Spring-注解方式 IOC/DI
2018-02-04 12:00
351 查看
在本知识点中,讲演示如何使用注解的方式完成注入对象中的效果
修改applicationContext.xml
1. 在15行添加
2. 注入对象的21行注释掉,这个行为在后面将使用注解来完成
@Autowired
在Product.java的category属性前加上@Autowired注解
运行测试

@Autowired的位置
除了前面的 在属性前加上@Autowired 这种方式外,也可以在setCategory方法前加上@Autowired,这样来达到相同的效果
@Resource
除了@Autowired之外,@Resource也是常用的手段
对Bean的注解
上述例子是对注入对象行为的注解,那么bean对象本身,比如Category,Product可不可以移出applicationContext.xml配置文件,也通过注解进行呢?
接下来就讲解如何对Bean进行注解配置
applicationContext.xml
修改applicationContext.xml,什么都去掉,只新增:
@Component
为Product类加上@Component注解,即表明此类是bean
为Category 类加上@Component注解,即表明此类是bean
另外,因为配置从applicationContext.xml中移出来了,所以属性初始化放在属性声明上进行了。
运行测试
运行TestSpring,可以发现运行结果是一样的

修改applicationContext.xml
1. 在15行添加
<context:annotation-config/>表示告诉Spring要用注解的方式进行配置
2. 注入对象的21行注释掉,这个行为在后面将使用注解来完成
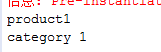
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <bean name="c" class="com.how2java.pojo.Category"> <property name="name" value="category 1" /> </bean> <bean name="p" class="com.how2java.pojo.Product"> <property name="name" value="product1" /> <!-- <property name="category" ref="c" /> --> </bean> </beans>
@Autowired
在Product.java的category属性前加上@Autowired注解
@Autowired private Category category;
package com.how2java.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class Product {
private int id;
private String name;
@Autowired private Category category;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Category getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(Category category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
运行测试

package com.how2java.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.how2java.pojo.Product;
public class TestSpring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] { "applicationContext.xml" });
Product p = (Product) context.getBean("p");
System.out.println(p.getName());
System.out.println(p.getCategory().getName());
}
}@Autowired的位置
除了前面的 在属性前加上@Autowired 这种方式外,也可以在setCategory方法前加上@Autowired,这样来达到相同的效果
@Autowired public void setCategory(Category category)

package com.how2java.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class Product {
private int id;
private String name;
private Category category;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Category getCategory() {
return category;
}
@Autowired public void setCategory(Category category){
this.category = category;
}
}
@Resource
除了@Autowired之外,@Resource也是常用的手段
@Resource(name="c") private Category category;

package com.how2java.pojo;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
public class Product {
private int id;
private String name;
@Resource(name="c") private Category category;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Category getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(Category category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
对Bean的注解
上述例子是对注入对象行为的注解,那么bean对象本身,比如Category,Product可不可以移出applicationContext.xml配置文件,也通过注解进行呢?
接下来就讲解如何对Bean进行注解配置
applicationContext.xml
修改applicationContext.xml,什么都去掉,只新增:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.how2java.pojo"/>其作用是告诉Spring,bean都放在com.how2java.pojo这个包下
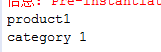
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.how2java.pojo"/> </beans>
@Component
为Product类加上@Component注解,即表明此类是bean
@Component("p")
public class Product {为Category 类加上@Component注解,即表明此类是bean
@Component("c")
public class Category {另外,因为配置从applicationContext.xml中移出来了,所以属性初始化放在属性声明上进行了。
private String name="product 1"; private String name="category 1";
package com.how2java.pojo;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("p") public class Product {
private int id;
private String name="product 1";
@Autowired private Category category;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Category getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(Category category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
package com.how2java.pojo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("c") public class Category {
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private int id;
private String name="category 1";
}
运行测试
运行TestSpring,可以发现运行结果是一样的

package com.how2java.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.how2java.pojo.Product;
public class TestSpring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] { "applicationContext.xml" });
Product p = (Product) context.getBean("p");
Syst
4000
em.out.println(p.getName());
System.out.println(p.getCategory().getName());
}
}
相关文章推荐
- Spring知识点总结(三)之注解方式实现IOC和DI
- ######【spring属性注入(Ioc的DI)总结】:注解方式属性注入,属性名任意.=for理解:Aop注入代理对象时,注入被增强类对象时,属性名为proxy(自定义)。
- spring注解方式实现DI和IOC
- Spring 使用注解的方式实现IOC和DI(控制反转和依赖注入)
- Spring.Net---4、IoC/DI注入方式
- Spring多种注入方式及注解实现DI
- spring----IOC注解方式以及AOP
- ssh框架 spring IOC注解的方式
- spring-04 之IOC 属性注入(注解方式 附代码)
- Spring--IoC--基于注解的DI-基本使用
- 模仿spring,自定义的一个mvc框架,有ioc和aop功能,全部采用注解的方式
- Spring系列之 (六):Spring实现IOC的两种方式(XML和注解)
- 框架学习—Spring的IOC容器之注解方式与AOP技术
- Spring--IoC--基于注解的DI-XML的优先级高于注解
- Spring(四)----IOC注解方式
- 04-Spring-使用ioc注解方式配置bean
- Spring IOC 注解annotation的几种方式
- Spring--IoC--基于注解的DI-@Scope
- Spring(二)IOC的注解方式用法
- Spring教程--IOC(注解方式)和整合junit
