图书管理系统【JavaWeb:部署开发环境、解决分类、图书、前台页面模块】
2018-02-27 10:08
706 查看
前言
巩固Servlet+JSP开发模式,做一个比较完整的小项目.成果图
该项目包含了两个部分,前台和后台。前台用于显示

后台用于管理
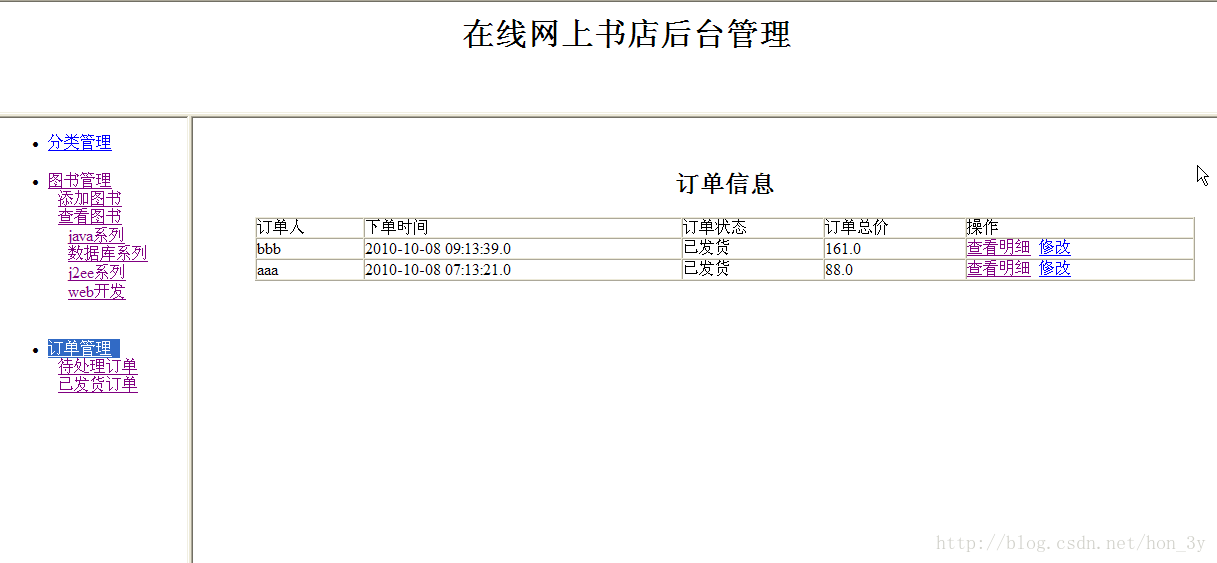
该项目可分为5个模块来组成:分类模块,用户模块,图书模块,购买模块,订单模块。
搭建环境
建立包结构
导入开发包
前台分帧页面
index.jsp【没有body标签的】<frameset rows="25%,*">
<frame src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/client/head.jsp"/>
<frame src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/client/body.jsp"/>
</frameset>head.jsp
<body style="text-align: center"> <h1>欢迎来到购物中心</h1>
body是空白的jsp页面
效果:

后台分帧页面
manager.jsp【嵌套了framset标签,也是没有body标签的】<frameset rows="25%,*">
<frame src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/background/head.jsp"/>
<frameset cols="15%,*">
<frame src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/background/left.jsp"/>
<frame src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/background/body.jsp"/>
</frameset>
</frameset>head.jsp
<body style="text-align: center"> <h1>后台管理</h1>
left.jsp
<a href="#">分类管理</a> <br> <br> <a href="#">图书管理</a> <br> <br> <a href="#">订单管理</a> <br> <br>
body.jsp是空白的
效果:

分帧的文件夹目录结构

值得注意的是:
文件夹的名字不能使用“manager”,不然会出现:403 Access Denied错误
frameset标签是可以嵌套的,分列用“cols”,分行用“rows”
导入工具类和方法的代码
过滤中文乱码数据HTML转义
DAOFactory
JDBC连接池
UUID工具类
c3p0.xml配置文件
这些代码都可以在我的博客分类:代码库中找到!
分类模块
首先,我们来做分类模块吧创建实体Category
private String id; private String name; private String description; //各种setter、getter
在数据库创建表
CREATE TABLE category ( id VARCHAR(40) PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL UNIQUE , description VARCHAR(255) );
编写CategoryDAO
/**
* 分类模块
* 1:添加分类
* 2:查找分类
* 3:修改分类
*
*
* */
public class CategoryImpl {
public void addCategory(Category category) {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
String sql = "INSERT INTO category (id, name, description) VALUES(?,?,?)";
try {
queryRunner.update(sql, new Object[]{category.getId(), category.getName(), category.getDescription()});
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Category findCategory(String id) {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
String sql = "SELECT * FROM category WHERE id=?";
try {
Category category = (Category) queryRunner.query(sql, id, new BeanHandler(Category.class));
return category;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public List<Category> getAllCategory() {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
String sql = "SELECT * FROM category";
try {
List<Category> categories = (List<Category>) queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler(Category.class));
return categories;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}测试DAO
public class demo {
@Test
public void add() {
Category category = new Category();
category.setId("2");
category.setName("数据库系列");
category.setDescription("这是数据库系列");
CategoryImpl category1 = new CategoryImpl();
category1.addCategory(category);
}
@Test
public void find() {
String id = "1";
CategoryImpl category1 = new CategoryImpl();
Category category = category1.findCategory(id);
System.out.println(category.getName());
}
@Test
public void getAll() {
CategoryImpl category1 = new CategoryImpl();
List<Category> categories = category1.getAllCategory();
for (Category category : categories) {
System.out.println(category.getName());
}
}
}抽取成DAO接口
public interface CategoryDao {
void addCategory(Category category);
Category findCategory(String id);
List<Category> getAllCategory();
}后台页面的添加分类
在超链接上,绑定显示添加分类的页面<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/background/addCategory.jsp" target="body">添加分类</a>显示添加分类的JSP页面
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/CategoryServlet?method=add" method="post">
分类名称:<input type="text" name="name"><br>
分类描述:<textarea name="description"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>处理添加分类的Servlet
if (method.equals("add")) {
try {
//把浏览器带过来的数据封装到bean中
Category category = WebUtils.request2Bean(request, Category.class);
category.setId(WebUtils.makeId());
service.addCategory(category);
request.setAttribute("message", "添加分类成功!");
} catch (Exception e) {
request.setAttribute("message","添加分类失败");
e.printStackTrace();
}
request.getRequestDispatcher("/message.jsp").forward(request, response);
}效果:

后台页面的查看分类
在超链接上,绑定处理请求的Servletelse if (method.equals("look")) {
List<Category> list = service.getAllCategory();
request.setAttribute("list", list);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/background/lookCategory.jsp").forward(request, response);
}显示分类页面的JSP
<c:if test="${empty(list)}">
暂时还没有分类数据哦,请你添加把
</c:if>
<c:if test="${!empty(list)}">
<table border="1px">
<tr>
<td>分类名字</td>
<td>分类描述</td>
<td>操作</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${list}" var="category">
<tr>
<td>${category.name}</td>
<td>${category.description}</td>
<td>
<a href="#">删除</a>
<a href="#">修改</a>
</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</c:if>效果:

图书模块
分析
在设计图书管理的时候,我们应该想到:图书和分类是有关系的。一个分类可以对应多本图书。为什么要这样设计?这样更加人性化,用户在购买书籍的时候,用户能够查看相关分类后的图书,而不是全部图书都显示给用户,让用户一个一个去找。
设计实体
private String id; private String name; private String author; private String description; private double price; //记住图片的名称 private String image; //记住分类的id private String category_id; //各种setter和getter
设计数据库表
CREATE TABLE book ( id VARCHAR(40) PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL UNIQUE, description VARCHAR(255), author VARCHAR(10), price FLOAT, image VARCHAR(100), category_id VARCHAR(40), CONSTRAINT category_id_FK FOREIGN KEY (category_id) REFERENCES category (id) );
编写DAO
/**
* 图书模块
* 1:添加图书
* 2:查看图书
* 3:查找图书的分页数据【图书一般来说有很多,所以要分页】
*/
public class BookDaoImpl {
public void addBook(Book book) {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
String sql = "INSERT INTO book (id,name,description,author,price,image,category_id) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
try {
queryRunner.update(sql, new Object[]{book.getId(), book.getName(), book.getDescription(), book.getAuthor(), book.getPrice(),book.getImage(), book.getCategory_id()});
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Book findBook(String id) {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
String sql = "SELECT * FROM book WHERE id=?";
try {
return (Book) queryRunner.query(sql, id, new BeanHandler(Book.class));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**得到图书的分页数据*/
public List<Book> getPageData(int start, int end) {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
String sql = "SELECT * FROM book limit ?,?";
try {
return (List<Book>) queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler(Book.class), new Object[]{start, end});
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**得到按照分类图书的分页数据*/
public List<Book> getPageData(int start, int end,String category_id) {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
//WHERE字句在limit字句的前边,注意Object[]的参数位置!
String sql = "SELECT * FROM book WHERE category_id=? limit ?,?";
try {
return (List<Book>) queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler(Book.class), new Object[]{ category_id,start, end});
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 得到图书的总记录数
*/
public int getTotalRecord() {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
String sql = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM book";
try {
return (int) queryRunner.query(sql, new ScalarHandler());
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 得到分类后图书的总记录数
* getCategoryTotalRecord
*/
public long getCategoryTotalRecord(String category_id) {
try {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(Utils2DB.getDataSource());
String sql = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM book WHERE category_id=?";
return (long) queryRunner.query(sql, category_id, new ScalarHandler());
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}测试DAO
public class BookDemo {
BookDaoImpl bookDao = new BookDaoImpl();
@Test
public void add() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId("5");
book.setName("SQLServer");
book.setAuthor("我也不知道");
book.setImage("33333332432");
book.setPrice(33.22);
book.setDescription("这是一本好书");
book.setCategory_id("2");
bookDao.addBook(book);
}
@Test
public void look() {
List<Book> bookList = bookDao.getPageData(3, 3);
for (Book book : bookList) {
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
List<Book> books = bookDao.getPageData(0,2,"2");
for (Book book : books) {
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
}
@Test
public void find() {
String id = "2";
Book book = bookDao.findBook(id);
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
}抽取成DAO接口
public interface BookDao {
void addBook(Book book);
Book findBook(String id);
List<Book> getPageData(int start, int end);
List<Book> getPageData(int start, int end, String category_id);
long getTotalRecord();
long getCategoryTotalRecord(String category_id);
}编写Service层
/*添加图书*/
public void addBook(Book book) {
bookDao.addBook(book);
}
/*查找图书*/
public Book findBook(String id) {
return bookDao.findBook(id);
}
/*查找图书*/
public Book findBook(String id) {
return bookDao.findBook(id);
}
/*获取图书的分页数据*/
public Page getPageData(String pageNum) {
Page page=null;
if (pageNum == null) {
page = new Page(1, bookDao.getTotalRecord());
} else {
page = new Page(Integer.valueOf(pageNum), bookDao.getTotalRecord());
}
List<Book> books = bookDao.getPageData(page.getStartIndex(), page.getLinesize());
page.setList(books);
return page;
}
/*获取图书分类后的分页数据*/
public Page getPageData(String currentPageCount,String category_id) {
Page page=null;
if (currentPageCount == null) {
page = new Page(1, bookDao.getCategoryTotalRecord(category_id));
} else {
page = new Page(Integer.valueOf(currentPageCount), bookDao.getCategoryTotalRecord(category_id));
}
List<Book> books = bookDao.getPageData(page.getStartIndex(), page.getLinesize(), category_id);
page.setList(books);
return page;
}后台添加图书
后台要添加图书的时候,应该说明图书的类型是什么。要想在显示添加图书的页面上知道全部类型的id,就要经过Servlet把类型的集合传送过去
绑定链接
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/BookServlet?method=addUI" target="body">添加图书</a><br>传送类型集合的Servlet
String method = request.getParameter("method");
BussinessServiceImpl service = new BussinessServiceImpl();
if (method.equals("addUI")) {
List<Category> list = service.getAllCategory();
request.setAttribute("list", list);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/background/addBook.jsp").forward(request, response);
}显示JSP页面
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/BookServlet?method=add" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<table border="1px" width="30%">
<tr>
<td> 图书名称:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="name"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 作者:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="author"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 图书价钱:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="price"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>类型:</td>
<td>
<select name="category_id">
<c:forEach items="${list}" var="category">
<option value="${category.id}">${category.name}</option>
</c:forEach>
</select>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> 上传图片</td>
<td><input type="file" name="image"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>详细描述</td>
<td><textarea name="description"></textarea></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
<input type="reset" value="重置">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>处理表单数据Servlet
else if (method.equals("add")) {
//上传文件和普通数据分割开,封装到Book对象上
Book book = uploadData(request);
book.setId(WebUtils.makeId());
service.addBook(book);
request.setAttribute("message", "添加图书成功");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/message.jsp").forward(request, response);
}uploadData()方法代码
private Book uploadData(HttpServletRequest request) {
Book book = new Book();
try{
//1.得到解析器工厂
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
//2.得到解析器
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
//设置编码
upload.setHeaderEncoding("UTF-8");
//为上传表单,则调用解析器解析上传数据
List<FileItem> list = upload.parseRequest(request); //FileItem
//遍历list,得到用于封装第一个上传输入项数据fileItem对象
for(FileItem item : list){
if(item.isFormField()){
//得到的是普通输入项
String name = item.getFieldName(); //得到输入项的名称
String value = item.getString("UTF-8");
//使用BeanUtils封装数据
BeanUtils.setProperty(book, name, value);
}else{
//得到上传输入项
//得到上传文件名全路径
String filename = item.getName();
//截取文件名
filename = filename.substring(filename.lastIndexOf("\\")+1);
InputStream in = item.getInputStream(); //得到上传数据
int len = 0;
byte buffer[]= new byte[1024];
//如果没有这个目录,就创建它
String savepath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/image");
File file = new File(savepath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdir();
}
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(savepath + "\\" + filename);
while((len=in.read(buffer))>0){
out.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
//设置图片的名字
book.setImage(filename);
in.close();
out.close();
//关闭临时文件
item.delete();
}
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return book;
}效果:

后台显示图书模块
由于我们用的是分页技术,所以我们导入之前写过的Page类和jsp吧…..这些代码可以在我分类的代码库中找到绑定超链接
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/BookServlet?method=look" target="body">查看图书</a>Servlet处理请求
else if (method.equals("look")) {
String currentPageCount = request.getParameter("currentPageCount");
Page page = service.getPageData(currentPageCount);
request.setAttribute("page",page);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/background/listBook.jsp").forward(request, response);
}显示图书JSP页面
Servlet端传过来的是Page对象,而不是list集合可以根据记载在Book对象的图片名称,弄一个超链接,超链接指向服务端的图片,这样就可以查看图片了!
<c:if test="${empty(page.list)}">
暂时还没有任何图书哦
</c:if>
<c:if test="${!empty(page.list)}">
<table border="1px">
<tr>
<td>书名</td>
<td>作者</td>
<td>价钱</td>
<td>描述</td>
<td>图片</td>
<td>操作</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach var="book" items="${page.list}" >
<tr>
<td>${book.name}</td>
<td>${book.author}</td>
<td>${book.price}</td>
<td>${book.description}</td>
<td><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/image/${book.image}">查看图片</a></td>
<td>
<a href="#">删除</a>
<a href="#">修改</a>
</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<br>
<jsp:include page="page.jsp"/>
</c:if>效果:

前台页面
看回我们前台页面的成果图,我们可以把整个body页面看成是三个divbody占整个div
导航条是一个div
显示图书的地方是一个div

设计好大概的布局
html代码引入css<link rel="stylesheet" href="body.css" type="text/css">
HTML三个div
<div id="body">
<div id="category">
<c:forEach items="${categorys}" var="category">
</c:forEach>
这是导航条
</div>
<div id="bookandpages">
<div id="books">
这是书籍的地方
</div>
<div id="page">
这是页码
</div>
</div>
</div>CSS代码:
#body {
position: relative;
}
#category {
border: 1px solid #000;
position: absolute;
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
float: left;
left: 200px;
top: 70px;;
}
#bookandpages {
border: 1px solid #000000;
position: absolute;
width: 600px;
height: 600px;;
float: left;
left: 500px;
margin-left: 50px;
}
#books {
border: 1px solid #000;
width: 600px;
height: 550px;;
}
#page {
border: 1px solid #000;
position: absolute;
height: 48px;
width: 600px;
}大概的布局

IndexServlet
在显示首页的下部分的时候,应该先去寻找一个Servlet来把数据交给对应的JSP。因为我们的JSP一般都是放在WEB-INF下,是不能直接访问的。还有就是JSP往往是需要我们后台的数据的,因此我们使用Servlet来获取得到数据,再交由JSP来展示就最好不过了。
<frame src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/IndexServlet"/>Servlet代码:
//得到所有的分类数据,给body页面
BussinessServiceImpl service = new BussinessServiceImpl();
List<Category> categories = service.getAllCategory();
request.setAttribute("categories", categories);
String currentPageCount = request.getParameter("currentPageCount");
//得到所有分类的图书,给body页面
Page page = service.getPageData(currentPageCount);
request.setAttribute("page", page);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/client/body.jsp").forward(request,response);JSP显示数据
<div id="body">
<div id="category">
书籍分类 :
<br>
<c:forEach items="${categories}" var="categories">
<li>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/ListBookServlet?category_id=${categories.id}">${categories.name}</a>
</li>
</c:forEach>
</div>
<div id="bookandpages">
<c:forEach items="${page.list}" var="book">
<div id="books">
<div id="image">
<img src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/image/${book.image}" width="83px" height="118px">
</div>
<div id="bookinfo">
<li>
书名:${book.name}
</li>
<li>价格:${book.price}</li>
<li>作者:${book.author}</li>
</div>
</div>
<%--这里要清除浮动,十分重要!--%>
<div style="clear: both"></div>
</c:forEach>
</div>
<div id="page">
<jsp:include page="/client/page.jsp"/>
</div>
</div>CSS代码:
重要的是:如果div浮动都黏贴在一起了,那么在后边多加个div,用于清除浮动效果#body {
position: relative;
}
#category {
border: 1px solid #000;
position: absolute;
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
float: left;
left: 200px;
top: 70px;;
}
#bookandpages {
border: 1px solid #000000;
position: absolute;
width: 780px;
height: 538px;;
float: left;
left: 500px;
margin-left: 50px;
}
#books{
margin-left: 50px;
margin-top: 30px;
}
#image{
float: left;
}
#bookinfo{
float: left;
}
#page {
height: 62px;
width: 780px;
position: fixed;
margin-left: 549px;
margin-top: 477px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 50px;
}效果:

按照分类显示图书
我们可以根据左边的导航条来显示相对应的分类图书。Servlet代码:
BussinessServiceImpl service = new BussinessServiceImpl();
String currentPageCount = request.getParameter("currentPageCount");
String category_id = request.getParameter("category_id");
Page page = service.getPageData(currentPageCount, category_id);
List<Category> categories = service.getAllCategory();
request.setAttribute("page", page);
request.setAttribute("categories", categories);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/client/body.jsp").forward(request,response);效果:

如果文章有错的地方欢迎指正,大家互相交流。习惯在微信看技术文章的同学,可以关注微信公众号:Java3y
相关文章推荐
- 图书管理系统【JavaWeb:部署开发环境、解决分类、图书、前台页面模块】
- bookStore案例第一篇【部署开发环境、解决分类模块】
- Linux学习掌握(二):CentOS系统中搭建java开发环境与部署web项目
- javaweb开发之---在线图书管理系统
- web day26 小项目练习图书商城 后台分类管理模块,图书管理模块,前台登陆过滤
- JAVA_WEB项目(结合Servlet+jsp+ckEditor编辑器+jquery easyui技术)实现新闻发布管理系统第四篇:前台首页,新闻分类(体育新闻,科技新闻等),新闻列表分页的实现
- bookStore案例第一篇【部署开发环境、解决分类模块】
- 去哪网实习总结:windows下配置JavaWeb环境、开发helloworld、发布系统(附截图,绝对详细)(JavaWeb)
- Windows系统配置Java Web开发环境Step by Step
- java web 项目 图书管理系统的设计与实现
- atitit.研发管理--标准化流程总结---java开发环境与项目部署环境的搭建工具包总结
- 【Android】【FAQ】解决windows7 64bit系统下部署android开发环境使用Android SDK Manager的failed to fetch问题
- 混合app开发:自己实现的页面历史记录管理模块,解决页面"回退难"的问题
- JavaWeb项目开发案例精粹-第6章报价管理系统-07View层
- java web 开发环境部署,zving框架
- Mac下JavaWeb开发环境部署
- java web 项目 图书管理系统的设计与实现
- 初装系统时javaweb开发环境的环境变量的配置
- JavaWeb项目开发案例精粹-第6章报价管理系统-001需求分析及设计
- JAVA_WEB项目(结合Servlet+jsp+ckEditor编辑器+jquery easyui技术)实现新闻发布管理系统第一篇:前期环境准备
