Mybatis底层原理(二)SqlSession运行过程
2018-01-12 10:20
411 查看
1.SqlSession是一个接口,包含了查询、修改、插入、删除的方法。我们既可以直接使用这些方法也可以使用Mapper来代理使用这些方法。
1.1 Mapper的动态代理
1.1.1 Mapper映射是通过动态代理来实现的,我们来看下MapperProxyFactory部分源码:
public class MapperProxyFactory<T>
/* */ {
/* */ private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
/* 28 */ private Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap();
/* */
/* */ public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
/* 31 */ this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
/* 35 */ return this.mapperInterface;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
/* 39 */ return this.methodCache;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy)
/* */ {
/* 44 */ return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { this.mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
/* 48 */ MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this.mapperInterface, this.methodCache);
/* 49 */ return newInstance(mapperProxy);
/* */ }
/* */ }
可以看到动态代理对接口的绑定,他的作用就是生成动态代理对象,而代理的方法则被放到了MapperProxy中;
1.1.2 查看MapperProxy的部分源码:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
/* 39 */ if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
/* 40 */ return method.invoke(this, args);
/* */ }
/* 42 */ MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
/* 43 */ return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
/* 47 */ MapperMethod mapperMethod = (MapperMethod)this.methodCache.get(method);
/* 48 */ if (mapperMethod == null) {
/* 49 */ mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration());
/* 50 */ this.methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
/* */ }
/* 52 */ return mapperMethod;
/* */ }一旦mapper是个代理对象,那么它会调用invoke方法,首先判断他是否是一个类,若不是则会生成MapperMethod对象,他是通过cachedMapperMethod方法初始化,然后执行execute方法把sqlSession和当前运行参数传
4000
入。
再看execute方法里面做了什么:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args)
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 44 */ if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == this.command.getType()) {
/* 45 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* 46 */ result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 47 */ if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == this.command.getType()) {
/* 48 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* 49 */ result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 50 */ if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == this.command.getType()) {
/* 51 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* 52 */ result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 53 */ if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == this.command.getType())
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 54 */ if ((this.method.returnsVoid()) && (this.method.hasResultHandler())) {
/* 55 */ executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
/* 56 */ result = null;
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 57 */ if (this.method.returnsMany()) {
/* 58 */ result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 59 */ if (this.method.returnsMap()) {
/* 60 */ result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
/* */ } else {
/* 62 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* 63 */ result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param); } }
/* */ }
/* */ } else {
/* 66 */ throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */ Object result;
/* 68 */ if ((result == null) && (this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive()) && (!(this.method.returnsVoid()))) {
/* 69 */ throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");
/* */ }
/* */
/* 72 */ return result;
/* */ }重点关注红色的方法executeForMany:
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args)
/* */ {
/* 109 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* */ List result;
/* */ List result;
/* 110 */ if (this.method.hasRowBounds()) {
/* 111 */ RowBounds rowBounds = this.method.extractRowBounds(args);
/* 112 */ result = sqlSession.selectList(this.command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
/* */ } else {
/* 114 */ result = sqlSession.selectList(this.command.getName(), param);
/* */ }
/* */
/* 117 */ if (!(this.method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass()))) {
/* 118 */ if (this.method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
/* 119 */ return convertToArray(result);
/* */ }
/* 121 */ return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
/* */ }
/* */
/* 124 */ return result;
/* */ }MapperMethod采用命令模式,根据上下文进行跳转,它可跳转到许多方法中,其中executeForMany方法实际就是通过sqlSession对象去运行SQL
映射器其实就是一个动态代理对象,进入到MapperMethod的execute方法中,经过判断就进入SqlSession的增删改查等方法,接下来会介绍这些方法如何执行。
1.2 SqlSession下的四大对象
Mapper执行的过程是通过Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler和ResultHandler来完成数据库的操作和返回结果。
Executor代表执行器,他来调度StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultHandler等来执行SQL;
StatementHandler的作用是使用数据库的statement执行操作,是四大对象的核心,起一个承上启下的作用;
ParameterHandler用来处理SQL的参数;
ResultHandler对结果集进行封装返回。
1.2.1 Executor执行器
Executor是真正执行Java与数据库交互的东西,在Mybatis中有三种执行器,默认是SimpleExecutor简易执行器
SimpleExecutor源码:
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor
/* */ {
/* */ public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction)
/* */ {
/* 36 */ super(configuration, transaction);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
/* 40 */ Statement stmt = null;
/* */ try {
/* 42 */ Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
/* 43 */ StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
/* 44 */ stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
/* 45 */ int i = handler.update(stmt);
/* */
/* 47 */ return i; } finally { closeStatement(stmt);
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
/* 52 */ Statement stmt = null;
/* */ try {
/* 54 */ Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
/* 55 */ StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 56 */ stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
/* 57 */ List localList = handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
/* */
/* 59 */ return localList; } finally { closeStatement(stmt);
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
/* 64 */ return Collections.emptyList();
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException
/* */ {
/* 69 */ Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
/* 70 */ Statement stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
/* 71 */ handler.parameterize(stmt);
/* 72 */ return stmt;
/* */ }
/* */ }Mybatis利用Configuration来构建StatementHandler,然后在preparedStatement方法中初始化参数,它调用了StatementHandler
的prepare方法进行预编译和基础设置,然后通过StatementHandler的parameterize来设置参数并执行,resultHandler在组装结果返回。
我们能看出其中的重点是StatementHandler;
1.2.2 StatementHandler数据库会话器
Mybatis通过RoutingStatementHandler来获取实际使用的handler:
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
/* */ {
/* 37 */ switch (1.$SwitchMap$org$apache$ibatis$mapping$StatementType[ms.getStatementType().ordinal()])
/* */ {
/* */ case 1:
/* 39 */ this.delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 40 */ break;
/* */ case 2:
/* 42 */ this.delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 43 */ break;
/* */ case 3:
/* 45 */ this.delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 46 */ break;
/* */ default:
/* 48 */ throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
/* */ }
/* */ }其中使用了适配模式,我们常用的是PreparedStatementHandler,其中主要的三个方法名为prepare、parameterize、query
public Statement prepare(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
/* 79 */ ErrorContext.instance().sql(this.boundSql.getSql());
/* 80 */ Statement statement = null;
/* */ try {
/* 82 */ statement = instantiateStatement(connection);
/* 83 */ setStatementTimeout(statement);
/* 84 */ setFetchSize(statement);
/* 85 */ return statement;
/* */ } catch (SQLException e) {
/* 87 */ closeStatement(statement);
/* 88 */ throw e;
/* */ } catch (Exception e) {
/* 90 */ closeStatement(statement);
/* 91 */ throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e);
/* */ }
/* */ }instantiateStatement()方法是对SQL进行预编译,然后Eexcutor会调用parameterize方法设置参数
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException
/* */ {
/* 68 */ String sql = this.boundSql.getSql();
/* 69 */ statement.execute(sql);
/* 70 */ return this.resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(statement);
/* */ }由于执行前参数和SQL都被prepare方法预编译了,参数也在parameterize方法设置了,所以现在只需要执行SQL返回结果即可。
整个流程:
Executor会先调用StatementHandler的prepare方法预编译SQL语句,外加一些基本运行参数,然后调用parameterize方法
启用ParameterHandler设置参数,完成预编译,跟着执行查询,通过resultSetHandler封装结果返回给调用者、
1.2.3
ParameterHandler参数处理器
MyBatis为ParameterHandler提供了一个DefaultParameterHandler实现类。其中部分源码:
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
/* 56 */ ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(this.mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
/* 57 */ List parameterMappings = this.boundSql.getParameterMappings();
/* 58 */ if (parameterMappings != null) {
/* 59 */ MetaObject metaObject = (this.parameterObject == null) ? null : this.configuration.newMetaObject(this.parameterObject);
/* 60 */ for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); ++i) {
/* 61 */ ParameterMapping parameterMapping = (ParameterMapping)parameterMappings.get(i);
/* 62 */ if (parameterMapping.getMode() == ParameterMode.OUT)
/* */ continue;
/* 64 */ String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
/* */ Object value;
/* */ Object value;
/* 65 */ if (this.boundSql.hasAdditionalParamete
98af
r(propertyName)) {
/* 66 */ value = this.boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object value;
/* 67 */ if (this.parameterObject == null) {
/* 68 */ value = null;
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object value;
/* 69 */ if (this.typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(this.parameterObject.getClass()))
/* 70 */ value = this.parameterObject;
/* */ else
/* 72 */ value = (metaObject == null) ? null : metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* 74 */ TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
/* 75 */ JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
/* 76 */ if ((value == null) && (jdbcType == null)) jdbcType = this.configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
/* 77 */ typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */ }它从patameterObject中去参数,然后使用typeHandler进行参数处理。
1.2.4 ResultHandler结果处理器
Mybatis提供了一个实现类DefaultResultHandler
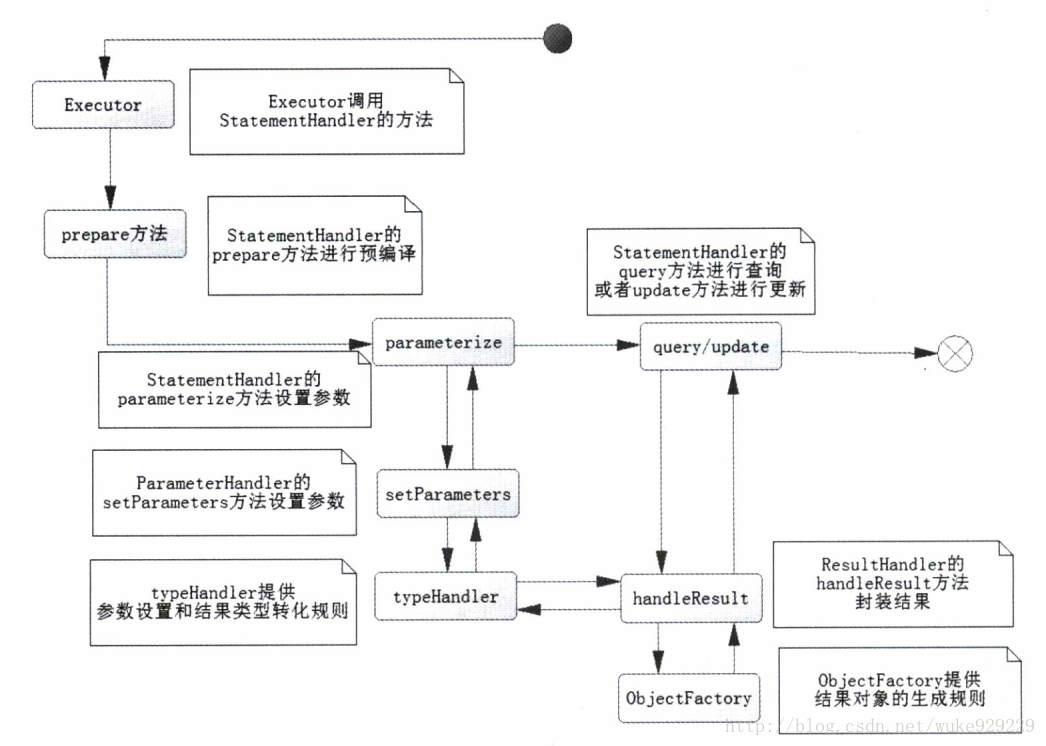
SqlSession内部运行图如上
SqlSession通过Executor创建StatementHandler来运行,而StatementHandler要经过下面三步:
① prepared预编译SQL
② parameterize设置参数
③ 执行SQL
其中parameterize是调用parameterHandler的方法去执行的,参数类型是通过typeHandler去处理的。
1.1 Mapper的动态代理
1.1.1 Mapper映射是通过动态代理来实现的,我们来看下MapperProxyFactory部分源码:
public class MapperProxyFactory<T>
/* */ {
/* */ private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
/* 28 */ private Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap();
/* */
/* */ public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
/* 31 */ this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
/* 35 */ return this.mapperInterface;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
/* 39 */ return this.methodCache;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy)
/* */ {
/* 44 */ return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { this.mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
/* 48 */ MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this.mapperInterface, this.methodCache);
/* 49 */ return newInstance(mapperProxy);
/* */ }
/* */ }
可以看到动态代理对接口的绑定,他的作用就是生成动态代理对象,而代理的方法则被放到了MapperProxy中;
1.1.2 查看MapperProxy的部分源码:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
/* 39 */ if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
/* 40 */ return method.invoke(this, args);
/* */ }
/* 42 */ MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
/* 43 */ return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
/* 47 */ MapperMethod mapperMethod = (MapperMethod)this.methodCache.get(method);
/* 48 */ if (mapperMethod == null) {
/* 49 */ mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration());
/* 50 */ this.methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
/* */ }
/* 52 */ return mapperMethod;
/* */ }一旦mapper是个代理对象,那么它会调用invoke方法,首先判断他是否是一个类,若不是则会生成MapperMethod对象,他是通过cachedMapperMethod方法初始化,然后执行execute方法把sqlSession和当前运行参数传
4000
入。
再看execute方法里面做了什么:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args)
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 44 */ if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == this.command.getType()) {
/* 45 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* 46 */ result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 47 */ if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == this.command.getType()) {
/* 48 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* 49 */ result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 50 */ if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == this.command.getType()) {
/* 51 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* 52 */ result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 53 */ if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == this.command.getType())
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 54 */ if ((this.method.returnsVoid()) && (this.method.hasResultHandler())) {
/* 55 */ executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
/* 56 */ result = null;
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 57 */ if (this.method.returnsMany()) {
/* 58 */ result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object result;
/* 59 */ if (this.method.returnsMap()) {
/* 60 */ result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
/* */ } else {
/* 62 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* 63 */ result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param); } }
/* */ }
/* */ } else {
/* 66 */ throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */ Object result;
/* 68 */ if ((result == null) && (this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive()) && (!(this.method.returnsVoid()))) {
/* 69 */ throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");
/* */ }
/* */
/* 72 */ return result;
/* */ }重点关注红色的方法executeForMany:
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args)
/* */ {
/* 109 */ Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
/* */ List result;
/* */ List result;
/* 110 */ if (this.method.hasRowBounds()) {
/* 111 */ RowBounds rowBounds = this.method.extractRowBounds(args);
/* 112 */ result = sqlSession.selectList(this.command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
/* */ } else {
/* 114 */ result = sqlSession.selectList(this.command.getName(), param);
/* */ }
/* */
/* 117 */ if (!(this.method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass()))) {
/* 118 */ if (this.method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
/* 119 */ return convertToArray(result);
/* */ }
/* 121 */ return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
/* */ }
/* */
/* 124 */ return result;
/* */ }MapperMethod采用命令模式,根据上下文进行跳转,它可跳转到许多方法中,其中executeForMany方法实际就是通过sqlSession对象去运行SQL
映射器其实就是一个动态代理对象,进入到MapperMethod的execute方法中,经过判断就进入SqlSession的增删改查等方法,接下来会介绍这些方法如何执行。
1.2 SqlSession下的四大对象
Mapper执行的过程是通过Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler和ResultHandler来完成数据库的操作和返回结果。
Executor代表执行器,他来调度StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultHandler等来执行SQL;
StatementHandler的作用是使用数据库的statement执行操作,是四大对象的核心,起一个承上启下的作用;
ParameterHandler用来处理SQL的参数;
ResultHandler对结果集进行封装返回。
1.2.1 Executor执行器
Executor是真正执行Java与数据库交互的东西,在Mybatis中有三种执行器,默认是SimpleExecutor简易执行器
SimpleExecutor源码:
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor
/* */ {
/* */ public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction)
/* */ {
/* 36 */ super(configuration, transaction);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
/* 40 */ Statement stmt = null;
/* */ try {
/* 42 */ Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
/* 43 */ StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
/* 44 */ stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
/* 45 */ int i = handler.update(stmt);
/* */
/* 47 */ return i; } finally { closeStatement(stmt);
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
/* 52 */ Statement stmt = null;
/* */ try {
/* 54 */ Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
/* 55 */ StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 56 */ stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
/* 57 */ List localList = handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
/* */
/* 59 */ return localList; } finally { closeStatement(stmt);
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
/* 64 */ return Collections.emptyList();
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException
/* */ {
/* 69 */ Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
/* 70 */ Statement stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
/* 71 */ handler.parameterize(stmt);
/* 72 */ return stmt;
/* */ }
/* */ }Mybatis利用Configuration来构建StatementHandler,然后在preparedStatement方法中初始化参数,它调用了StatementHandler
的prepare方法进行预编译和基础设置,然后通过StatementHandler的parameterize来设置参数并执行,resultHandler在组装结果返回。
我们能看出其中的重点是StatementHandler;
1.2.2 StatementHandler数据库会话器
Mybatis通过RoutingStatementHandler来获取实际使用的handler:
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
/* */ {
/* 37 */ switch (1.$SwitchMap$org$apache$ibatis$mapping$StatementType[ms.getStatementType().ordinal()])
/* */ {
/* */ case 1:
/* 39 */ this.delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 40 */ break;
/* */ case 2:
/* 42 */ this.delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 43 */ break;
/* */ case 3:
/* 45 */ this.delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
/* 46 */ break;
/* */ default:
/* 48 */ throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
/* */ }
/* */ }其中使用了适配模式,我们常用的是PreparedStatementHandler,其中主要的三个方法名为prepare、parameterize、query
public Statement prepare(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
/* 79 */ ErrorContext.instance().sql(this.boundSql.getSql());
/* 80 */ Statement statement = null;
/* */ try {
/* 82 */ statement = instantiateStatement(connection);
/* 83 */ setStatementTimeout(statement);
/* 84 */ setFetchSize(statement);
/* 85 */ return statement;
/* */ } catch (SQLException e) {
/* 87 */ closeStatement(statement);
/* 88 */ throw e;
/* */ } catch (Exception e) {
/* 90 */ closeStatement(statement);
/* 91 */ throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e);
/* */ }
/* */ }instantiateStatement()方法是对SQL进行预编译,然后Eexcutor会调用parameterize方法设置参数
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException
/* */ {
/* 68 */ String sql = this.boundSql.getSql();
/* 69 */ statement.execute(sql);
/* 70 */ return this.resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(statement);
/* */ }由于执行前参数和SQL都被prepare方法预编译了,参数也在parameterize方法设置了,所以现在只需要执行SQL返回结果即可。
整个流程:
Executor会先调用StatementHandler的prepare方法预编译SQL语句,外加一些基本运行参数,然后调用parameterize方法
启用ParameterHandler设置参数,完成预编译,跟着执行查询,通过resultSetHandler封装结果返回给调用者、
1.2.3
ParameterHandler参数处理器
MyBatis为ParameterHandler提供了一个DefaultParameterHandler实现类。其中部分源码:
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
/* 56 */ ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(this.mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
/* 57 */ List parameterMappings = this.boundSql.getParameterMappings();
/* 58 */ if (parameterMappings != null) {
/* 59 */ MetaObject metaObject = (this.parameterObject == null) ? null : this.configuration.newMetaObject(this.parameterObject);
/* 60 */ for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); ++i) {
/* 61 */ ParameterMapping parameterMapping = (ParameterMapping)parameterMappings.get(i);
/* 62 */ if (parameterMapping.getMode() == ParameterMode.OUT)
/* */ continue;
/* 64 */ String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
/* */ Object value;
/* */ Object value;
/* 65 */ if (this.boundSql.hasAdditionalParamete
98af
r(propertyName)) {
/* 66 */ value = this.boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object value;
/* 67 */ if (this.parameterObject == null) {
/* 68 */ value = null;
/* */ }
/* */ else
/* */ {
/* */ Object value;
/* 69 */ if (this.typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(this.parameterObject.getClass()))
/* 70 */ value = this.parameterObject;
/* */ else
/* 72 */ value = (metaObject == null) ? null : metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* 74 */ TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
/* 75 */ JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
/* 76 */ if ((value == null) && (jdbcType == null)) jdbcType = this.configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
/* 77 */ typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */ }它从patameterObject中去参数,然后使用typeHandler进行参数处理。
1.2.4 ResultHandler结果处理器
Mybatis提供了一个实现类DefaultResultHandler

SqlSession内部运行图如上
SqlSession通过Executor创建StatementHandler来运行,而StatementHandler要经过下面三步:
① prepared预编译SQL
② parameterize设置参数
③ 执行SQL
其中parameterize是调用parameterHandler的方法去执行的,参数类型是通过typeHandler去处理的。
相关文章推荐
- MyBatis框架原理2:SqlSession运行过程
- mybatis底层原理学习(一):SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession的创建过程
- Mybatis的SqlSession运行原理
- MyBatis 动态 SQL 底层原理分析
- MyBATIS原理第三篇: SqlSession下的四大对象之一——执行器(executor)
- MyBatis动态SQL底层原理分析
- 深入理解mybatis原理, Mybatis初始化SqlSessionFactory机制详解
- mybatis原理解析---SqlSession运行过程(下)
- mybatis源码分析——SqlSessionFactory实例的产生过程
- Mybatis底层原理学习(二):从源码角度分析一次查询操作过程
- MyBatis动态SQL底层原理分析
- mybatis源码解析(三)-SqlSession.selectOne类似方法调用过程
- mybatis源码学习之执行过程分析(1)——SqlSessionFactory及SqlSession的创建
- Mybatis SqlSessionFactory创建过程
- MyBatis 构建 SqlSessionFactory 过程
- MyBatis源码分析——SqlSessionFactory实例的产生过程
- (SqlSessionTemplate和SessionFactory)sqlsession的产生过程,hibernate和mybatis的对比
- mybatis 3.4.2 启动过程-配置文件的解析与SqlSessionFactory的获得
- Spring和Mybatis整合过程中遇到的一个找不到sqlSessionFactory或sqlSessionTemplate的异常
- mybatis的探索过程之SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,SqlSessionFactory,SqlSession作用域和生命周期
