Java算法之串的简单处理
2019-03-31 21:36
253 查看
题目如下:
串的处理
在实际的开发工作中,对字符串的处理是最常见的编程任务。
本题目即是要求程序对用户输入的串进行处理。具体规则如下:
1. 把每个单词的首字母变为大写。
2. 把数字与字母之间用下划线字符(_)分开,使得更清晰
3. 把单词中间有多个空格的调整为1个空格。
例如:
用户输入:
you and me what cpp2005program
则程序输出:
You And Me What Cpp_2005_program
用户输入:
this is a 99cat
则程序输出:
This Is A 99_cat
我们假设:用户输入的串中只有小写字母,空格和数字,不含其它的字母或符号。
每个单词间由1个或多个空格分隔。
假设用户输入的串长度不超过200个字符。
方法一:
public class 串的简单处理 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String string = scanner.nextLine();
Vector<Character> vector = new Vector<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < string.length(); i++) {
vector.add(string.charAt(i));
}
try {
int index = 0;
while (index < vector.size()) {
//判断第一个是否为小写的英文字符,是的话进行操作
if (index == 0 && vector.elementAt(index) >= 'a'
&& vector.elementAt(index) <= 'z') {
//Replaces the element at the specified position in this Vector with the specified element
vector.set(index,(char) (vector.elementAt(index) - ('a' - 'A')));
} else if (vector.elementAt(index - 1) == ' '&& vector.elementAt(index) == ' ') {
//处理有多个空格的可能
vector.remove(index);
index--;
} else if (vector.elementAt(index - 1) == ' '
&& (vector.elementAt(index) >= 'a' && vector
.elementAt(index) <= 'z')) {
//判断是空格后边的字符
vector.set(index,
(char) (vector.elementAt(index) - ('a' - 'A')));
} else if ((vector.elementAt(index) >= 'a' && vector
.elementAt(index) <= 'z')
&& (vector.elementAt(index - 1) >= '0' && vector
.elementAt(index - 1) <= '9')) {
vector.add(index, '_');
index++;
} else if ((vector.elementAt(index - 1) >= 'a' && vector
.elementAt(index - 1) <= 'z')
&& (vector.elementAt(index) >= '0' && vector
.elementAt(index) <= '9')) {
//判断的是数字
vector.add(index, '_');
index++;
}
index++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vector.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(vector.elementAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
}
}
}
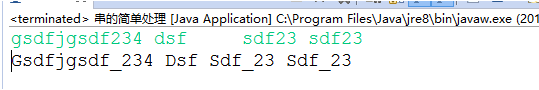
方法二:主要用到正则表达式对字符串进行截取,然后对每一个字符数组的元素进行正则匹配,含有数字的单独进行处理
public class SimpleString {
// 打印字符串的函数
public static void print(String[] s) {
for (int i = 0; i < s.length - 1; i++) {
System.out.print(s[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(s[s.length - 1]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = scan.nextLine();
String[] ss = s.split("[\\s]+"); // 根据正则表达式,删除一个或多个空格,将字符串保存为字符数组
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
// 将每一个字符数组的首字母改为大写
String up = ("" + ss[i].charAt(0)).toUpperCase(); // 大写
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(ss[i]);
ss[i] = sb.replace(0, 1, up).toString();
// 上边已经把字符串数组的首字母该为大写,然后对更改后的字符数组判断是否有数字
Matcher m = Pattern.compile("\\d+").matcher(ss[i]);// 0-9出现一次或多次
while (m.find()) {
// m.group():Returns the input subsequence matched by the previous match
String num = new String(m.group());
String num2 = num;
num2 = "_" + num + "_"; // 数字前后都添加"_"
ss[i] = ss[i].replace(num, num2);
if (ss[i].startsWith("_")) { // 去头"_"
ss[i] = ss[i].substring(1);
}
if (ss[i].endsWith("_")) { // 去尾"_"
ss[i] = ss[i].substring(0, ss[i].length() - 1);
}
}
}
print(ss);
}
}
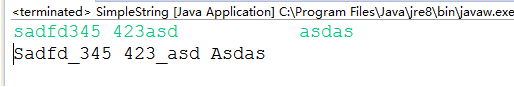
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对脚本之家的支持。如果你想了解更多相关内容请查看下面相关链接
您可能感兴趣的文章:
相关文章推荐
- Java算法--串的简单处理
- Java算法--串的简单处理
- 【ACM-Steps1.2】简单字符串处理、简单数学题、进制转换系列8题(一)
- 简单缓存处理---UDT
- nyoj 218 Dinner【简单字符串处理】
- 图形处理(三)简单拉普拉斯网格变形-Siggraph 2004
- AOP注解日志处理简单理解
- 多点触摸简单手势处理方法
- 几个简单的数据点平滑处理算法
- 串的简单处理
- redis事务处理抢购简单代码(已验证)
- Android实验二简单事件处理
- Java中的异常处理机制的简单原理和应用。
- Linux简单处理CC攻击shell脚本
- C#读取摄像头并对图像做简单处理--AVICap32篇
- spark on hdfs spark处理hdfs上的文件简单的wordcount
- Java 简单高效处理字符串-删除所有标点,正则表达式
- JS对小数的简单处理
- 处理PHP字符串的10个简单方法
