物联网时代 跟着Thingsboard学IOT架构-CoAP设备协议
thingsboard官网: https://thingsboard.io/
thingsboard GitHub: https://github.com/thingsboard/thingsboard
thingsboard提供的体验地址: http://demo.thingsboard.io/
BY Thingsboard team
以下内容是在原文基础上演绎的译文。除非另行注明,页面上所有内容采用知识共享-署名(CC BY 2.5 AU)协议共享。
原文地址: ThingsBoard API参考:CoAP设备API
CoAP
协议介绍
CoAP是一种在物联网世界的类web协议,它的详细规范定义在RFC 7252。COAP名字翻译来就是“受限应用协议”,顾名思义,使用在资源受限的物联网设备上。物联网设备的ram,rom都通常非常小,运行TCP和HTTP是不可以接受的。
协议特点
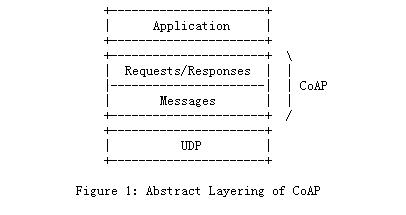
-
CoAP协议网络传输层由TCP改为UDP。
-
它基于REST,server的资源地址和互联网一样也有类似url的格式,客户端同样有POST,GET,PUT,DELETE方法来访问server,对HTTP做了简化。
-
COAP是二进制格式的,HTTP是文本格式的,COAP比HTTP更加紧凑。
-
轻量化,COAP最小长度仅仅4B,一个HTTP的头都几十个B了。
-
支持可靠传输,数据重传,块传输。 确保数据可靠到达。
-
支持IP多播, 即可以同时向多个设备发送请求。
-
非长连接通信,适用于低功耗物联网场景。
客户端库设置
安装
安装node.js,然后执行以下命令:
npm install coap-cli -g
用法
Usage: coap [command] [options] url Commands: get performs a GET request put performs a PUT request post performs a POST request delete performs a DELETE request Options: -h, --help output usage information -V, --version output the version number -o, --observe Observe the given resource -n, --no-new-line No new line at the end of the stream -p, --payload <payload> The payload for POST and PUT requests -b, --block2 <option> set the block2 size option -q, --quiet Do not print status codes of received packets -c, --non-confirmable non-confirmable -t, --timeout <seconds> The maximum send time in seconds -T, --show-timing Print request time, handy for simple performance tests -O, --coap-option <key,value> Add COAP-Option to the request (repeatable)
PUT和POST
PUT和POST请求如下例所示
echo -n 'hello world' | coap post coap://localhost/message
Thingsboard的CoAP传输协议架构
因为Thingsboard最新release,是基于微服务架构,不利用单独理解代码。
Thingsboard CoAP设备传输协议源代码:https://github.com/thingsboard/thingsboard/tree/release-2.0/transport/coap
本文基于上面源代码后,剔除相关的安全验证和处理之后搭建简易的讲解项目:
https://github.com/sanshengshui/IOT-Technical-Guide/tree/master/IOT-Guide-Coap
CoAP框架
Thingsboard的CoAP设备传输协议是基于Californium。Californium 是一款基于Java实现的Coap技术框架,该项目实现了Coap协议的各种请求响应定义,支持CON/NON不同的可靠性传输模式。 Californium 基于分层设计且高度可扩展,其内部模块设计及接口定义存在许多学习之处;
值得一提的是,在同类型的 Coap技术实现中,Californium的性能表现是比较突出的,如下图:
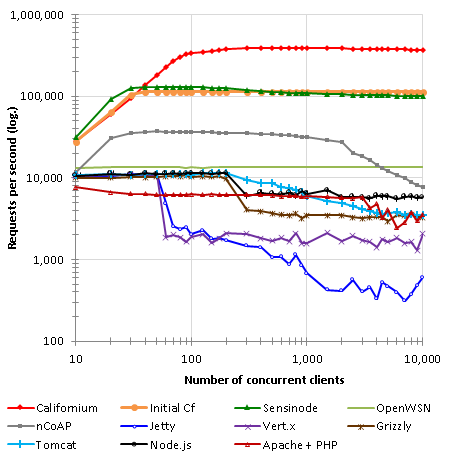
更多的数据可以参考Californium-可扩展云服务白皮书 本文以框架的源码分析为主,其他内容不做展开。
项目结构
. └── main └── java ├── com │ └── sanshengshui │ └── coap │ ├── adaptors │ │ └── JsonCoapAdaptor.java │ ├── CoapTransportResource.java │ ├── common │ │ └── FeatureType.java │ └── session │ └── SessionMsgType.java └── IOTCoapServer.java
代码讲解
IOTCoapServer
public class IOTCoapServer {
private static final String V1 = "v1";
private static final String API = "api";
private static String host = "127.0.0.1";
private static Integer port = 5683;
private static long timeout = 10000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
CoapServer coapServer = new CoapServer();
CoapResource api = new CoapResource(API);
api.add(new CoapTransportResource(V1,timeout));
coapServer.add(api);
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getByName(host);
InetSocketAddress sockAddr = new InetSocketAddress(addr, port);
coapServer.addEndpoint(new CoapEndpoint(sockAddr));
coapServer.start();
}
}
-
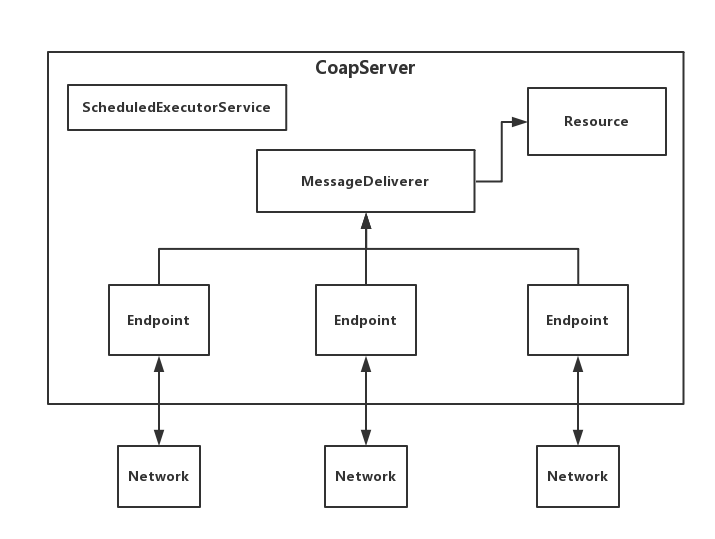
第12行代码:
CoapServer
用作创建服务端。 -
第12-15行:
CoapResource
是resource
的基本实现,扩展这个类来编写您自己的资源。通过向资源添加“v1”、"api"和超时时间的设置,则coap的基础url为:coap://localhost:port/api/v1/
。 -
第16-18行: Endpoint负责与网络进行通信, 如果没有一个Endpoint与CoapServer进行绑定,那就创建一个默认的Endpoint,默认就是ucp实现传输层。
-
第19行,启动CoAP服务。
以下图片展示服务端的基础架构:
CoapTransportResource
此类负责处理请求
GET
@Override
public void handleGET(CoapExchange exchange) {
Optional<FeatureType> featureType = getFeatureType(exchange.advanced().getRequest());
if (!featureType.isPresent()) {
} else if (featureType.get() == FeatureType.TELEMETRY) {
exchange.respond(CoAP.ResponseCode.BAD_REQUEST);
} else if (featureType.get() == FeatureType.ATTRIBUTES) {
processRequest(exchange, SessionMsgType.GET_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST);
} else {
exchange.respond(CoAP.ResponseCode.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}
-
如果我们客户端发起的是GET请求,那么将会进入到
handleGET(CoapExchange exchange)
方法。 -
getFeatureType(Request request)
判断coap协议长度是否大于3。当大于等于3,获取/api/v1/${param}的param元素。
public static final int FEATURE_TYPE_POSITION = 3;
private Optional<FeatureType> getFeatureType(Request request) {
List<String> uriPath = request.getOptions().getUriPath();
try {
if (uriPath.size() >= FEATURE_TYPE_POSITION) {
return Optional.of(FeatureType.valueOf(uriPath.get(FEATURE_TYPE_POSITION - 1).toUpperCase()));
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
}
return Optional.empty();
}
-
通过判断param是否是temperature还是attributes进行相关的逻辑操作。
-
当不是上述类型,回复状态为
BAD_REQUEST
的状态码。
POST
@Override
public void handlePOST(CoapExchange exchange) {
Optional<FeatureType> featureType = getFeatureType(exchange.advanced().getRequest());
if (!featureType.isPresent()) {
exchange.respond(CoAP.ResponseCode.BAD_REQUEST);
} else {
switch (featureType.get()) {
case ATTRIBUTES:
processRequest(exchange, SessionMsgType.POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST);
break;
case TELEMETRY:
processRequest(exchange, SessionMsgType.POST_TELEMETRY_REQUEST);
break;
}
}
}
-
如果我们客户端发起的是POST请求,那么将会进入到
handlePOST(CoapExchange exchange)
方法。 -
对获取的uri的类型是temperature还是attributes来做相关的逻辑操作。
逻辑处理
private void processRequest(CoapExchange exchange, SessionMsgType type) {
exchange.accept();
Exchange advanced = exchange.advanced();
Request request = advanced.getRequest();
try {
switch (type) {
case GET_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST:
case POST_TELEMETRY_REQUEST:
case POST_ATTRIBUTES_REQUEST:
//这个类在之前的物模型博文中有所讲解,大家可以翻看!
JsonCoapAdaptor.convertToMsg(type,request);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported msg type: " + type);
}
exchange.respond("Data has been received");
} catch (AdaptorException e){
exchange.respond(CoAP.ResponseCode.BAD_REQUEST, e.getMessage());
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
exchange.respond(CoAP.ResponseCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e.getMessage());
}
}
项目演示
遥测上传API
要将遥测数据发布到服务器节点,请将POST请求发送到以下URL:
coap://host/api/v1/telemetry
最简单的支持数据格式是:
{"key1":"value1", "key2":"value2"}
要么
[{"key1":"value1"}, {"key2":"value2"}]
请注意,在这种情况下,服务器端时间戳将分配给上传的数据!
如果您的设备能够获取客户端时间戳,您可以使用以下格式:
{"ts":1451649600512, "values":{"key1":"value1", "key2":"value2"}}
在上面的示例中,我们假设“1451649600512”是具有毫秒精度的unix时间戳。例如,值'1451649600512'对应于'Fri,2016年1月1日12:00:00.512 GMT'
例子:
echo -n '{"size":21,"type":"device"}' | coap post coap://demo.thingsboard.io/api/v1/telemetry
结果:
key= 1564105084015 属性名=size 属性值=21 属性名=type 属性值=device
属性API
属性API允许设备
-
将客户端设备属性上载到服务器。
-
从服务器请求客户端和共享设备属性。
将属性更新发布到服务器
要将客户端设备属性发布到ThingsBoard服务器节点,请将POST请求发送到以下URL:
coap://host/api/v1/attributes
例子:
echo -n '{"size":21,"type":"device","status":true}' | coap post coap://localhost:5683/api/v1/attributes
结果:
key= 1564105158573 属性名=size 属性值=21 属性名=type 属性值=device 属性名=status 属性值=true
从服务器请求属性值
要向ThingsBoard服务器节点请求客户端或共享设备属性,请将GET请求发送到以下URL:
coap://host/api/v1/attributes?clientKeys=attribute1,attribute2&sharedKeys=shared1,shared2
例子:
coap get coap://localhost:5683/api/v1/attributes?clientKeys=attribute1,attribute2&sharedKeys=shared1,shared2
结果:
(2.05) Data has been received
到此,物联网时代,相信大家对IOT架构下的CoAP协议有所了解了,感谢大家的阅读!
- 物联网时代-跟着Thingsboard学IOT架构-MQTT设备协议
- 边缘计算在物联网(IoT)当中的运用「物联网架构探索系列」
- IoTSeeker:物联网设备默认密码扫描检测工具
- 物联网架构及五大通信协议
- 物联网设备网关系统架构设计
- 阿里云新推出 HiTSDB + IoT套件 物联网设备上云步入快车道
- 【物联网】IoT与智能时代
- 无线物联网中CoAP协议的研究与实现【转】
- 阿里云新推出 HiTSDB + IoT套件 物联网设备上云步入快车道
- 阿里云新推出 HiTSDB + IoT套件 物联网设备上云步入快车道
- 物联网协议比较 MQTT CoAP RESTful/HTTP XMPP
- 支付宝小程序-MQTT模器,IoT设备通过WSS接入阿里云IoT物联网平台
- MQTT协议与阿里云IoT物联网平台
- 物联网架构分析之一:传输协议选择
- 《连载 | 物联网框架ServerSuperIO教程》-4.如开发一套设备驱动,同时支持串口和网络通讯。附:将来支持Windows 10 IOT
- 阿里云物联网 .NET Core 客户端 | CZGL.AliIoTClient:4. 设备上报属性
- 阿里云新推出 HiTSDB + IoT套件 物联网设备上云步入快车道
- 物联网安全研究之一:IoT架构介绍
- 开源物联网框架ServerSuperIO 3.0正式发布(C#),跨平台:Win&Win10 Iot&Ubuntu&Ubuntu Mate,一套设备驱动跨平台挂载,附:开发套件和教程。
