十五、Spring cloud 消息总线(Bus)
2018-11-29 21:51
766 查看
一、回顾 Spring 事件/监听器
- Spring 事件 ApplicationEvent
-
ApplicationListener/@EventListener
-
ApplicationEventPublisher
Demo:
/**
* Spring 事件/监听器 Demo
* @author 咸鱼
* @date 2018/11/29 18:58
*/
public class SpringEventDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建 Annotation 驱动 Spring 应用上下文
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
//注册 EventConfiguration 到 Spring 应用上下文
context.register(EventConfiguration.class);
//启动 Spring 应用上下文
context.refresh();
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 是 ApplicationEventPublisher 的一种具体实现
ApplicationEventPublisher publisher = context;
//发布一个
publisher.publishEvent(new MyApplicationEvent("hello java"));
}
/**
* 自定义事件
*/
private static class MyApplicationEvent extends ApplicationEvent{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5938169569156916456L;
public MyApplicationEvent(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
/**
* 监听事件
*/
@Configuration
public static class EventConfiguration{
/**
* 监听 {@link MyApplicationEvent}
* @param event
*/
@EventListener
public void onEvent(MyApplicationEvent event){
System.out.println("监听到事件:" + event);
}
}
}
二、Spring Cloud Bus
(一)使用场景
用于广播应用状态变更到分布式系统中的各个关联的节点。应用节点不直接相互通讯,而通过消息总线来实现通知。
简单点说:比如有一个
配置服务器,有多个
配置客户端。以前没用消息总线之前,一旦
配置服务器的配置项发生改变,那么需要由每个
配置客户端调用 POST请求
/actuator/refresh才能刷新本地配置项。这样带来的问题是,一旦系统越来越大,那么若要改变配置项,则需要大量的
配置客户端手动刷新本地配置项。而引入了
消息总线以后,则由
消息总线来通知各个客户端配置项发生改变了,并触发刷新本地配置项操作。
(二)架构:
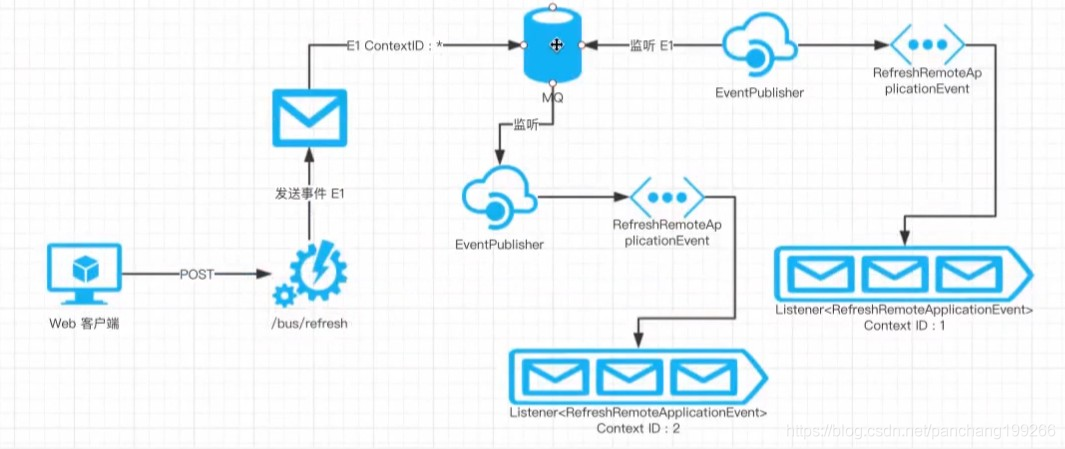
架构解析:
客户端发送
POST请求 /actuator/bus-refresh/${contextId}:*,消息总线会根据请求生成一个事件(E1),并将该事件发送给消息中间件(比如 Kafka)。此时会有两种情况:单点传播 和 集群传播。这主要适用于同样的应用会有多个同样的实例(这些实例靠端口进行区分,但 serviceId 都是一样的)。单点传播就是只向其中的一个实例传播,集群传播向所有的实例传播。在消息中间件在接收消息时,所有的应用同时也在监听这些事件(比如 E1)。在监听到 E1 事件以后,根据上面的规则,消息总线会将 E1 事件包装成不同类型的内部事件(比如
RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent)。然后让目的应用的 EventPublisher 将包装后的事件发布给事件监听器队列,等待下一步的处理。
暂时这么理解,后续如果不对,再进行改正。
(三)默认实现
- AMQP(Rabbit MQ)
- Kafka
现阶段,Spring Cloud Bus 只支持 AMQP(Rabbit MQ) 和 Kafka两个消息中间件。
三、案例(使用 Kafka)
激活总线:
AMQP:spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp
Kafka:spring-cloud-starter-bus-kafka
spring-cloud-bus
改造 user-service-client:使用 Kafka 整合 Spring Cloud Bus
(一)增加依赖
<!-- 整合 Spring Cloud Bus:Kafka --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-kafka</artifactId> </dependency>
(二)总线事件传播
1、事件传播类型
- 单点传播
Endpoint:
/actuator/bus-refresh/${applicationContextId}:*(POST请求) - 案例:
localhost:8080/actuator/bus-refresh/user-service-client:8080
-
Endpoint:
/actuator/bus-refresh/${applicationContextId}:**(POST请求)localhost:8080/actuator/bus-refresh/user-service-client:**
备注1:
${applicationContextId}:*一般是serviceId:port,而serviceId就是在application.properties中配置的spring.application.name=user-service-client属性。
备注2:消息总线提供的端点
/actuator/bus-refresh/${applicationContextId}:*和 Actuator 自带的端点/actuator/refresh作用是相同的,都是刷新配置项,区别主要在于:
/actuator/refresh:刷新本地配置项
/actuator/bus-refresh/${applicationContextId}:*:刷新远程应用配置项
问题:如何定位 Application Context ID?
通过访问
/actuator/beans确认当前 Application Context ID(PS:2.0版本的找不着。。。)
2、事件传播监听器
(1)通过日志可知 单点传播/集群传播 监听器均为
org.springframework.cloud.bus.event.RefreshListener:
public class RefreshListener
implements ApplicationListener<RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent> {
private static Log log = LogFactory.getLog(RefreshListener.class);
private ContextRefresher contextRefresher;
public RefreshListener(ContextRefresher contextRefresher) {
this.contextRefresher = contextRefresher;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent event) {
Set<String> keys = contextRefresher.refresh();
log.info("Received remote refresh request. Keys refreshed " + keys);
}
}
RefreshListener监听事件
RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent
(2)自定义
RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent事件监听器,监听
总线事件传播。
/**
* @author 咸鱼
* @date 2018/11/29 20:44
*/
@Configuration
public class BusConfiguration {
@EventListener
public void onRefreshRemoteApplicationEvent(RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent event){
System.out.printf("Source : %s , originService : %s, destinationService : %s\n",
event.getSource(), event.getOriginService(), event.getDestinationService());
}
}
(三)总线事件跟踪
1、端点:
/trace
默认事件跟踪功能是失效的,需要通过配置项激活:
spring.cloud.bus.trace.enabled=true
2、总线内部事件
EnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent
RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent
AckRemoteApplicationEvent
EnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent:应用环境变量(env)改变触发该事件,比如执行:POST请求/actuator/bus-env
RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent:刷新配置项,触发该事件,比如执行:POST请求/actuator/bus-refresh
3、自定义事件监听器
我们可以自定义监听器,来监听这两个事件的发生,可以相应的做一些处理,比如:
@Configuration
public class BusConfiguration {
/**
* 监听 RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent 事件
* POST请求 `/actuator/bus-env` 触发
*/
@EventListener
public void onRefreshRemoteApplicationEvent(RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent event){
System.out.printf("RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent - Source : %s , originService : %s, destinationService : %s\n",
event.getSource(), event.getOriginService(), event.getDestinationService());
}
/**
* 监听 EnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent 事件
* POST请求 `/actuator/bus-refresh` 触发
*/
@EventListener
public void onEnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent(EnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent event){
System.out.printf("EnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent - Source : %s , originService : %s, destinationService : %s\n",
event.getSource(), event.getOriginService(), event.getDestinationService());
}
}
(四)自定义事件
- 事件扩展 RemoteApplicationEvent
-
@RemoteApplicationEventScan
1、扩展
RemoteApplicationEvent
/**
* 自定义事件 {@link RemoteApplicationEvent}
* @author 咸鱼
* @date 2018/12/1 10:11
*/
public class UserRemoteApplicationEvent extends RemoteApplicationEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1624266233141574546L;
/**
* 这个默认构造函数必须有,否则无法将 originService 传递到 目标应用中
*/
private UserRemoteApplicationEvent() {
}
public UserRemoteApplicationEvent(User user, String originService,
String destinationService) {
super(user, originService, destinationService);
}
}
2、添加 @RemoteApplicationEventScan
/**
* 注解 @RemoteApplicationEventScan(basePackageClasses = UserRemoteApplicationEvent.class):
* 扫面自定义事件
*/
@RemoteApplicationEventScan(basePackageClasses = UserRemoteApplicationEvent.class)
@Configuration
public class BusConfiguration {
/**
* 监听自定义的 UserRemoteApplicationEvent 事件
*/
@EventListener
public void onUserRemoteApplicationEvent(UserRemoteApplicationEvent event){
System.out.printf("UserRemoteApplicationEvent - Source : %s , originService : %s, destinationService : %s\n",
event.getSource(), event.getOriginService(), event.getDestinationService());
}}
3、发布
RemoteApplicationEvent
/**
* Bus 事件 Controller
* @author 咸鱼
* @date 2018/12/1 10:09
*/
@RestController
public class BusApplicationEventController implements ApplicationContextAware,ApplicationEventPublisherAware{
/**
* 事件发布器(通过实现 ApplicationEventPublisherAware 实现自动装载)
* 补充: AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 是 ApplicationEventPublisher 的一种具体实现
*/
private ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
/**
* 应用上下文(通过实现 ApplicationContextAware 实现自动装载)
*/
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
this.eventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
/**
* 问题:为什么这里发布的的自定义事件,可以被框架监听到?
* 因为在 BusAutoConfiguration#acceptLocal() 中,注册了下面的监听器:
@EventListener(classes = RemoteApplicationEvent.class)
public void acceptLocal(RemoteApplicationEvent event) {
if (this.serviceMatcher.isFromSelf(event)&& !(event instanceof AckRemoteApplicationEvent)) {
this.cloudBusOutboundChannel.send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(event).build());
}
}
* 而我们自定义的事件 UserRemoteApplicationEvent 是 RemoteApplicationEvent 的子类,所以我们在
* 发布自定义事件以后,可以被框架监听到。
*/
@PostMapping("/bus/event/publish/user")
public boolean publishUserEvent(@RequestBody User user,
@RequestParam(value = "destination", required = false) String destination) {
//获取应用id
String serviceInstanceId = applicationContext.getId();
//新建 自定义事件 对象
UserRemoteApplicationEvent event = new UserRemoteApplicationEvent(user, serviceInstanceId, destination);
//发布事件
eventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
return true;
}
}
4、监听
RemoteApplicationEvent
/**
* 监听自定义的 UserRemoteApplicationEvent 事件
*/
@EventListener
public void onUserRemoteApplicationEvent(UserRemoteApplicationEvent event){
System.out.printf("UserRemoteApplicationEvent - Source : %s , originService : %s, destinationService : %s\n",
event.getSource(), event.getOriginService(), event.getDestinationService());
}
四、源码分析
(一)BusAutoConfiguration
1、监听
Spring Event(本地事件)
@EventListener(classes = RemoteApplicationEvent.class)
public void acceptLocal(RemoteApplicationEvent event) {
if (this.serviceMatcher.isFromSelf(event)&& !(event instanceof AckRemoteApplicationEvent)) {
this.cloudBusOutboundChannel.send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(event).build());
}
}
由于
@EventListener监听
Spring Event,所以事件
RemoteApplicationEvent属于本地事件,因必然有发布该事件的源头。
2、监听 Stream 事件(远程事件)
@StreamListener(SpringCloudBusClient.INPUT)
public void acceptRemote(RemoteApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof AckRemoteApplicationEvent) {
if (this.bus.getTrace().isEnabled() && !this.serviceMatcher.isFromSelf(event)&& this.applicationEventPublisher != null) {
this.applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
}
// If it's an ACK we are finished processing at this point
return;
}
if (this.serviceMatcher.isForSelf(event)&& this.applicationEventPublisher != null) {
if (!this.serviceMatcher.isFromSelf(event)) {
this.applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
}
if (this.bus.getAck().isEnabled()) {
AckRemoteApplicationEvent ack = new AckRemoteApplicationEvent(this,
this.serviceMatcher.getServiceId(),
this.bus.getAck().getDestinationService(),
event.getDestinationService(), event.getId(), event.getClass());
this.cloudBusOutboundChannel
.send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(ack).build());
this.applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(ack);
}
}
if (this.bus.getTrace().isEnabled() && this.applicationEventPublisher != null) {
// We are set to register sent events so publish it for local consumption,
// irrespective of the origin
this.applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new SentApplicationEvent(this,
event.getOriginService(), event.getDestinationService(),
event.getId(), event.getClass()));
}
}
acceptRemote() 监听 Stream 事件,同时发送 Spring Event(本地事件)
ServiceMatcher#isForSelf()用于匹配
RemoteApplicationEvent是否为当前应用实例而来。
this.serviceMatcher.isForSelf(event)
ServiceMatcher#isFromSelf()用于判断当前事件是否为自己发送。
this.serviceMatcher.isFromSelf(event)
3、整体流程
假设
user-service-client:8080执行
/actuator/bus-refresh端口,发送一个
RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent事件:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/bus-refresh/user-service-client:8080
- user-service-client:8080:Bus事件的发布者、监听者
- user-service-client:8081:Bus事件的监听者
- user-service-client:8080:Bus事件的监听者
当 Stream Binder 接收到发布者
RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent事件,广播该事件到所有的监听者:
user-service-client:8080
:判断事件不是为自己发送,发布SentApplicationEvent
事件(主要发布到/trace
中)user-service-client:8081
:判断事件不是为自己发送,发布SentApplicationEvent
事件(主要发布到/trace
中)user-service-client:8082
:判断事件是为自己发送,执行RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent
事件监听。如果ack
激活的(默认激活),cloudBusOutboundChannel
会发送AckRemoteApplicationEvent
到管道里。可以由以下代码监听:
/**
* 监听 AckRemoteApplicationEvent 事件
*/
@StreamListener(SpringCloudBusClient.OUTPUT)
public void onAckRemoteApplicationEvent(AckRemoteApplicationEvent event) {
System.out.printf("AckRemoteApplicationEvent - Source : %s , originService : %s, destinationService : %s\n",
event.getSource(), event.getOriginService(), event.getDestinationService());
}
相关文章推荐
- 一起来学SpringCloud之 - 消息总线(Bus)
- SpringCloud 教程 (一) 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 史上最简单的SpringCloud教程 | 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- SpringCloud入门教学|第七篇:消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 史上最简单的SpringCloud教程 | 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 史上最简单的SpringCloud教程 | 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 史上最简单的SpringCloud教程 | 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- SpringCloud之消息总线Spring Cloud Bus实例代码
- SpringCloud微服务云架构构建B2B2C电子商务平台之-(八)消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- Spring Cloud Bus 消息总线集成Kafka
- Spring Cloud(十一)高可用的分布式配置中心 Spring Cloud Bus 消息总线集成(RabbitMQ)
- 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 史上最简单的SpringCloud教程 | 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- 史上最简单的SpringCloud教程 | 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- spring cloud 中消息总线(bus)使用
- 第八篇: 消息总线(Spring Cloud Bus)
- Spring Cloud (20) | Spring Cloud Bus 使用kafka消息总线、gitlab添加webhooks实现自动刷新配置
