU对高速缓存的命中率都在90%以上,所以大大提高了性能。在内存和磁盘之间加上一个高速缓存也可提高系统的新性能,减少对磁盘的IO次数
4.如何在nhibernate中启动二级缓存
在nhiernate中的ISession对象中,已经存在了一级缓存,但是在ISession级别的,我们从上一节可以看出,ISession对象应该是尽早释放的,那依赖它的一级缓存会在它销毁的地时候销毁,所以一级缓存命中率比较低。而ISessionFactory对象推荐为不频繁创建,非常适用于Cache的使用,那这里的二级缓存正是ISessionFactory级别的。
要想在nhibernate中启用二级缓存,请在hibernate.cfg.xml中添加如下代码:

<property name="hibernate.cache.provider_class">NHibernate.Caches.SysCache.SysCacheProvider, NHibernate.Caches.SysCache</property>

<property name="expiration">120</property>
NHibernate.Caches.SysCache.SysCacheProvider, NHibernate.Caches.SysCache还可以替换为NHibernate.Caches.
expiration代表缓存过期时间,单位S
设置完后,还需要在对象的映射文件中配置二级缓存的策略,比如我在User.hbm.xml中如下配置

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>

<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2">

<class name="NhibernateSample1.User,NhibernateSample1" table="Users" lazy="false">

<cache usage="read-write"/>

<id name="Id" column="Id" unsaved-value="0">

<generator class="native" />

</id>

<property name="Name" column="Name" type="string" length="64" not-null="true" unique="true"></property>

<property name="Pwd" column="Pwd" type="string" length="64" not-null="true"></property>

<many-to-one name="Role" class="NhibernateSample1.Role,NhibernateSample1" column="RoleID"></many-to-one>

</class>

</hibernate-mapping>
NHibernateHelper.cs

using System;

using System.Data;

using System.Configuration;

using System.Web;

using System.Web.Security;

using System.Web.UI;

using System.Web.UI.WebControls;

using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;

using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;

using NHibernate;

using NHibernate.Cfg;



namespace WebApp



{

public sealed class NHibernateHelper



{

private const string CurrentSessionKey = "nhibernate.current_session";

private static readonly ISessionFactory sessionFactory;


static NHibernateHelper()



{

string cfgPath = @"E:/my project/nhibernate study/simple4/NHibernateStudy1/NhibernateSample1/hibernate.cfg.xml";

sessionFactory = new NHibernate.Cfg.Configuration().Configure(cfgPath).BuildSessionFactory();

}


public static ISession GetCurrentSession()



{

HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;

ISession currentSession = context.Items[CurrentSessionKey] as ISession;


if (currentSession == null)



{

currentSession = sessionFactory.OpenSession();

context.Items[CurrentSessionKey] = currentSession;

}


return currentSession;

}


public static void CloseSession()



{

HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;

ISession currentSession = context.Items[CurrentSessionKey] as ISession;


if (currentSession == null)



{

// No current session

return;

}


currentSession.Close();

context.Items.Remove(CurrentSessionKey);

}


public static void CloseSessionFactory()



{

if (sessionFactory != null)



{

sessionFactory.Close();

}

}

}


}

页面代码:

System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch sw = new System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch();

sw.Start();

ISession session = NHibernateHelper.GetCurrentSession();

ITransaction tra = session.BeginTransaction();

session.Load(typeof(NhibernateSample1.User), 1);

tra.Commit();

sw.Stop();

Response.Write(sw.ElapsedTicks+"<br>");

sw.Reset();

sw.Start();

session = NHibernateHelper.GetCurrentSession();

tra = session.BeginTransaction();

session.Load(typeof(NhibernateSample1.User), 1);

tra.Commit();

sw.Stop();

Response.Write(sw.ElapsedTicks + "<br>");

sw.Reset();

sw.Start();

session = NHibernateHelper.GetCurrentSession();

session.Close();

sw.Stop();

Response.Write(sw.ElapsedTicks + "<br>");
第一次运行,用SQL事件探查器,结果为
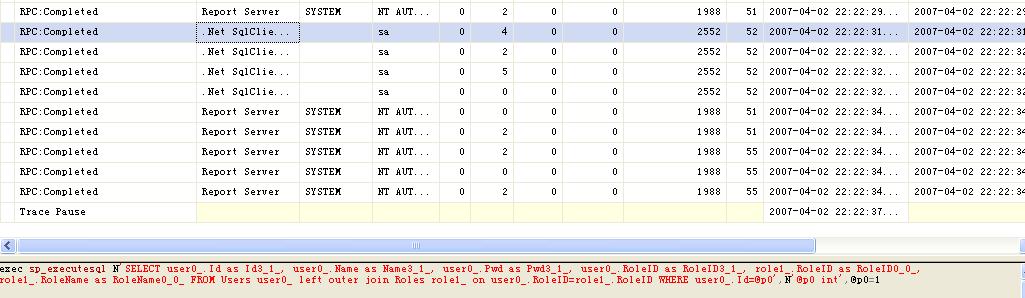
从截图中的SQL语句看,第一次从数据库中加在User数据
第二次
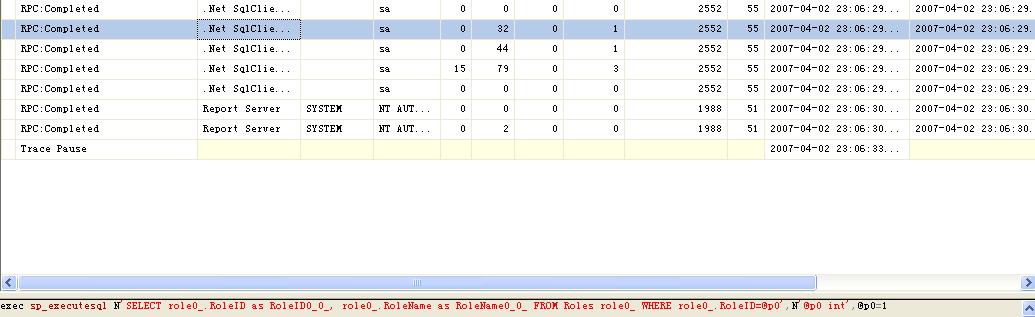
从图中可以看出,第二次加载User对象,并没有从数据中获取数据,而是将没有设置Cache的Role信息从User里面获取。
当然在利用缓存的时候,缓存不会知道另外一个进程存储的实体发生变化,应该自己建立一些策略来及时地更新缓存快照。而且当ISessionFactory销毁的时候,二级缓存也会随之销毁,这也是应用的时候,应该注意的。今天先写到这,有点困了。
通过进一步学习nhibernate,了解二级缓存在nhiernate中的工作机制以及使用方法
2.开发环境和必要准备
开发环境为:windows 2003,Visual studio .Net 2005,Sql server 2005 developer edition
必要准备:学习前五篇nhibernate学习系列Nhibernate学习之起步篇-1 ,Nhibernate学习起步之many-to-one篇 ,Nhibernate学习之many-to-many篇 ,nhibernate学习之三级联(Ternary Associations)篇 ,Nhibernate学习之性能改善1
3.学前分析
在买电脑的时候,我们经常会看CPU的配置,其中衡量CPU性能的一项指标为二级缓存-Level 2 Cache,二级缓存越大,CPU性能越高。这是为什么,大家知道CPU的处理速度非常快,比在内存(memory)中的操作快上很多倍,这样在系统运行的时候,势必会造成一定的瓶颈效应,在内存和CPU之间加上一块处理速度在内存和处理器之间的介质-高速缓存,可以起到平衡的作用,每次CPU都试图先从高速缓存中读取数据,如果没有的话,再去内存中读取,一般CPU对高速缓存的命中率都在90%以上,所以大大提高了性能。在内存和磁盘之间加上一个高速缓存也可提高系统的新性能,减少对磁盘的IO次数
4.如何在nhibernate中启动二级缓存
在nhiernate中的ISession对象中,已经存在了一级缓存,但是在ISession级别的,我们从上一节可以看出,ISession对象应该是尽早释放的,那依赖它的一级缓存会在它销毁的地时候销毁,所以一级缓存命中率比较低。而ISessionFactory对象推荐为不频繁创建,非常适用于Cache的使用,那这里的二级缓存正是ISessionFactory级别的。
要想在nhibernate中启用二级缓存,请在hibernate.cfg.xml中添加如下代码:

<property name="hibernate.cache.provider_class">NHibernate.Caches.SysCache.SysCacheProvider, NHibernate.Caches.SysCache</property>

<property name="expiration">120</property>
NHibernate.Caches.SysCache.SysCacheProvider, NHibernate.Caches.SysCache还可以替换为NHibernate.Caches.
Prevalence
.PrevalenceCacheProvider, NHibernate.Caches.Prevalence,代表缓存的实现类,在bin目录中有这样两个dllNHibernate.Caches.SysCache.dll,NHibernate.Caches.Prevalence.dll用哪个就把哪个拷贝到应用程序的bin目录下
expiration代表缓存过期时间,单位S
设置完后,还需要在对象的映射文件中配置二级缓存的策略,比如我在User.hbm.xml中如下配置

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>

<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2">

<class name="NhibernateSample1.User,NhibernateSample1" table="Users" lazy="false">

<cache usage="read-write"/>

<id name="Id" column="Id" unsaved-value="0">

<generator class="native" />

</id>

<property name="Name" column="Name" type="string" length="64" not-null="true" unique="true"></property>

<property name="Pwd" column="Pwd" type="string" length="64" not-null="true"></property>

<many-to-one name="Role" class="NhibernateSample1.Role,NhibernateSample1" column="RoleID"></many-to-one>

</class>

</hibernate-mapping>
NHibernateHelper.cs

using System;

using System.Data;

using System.Configuration;

using System.Web;

using System.Web.Security;

using System.Web.UI;

using System.Web.UI.WebControls;

using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;

using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;

using NHibernate;

using NHibernate.Cfg;



namespace WebApp



{

public sealed class NHibernateHelper



{

private const string CurrentSessionKey = "nhibernate.current_session";

private static readonly ISessionFactory sessionFactory;


static NHibernateHelper()



{

string cfgPath = @"E:/my project/nhibernate study/simple4/NHibernateStudy1/NhibernateSample1/hibernate.cfg.xml";

sessionFactory = new NHibernate.Cfg.Configuration().Configure(cfgPath).BuildSessionFactory();

}


public static ISession GetCurrentSession()



{

HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;

ISession currentSession = context.Items[CurrentSessionKey] as ISession;


if (currentSession == null)



{

currentSession = sessionFactory.OpenSession();

context.Items[CurrentSessionKey] = currentSession;

}


return currentSession;

}


public static void CloseSession()



{

HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;

ISession currentSession = context.Items[CurrentSessionKey] as ISession;


if (currentSession == null)



{

// No current session

return;

}


currentSession.Close();

context.Items.Remove(CurrentSessionKey);

}


public static void CloseSessionFactory()



{

if (sessionFactory != null)



{

sessionFactory.Close();

}

}

}


}

页面代码:

System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch sw = new System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch();

sw.Start();

ISession session = NHibernateHelper.GetCurrentSession();

ITransaction tra = session.BeginTransaction();

session.Load(typeof(NhibernateSample1.User), 1);

tra.Commit();

sw.Stop();

Response.Write(sw.ElapsedTicks+"<br>");

sw.Reset();

sw.Start();

session = NHibernateHelper.GetCurrentSession();

tra = session.BeginTransaction();

session.Load(typeof(NhibernateSample1.User), 1);

tra.Commit();

sw.Stop();

Response.Write(sw.ElapsedTicks + "<br>");

sw.Reset();

sw.Start();

session = NHibernateHelper.GetCurrentSession();

session.Close();

sw.Stop();

Response.Write(sw.ElapsedTicks + "<br>");
第一次运行,用SQL事件探查器,结果为

从截图中的SQL语句看,第一次从数据库中加在User数据
第二次

从图中可以看出,第二次加载User对象,并没有从数据中获取数据,而是将没有设置Cache的Role信息从User里面获取。
当然在利用缓存的时候,缓存不会知道另外一个进程存储的实体发生变化,应该自己建立一些策略来及时地更新缓存快照。而且当ISessionFactory销毁的时候,二级缓存也会随之销毁,这也是应用的时候,应该注意的。今天先写到这,有点困了。
相关文章推荐
- nhibernate性能之二级缓存篇
- 在Spring.Net中利用NHibernate配置增加二级缓存
- Hibernate4教程六:性能提升和二级缓存
- NHibernate 二级缓存使用心得
- [Nhibernate]二级缓存(一)
- NHibernate之旅(24):探索NHibernate二级缓存(下)
- 性能优化(一)Hibernate 利用缓存(一级、二级、查询)提高系统性能
- 在NHibernate中使用memcache二级缓存
- 【Hibernate框架开发之九】Hibernate 性能优化笔记!(遍历、一级/二级/查询/缓存、乐观悲观锁等优化算法)
- 【Hibernate框架开发之九】Hibernate 性能优化笔记!(遍历、一级/二级/查询/缓存/乐观悲观锁等优化算法)
- 性能优化(一)Hibernate 利用缓存(一级、二级、查询)提高系统性能
- 系统性能之二级缓存大揭秘 从512K到12M[我们该如何选择I族CPU]
- 十五、NHibernate之二级缓存
- 19hibernate hibernate的性能优化之一级缓存、二级缓存和查询缓存
- NHibernate之旅(23):探索NHibernate二级缓存(上)
- 01-08-02【Nhibernate (版本3.3.1.4000) 出入江湖】二级缓存:NHibernate自带的HashtableProvider
- 性能优化之Hibernate4配置二级缓存
- 性能优化(一)Hibernate 利用缓存(一级、二级、查询)提高系统性能
- hibernate 二级缓存设置性能提升对比
- 实现asp.net mvc页面二级缓存,提高访问性能
