C#各种异常处理方式
2019-08-13 22:18
1381 查看
原文链接:https://www.geek-share.com/detail/2621361562.html
○ finally语句块是必须执行的
○ 这里的catch和finally语句块是可选的。try语句块后面可以跟1个或多个catch语句块,try语句块后面可以直接跟finally语句块。
○ Exception是所有异常的基类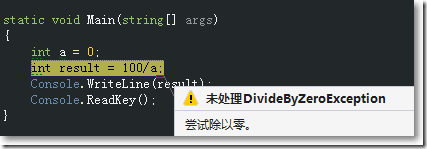



.NET的异常处理机制用来发现、处理运行时错误。如果开发人员没有提供异常的处理机制,就默认采用.NET的机制。
通常使用try...catch...finally捕获异常。
try
{//有可能发生异常
}
catch(Exception ex)
{//处理异常
}
finally
{//清理
}○ 如果没有异常发生,就直接到finally语句块中。
○ finally语句块是必须执行的
○ 这里的catch和finally语句块是可选的。try语句块后面可以跟1个或多个catch语句块,try语句块后面可以直接跟finally语句块。
○ Exception是所有异常的基类
□ 使用.NET默认异常处理机制捕获异常
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args)
{int a = 0;
int result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}

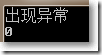
□ 使用try...catch手动捕获异常
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args)
{int a = 0;
int result = 0;
try
{result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine("这里不会执行");}
catch (DivideByZeroException exception)
{Console.WriteLine("出现异常");}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}

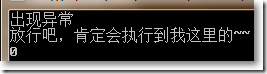
□ 使用try...catch...finally手动捕获异常
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args)
{int a = 0;
int result = 0;
try
{result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine("这里不会执行");}
catch (DivideByZeroException exception)
{Console.WriteLine("出现异常");}
finally
{Console.WriteLine("放行吧,肯定会执行到我这里的~~");}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}

可见,finally语句块中的内容一定会被执行。
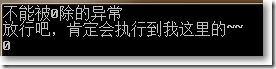
□ 使用try...多个catch...finally手动捕获异常
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args)
{int a = 0;
int result = 0;
try
{result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine("这里不会执行");}
catch (DivideByZeroException exception)
{Console.WriteLine("不能被0除的异常");}
catch (Exception ex)
{Console.WriteLine("异常");}
finally
{Console.WriteLine("放行吧,肯定会执行到我这里的~~");}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}

可见,只要有一个catch语句块捕获到异常,其它catch语句块不执行。
□ 使用try...catch(不带括号,不带参数)手动捕获异常
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args)
{int a = 0;
int result = 0;
try
{result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine("这里不会执行");}
catch
{Console.WriteLine("异常");}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}

通过以上方法,可以捕获任何异常。
□ try...catch手动捕获抛出的异常
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args)
{try
{throw new DivideByZeroException("除数不能为零");}
catch (DivideByZeroException e)
{Console.WriteLine("异常");}
Console.WriteLine("最后想说的");Console.ReadKey();
}
}

抛出异常本身并没有显示。
□ 较高层次上下文捕获较低抛出的异常
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args)
{Calculate c = new Calculate();
try
{c.Divide();
}
catch (Exception e)
{Console.WriteLine("捕获异常");}
Console.WriteLine("最后想说的");Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Calculate
{public void Divide()
{try
{int a = 0;
int result = 100/a;
}
catch (DivideByZeroException e)
{throw;
}
}
}

在Calculate内部抛出的异常,被更高层次的客户端捕获。
□ 自定义异常
class Program
{static void Main(string[] args)
{try
{throw new MyException("i am exception");}
catch (Exception e)
{Console.WriteLine("捕获到自定义异常了~~");}
Console.WriteLine("最后想说的");Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class MyException : Exception
{public MyException(string str)
{Console.WriteLine("这是我自定义的异常:" + str);}
}

总结:
○ .NET异常处理并不是标准的try...catch...finally,可以是很灵活的。
○ 尽量在较低层次抛异常,在较高层次捕获异常。
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/darrenji/p/3965443.html
相关文章推荐
- C#各种异常处理方式
- 【C#】常见的异常及异常处理方式
- 在struts应用中处理异常的各种方式
- 在C#中 IPAddresss.Parse 的异常与处理方式
- 深入剖析Java中的各种异常处理方式
- C# 阻塞方式Socket接受异常处理(不定期更新)
- .天轰穿C# -vs2010 - 03C#的异常处理之.NET中异常处理方式【原创】
- 解析C#中断言与异常的应用方式及异常处理的流程控制
- 在C#中利用Keep-Alive处理Socket网络异常断开的方法
- Head First C# 中文版 第10章 异常处理 翻译完毕 PDF下载
- JAVA编程中异常问题处理方式的区别和分析
- SpringMVC 处理异常的4种方式
- 函数参数是数组且是传址方式的处理办法(C#)
- <转载>在C#中利用Keep-Alive处理Socket网络异常断开的方法
- C# .NET编程基础-throw异常处理-Email格式检测示例
- 1.2.14、ARM的异常处理方式简单介绍
- Android各种常见异常及处理----未完成
- C#中unhandled异常处理的问题
- C#中采用HTTP方式发送并处理SOAP格式的XML数据
- (C#基础)异常处理二三事
