Vulkan(1)用apispec生成Vulkan库
Vulkan(1)用apispec生成Vulkan库
我的Vulkan.net库已在(https://github.com/bitzhuwei/Vulkan.net)开源,欢迎交流。
apispec.html
在Vulkan SDK的安装文件夹里,有一个Documentation\apispec.html文件。这是一个由代码生成的对Vulkan API的说明。它包含了Vulkan API的枚举类型、结构体、函数声明以及这一切的详细注释。
由于它是自动生成的,所以其格式非常规则。只需将少数几处<br>改为<br />,几处<col .. >改为<col .. />,就可以直接用 XElement 来加载和解析它。
由于它包含了每个枚举类型及其成员的注释,包含了每个结构体及其成员的注释,包含了每个函数声明及其参数的注释,我就想,如果我能将它转换为C#代码,那会是多么美妙的一个Vulkan库啊!
我在网上找到的几个Vulkan库,基本上都没有什么注释,这让我使用起来很不方便,严重妨碍了学习速度。很多结构体的成员类型都是粗糙的 IntPtr ,而不是具体类型的指针,这也使得用起来很麻烦。
那么就动手做自己的Vulkan库吧!
分类
首先,要将巨大的apispec.html文件里的内容分为几个类别,即C宏定义、Command(函数声明)、Enum、Extension、Flag、Handle、PFN、Scalar Type和Struct。其中的C宏定义和Extension暂时用不到,就不管了,Scalar Type数量很少,又不包含实质内容,直接手工编写即可。
我们按照Enum、Handle、Flag、PFN、Struct和Command的顺序依次分析,因为后者可能依赖前者。
Enum
我们来观察apispec.html中对Enum的描述:
<h4 id="_name_798">Name</h4>
<div class="paragraph">
<p>VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsTypeNV - Acceleration structure memory requirement type</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="sect3">
<h4 id="_c_specification_798">C Specification</h4>
<div class="paragraph">
<p>Possible values of <code>type</code> in
<code>VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsInfoNV</code> are:,</p>
</div>
<div id="VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsTypeNV" class="listingblock">
<div class="content">
<pre class="highlight"><code class="language-c++" data-lang="c++">typedef enum VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsTypeNV {
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_OBJECT_NV = 0,
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_BUILD_SCRATCH_NV = 1,
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_UPDATE_SCRATCH_NV = 2,
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_MAX_ENUM_NV = 0x7FFFFFFF
} VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsTypeNV;</code></pre>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="sect3">
<h4 id="_description_798">Description</h4>
<div class="ulist">
<ul>
<li>
<p><code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_OBJECT_NV</code>
requests the memory requirement for the <code>VkAccelerationStructureNV</code>
backing store.</p>
</li>
<li>
<p><code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_BUILD_SCRATCH_NV</code>
requests the memory requirement for scratch space during the initial
build.</p>
</li>
<li>
<p><code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_UPDATE_SCRATCH_NV</code>
requests the memory requirement for scratch space during an update.</p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<div class="sect3">
<h4 id="_see_also_798">See Also</h4>
我们将发现,对于每个Enum类型,apispec都有这样的规律:从一个<h4>Name</h4>标签开始,接下来的<p></p>标签是对这个Enum的注释,接下来的<code class="language-c++"></code>标签是这个Enum的定义;然后,从<h4>Descriptor</h4>开始到<h4>See Also</h4>结束,这两个标签之间的所有<p></p>标签,分别是Enum的某个成员的注释,而且,这个注释都是以<code>此成员的名字</code>开头(这可以用于识别此注释属于哪个成员)。
有了这些规律,就可以将其解析为C#代码了。解析代码很简单,就不解释了。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Xml.Linq;
namespace ApiSpec {
class EnumsParser {
static readonly char[] inLineSeparator = new char[
ae4
] { ' ', '\t', '\r', '\n', };
static readonly char[] lineSeparator = new char[] { '\r', '\n' };
const string leftBrace = "{";
const string rightBrace = "}";
const string filename = "Enums.content.xml";
const string strName = "Name";
const string strCSpecification = "C Specification";
const string strDescription = "Description";
const string strSeeAlso = "See Also";
const string strDocNotes = "Document Notes";
class EnumDefinetion {
/*typedef enum VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsTypeNV {
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_OBJECT_NV = 0,
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_BUILD_SCRATCH_NV = 1,
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_UPDATE_SCRATCH_NV = 2,
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_MAX_ENUM_NV = 0x7FFFFFFF
} VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsTypeNV;
*/
public string raw;
public string[] Dump() {
string[] lines = this.raw.Split(lineSeparator, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
if (lines == null || lines.Length < 2) { return lines; }
{
string[] parts = lines[0].Split(inLineSeparator, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
lines[0] = $"public enum {parts[2]} {leftBrace}";
}
{
int last = lines.Length - 1;
lines[last] = $"{rightBrace}";
}
return lines;
}
}
class EnumItemComment {
public List<string> lstComment = new List<string>();
public Dictionary<string, string> Dump() {
Dictionary<string, string> dict = new Dictionary<string, string>();
foreach (var item in lstComment) {
int left = item.IndexOf("<code>");
int right = item.IndexOf("</code>");
if (left != -1 && right != -1) {
string key = item.Substring(left + "<code>".Length, right - (left + "<code>".Length));
if (!dict.ContainsKey(key)) {
dict.Add(key, item);
}
}
}
return dict;
}
}
public static void DumpEnums() {
XElement root = XElement.Load(filename);
var lstDefinition = new List<EnumDefinetion>(); bool inside = false;
TraverseNodesEnumDefinitions(root, lstDefinition, ref inside);
var listEnumItemComment = new List<EnumItemComment>(); inside = false;
TraverseNodesEnumItemComments(root, listEnumItemComment, ref inside);
var lstEnumComment = new List<string>(); inside = false;
TraverseNodesEnumComments(root, lstEnumComment, ref inside);
using (var sw = new System.IO.StreamWriter("Enums.gen.cs")) {
for (int i = 0; i < lstDefinition.Count; i++) {
EnumDefinetion definition = lstDefinition[i];
//sw.WriteLine(definition.raw);
string[] definitionLines = definition.Dump();
EnumItemComment itemComment = listEnumItemComment[i];
Dictionary<string, string> item2Comment = itemComment.Dump();
sw.WriteLine($"// Enum: {i}");
string enumComment = lstEnumComment[i];
sw.WriteLine($"/// <summary>{enumComment}</summary>");
{
string line = definitionLines[0];
if (line.Contains("FlagBits")) { sw.WriteLine("[Flags]"); }
sw.WriteLine(line);
}
for (int j = 1; j < definitionLines.Length - 1; j++) {
string line = definitionLines[j];
if (item2Comment != null) {
string strComment = ParseItemComment(line, item2Comment);
if (strComment != string.Empty) {
strComment = strComment.Replace("\r\n", "\n");
strComment = strComment.Replace("\r", "\n");
strComment = strComment.Replace("\n", $"{Environment.NewLine} /// ");
sw.WriteLine($" /// <summary>{strComment}</summary>");
}
}
sw.WriteLine(line);
}
{
string line = definitionLines[definitionLines.Length - 1];
sw.WriteLine(line); // }
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Done");
}
/*<h4 id="_name_800">Name</h4>
<div class="paragraph">
<p>VkAccessFlagBits - Bitmask specifying memory access types that will participate
aec
in a memory dependency</p>
</div>*/
private static void TraverseNodesEnumComments(XElement node, List<string> list, ref bool inside) {
if (node.Name == "h4") {
if (node.Value == "Name") {
inside = true;
}
}
else if (node.Name == "p") {
if (inside) {
string text = node.ToString();
text = text.Substring("<p>".Length, text.Length - "<p></p>".Length);
text = text.Trim();
list.Add(text);
inside = false;
}
}
foreach (XElement item in node.Elements()) {
TraverseNodesEnumComments(item, list, ref inside);
}
}
/* line: VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_TYPE_TOP_LEVEL_NV = 0,
*
comment: <code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_TYPE_TOP_LEVEL_NV</code> is a top-level
142 acceleration structure containing instance data referring to
bottom-level level acceleration structures.
<code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_TYPE_BOTTOM_LEVEL_NV</code> is a bottom-level
acceleration structure containing the AABBs or geometry to be
intersected.
*/
static readonly char[] equalSeparator = new char[] { '=', ' ', '\t', '\r', '\n', };
private static string ParseItemComment(string line, Dictionary<string, string> dict) {
string result = string.Empty;
string[] parts = line.Split(equalSeparator, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
if (parts.Length == 2) {
string key = parts[0];
if (dict.ContainsKey(key)) {
result = dict[key];
}
}
return result;
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="node"></param>
/// <param name="list"></param>
/// <param name="inside"></param>
private static void TraverseNodesEnumItemComments(XElement node, List<EnumItemComment> list, ref bool inside) {
if (node.Name == "h4") {
if (node.Value == "Description") {
inside = true;
var comment = new EnumItemComment();
list.Add(comment);
}
else if (node.Value == "See Also") {
inside = false;
}
}
else if (node.Name == "p") {
if (inside) {
EnumItemComment comment = list[list.Count - 1];
string text = node.ToString();
text = text.Substring("<p>".Length, text.Length - "<p></p>".Length);
text = text.Trim();
comment.lstComment.Add(text);
}
}
foreach (XElement item in node.Elements()) {
TraverseNodesEnumItemComments(item, list, ref inside);
}
}
private static void TraverseNodesEnumDefinitions(XElement node, List<EnumDefinetion> list, ref bool inside) {
if (node.Name == "h4") {
if (node.Value == "C Specification") {
inside = true;
}
}
else if (node.Name == "code") {
if (inside) {
XAttribute attrClass = node.Attribute("class");
if (attrClass != null && attrClass.Value == "language-c++") {
string v = node.Value;
var item = new EnumDefinetion() { raw = v, };
list.Add(item);
inside = false;
}
}
}
foreach (XElement item in node.Elements()) {
TraverseNodesEnumDefinitions(item, list, ref inside);
}
}
}
}
EnumsParser
解析得到了143个Enum类型,其中前2个如下:
// Enum: 0
/// <summary>VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsTypeNV - Acceleration structure memory requirement type</summary>
public enum VkAccelerationStructureMemoryRequirementsTypeNV {
/// <summary><code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_OBJECT_NV</code>
/// requests the memory requirement for the <code>VkAccelerationStructureNV</code>
/// backing store.</summary>
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_OBJECT_NV = 0,
/// <summary><code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_BUILD_SCRATCH_NV</code>
/// requests the memory requirement for scratch space during the initial
/// build.</summary>
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_BUILD_SCRATCH_NV = 1,
/// <summary><code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_UPDATE_SCRATCH_NV</code>
/// requests the memory requirement for scratch space during an update.</summary>
14 VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_UPDATE_SCRATCH_NV = 2,
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_MEMORY_REQUIREMENTS_TYPE_MAX_ENUM_NV = 0x7FFFFFFF
}
// Enum: 1
/// <summary>VkAccelerationStructureTypeNV - Type of acceleration structure</summary>
public enum VkAccelerationStructureTypeNV {
/// <summary><code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_TYPE_TOP_LEVEL_NV</code> is a top-level
/// acceleration structure containing instance data referring to
/// bottom-level level acceleration structures.</summary>
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_TYPE_TOP_LEVEL_NV = 0,
/// <summary><code>VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_TYPE_BOTTOM_LEVEL_NV</code> is a bottom-level
/// acceleration structure containing the AABBs or geometry to be
/// intersected.</summary>
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_TYPE_BOTTOM_LEVEL_NV = 1,
VK_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_TYPE_MAX_ENUM_NV = 0x7FFFFFFF
}
为了保持Vulkan API的原汁原味(也为了我自己省事),Enum的成员名字就保持这么长的大写+下划线版本好了。
Handle
这里的Handle指的是Vulkan中的不透明对象提供给程序员的句柄,例如一个VkInstance类型的对象,在程序员这里看到的只是一个UInt32的句柄,它的实际内容由Vulkan内部来管理。因此这里只需找到各个Handle的名字,将其改写为一个struct即可。
在apispec.html中对Handle的描述如下:
<h3 id="_vkaccelerationstructurenv3">VkAccelerationStructureNV(3)</h3>
只需找到各个<h3></h3>标签,就可以找到各个Handle的名字了。解析后得到37个Handle,其中的2个Handle如下:
// Object Handles: 1
/// <summary>VkBuffer - Opaque handle to a buffer object
/// <para>Buffers represent linear arrays of data which are used for various purposesby binding them to a graphics or compute pipeline via descriptor sets or viacertain commands, or by directly specifying them as parameters to certaincommands.</para>
/// <para>Buffers are represented by VkBuffer handles:</para>
/// </summary>
public struct VkBuffer {
public UInt64 handle;
}
// Object Handles: 21
/// <summary>VkInstance - Opaque handle to an instance object
/// <para>There is no global state in Vulkan and all per-application state is storedin a VkInstance object.Creating a VkInstance object initializes the Vulkan library and allowsthe application to pass information about itself to the implementation.</para>
/// <para>Instances are represented by VkInstance handles:</para>
/// </summary>
public struct VkInstance {
public UInt32 handle;
}
对于上述这样的struct,其长度等于内部成员的长度。因此,实际上VkInstance只是UInt32的一个别名,这样的别名大大强化了类型的作用,加快了编程速度。
要注意的是,有的Handle使用UInt64,有的使用UInt32,这是不可以随意改变的,否则Vulkan会卡住不动。当然,只要字节长度相同,就可以代替,例如可以用IntPtr代替UInt32,因为两者都是4字节的。
Flag
在apispec.html中,Flag实际上是一个别名,即C语言中用 typedef 定义的一个名字。2个例子如下:
<p>VkAccessFlags - Bitmask of VkAccessFlagBits</p> <p>VkBufferViewCreateFlags - Reserved for future use</p>
这是目前的apispec中仅有的2种Flag的说明形式。对于它们,我们分别可以用下面的代码代替:
using VkAccessFlags = ApiSpec.Generated.VkAccessFlagBits; // VkBufferViewCreateFlags - Reserved for future use
解析方法也很简单,用 string.Split() 拆分一下即可。
最后得到的这些using代码,将用于后面解析的Struct和Command中。
PFN
这里的PFN是函数指针的意思,也就是C#里的delegate那一套。其解析方式与Enum十分相似,不再赘述。解析后得到了8个函数指针的定义,其中几个如下:
// PFN: 0 /// <summary>PFN_vkAllocationFunction - Application-defined memory allocation function</summary> public unsafe delegate void* PFN_vkAllocationFunction( /// <summary>pUserData is the value specified for /// VkAllocationCallbacks::pUserData in the allocator specified /// by the application.</summary> void* pUserData, /// <summary>size is the size in bytes of the requested allocation.</summary> Int32 size, /// <summary>alignment is the requested alignment of the allocation in bytes /// and must be a power of two.</summary> Int32 alignment, /// <summary>allocationScope is a VkSystemAllocationScope value /// specifying the allocation scope of the lifetime of the allocation, as /// described here.</summary> VkSystemAllocationScope allocationScope); // PFN: 1 /// <summary>PFN_vkDebugReportCallbackEXT - Application-defined debug report callback function</summary> public unsafe delegate VkBool32 PFN_vkDebugReportCallbackEXT( /// <summary>flags specifies the VkDebugReportFlagBitsEXT that triggered /// this callback.</summary> VkDebugReportFlagBitsEXT flags, /// <summary>objectType is a VkDebugReportObjectTypeEXT value specifying /// the type of object being used or created at the time the event was /// triggered.</summary> VkDebugReportObjectTypeEXT _objectType, /// <summary>object is the object where the issue was detected. /// If objectType is VK_DEBUG_REPORT_OBJECT_TYPE_UNKNOWN_EXT, /// object is undefined.</summary> UInt64 _object, /// <summary>location is a component (layer, driver, loader) defined value that /// specifies the location of the trigger. /// This is an optional value.</summary> Int32 location, /// <summary>messageCode is a layer-defined value indicating what test /// triggered this callback.</summary> Int32 messageCode, /// <summary>pLayerPrefix is a null-terminated string that is an abbreviation /// of the name of the component making the callback. /// pLayerPrefix is only valid for the duration of the callback.</summary> IntPtr pLayerPrefix, /// <summary>pMessage is a null-terminated string detailing the trigger /// conditions. /// pMessage is only valid for the duration of the callback.</summary> IntPtr pMessage, /// <summary>pUserData is the user data given when the /// VkDebugReportCallbackEXT was created.</summary> void* pUserData);
可以看到,函数注释和参数注释都十分详尽,看了就开心。
Struct
对于Struct的解析也与Enum类似,不再赘述。解析后得到434个结构体。其中几个如下:
// Struct: 4
/// <summary>VkAllocationCallbacks - Structure containing callback function pointers for memory allocation
/// </summary>
public unsafe struct VkAllocationCallbacks {
/// <summary> pUserData is a value to be interpreted by the implementation of
/// the callbacks.
/// When any of the callbacks in VkAllocationCallbacks are called, the
/// Vulkan implementation will pass this value as the first parameter to the
/// callback.
/// This value can vary each time an allocator is passed into a command,
/// even when the same object takes an allocator in multiple commands.</summary>
public void* pUserData;
/// <summary> pfnAllocation is a pointer to an application-defined memory
/// allocation function of type PFN_vkAllocationFunction.</summary>
public /*PFN_vkAllocationFunction*/IntPtr pfnAllocation;
/// <summary> pfnReallocation is a pointer to an application-defined memory
/// reallocation function of type PFN_vkReallocationFunction.</summary>
public /*PFN_vkReallocationFunction*/IntPtr pfnReallocation;
/// <summary> pfnFree is a pointer to an application-defined memory free
/// function of type PFN_vkFreeFunction.</summary>
public /*PFN_vkFreeFunction*/IntPtr pfnFree;
/// <summary> pfnInternalAllocation is a pointer to an application-defined
/// function that is called by the implementation when the implementation
/// makes internal allocations, and it is of type
/// PFN_vkInternalAllocationNotification.</summary>
public /*PFN_vkInternalAllocationNotification*/IntPtr pfnInternalAllocation;
/// <summary> pfnInternalFree is a pointer to an application-defined function
/// that is called by the implementation when the implementation frees
/// internal allocations, and it is of type
/// PFN_vkInternalFreeNotification.</summary>
public /*PFN_vkInternalFreeNotification*/IntPtr pfnInternalFree;
}
// Struct: 9
/// <summary>VkApplicationInfo - Structure specifying application info
/// </summary>
public unsafe struct VkApplicationInfo {
/// <summary> sType is the type of this structure.</summary>
public VkStructureType sType;
/// <summary> pNext is NULL or a pointer to an extension-specific structure.</summary>
public /*-const-*/ void* pNext;
/// <summary> pApplicationName is NULL or is a pointer to a null-terminated
/// UTF-8 string containing the name of the application.</summary>
public IntPtr pApplicationName;
/// <summary> applicationVersion is an unsigned integer variable containing the
/// developer-supplied version number of the application.</summary>
public UInt32 applicationVersion;
/// <summary> pEngineName is NULL or is a pointer to a null-terminated UTF-8
/// string containing the name of the engine (if any) used to create the
/// application.</summary>
public IntPtr pEngineName;
/// <summary> engineVersion is an unsigned integer variable containing the
/// developer-supplied version number of the engine used to create the
/// application.</summary>
public UInt32 engineVersion;
/// <summary> apiVersion
/// must be the highest version of Vulkan that the
/// application is designed to use, encoded as described in
/// html/vkspec.html#extendingvulkan-coreversions-versionnumbers.
/// The patch version number specified in apiVersion is ignored when
/// creating an instance object.
/// Only the major and minor versions of the instance must match those
/// requested in apiVersion.</summary>
public UInt32 apiVersion;
}
// Struct: 193
/// <summary>VkInstanceCreateInfo - Structure specifying parameters of a newly created instance
/// </summary>
public unsafe struct VkInstanceCreateInfo {
/// <summary> sType is the type of this structure.</summary>
public VkStructureType sType;
/// <summary> pNext is NULL or a pointer to an extension-specific structure.</summary>
public /*-const-*/ void* pNext;
/// <summary> flags is reserved for future use.</summary>
public VkInstanceCreateFlags flags;
/// <summary> pApplicationInfo is NULL or a pointer to an instance of
/// VkApplicationInfo.
/// If not NULL, this information helps implementations recognize behavior
/// inherent to classes of applications.
/// VkApplicationInfo is defined in detail below.</summary>
public /*-const-*/ VkApplicationInfo* pApplicationInfo;
/// <summary> enabledLayerCount is the number of global layers to enable.</summary>
public UInt32 enabledLayerCount;
/// <summary> ppEnabledLayerNames is a pointer to an array of
/// enabledLayerCount null-terminated UTF-8 strings containing the
/// names of layers to enable for the created instance.
/// See the html/vkspec.html#extendingvulkan-layers section for further details.</summary>
public IntPtr /*-const-*/ * ppEnabledLayerNames;
/// <summary> enabledExtensionCount is the number of global extensions to
/// enable.</summary>
public UInt32 enabledExtensionCount;
/// <summary> ppEnabledExtensionNames is a pointer to an array of
/// enabledExtensionCount null-terminated UTF-8 strings containing the
/// names of extensions to enable.</summary>
public IntPtr /*-const-*/ * ppEnabledExtensionNames;
}
这里有几点要注意。
函数委托用在struct中后,这个struct无法使用指针形式(SomeStruct*),所以这里不得不用IntPtr代替了具体的函数委托。
在 IntPtr pApplicationName 中应当用 Marshal.StringToHGlobalAnsi(string s) 为其赋值。函数 Marshal.StringToHGlobalAnsi(string s) 会在非托管内存中为s创建一个副本,然后返回此副本的指针。这样pApplicationName才会指向一个固定位置的字符串。当然,用完后,这个副本应当用 Marshal.FreeHGlobal(IntPtr hglobal) 释放掉。为了简化这一过程,我提供一个扩展函数:
/// <summary>
/// Set a string to specified <paramref name="target"/>.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <param name="target">address of string.</param>
public static void Set(this string value, ref IntPtr target) {
{ // free unmanaged memory.
if (target != IntPtr.Zero) {
Marshal.FreeHGlobal(target);
target = IntPtr.Zero;
}
}
{
if (value != null && value.Length > 0) {
target = Marshal.StringToHGlobalAnsi(value);
}
else {
target = IntPtr.Zero;
}
}
}
这个扩展函数会将上一次 Marshal.StringToHGlobalAnsi() 的内存释放,但是无法保证这次的。也就是说,它可以保证,最多还只需调用1次内存释放函数Marshal.FreeHGlobal(IntPtr hglobal)。
在 public IntPtr /*-const-*/ * ppEnabledLayerNames; 中也有类似的问题,这个成员指向一个IntPtr数组,这个数组的每个成员都是一个IntPtr,每个IntPtr都指向一个由 Marshal.StringToHGlobalAnsi(string s) 提供的返回值。所以这需要另一个扩展函数来简化之:
/// <summary>
/// Set an array of structs to specified <paramref name="target"/> and <paramref name="count"/>.
/// <para>Enumeration types are not allowed to use this method.
/// If you have to, convert them to byte/short/ushort/int/uint according to their underlying types first.</para>
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <param name="target">address of first element/array.</param>
/// <param name="count">How many elements?</param>
public static void Set<T>(this T[] value, ref IntPtr target, ref UInt32 count) where T : struct {
{ // free unmanaged memory.
if (target != IntPtr.Zero) {
Marshal.FreeHGlobal(target);
target = IntPtr.Zero;
count = 0;
}
}
{
count = (UInt32)value.Length;
int elementSize = Marshal.SizeOf<T>();
int byteLength = (int)(count * elementSize);
IntPtr array = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(byteLength);
var dst = (byte*)array;
GCHandle pin = GCHandle.Alloc(value, GCHandleType.Pinned);
IntPtr address = Marshal.UnsafeAddrOfPinnedArrayElement(value, 0);
var src = (byte*)address;
for (int i = 0; i < byteLength; i++) {
dst[i] = src[i];
}
pin.Free();
31
target = array;
}
}
在此函数参数中,我使用 ref IntPtr target ,而不是 ref T* target ,是因为C#不允许这样。编译器说,无法获取托管类型(”T”)的大小,或声明指向它的指针。那么在调用此扩展函数时,就得先创建一个临时变量 IntPtr ptr = IntPtr.Zero ,调用完扩展函数后,再将ptr赋予具体类型的指针。例如:
var deviceInfo = new VkDeviceCreateInfo();
IntPtr ptr = IntPtr.Zero;
new VkDeviceQueueCreateInfo[] { queueInfo }.Set(ref ptr, ref deviceInfo.queueCreateInfoCount);
deviceInfo.pQueueCreateInfos = (VkDeviceQueueCreateInfo*)ptr;
好消息是,对于字符串数组string[]和(
bool、byte、short、int、long、char、sbyte、ushort、uint、ulong、float、double
)这12种特殊基础类型的数组,可以直接使用Set扩展函数。因为我专门为它们编写了特定的扩展函数。
Command
对于Command的解析也与Struct类似,不再赘述。解析后得到326个command,几个例子如下:
// Command: 4 /// <summary>vkAllocateCommandBuffers - Allocate command buffers from an existing command pool /// </summary> /// <param name="device"> device is the logical device that owns the command pool.</param> /// <param name="pAllocateInfo"> pAllocateInfo is a pointer to an instance of the /// VkCommandBufferAllocateInfo structure describing parameters of the /// allocation.</param> /// <param name="pCommandBuffers"> pCommandBuffers is a pointer to an array of VkCommandBuffer /// handles in which the resulting command buffer objects are returned. /// The array must be at least the length specified by the /// commandBufferCount member of pAllocateInfo. /// Each allocated command buffer begins in the initial state.</param> [DllImport(VulkanLibrary, CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Winapi)] public static extern VkResult vkAllocateCommandBuffers( VkDevice device, /*-const-*/ VkCommandBufferAllocateInfo* pAllocateInfo, VkCommandBuffer* pCommandBuffers); // Command: 324 /// <summary>vkUpdateDescriptorSets - Update the contents of a descriptor set object /// </summary> /// <param name="device"> device is the logical device that updates the descriptor sets.</param> /// <param name="descriptorWriteCount"> descriptorWriteCount is the number of elements in the /// pDescriptorWrites array.</param> /// <param name="pDescriptorWrites"> pDescriptorWrites is a pointer to an array of /// VkWriteDescriptorSet structures describing the descriptor sets to /// write to.</param> /// <param name="descriptorCopyCount"> descriptorCopyCount is the number of elements in the /// pDescriptorCopies array.</param> /// <param name="pDescriptorCopies"> pDescriptorCopies is a pointer to an array of /// VkCopyDescriptorSet structures describing the descriptor sets to /// copy between.</param> [DllImport(VulkanLibrary, CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Winapi)] public static extern void vkUpdateDescriptorSets( VkDevice device, UInt32 descriptorWriteCount, /*-const-*/ VkWriteDescriptorSet* pDescriptorWrites, UInt32 descriptorCopyCount, /*-const-*/ VkCopyDescriptorSet* pDescriptorCopies);
其中有一个函数使用了 void** 这个二级指针,我觉得实在难看又难用,就用 IntPtr* 代替了。
对非托管内存的管理(释放)问题
每个struct都应该自己负责自己使用的非托管资源的释放问题。给这样的struct的指针成员 T* p; 赋值时,也应当为数据复制一个副本,将副本赋值给p。这样它释放资源时,就不会影响到其它地方了。实际上,在各个扩展函数 Set(..) 中,我就是用副本赋值的。
如果struct的指针成员 T* p; 实际上只需得到1个对象,也就是说,数组中的元素只有1个,那么可以直接将此元素的地址赋值给p,并且不释放资源。例如:
UInt32 index = 0;
var info = new VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR();
{
info.sType = VkStructureType.VK_STRUCTURE_TYPE_SWAPCHAIN_CREATE_INFO_KHR;
// other stuff ..
//new UInt32[] { 0 }.Set(ref info.QueueFamilyIndices, ref info.QueueFamilyIndexCount);
info.pQueueFamilyIndices = &index; info.queueFamilyIndexCount = 1;
}
VkSwapchainKHR swapchain;
vkAPI.vkCreateSwapchainKHR(device, &info, null, &swapchain);
这是稳妥、可移植、无需程序员直接写 Marshal. AllocHGlobal() 的内存管理方法。
那么,如果程序员忘记释放某些struct的资源了呢?Vulkan说,程序员应当清楚自己在做什么,不然它们何必用Vulkan。我觉得呢,这些struct不会被反复使用,因此,它们最多泄漏一点点内存,不会像服务器代码那样占用越来越多的内存,所以不碍事的。
总结
有了这么带劲的注释,整个档次都不一样了。


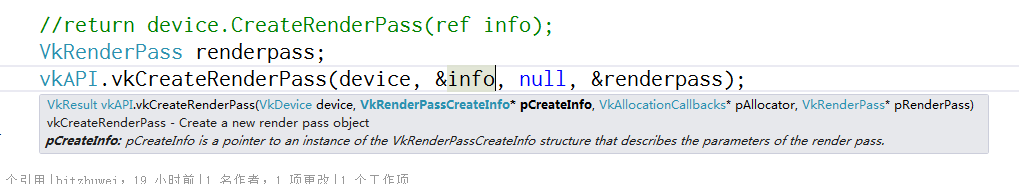
- Spring MVC 集成 Swagger,API文档自动生成~
- 使用新浪API生成短连接
- qq音乐 ,百度新闻,二维码生成,接口 api .
- AMD发布Adrenalin Edition 19.7.3驱动,新增 Vulkan API 扩展支持
- 短URL代码也可利用百度API生成
- php自写api文档生成工具
- java生成API文档
- swagger生成API文档
- Qt开发:设置QMAKESPEC,生成不同平台的makefile .
- 任意位置生成右键自定义菜单插件context.js之API与调用
- 使用百度服务API生成二维码
- Api开发者福利:Api在线管理,模拟请求测试,文档生成利器之Apizza
- 利用ApiPost接口调试与文档生成工具,提升前、后端工作效率
- Spring Boot如何让Web API自动生成文档,并解决swagger-annotations的API注解description属性废弃的问题
- 从服务器上获取api接口数据 生成实体类并显示在listview或TextView中
- Wisdom RESTClient支持自动化测试并可以生成API文档
- 上传ipa出现的错误提示“application loader上传出错 生成的API分析文件太大”解决方法
- 使用apidoc生成restful-api文档:安装nodejs+npm+apidoc
- 生成CTP_API结构体的标准输出
- spring boot +Swagger-ui 自动生成API文档
