Vue.js——快速入门Vuex
2019-02-14 20:08
288 查看
一. 什么是Vuex?

Vuex是一个专门为Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式, 它采用集中式存储管理所有组件的公共状态, 并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化.
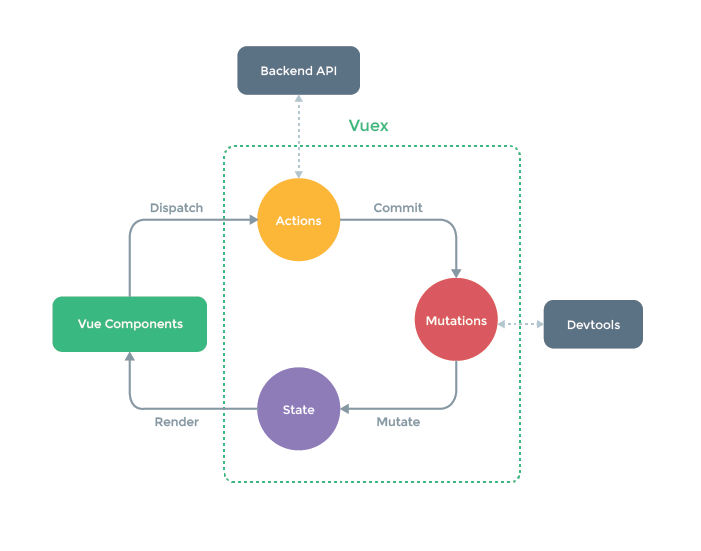
上图中绿色虚线包裹起来的部分就是Vuex的核心,
state中保存的就是公共状态, 改变
state的唯一方式就是通过
mutations进行更改. 可能你现在看这张图有点不明白, 等经过本文的解释和案例演示, 再回来看这张图, 相信你会有更好的理解.
二. 为什么要使用Vuex?
试想这样的场景, 比如一个Vue的根实例下面有一个根组件名为App.vue, 它下面有两个子组件
A.vue和
B.vue,
App.vue想要与
A.vue或者
B.vue通讯可以通过props传值的方式, 但是如果
A.vue和
B.vue之间的通讯就很麻烦了, 他们需要共有的父组件通过自定义事件进行实现, A组件想要和B组件通讯往往是这样的:
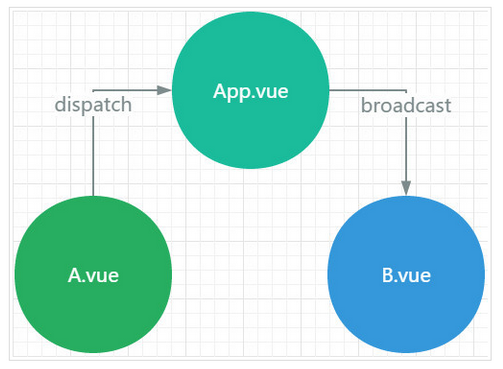
- A组件说: "报告老大, 能否帮我托个信给小弟B" => dispatch一个事件给App
- App老大说: "包在我身上, 它需要监听A组件的dispatch的时间, 同时需要broadcast一个事件给B组件"
- B小弟说: "信息已收到", 它需要on监听App组件分发的事件
这只是一条通讯路径, 如果父组件下有多个子组件, 子组件之间通讯的路径就会变的很繁琐, 父组件需要监听大量的事件, 还需要负责分发给不同的子组件, 很显然这并不是我们想要的组件化的开发体验.
Vuex就是为了解决这一问题出现的三.如何引入Vuex?
- 下载
vuex
:npm install vuex --save
- 在
main.js
添加:
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use( Vuex );
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//待添加
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
四. Vuex的核心概念?
在介绍Vuex的核心概念之前, 我使用vue-cli初始化了一个demo, 准备以代码的形式来说明Vuex的核心概念.这个demo分别有两个组件
ProductListOne.vue和
ProductListTwo.vue, 在
App.vue的
datat中保存着共有的商品列表, 代码和初始化的效果如下图所示:
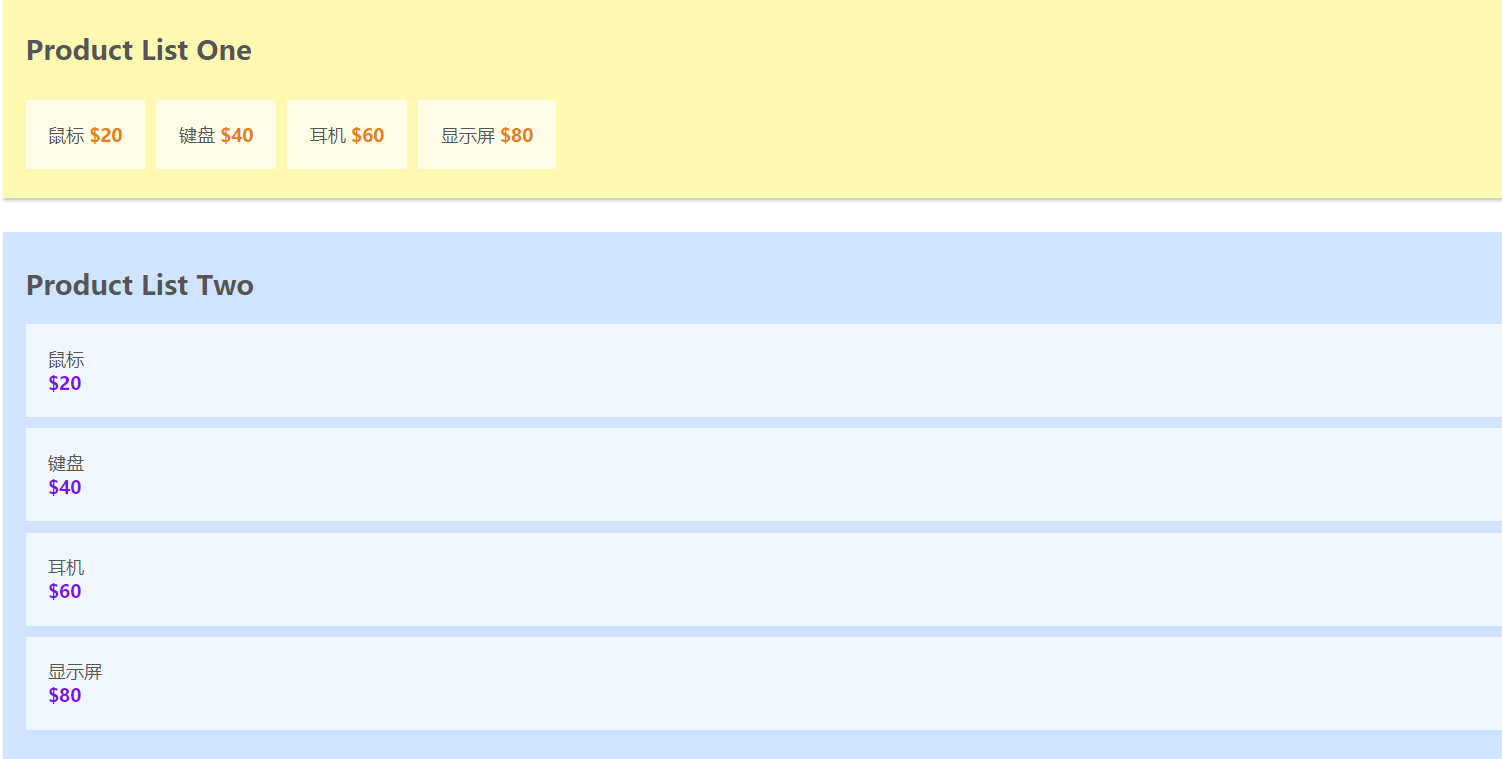
//App.vue中的初始化代码
<template>
<div id="app">
<product-list-one v-bind:products="products"></product-list-one>
<product-list-two v-bind:products="products"></product-list-two>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ProductListOne from './components/ProductListOne.vue'
import ProductListTwo from './components/ProductListTwo.vue'
export default {
name: 'app',
components: {
'product-list-one': ProductListOne,
'product-list-two': ProductListTwo
},
data () {
return {
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
body{
font-family: Ubuntu;
color: #555;
}
</style>
//ProductListOne.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-one">
<h2>Product List One</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['products'],
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#product-list-one{
background: #FFF8B1;
box-shadow: 1px 2px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
margin-bottom: 30px;
padding: 10px 20px;
}
#product-list-one ul{
padding: 0;
}
#product-list-one li{
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 10px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 20px;
background: rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
.price{
font-weight: bold;
color: #E8800C;
}
</style>
//ProductListTwo.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['products'],
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#product-list-two{
background: #D1E4FF;
box-shadow: 1px 2px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
margin-bottom: 30px;
padding: 10px 20px;
}
#product-list-two ul{
padding: 0;
list-style-type: none;
}
#product-list-two li{
margin-right: 10px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 20px;
background: rgba(255,255,255,0.7);
}
.price{
font-weight: bold;
color: #860CE8;
display: block;
}
</style>
核心概念1: State
state就是Vuex中的公共的状态, 我是将
state看作是所有组件的
data, 用于保存所有组件的公共数据.
- 此时我们就可以把
App.vue
中的两个组件共同使用的data抽离出来, 放到state
中,代码如下:
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use( Vuex )
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
}
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
- 此时,
ProductListOne.vue
和ProductListTwo.vue
也需要做相应的更改
//ProductListOne.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products : this.$store.state.products //获取store中state的数据
}
}
}
//ProductListTwo.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products //获取store中state的数据
}
}
}
此时的页面如下图所示, 可以看到, 将公共数据抽离出来后, 页面没有发生变化.
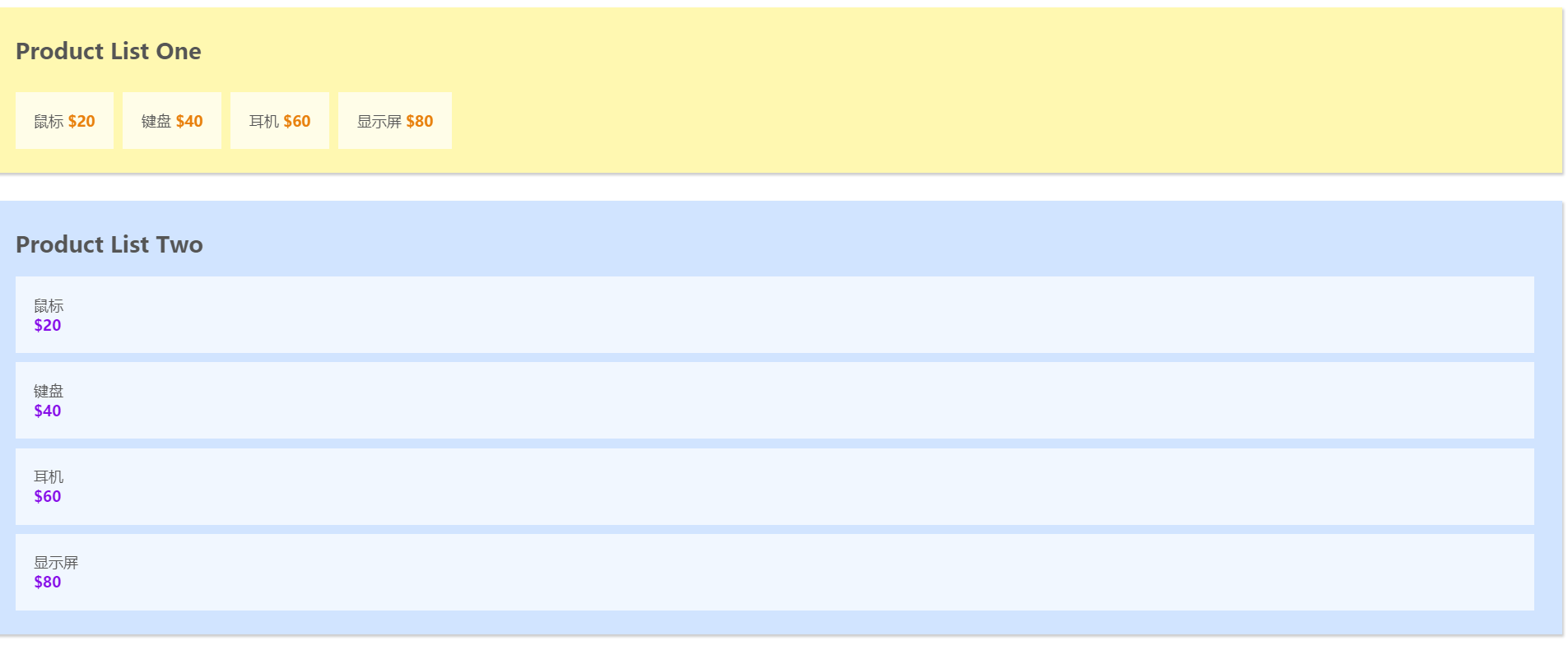
核心概念2: Getters
我将
getters属性理解为所有组件的
computed属性, 也就是计算属性. vuex的官方文档也是说到可以将getter理解为store的计算属性, getters的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
- 此时,我们可以在
main.js
中添加一个getters
属性, 其中的saleProducts
对象将state
中的价格减少一半(除以2)
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{ //添加getters
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
}
})
- 将
productListOne.vue
中的products
的值更换为this.$store.getters.saleProducts
export default {
data () {
return {
products : this.$store.getters.saleProducts
}
}
}
- 现在的页面中,Product List One中的每项商品的价格都减少了一半

核心概念3: Mutations
我将
mutaions理解为
store中的
methods,
mutations对象中保存着更改数据的回调函数,该函数名官方规定叫
type, 第一个参数是
state, 第二参数是
payload, 也就是自定义的参数.
- 下面,我们在
main.js
中添加mutations
属性,其中minusPrice
这个回调函数用于将商品的价格减少payload
这么多, 代码如下:
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
},
mutations:{ //添加mutations
minusPrice (state, payload ) {
let newPrice = state.products.forEach( product => {
product.price -= payload
})
}
}
})
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue
中添加一个按钮,为其添加一个点击事件, 给点击事件触发minusPrice
方法
//ProductListTwo.vue
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
<button @click="minusPrice">减少价格</button> //添加按钮
</ul>
</div>
</template>
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue
中注册minusPrice
方法, 在该方法中commitmutations
中的minusPrice
这个回调函数
注意:调用mutaions中回调函数, 只能使用store.commit(type, payload)
//ProductListTwo.vue
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products
}
},
methods: {
minusPrice() {
this.$store.commit('minusPrice', 2); //提交`minusPrice,payload为2
}
}
}
添加按钮, 可以发现, Product List Two中的价格减少了2, 当然你可以自定义
payload,以此自定义减少对应的价格.

(Product List One中的价格没有发生变化, 是因为
getters将价格进行了缓存)
核心概念4: Actions
actions类似于
mutations,不同在于:
-
actions
提交的是mutations
而不是直接变更状态 -
actions
中可以包含异步操作,mutations
中绝对不允许出现异步 -
actions
中的回调函数的第一个参数是context
, 是一个与store
实例具有相同属性和方法的对象 -
此时,我们在
store
中添加actions
属性, 其中minusPriceAsync
采用setTimeout
来模拟异步操作,延迟2s执行 该方法用于异步改变我们刚才在mutaions
中定义的minusPrice
//main.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
products: [
{name: '鼠标', price: 20},
{name: '键盘', price: 40},
{name: '耳机', price: 60},
{name: '显示屏', price: 80}
]
},
getters:{
saleProducts: (state) => {
let saleProducts = state.products.map( product => {
return {
name: product.name,
price: product.price / 2
}
})
return saleProducts;
}
},
mutations:{
minusPrice (state, payload ) {
let newPrice = state.products.forEach( product => {
product.price -= payload
})
}
},
actions:{ //添加actions
minusPriceAsync( context, payload ) {
setTimeout( () => {
context.commit( 'minusPrice', payload ); //context提交
}, 2000)
}
}
})
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue
中添加一个按钮,为其添加一个点击事件, 给点击事件触发minusPriceAsync
方法
<template>
<div id="product-list-two">
<h2>Product List Two</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="product in products">
<span class="name">{{ product.name }}</span>
<span class="price">${{ product.price }}</span>
</li>
<button @click="minusPrice">减少价格</button>
<button @click="minusPriceAsync">异步减少价格</button> //添加按钮
</ul>
</div>
</template>
- 在
ProductListTwo.vue
中注册minusPriceAsync
方法, 在该方法中dispatchactions
中的minusPriceAsync
这个回调函数
export default {
data () {
return {
products: this.$store.state.products
}
},
methods: {
minusPrice() {
this.$store.commit('minusPrice', 2);
},
minusPriceAsync() {
this.$store.dispatch('minusPriceAsync', 5); //分发actions中的minusPriceAsync这个异步函数
}
}
}
添加按钮, 可以发现, Product List Two中的价格延迟2s后减少了5

核心概念5: Modules
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
相关文章推荐
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
- Vue.js—快速入门及实现用户信息的增删
- 转: Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门(上篇)
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门(转载)
- Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门(上篇)
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
- Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门(上篇)
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
- Vue.js快速入门示例
- vue.js快速入门
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
- Vue.js——vue-router 60分钟快速入门
- 第二节、简易安装 和 快速入门Vue.js
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
- Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门(上篇)
- Vue.js入门—快速搭建环境
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
- Vue.js——60分钟快速入门
