Docker2 - docker 常用命令
2018-01-07 14:07
621 查看
直接输入
输入
OPTIONS 可以让用户控制容器的生命周期,并覆盖容器构建时所设定的参数。可用的 OPTIONS 参考这里 分为两类:
设置运行方式:
容器默认前台执行,加上
设置containerID;
设置网络参数;
设置容器的CPU和内存参数;
设置权限和LXC参数;
设置镜像的默认资源,也就是说用户可以使用该命令来覆盖在镜像构建时的一些默认配置。
Docker默认会挂载所有标准数据流,可以单独指定挂载哪个标准流。
要进行交互式操作(例如 Shell 脚本),必须使用
通过管道同容器进行交互,或只执行一次命令时,就不需要使用
命名:
镜像名或镜像名加版本号: ·Image[:tag]·
PID
为容器命名可以通过三种方式:UUID 长命名(”f78375b1c487e03c9438c729345e54db9d20cfa2ac1fc349”),UUID 短命名(”f78375b1c487”) 或 名字Name (“evil_ptolemy”)。UUID 标示是由守护进程 Docker deamon 生成的。没有指定
有自动化的需求时,你可以将 containerID 输出到指定的文件中(PIDfile),类似于某些应用程序将自身ID输出到文件中,方便后续脚本操作。
镜像来自同一个仓库时可以通过 TAG 区分。
/etc/hosts 文件中会包含容器的hostname信息,可以用
–rm=false:容器退出时,自动清理(不能和 -d 参数一同出现)
例如:
启动
交互式启动 ubuntu 的 lastest 版本,只打开标准输入流和标准输出流。
如果没有指定
关于镜像,可以在 官方镜像仓库 中选择,也可以用
例如:
从镜像仓库下载
查找镜像。
查看镜像的历史版本。
查看所有已安装镜像的列表。
RESOSITORY 列表示镜像所在仓库。
TAG 列表示镜像的版本标记。
将镜像推送到 registry。
查看 Docker 命令 info 的说明。
停止有名字的容器。
和 kill 命令的区别:stop 发送信号给容器,并等待容器停止。kill 命令则直接停止容器。
重新启动容器。
完全移除容器,需要先将该容器停止,然后才能移除。
将容器的状态保存为镜像。
查看容器的日志。
每个容器都可以在执行
也可以通过 shell 实现(未验证):
通过 Dockerfile 构建镜像。
可用的 options 有:
–rm=true表示构建成功后,移除所有中间容器
–no-cache=false表示在构建过程中不使用缓存
与运行中的容器交互。退出容器可以通过 3 种方式实现:
Ctrl+P 然后 Ctrl+Q 使容器后台运行
Ctrl+C 或 exit 命令直接退出
Ctrl+\ 退出并显示堆栈信息(stack trace)
列出容器内发生变化的文件和目录。包括添加(A-add)、删除(D-delete)、修改(C-change)。
docker命令并回车可以看到所有可用命令和概述(win10 的 PowerShell 环境):
[root@VM_157_18_centos tmp]# docker
Usage: docker COMMAND
A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default
"C:\Users\kika\.docker")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
--help Print usage
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level
("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal")
(default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default
"C:\Users\kika\.docker\ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default
"C:\Users\kika\.docker\cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default
"C:\Users\kika\.docker\key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
checkpoint Manage checkpoints
config Manage Docker configs
container Manage containers
image Manage images
network Manage networks
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
volume Manage volumes
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
deploy Deploy a new stack or update an existing stack
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.输入
docker COMMAND --help可以查到指定命令的文档:
[root@VM_157_18_centos tmp]# docker images --help Usage: docker images [OPTIONS] [REPOSITORY[:TAG]] List images Options: -a, --all Show all images (default hides intermediate images) --digests Show digests -f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided --format string Pretty-print images using a Go template --no-trunc Don't truncate output -q, --quiet Only show numeric IDs
1. run 运行容器
docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE[:TAG] [COMMAND] [ARG...]
OPTIONS 可以让用户控制容器的生命周期,并覆盖容器构建时所设定的参数。可用的 OPTIONS 参考这里 分为两类:
设置运行方式:
容器默认前台执行,加上
-d参数后,容器后台运行
设置containerID;
设置网络参数;
设置容器的CPU和内存参数;
设置权限和LXC参数;
设置镜像的默认资源,也就是说用户可以使用该命令来覆盖在镜像构建时的一些默认配置。
后台模式 -d(后台模式的容器未必会长久运行。容器运行多久和 docker run 指定的命令有关,和 -d 参数无关。)
-d=true或
-d参数使容器运行在后台模式,此时只能通过网络或者共享卷组来进行交互。因为容器不再监听你执行
docker run的这个终端窗口。可以通过执行
docker attach重新进入容器。后台模式下运行的容器,不能用
--rm选项的删除。
docker run -d=true ubuntu
docker attach ubuntu
前台模式
不指定-d参数就是前台模式,Docker 可以吧当前的命令行窗口附着到容器的STDIN、STDOUT 和 STDERR (标准输入流,标准输出流和标准错误流)中。当前窗口可以配置为容器窗口的映射。
-a=[]:单独指定挂载哪个标准流,STDIN、STDOUT 和 STDERR 。默认挂载所有标准流 -t=false:打开容器的 TTY 命令行终端。通过管道同容器交互时,不需要使用-t参数 -i=false:STDIN 保持打开状态,即使容器在后台运行,用于交互式操作如Shell脚本
Docker默认会挂载所有标准数据流,可以单独指定挂载哪个标准流。
要进行交互式操作(例如 Shell 脚本),必须使用
-i -t参数同容器进行数据交互:
docker run -a stdin -a stdout -i -t ubuntu /bin/bash
通过管道同容器进行交互,或只执行一次命令时,就不需要使用
-t参数:
echo test | docker run -i busybox cat
docker run -i ubuntu echo "hello world"
容器识别
容器识别有三种方式:命名:
--name
镜像名或镜像名加版本号: ·Image[:tag]·
PID
为容器命名可以通过三种方式:UUID 长命名(”f78375b1c487e03c9438c729345e54db9d20cfa2ac1fc349”),UUID 短命名(”f78375b1c487”) 或 名字Name (“evil_ptolemy”)。UUID 标示是由守护进程 Docker deamon 生成的。没有指定
--name时默认用一个随机字符串 UUID 做容器名。
有自动化的需求时,你可以将 containerID 输出到指定的文件中(PIDfile),类似于某些应用程序将自身ID输出到文件中,方便后续脚本操作。
--cidfile=""
镜像来自同一个仓库时可以通过 TAG 区分。
docker run ubuntu:14.04
IPC 设置
默认情况下,所有容器都开启了 IPC 命名空间。--ipc:为容器设置 IPC 命名空间的模式,有以下两个可选值:
container:<name|id>: 复用另一个容器的 IPC 命名空间
host: 在容器内部使用宿主机的 IPC 命名空间
Network 设置
默认情况下,所有的容器都开启了网络接口,可以接受任何外部的数据请求。--dns=[]:为容器配置 DNS 服务器。容器默认使用主机的 DNS 设置 --net="bridge":设置容器的网络模式,有四种 --add-host="":在配置文件/etc/hosts 中增加一条数据 (host:IP) --mac-address="":设置容器的 MAC 地址
--net可用的四种网络模式:
bridge:默认配置,通过 veth 接口来连接容器。主机上会创建 docker0 网络接口,同时会针对容器创建一对veth接口。其中一个veth接口是在主机充当网卡桥接作用,另外一个veth接口存在于容器的命名空间中,并且指向容器的loopback。Docker会自动给这个容器分配一个IP,并且将容器内的数据通过桥接转发到外部。。
none:关闭网络接口,此时只能通过标准流或文件卷来完成 I/O 操作。
container:<name|id>:使用另外一个容器的网络堆栈信息。
host:使用宿主机的网络堆栈信息。不安全。host所有的网络接口将完全对容器开放。容器的主机名也会存在于主机的hostname中。这时,容器所有对外暴露的端口和对其它容器的连接,将完全失效。
--add-host管理/etc/hosts
/etc/hosts 文件中会包含容器的hostname信息,可以用
--add-host参数来动态添加 /etc/hosts 中的数据。
$ /docker run -ti --add-host db-static:86.75.30.9 ubuntu cat /etc/hosts 172.17.0.22 09d03f76bf2c fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback 86.75.30.9 db-static
Clean up (–rm) 容器结束时自动清理
默认情况下,容器在退出时,文件系统会保存下来,这样一方面调试会方便些,因为你可以通过查看日志等方式来确定最终状态。另外一方面,你也可以保存容器所产生的数据。需要短暂的运行一个容器时,并且这些数据不需要保存,你可能就希望Docker能在容器结束时自动清理其所产生的数据,就需要--rm参数。 注意:–rm 和 -d 不能共用!
–rm=false:容器退出时,自动清理(不能和 -d 参数一同出现)
ENV (environment variables) 环境变量
-e:设定环境变量,可以覆盖在 Dockerfile 中通过 ENV 设定的环境变量。docker run -e "deep=purple" ubuntu
例如:
docker run php:7.0.8-fpm-alpine
启动
TAG为
7.0.8-fpm-alpine的 php 镜像。如果还没有安装镜像,则首先自动安装。
docker run -a stdin -a stdout -i -t ubuntu /bin/bash
交互式启动 ubuntu 的 lastest 版本,只打开标准输入流和标准输出流。
如果没有指定
TAG,则默认启动或安装
latest版本。
关于镜像,可以在 官方镜像仓库 中选择,也可以用
search命令查找。
2. pull 下载镜像
docker pull REPOSITORY:TAG
例如:
docker pull busybox
从镜像仓库下载
latest版本的
busybox镜像到本地 Docker。
3. search 查找镜像
docker search (image-name)
查找镜像。
4. history 查看镜像的历史版本
docker history (image_name)
查看镜像的历史版本。
5. images 查看已安装镜像
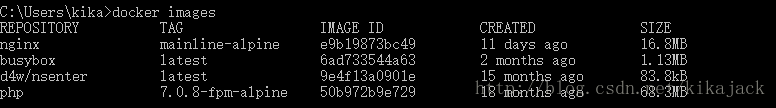
docker images
查看所有已安装镜像的列表。
RESOSITORY 列表示镜像所在仓库。
TAG 列表示镜像的版本标记。

6. push 将镜像推送到 registry
docker push (user)/(repo_name)将镜像推送到 registry。
7. help 帮助
docker info --help
查看 Docker 命令 info 的说明。
8. stop 停止容器
docker stop $sample_job
停止有名字的容器。
和 kill 命令的区别:stop 发送信号给容器,并等待容器停止。kill 命令则直接停止容器。
9. restart 重启容器
docker restart $sample_job
重新启动容器。
10. rm 移除容器(需要先停止)
docker rm $sample_job
完全移除容器,需要先将该容器停止,然后才能移除。
11. commit 保存容器状态为镜像
docker commit $sample_job job1
将容器的状态保存为镜像。
12. logs 查看容器日志
docker logs [-f] [-t] [--tail] CONTAINER
-f, --follow:跟踪日志输出,用于容器一直输出日志时的查看。 --since:打印指定时间之后的日志 (例如 2013-01-02T13:23:37) 或相对时间(例如 42m 表示 42分钟) --tail:默认是 all,查看指定最后几条的日志 -t, --timestamps:显示时间戳
查看容器的日志。
每个容器都可以在执行
docker run时通过
--name your-name起名字,以方便跟踪:
docker run -d --name your-name busybox /bin/sh -c "while true; do echo Docker; sleep 1; done" docker logs your-name
也可以通过 shell 实现(未验证):
sample_job=$(docker run -d busybox /bin/sh -c "while true; do echo Docker; sleep 1; done") docker logs $sample_job
-d参数表示后台运行。
13. build 通过 Dockerfile 构建镜像
docker build [options] PATH | URL
通过 Dockerfile 构建镜像。
可用的 options 有:
–rm=true表示构建成功后,移除所有中间容器
–no-cache=false表示在构建过程中不使用缓存
14. attach 与运行中的容器交互
docker attach container
与运行中的容器交互。退出容器可以通过 3 种方式实现:
Ctrl+P 然后 Ctrl+Q 使容器后台运行
Ctrl+C 或 exit 命令直接退出
Ctrl+\ 退出并显示堆栈信息(stack trace)
15. diff 列出容器内发生变化的文件和目录
docker diff container
列出容器内发生变化的文件和目录。包括添加(A-add)、删除(D-delete)、修改(C-change)。
16. import 导入远程文件、本地文件和目录
docker import http://example.com/example.tar[/code]docker import - localfile
导入远程文件、本地文件和目录。使用HTTP的URL从远程位置导入,而本地文件或目录的导入需要使用-参数。17. export 将容器的系统文件打包成tar文件
将容器的系统文件打包成tar文件。18. cp 从容器内复制文件到指定的路径上
docker cp container:path hostpath.
从容器内复制文件到指定的路径上。19. login 登录 Docker registry 服务器
docker login [options] [server]
登录 Docker registry 服务器。20. ps 查看容器状态
docker ps [options]
-a:all,查看所有的容器,包括 stop 状态的。默认只展示运行状态的容器。
-l: latest,查看最后一个创建的容器,不管是什么运行状态。
-q:quiet,只显示容器的 ID。21. inspect 查看容器配置信息
docker inspect [options]
返回一个 JSON 文件。22. top 查看指定容器内的进程
docker top CONTAINER [ps OPTIONS]23. exec 在容器中启动新进程
docker exec [-d] [-i] [-t] CONTAINER [COMMAND] [ARG...]
相关文章推荐
- docker常用命令
- Docker_2 常用命令
- 常用Docker命令
- docker 容器管理常用命令
- 常用Docker命令
- Docker 常用命令总结 [五]
- docker常用命令
- docker常用命令操作方法
- 如何在docker中部署springboot的web应用 以及docker的常用命令大全
- docker常用命令
- docker 常用命令与常用容器(containers)环境
- docker常用命令详解
- Docker常用命令
- Docker常用命令
- Docker新手入门之九:Docker常用命令总结
- docker常用命令
- docker的常用命令
- docker常用命令
- docker 容器的常用命令操作
- docker常用命令总结
