【Java并发编程】之九:死锁(含代码)
2018-01-17 11:13
411 查看
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17200937
当线程需要同时持有多个锁时,有可能产生死锁。考虑如下情形:
线程A当前持有互斥所锁lock1,线程B当前持有互斥锁lock2。接下来,当线程A仍然持有lock1时,它试图获取lock2,因为线程B正持有lock2,因此线程A会阻塞等待线程B对lock2的释放。如果此时线程B在持有lock2的时候,也在试图获取lock1,因为线程A正持有lock1,因此线程B会阻塞等待A对lock1的释放。二者都在等待对方所持有锁的释放,而二者却又都没释放自己所持有的锁,这时二者便会一直阻塞下去。这种情形称为死锁。
下面给出一个两个线程间产生死锁的示例,如下:
[java] view
plain copy
public class Deadlock extends Object {
private String objID;
public Deadlock(String id) {
objID = id;
}
public synchronized void checkOther(Deadlock other) {
print("entering checkOther()");
try { Thread.sleep(2000); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
print("in checkOther() - about to " + "invoke 'other.action()'");
//调用other对象的action方法,由于该方法是同步方法,因此会试图获取other对象的对象锁
other.action();
print("leaving checkOther()");
}
public synchronized void action() {
print("entering action()");
try { Thread.sleep(500); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
print("leaving action()");
}
public void print(String msg) {
threadPrint("objID=" + objID + " - " + msg);
}
public static void threadPrint(String msg) {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + ": " + msg);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Deadlock obj1 = new Deadlock("obj1");
final Deadlock obj2 = new Deadlock("obj2");
Runnable runA = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
obj1.checkOther(obj2);
}
};
Thread threadA = new Thread(runA, "threadA");
threadA.start();
try { Thread.sleep(200); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
Runnable runB = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
obj2.checkOther(obj1);
}
};
Thread threadB = new Thread(runB, "threadB");
threadB.start();
try { Thread.sleep(5000); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
threadPrint("finished sleeping");
threadPrint("about to interrupt() threadA");
threadA.interrupt();
try { Thread.sleep(1000); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
threadPrint("about to interrupt() threadB");
threadB.interrupt();
try { Thread.sleep(1000); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
threadPrint("did that break the deadlock?");
}
}
运行结果如下:
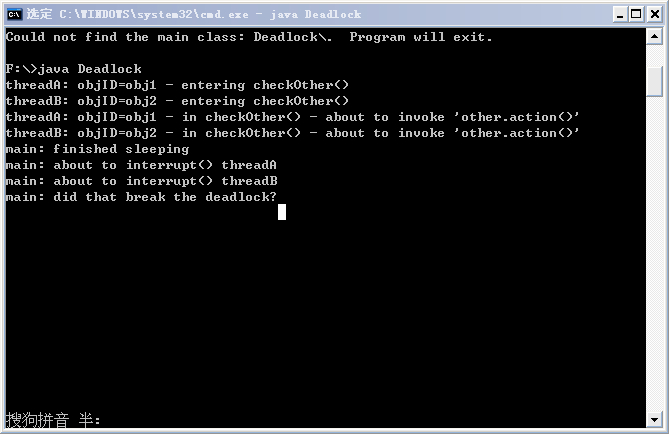
从结果中可以看出,在执行到other.action()时,由于两个线程都在试图获取对方的锁,但对方都没有释放自己的锁,因而便产生了死锁,在主线程中试图中断两个线程,但都无果。
大部分代码并不容易产生死锁,死锁可能在代码中隐藏相当长的时间,等待不常见的条件地发生,但即使是很小的概率,一旦发生,便可能造成毁灭性的破坏。避免死锁是一件困难的事,遵循以下原则有助于规避死锁:
1、只在必要的最短时间内持有锁,考虑使用同步语句块代替整个同步方法;
2、尽量编写不在同一时刻需要持有多个锁的代码,如果不可避免,则确保线程持有第二个锁的时间尽量短暂;
3、创建和使用一个大锁来代替若干小锁,并把这个锁用于互斥,而不是用作单个对象的对象级别锁;
当线程需要同时持有多个锁时,有可能产生死锁。考虑如下情形:
线程A当前持有互斥所锁lock1,线程B当前持有互斥锁lock2。接下来,当线程A仍然持有lock1时,它试图获取lock2,因为线程B正持有lock2,因此线程A会阻塞等待线程B对lock2的释放。如果此时线程B在持有lock2的时候,也在试图获取lock1,因为线程A正持有lock1,因此线程B会阻塞等待A对lock1的释放。二者都在等待对方所持有锁的释放,而二者却又都没释放自己所持有的锁,这时二者便会一直阻塞下去。这种情形称为死锁。
下面给出一个两个线程间产生死锁的示例,如下:
[java] view
plain copy
public class Deadlock extends Object {
private String objID;
public Deadlock(String id) {
objID = id;
}
public synchronized void checkOther(Deadlock other) {
print("entering checkOther()");
try { Thread.sleep(2000); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
print("in checkOther() - about to " + "invoke 'other.action()'");
//调用other对象的action方法,由于该方法是同步方法,因此会试图获取other对象的对象锁
other.action();
print("leaving checkOther()");
}
public synchronized void action() {
print("entering action()");
try { Thread.sleep(500); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
print("leaving action()");
}
public void print(String msg) {
threadPrint("objID=" + objID + " - " + msg);
}
public static void threadPrint(String msg) {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + ": " + msg);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Deadlock obj1 = new Deadlock("obj1");
final Deadlock obj2 = new Deadlock("obj2");
Runnable runA = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
obj1.checkOther(obj2);
}
};
Thread threadA = new Thread(runA, "threadA");
threadA.start();
try { Thread.sleep(200); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
Runnable runB = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
obj2.checkOther(obj1);
}
};
Thread threadB = new Thread(runB, "threadB");
threadB.start();
try { Thread.sleep(5000); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
threadPrint("finished sleeping");
threadPrint("about to interrupt() threadA");
threadA.interrupt();
try { Thread.sleep(1000); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
threadPrint("about to interrupt() threadB");
threadB.interrupt();
try { Thread.sleep(1000); }
catch ( InterruptedException x ) { }
threadPrint("did that break the deadlock?");
}
}
运行结果如下:

从结果中可以看出,在执行到other.action()时,由于两个线程都在试图获取对方的锁,但对方都没有释放自己的锁,因而便产生了死锁,在主线程中试图中断两个线程,但都无果。
大部分代码并不容易产生死锁,死锁可能在代码中隐藏相当长的时间,等待不常见的条件地发生,但即使是很小的概率,一旦发生,便可能造成毁灭性的破坏。避免死锁是一件困难的事,遵循以下原则有助于规避死锁:
1、只在必要的最短时间内持有锁,考虑使用同步语句块代替整个同步方法;
2、尽量编写不在同一时刻需要持有多个锁的代码,如果不可避免,则确保线程持有第二个锁的时间尽量短暂;
3、创建和使用一个大锁来代替若干小锁,并把这个锁用于互斥,而不是用作单个对象的对象级别锁;
相关文章推荐
- 【Java并发编程】之九:死锁(含代码)(r)
- 转:【Java并发编程】之九:死锁(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之九:死锁(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之九:死锁(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之九:死锁(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之九:死锁(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之九:死锁(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之十六:深入Java内存模型——happen-before规则及其对DCL的分析(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之三:线程挂起、恢复与终止的正确方法(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之二十:并发新特性—Lock锁和条件变量(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之十二:线程间通信中notifyAll造成的早期通知问题(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之二十一:并发新特性—阻塞队列和阻塞栈(含代码)
- 探索并发编程(二)------写线程安全的Java代码
- 【Java并发编程】:并发新特性—阻塞队列和阻塞栈(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】:生产者—消费者模型(含代码)
- java并发编程之同步器代码示例
- 【Java并发编程】之十八:第五篇中volatile意外问题的正确分析解答(含代码)
- 【Java并发编程】之二:线程中断(含代码)
- 转: 【Java并发编程】之三:线程挂起、恢复与终止的正确方法(含代码)
- 探索并发编程(二)------写线程安全的Java代码
