C++实现二叉树的基本操作:建立、遍历、计算深度、节点数、叶子数等
2020-06-22 04:33
1496 查看
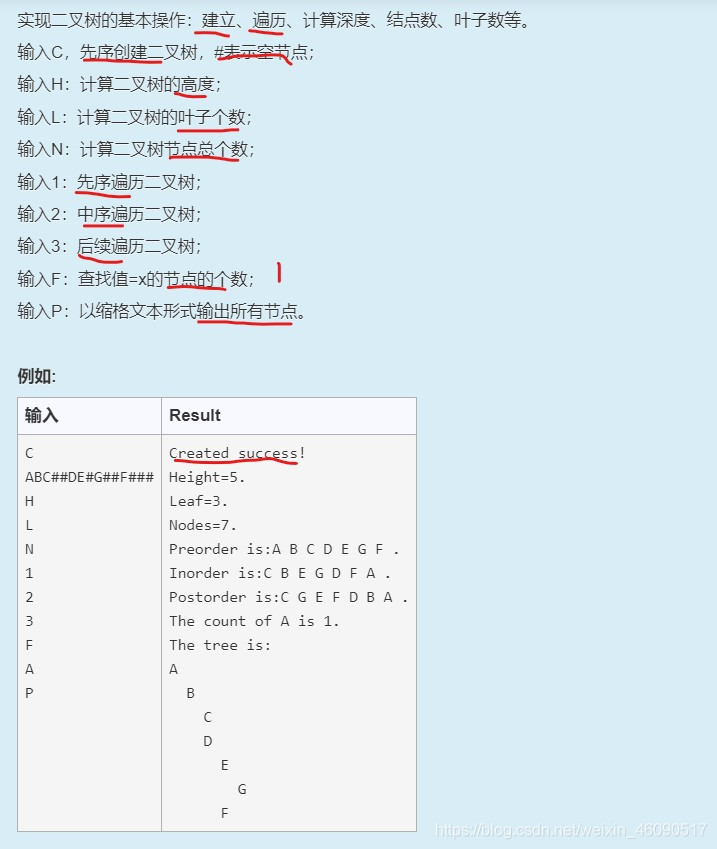
题意:
代码实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
//二叉树节点
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
char data;
BinaryTreeNode* leftChild;
BinaryTreeNode* rightChild;
};
//堆栈节点,用于深度遍历
struct stackNode
{
BinaryTreeNode* ptr;
char tag;//tag=0标志进入左子树,tag=1标志进入右子树
};
class BinaryTree //二叉树的类
{
public:
//根据完全前序遍历创建二叉树
void createBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
root=new BinaryTreeNode();
char newData;
cin>>newData;
if(newData=='#')
{
root=NULL;
}
else
{
root->data=newData;
createBinaryTree(root->leftChild);
createBinaryTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
//递归实现前序遍历
void preTraversal(BinaryTreeNode* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
cout<<root->data<<" ";
preTraversal(root->leftChild);
preTraversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
//递归实现后续遍历
void lastTraversal(BinaryTreeNode* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
lastTraversal(root->leftChild);
lastTraversal(root->rightChild);
cout<<root->data<<" ";
}
}
//非递归实现中序遍历
void mid(BinaryTreeNode* root)
{
stack<BinaryTreeNode*> S;
BinaryTreeNode* p=root;
do
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
S.push(p);
p=p->leftChild;
}
if(!S.empty())
{
p=S.top();
cout<<p->data<<" ";
S.pop();
p=p->rightChild;
}
}
while(p!=NULL||!S.empty());
}
//计算节点总数
int nodeCount(BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return nodeCount(root->leftChild)+nodeCount(root->rightChild)+1;
}
}
//计算二叉树的高度
int treeHight(BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
int LH=treeHight(root->leftChild);
int RH=treeHight(root->rightChild);
return LH > RH ? LH+1 : RH+1;
}
}
//计算二叉树的叶子个数
int getLeavesCount(BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else if (root->leftChild == NULL && root->rightChild == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
int leftLeavesCount = getLeavesCount(root->leftChild);
int rightLeavesCount = getLeavesCount(root->rightChild);
return leftLeavesCount + rightLeavesCount;
}
}
//查找值=x的节点个数
int findNode(BinaryTreeNode* &root,char x,int coun)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
if(root->data==x) coun++;
findNode(root->leftChild,x,coun);
findNode(root->rightChild,x,coun);
}
return coun;
}
//以缩格文本形式输出所有节点
void outputNode(BinaryTreeNode* &root,int x)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
for(int i=0;i<x;i++) cout<<" ";
cout<<root->data<<endl;
x=x+2;
outputNode(root->leftChild,x);
outputNode(root->rightChild,x);
}
}
};
int main()
{
BinaryTree tree;
BinaryTreeNode* treeRoot;
char func;
while(cin>>func){
if(func=='C')
{
tree.createBinaryTree(treeRoot);
cout<<"Created success!";
}
if(func=='1') {cout<<"Preorder is:";tree.preTraversal(treeRoot);cout<<".";}
if(func=='2') {cout<<"Inorder is:";tree.mid(treeRoot);cout<<".";}
if(func=='3') {cout<<"Postorder is:";tree.lastTraversal(treeRoot);cout<<".";}
if(func=='N') cout<<"Nodes="<<tree.nodeCount(treeRoot)<<".";
if(func=='H') cout<<"Height="<<tree.treeHight(treeRoot)<<".";
if(func=='L') cout<<"Leaf="<<tree.getLeavesCount(treeRoot)<<".";
if(func=='F')
{
char x;
cin>>x;
cout<<"The count of "<<x<<" is "<<tree.findNode(treeRoot,x,0)<<".";
}
if(func=='P')
{
cout<<"The tree is:"<<endl;
tree.outputNode(treeRoot,0);
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
PS:有时间再补充注意点吧
相关文章推荐
- 基本数据结构——二叉树的建立,遍历,求叶子节点,深度计算
- C++实现前序建立二叉树,层序遍历,前序中序后序遍历,计算节点数和叶子数,删除二叉树
- 八.二叉树各种操作的C语言实现 深度遍历求深度,广度遍历求深度,交换左右子树,求叶子节点数
- 二叉树的建立(非递归建立与定义建立)与基本操作(广度和深度遍历,求叶子树高)实现
- 数据结构-二叉树操作(创建、先序、中序、后序遍历、计算叶子节点数目、计算二叉树深度、左右子树交换、随机数列产生排序树、查找结点、删除节点、广度遍历、非递归先序遍历)C语言源码(全)
- [C/C++] 先序建立二叉树| 先序、中序、后序遍历二叉树| 求二叉树深度、节点数、叶节点数 算法实现
- 二叉树基本操作的递归实现(二叉树建立,先序,中序,后序,深度的递归遍历。广度优先,高度优先的非递归遍历)
- 二叉树的建立、遍历、叶子节点计数、深度计算
- java语言实现的二叉树的各种操作(包括递归与非递归遍历二叉树,求二叉树的高度,节点总数,叶子节点等)
- c++实现二叉树的查找,插入,删除,深度,叶子节点数,度为1的节点数(递归方法)及运行实例结果
- c++实现二叉树的查找,插入,删除,深度,叶子节点数,度为1的节点数(递归方法)及运行实例结果
- c++实现二叉树的查找,插入,删除,深度,叶子节点数,度为1的节点数(递归方法)及运行实例结果
- 二叉树建立与遍历递归操作c++实现
- 二叉树基本操作--创建,三种遍历,叶子节点
- 八.二叉树各种操作的C语言实现 树的一些基本的操作,包括,树的建立,树的深度,
- c++实现二叉树的查找,插入,删除,深度,叶子节点数,度为1的节点数(递归方法)及运行实例结果
- 【数据结构】二叉树的实现(如:默认成员函数、(叶子)节点数、深度、四种遍历)
- C++使用递归和非递归算法实现的二叉树叶子节点个数计算方法
- 数据结构(C语言实现) - 二叉树的基本操作(建立,遍历,结点数,叶子结点数,高度,按树状打印,输出叶子结点等)
- java实现二叉树的建立,前中后序遍历,层次遍历,深度,节点个数等
