Mybatis公司开发常用!
Mybatis核心
- 本文重点:注解开发,mybatis多表操作,动态SQL(WHERE,SET,IF,SQL—ID减少复用)
- 代码地址--https://gitee.com/zhangjzm/my-batis.git1
面向接口编程
- 真正的开发中,很多时候我们会选择面向接口编程
- 根本原因 : 解耦,可拓展,提高复用,分层开发中,上层不用管具体的实现,大家都遵守共同的标准,使得开发变得容易,规范性更好
关于接口的理解
- 接口从更深层次的理解,应是定义(规范,约束)与实现(名实分离的原则)的分离。
- 接口的本身反映了系统设计人员对系统的抽象理解。
- 接口应有两类: 第一类是对一个个体的抽象,它可对应为一个抽象体(abstract class);
- 第二类是对一个个体某一方面的抽象,即形成一个抽象面(interface);
- 一个体有可能有多个抽象面。抽象体与抽象面是有区别的
三个面向区别
- 面向对象是指,我们考虑问题时,以对象为单位,考虑它的属性及方法 .
- 面向过程是指,我们考虑问题时,以一个具体的流程(事务过程)为单位,考虑它的实现 .
- 接口设计与非接口设计是针对复用技术而言的,与面向对象(过程)不是一个问题.更多的体现就是对系统整体的架构
Mybatis详细执行流程
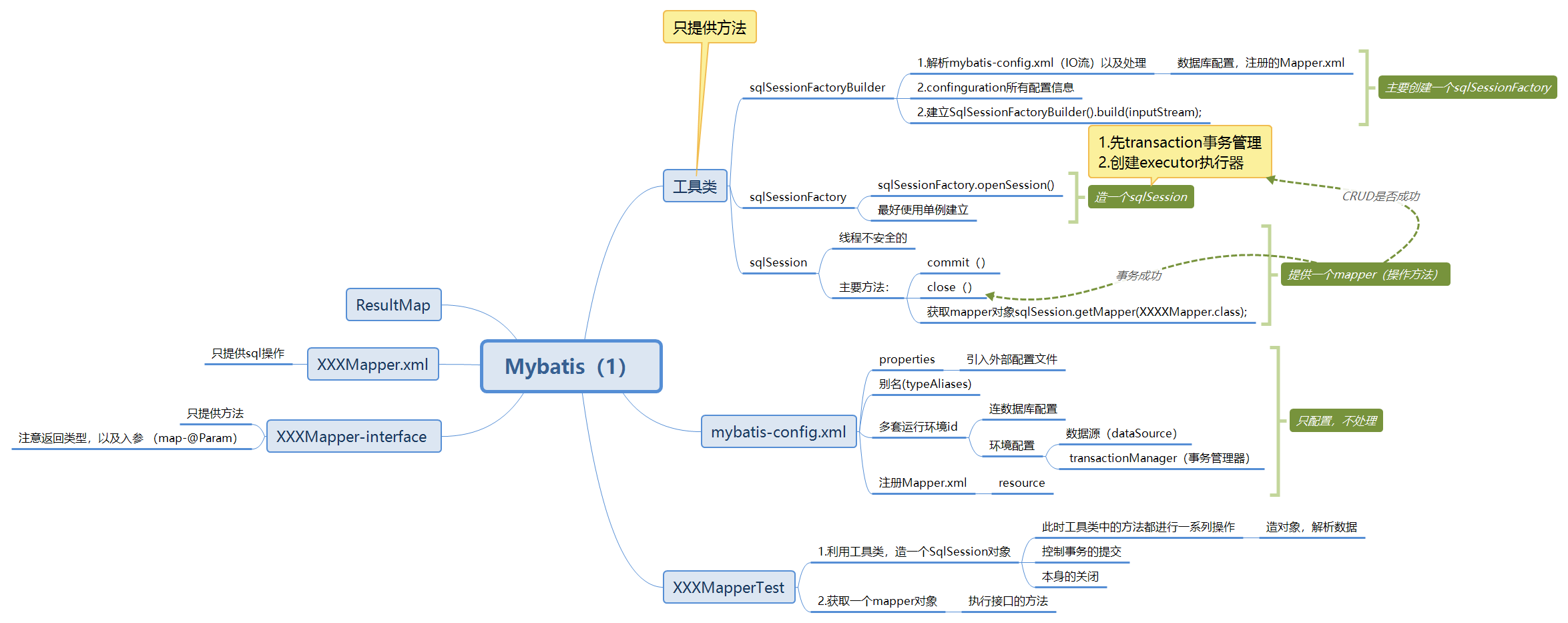
- 设置事务自动提交
- 虽说可以自动提交,但是有些时候出错了,他也会提交了。。。 工具类中
public static SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); // true 意味着开始事务自动提交,不写的话需手动提交
}
注解开发
-
所有注解底层都是通过反射机制来运行的
-
mybatis最初配置信息是基于 XML ,映射语句(SQL)也是定义在 XML 中的。而到MyBatis 3提供了
新的基于注解的配置。不幸的是,Java 注解的的表达力和灵活性十分有限。最强大的 MyBatis 映
射并不能用注解来构建。多表的时候。。。 -
sql 类型主要分成 :
@select () - @update ()
- @Insert ()
- @delete ()
【注意】利用注解开发就不需要resource mapper.xml映射文件了.但是需要配置class。。
注解CRUD
-
地址 Mybatis-05
-
1.使用注解开发需要改·
mybatis-config.xml
<!--绑定接口--> `《mappers》` `《mapper class="com.zjz.dao.UserMapper"/》` `《/mappers》`
-
2.Mapper代码
-
入参为User时,测试时直接方法(new User(XX,XX,XX));
< 56c pre>@Select("select * from user") List<User> GetUsers(); // 方法存在多个参数,所有参数前面必须加@Param("X")注解 @Select("select * from user where id =#{id} AND name = #{name}") List<User> getUserByIdName(@Param("id")int id,@Param("name")String name); @Insert("insert into user(id,name,password) values(#{id},#{name},#{password})") int addUser(User user); // 测试时的送参:mapper.updateUser(new User(4,"zjz4","123456")); @Update("update user set name=#{name},password=#{password} where id=#{id}") int updateUser(User user); // 测试时的送参: mapper.updateUser(new User(4,"zjz4","123456")); @Delete("delete from user where id=#{id}") int deleteUser(@Param("id")int id); -
查看
@param
源码

映射(mapper)---特别重要,不要忘记了
resource class 两种映射方式
普通方法--一个个xml绑定。
<mapper resource="com/zjz/dao/UserMapper.xml"/>使用注解开发就需要专门绑定接口了
<mapper class="com.zjz.dao.UserMappe 56c r"/>
- 遇到的问题,resultType的pojo没解析出来
Cause: org.apache.ibatis.builder.BuilderException: Error resolving class. Cause: org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeException: Could not resolve type alias 'Student'. Cause: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: Cannot find class: Student <!--起别名--> <typeAliases> <typeAlias type="com.zjz.pojo.BEAN" alias="BEAN"/> </typeAliases> 或者resultType直接com.zjz.pojo.BEAN
多表连接查询
- 地址 Mybatis-06,7
多对一,一对多--怎么区分:
一种是看结果要什么?(设计思想)---要一个老师手下有多个学生? 还是要多个学生,后面有个备注(教师:---)
关键:编码的主体(因为一对多反过来就是多对一,所以主体要分清) --外键(联系)
- 核心涉及:
- 复杂的属性,我们需要单独处理 对象:association 集合:collection
- 对象用来多对一(每个人都对应这个师傅(对象)) 集合用来一对多 (一个人有多个徒弟(集合))
- 类型获取: 对象中 javaType="" 指定的属性类型---对象
- 集合中的 ad8 泛型信息。使用ofType获取--对象
resultMap(重中之重,。)
-
主要作用:实现多表查询
-
体系图
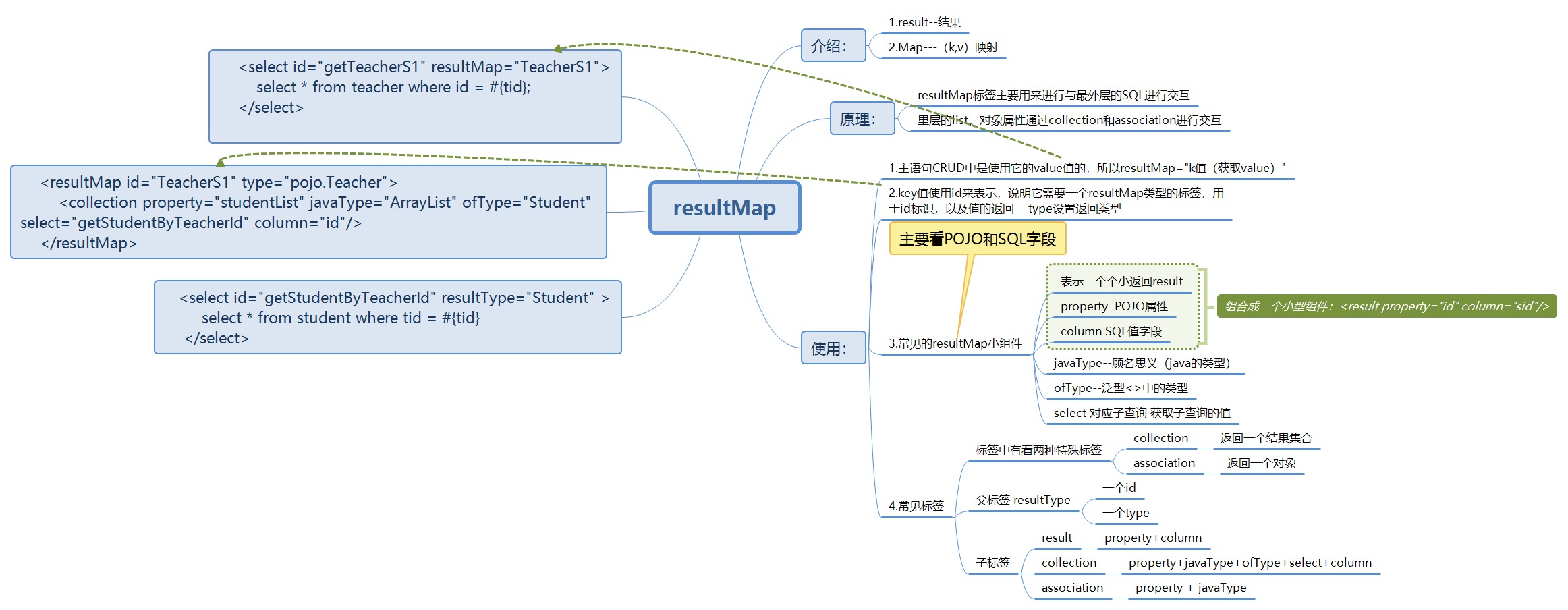
多表连接查询——多对一
重点 association resultMap property column javaType
- association 对象
- javaType="" 指定的属性!!类型(对象)
多个学生对应一个老师 主要是看主体,外键 使用学生时多个学生的外键相同,映射一个老师
思想:子查询,联表查询
引入Teacher对象查询--毕竟每个学生后面都映射着老师
- 区别:
《association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher"》 《result property="name" column="tname"/》 《/association》
《association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="com.pojo.Teacher" select="getTeacher"/》
--类似子查询
- pojo(此时便区分出,多个学生属于一个老师)
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private Teacher teacher; // 引入老师对象(每个学生都有老师的id)
}
public class Teacher {
private int id;
private String name;
}
- mybatis-config
《mappers》 《mapper class="com.dao.TeacherMapper"/》 《mapper class="com.dao.StudentMapper"/》 《/mappers》
- StudentMapper (查每个学生)
// 查询所有的学生信息,以及对应的老师的信息 public List<Student> getStudentList();
- StudentMapper.xml
<!--子查询 -->
《select id="getStudentList" resultMap="StudentTeacher"》
select * from student
《/select》
《resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="com.pojo.Student"》
《result property="id" column="id"/》
《result property="name" column="name"/》
<!--
复杂的属性,我们需要单独处理 对象:association 集合:collection
javaType="" 指定的属性!!类型(对象)
-->
《association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="com.pojo.Teacher" select="getTeacher"/》
《/resultMap》
《select id="getTeacher"
103c
resultType="com.pojo.Teacher"》
select * from teacher where id = #{id}
《/select》
类似嵌套查询 推荐使用::
- mapper.xml
<!--按照结果嵌套查询--> 《select id="getStudentList2" resultMap="StudentTeacher2"》 select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname from student s ,teacher t where s.tid = t.id; 《/select》 <!--resultType Aliases 已经配置Student Teacher --> 《resultMap id="StudentTeacher2" type="Student"》 《result property="id" column="sid"/》 《result property="name" column="sname"/》 《association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher"》 《result property="name" column="tname"/》 《association》 《/resultMap》
结果:多对一
-
发现每个学生后面写的个老师,说明学生为主体。每个后面有一个老师
-
[Student(id=1, name=小明, teacher=Teacher(id=0, name=zjzTeacher)), Student(id=2, name=小红, teacher=Teacher(id=0, name=zjzTeacher)), Student(id=3, name=小黄, teacher=Teacher(id=0, name=zjzTeacher)), Student(id=4, name=小蓝, teacher=Teacher(id=0, name=zjzTeacher)), Student(id=5, name=小白, teacher=Teacher(id=0, name=zjzTeacher))]
-
总体构造及使用:
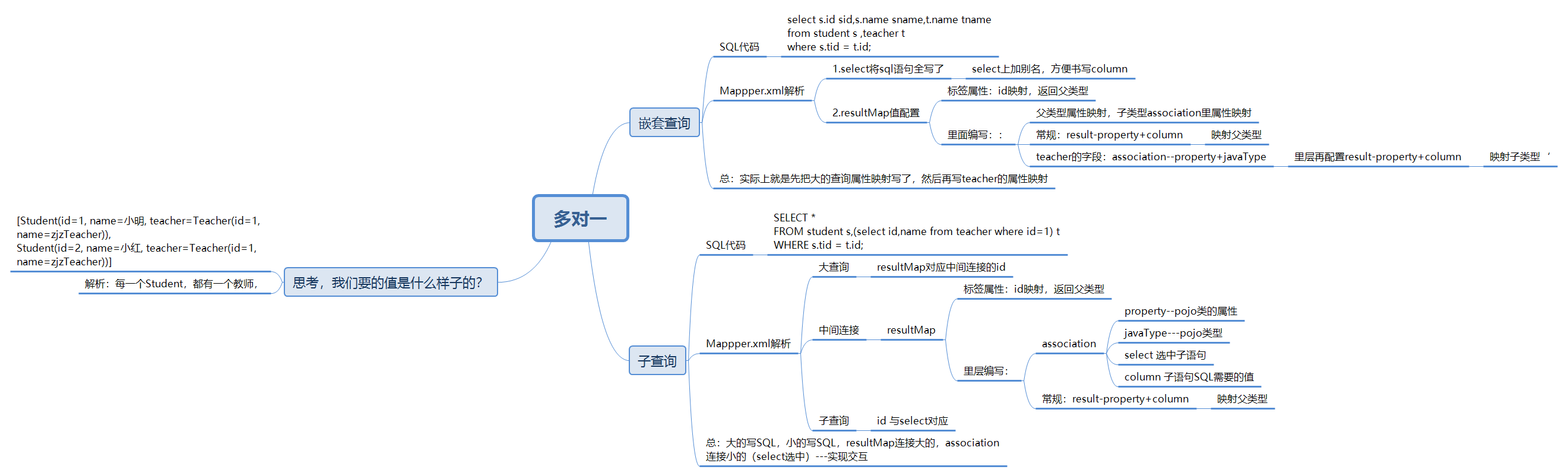
多表连接查询——多对一的查询方式
嵌套查询(链表查询)
-
pojo
// student的属性 public class Student { private int id; private String name; private int tid; } public class Teacher { private int id; private String name; // 一个老师对应多个学生 public List<Student> studentList; } -
dao
-
Teacher getTeacherS(@Param("tid")int id); -
TeacherMapper.xml
<!--按结果嵌套查询-->
《select id="getTeacherS" resultMap="TeacherS"》
select t.name tname,t.id tid,s.id sid,s.name sname
from student s ,teacher t
where s.tid = t.id and t.id = #{tid}
《/select》
<!--typeAliases 已经配置好 Teacher Student-->
《resultMap id="TeacherS" type="Teacher"》
《result property="id" column="tid"/》
《result property="name" column="tname"/》
<!--
复杂的属性,我们需要单独处理 对象:association 集合:collection
javaType="" 指定的属性!!类型
集合中的泛型信息。使用ofType获取
-->
《collection property="studentList" ofType="Student"》
《result property="id" column="sid"/》
《result property="name" column="sname"/》
《result property="tid" column="tid"/》
《/collection》
《/resultMap》
子查询
- TeacherMapper
Teacher getTeacherS1(@Param("id")int id);
- TeacherMapper.xml
<!-- 子查询-->
《select id="getTeacherS1" resultMap="TeacherS1"》
select * from teacher where id = #{id};
《/select>
《resultMap id="TeacherS1" type="Teacher"》
<!--Teacher底下的属性,此时加id,普通查询不出来了-->
<result property="id" column="id"/》
<collection property="studentList" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="Student" select="getStudentByTeacherId" column="id"/》
《/resultMap》
《select id="getStudentByTeacherId" resultType="Student" 》
select * from student where ti
1044
d = #{id}
《/select》
- 结果:一个老师的集合下有5个学生
Teacher(id=1, name=zjzTeacher, studentList=[ Student(id=1, name=小明, tid=1), Student(id=2, name=小红, tid=1), Student(id=3, name=小黄, tid=1), Student(id=4, name=小蓝, tid=1), Student(id=5, name=小白, tid=1)])
- 核心体系图
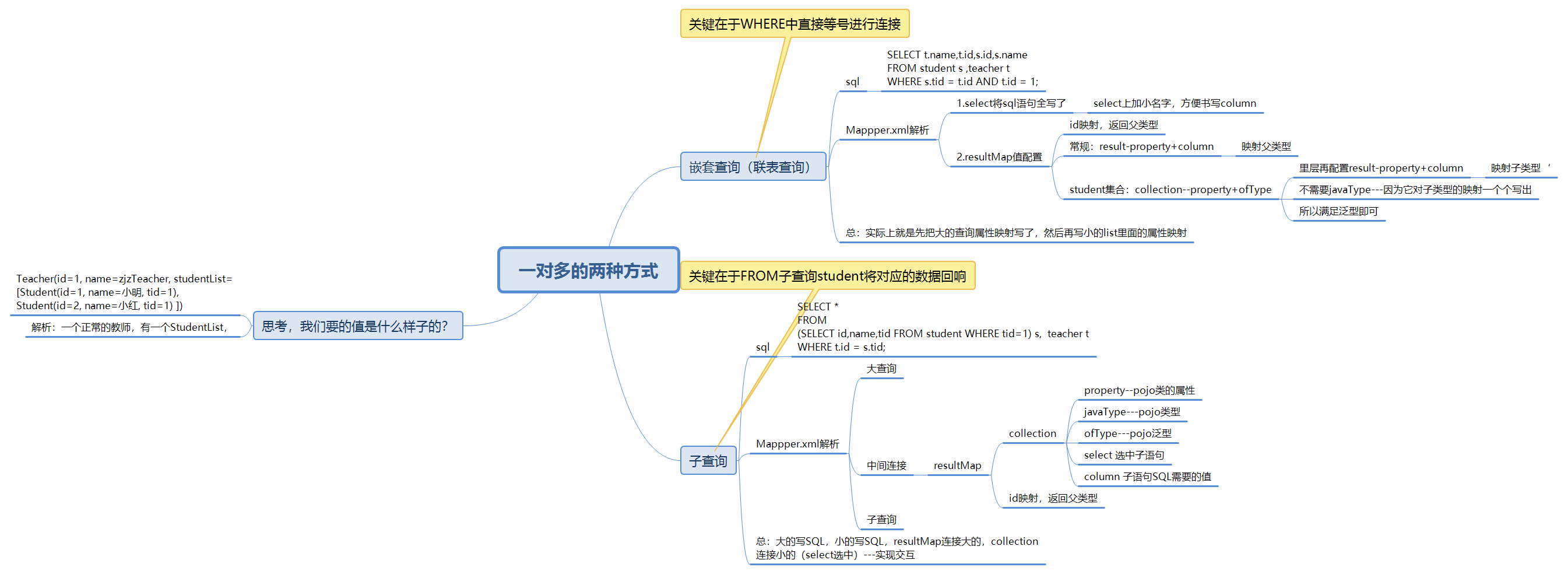
关于多表总结
- 1.三个图 resultMap 多对一 一对多
- 2.保证sql的可读性
- 3.属性名(property),字段(column)
- 4.日志要用好,好找问题
- 5.复杂的多表要注意速率---慢SQL 1000s,快 1s SQL优化,引擎,InnoDB底层原理,索引,索引优化
动态SQL
定义:所谓动态SQL,本质还是SQL语句,只是我们可以在SQL层面,去执行一个逻辑代码
作用:非常方便的进行SQL语句拼接
关键:逻辑代码怎么操作
- 动态SQL,根据不同的条件生成不同的SQL(以前JDBC时的SQL拼接)
介绍
- 动态 SQL 元素和 JSTL 或基于类似 XML 的文本处理器相似。
在 MyBatis 之前的版本中,有很多元素需要花时间了解。
MyBatis 3 大大精简了元素种类,现在只需学习原来一半的元素便可。
MyBatis 采用功能强大的基于 OGNL 的表达式来淘汰其它大部分元素。
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
where标签
-
在SQL语句之下编写
-
<where>中间写IF啥的</where>
-
作用:如果没有前置元素,它会自动去掉语句中的and或or,然后作为前置元素,如果什么属性都不传,自动清除where
如果不加的话会是这样的运行,肯定报错,所以它的作用就是去掉and select * from blog where and author = #{author}
if操作(常用)
- 代码在:mybatis-08
操作
-
XXXMapper中
// 查询博客IF List<Blog> QueryBlogIF(Map map);
-
XXXMapper.xml
《select id="QueryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog"》 select * from blog 《where》 《if test="title != null"》 and title = #{title} 《/if》 《if test="author != null"》 and author = #{author} 《/if》 《/where》 《/select》 -
Test中
@Test public void Test3(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); logger.info("QueryBlogIF开始"); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("title","MYTitle1"); List《Blog》 blogs = mapper.QueryBlogIF(map); for (Blog blog : blogs) { System.out.print(blog); } System.out.println(); logger.info("QueryBlogIF结束"); sqlSession.close(); }
choose
choose 类似于switch 比起if 它是从上到下进行的,执行一个后停止后面的
适用于优先级查询,比如VIP来了,优先买了,后来再看有没有
when---otherwise 两个小标签
当然少不了where标签
-
Mapper接口
// 查询博客Choose List《Blog》 QueryBlogChoose(Map map) ad8 ;
-
Mapper.xml
《select id="QueryBlogChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog"》 select * from blog 《where》 《choose》 《when test="title != null"》 title = #{title} 《/when》 《when test="author != null"》 and author = #{author} 《/when》 《otherwise》 and views 》 #{views} 《/otherwise》 《/choose》 《/where》 《/select》
SET
目的:update中用啊
作用:前置SET关键字 同时删掉无关的逗号
- 注:SET中如果没,逗号是会报错的
使用
-
Mapper接口
// 更新博客 int updateBlog(Map map);
-
Mapper.xml
《update id="updateBlog" parameterType="map"》
update blog
《set》
《if test="title != null"》
title = #{title},
《/if》
《if test="author != null"》
author = #{author},
《/if》
《/set》
where id = #{id}
《/update》
trim
prefixOverrides 属性会忽略通过管道符分隔的文本序列(注意此例中的空格是必要的)。
会移除所有 prefixOverrides 属性中指定的内容,并且插入 prefix 属性中指定的内容。prefixOverrides 除去前面的 suffixOverrides 除去后面的
-
trim 元素来定制 where 元素的功能。比如,和 where 元素等价的自定义 trim 元素为
《trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR "》 ... 《/trim》
《trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=","》 ... 《/trim》
SQL片段
-
目的:实现代码的复用,减少重复性操作
-
存值的地方----
《sql id="ID"》代码《/sql》
-
怎么使用? ----
《include refid="ID"》《/include》
-
使用SQL标签抽取公共部分,
-
在需要使用的地方使用include标签引用即可
-
注意事项,最好基于单表来定义SQL片段
-
SQL-ID不要有WEHER标签
-
最好就if test-----
-
代码
《sql id="if-title-author"》
《
1044
if test="title != null"》
and title = #{title}
《/if》
《if test="author != null"》
and author = #{author}
《/if》
《/sql》
《select id="QueryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog"》
select * from blog
《where》
《include refid="if-title-author"》《/include》
《/where》
《/select》
foreach
目的:遍历一些操作,如(id=1 or id=2 or id=3)
使用:
关键字:collection item open close separator
- collection 集合名字
- item 集合中的子元素的名字
- open 以什么东西开始
- close 以什么东西结束
- separate 每执行一个item中间加什么操作--

-
Mapper.xml
《!-- SQL语句:select * from blog where 1=1 and (id=1 or id=2 or id=3) 我们现在传递一个万能的map,这个map中可以传递=一个集合= open close 中要注意空格的使用,如果连起来,会被视为一个整体 --》 《select id="QueryBlogForeach" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog"》 select * from blog 《where》 《foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and (" close=")" separator="or"》 id = #{id} 《/foreach》 《/where》 《/select》 -
测试:
@Test public void TestQueryBlogForeach(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); BlogMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); logger.info("QueryBlogForeach开始"); HashMap map = new HashMap(); List《Integer》 ids = new ArrayList《》(); ids.add(1); ids.add(2); map.put("ids",ids); List《Blog》 blogs = mapper.QueryBlogForeach(map); System.out.println(blogs.toString()); logger.info("QueryBlogForeach结束"); sqlSession.close(); } -
总体构造及使用:

- web开发中常用的, 做成cs文件的js代码
- GIS开发常用算法原理分析
- Linux 服务器开发常用命令操作
- IOS 程序员开发最常用宏定义
- android开发中常用的快捷键
- 002 java开发常用集合总结
- Windows 下开发常用快捷键小结
- VS中的常用快捷键,可以提高开发效率
- android开发常用命令
- 原型对象的常用开发模式
- 2016年公司中开发中常用的Swift和iOS开源框架
- VISUAL C++软件开发中几个常用功能的实现
- Android开发中常用的一些小技巧(转载)
- linux开发环境常用命令-文件查看编辑命令
- iOS开发中那些高效常用的宏
- 前端开发中常用正则表达式
- IOS开发之----常用函数和常数
- asp.net常用开发技巧(1)
- iOS开发中那些高效常用的宏
- iOS 开发常用宏
