通过debug过程分析Struts2什么时候将Action对象放入了值栈ValueStack中
2017-12-14 10:30
477 查看
问题提出:
1、Struts2框架在什么时候将Action对象放到了值栈ValueStack的栈顶了?2、在哪里设置Debug断点能够最恰当的观察到这一过程?
问题解决:
2、我们知道,在值栈ValueStack中有两个逻辑部分Map栈和对象栈ObjectStack,而Action对象是被默认放在了对象栈的栈顶的(这一点我们通过<s:debug/>标签可以在页面中看到),因此我们将该断点设置在对象栈所对应的类CompoundRoot的push方法中最合适。1、通过Debug过程来分析值栈ValueStack的变化过程:
1)当我们在CompoundRoot类的push方法中打上断点后,程序执行到此处,如下图:
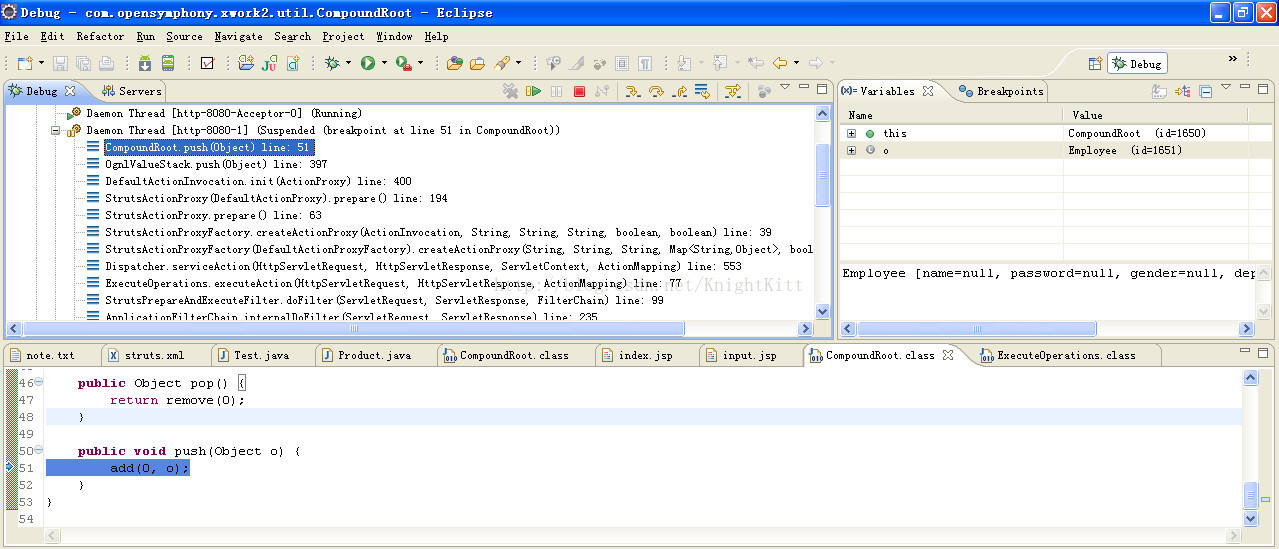
2)这时,我们从Struts2框架的入口StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter类开始分析。在Debug视图中,我们将程序定位到StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter类,如下图:
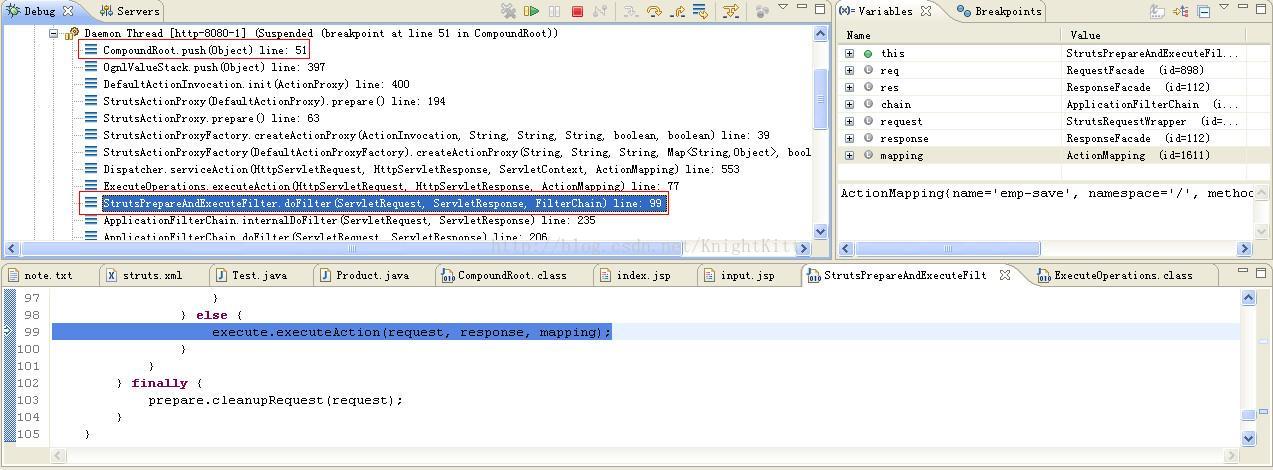
附上StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter中doFilter()方法的源代码:
[java] view
plain copy
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) {
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
} else {
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
} finally {
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}
这里我们可以看到,doFilter()方法中通过调用execute对象的executeAction()方法来执行Action,接下来我们继续看一看executeAction()方法,如下图:
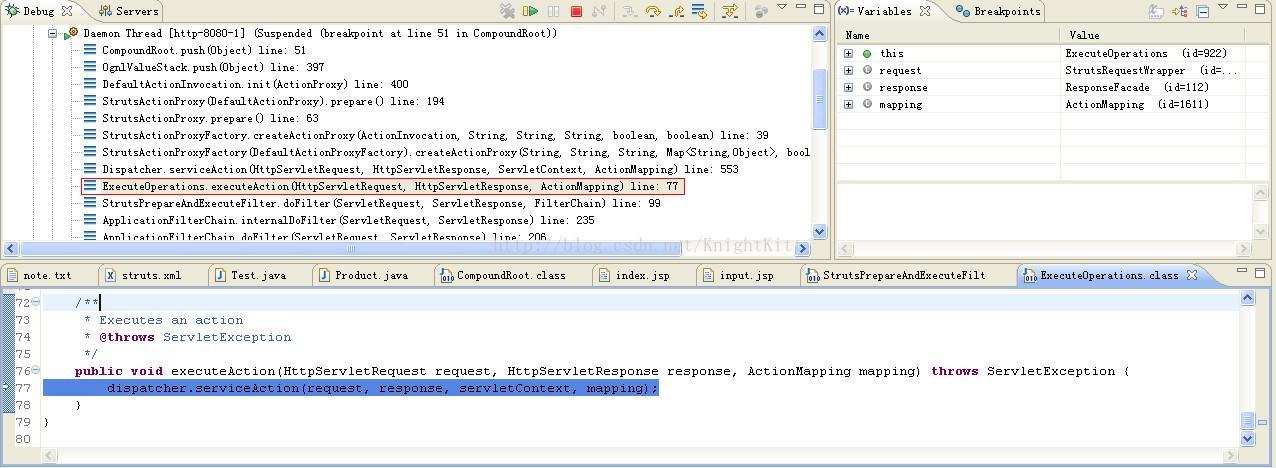
可以看出executeAction()方法中只是调用了dispatcher对象的serviceAction()方法,因此,我们再继续查看serviceAction()方法,如下图:
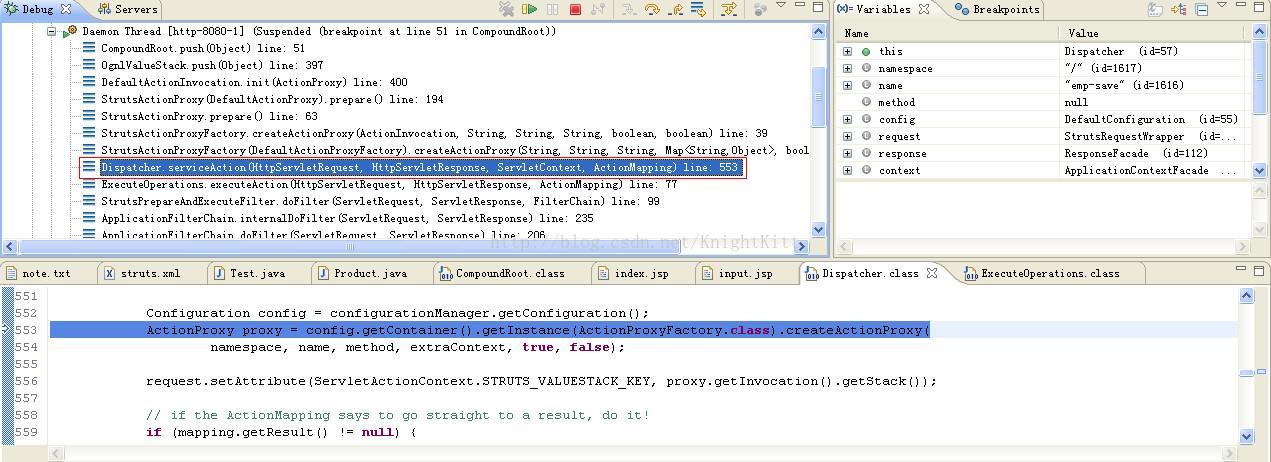
可以看到,在serviceAction()方法中实际上是创建了一个Action的代理类ActionProxy的对象,而并没有直接去执行Action。这是因为在执行Action之前Struts2还要去调用许多的拦截器,因此创建了Action的代理类。
附Dispatcher类中serviceAction()方法的源代码:
[java] view
plain copy
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context,
ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);
// If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action
ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
boolean nullStack = stack == null;
if (nullStack) {
ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext();
if (ctx != null) {
stack = ctx.getValueStack();
}
}
if (stack != null) {
extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack));
}
String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
String name = mapping.getName();
String method = mapping.getMethod();
Configuration config = configurationManager.getConfiguration();
ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
// if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it!
if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
Result result = mapping.getResult();
result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
} else {
proxy.execute();
}
// If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request
if (!nullStack) {
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack);
}
} catch (ConfigurationException e) {
// WW-2874 Only log error if in devMode
if (devMode) {
String reqStr = request.getRequestURI();
if (request.getQueryString() != null) {
reqStr = reqStr + "?" + request.getQueryString();
}
LOG.error("Could not find action or result\n" + reqStr, e);
} else {
if (LOG.isWarnEnabled()) {
LOG.warn("Could not find action or result", e);
}
}
sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (handleException || devMode) {
sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
} else {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}
继续往下进行,如下图:
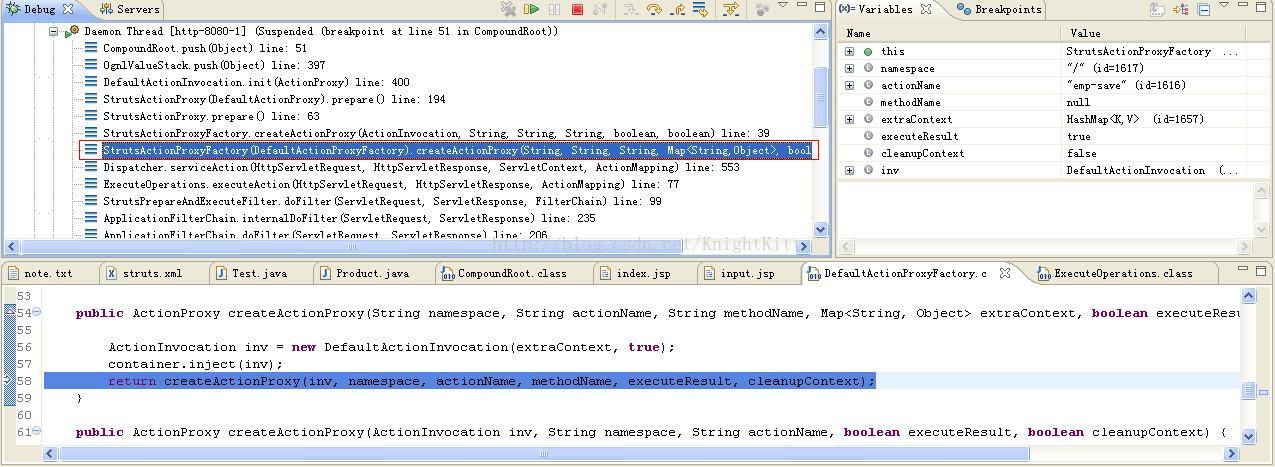
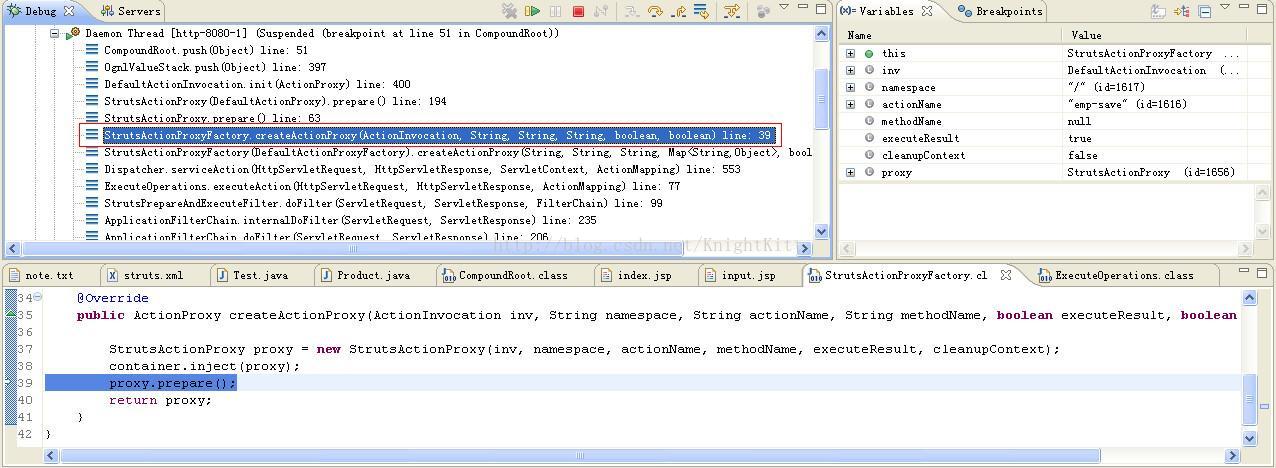
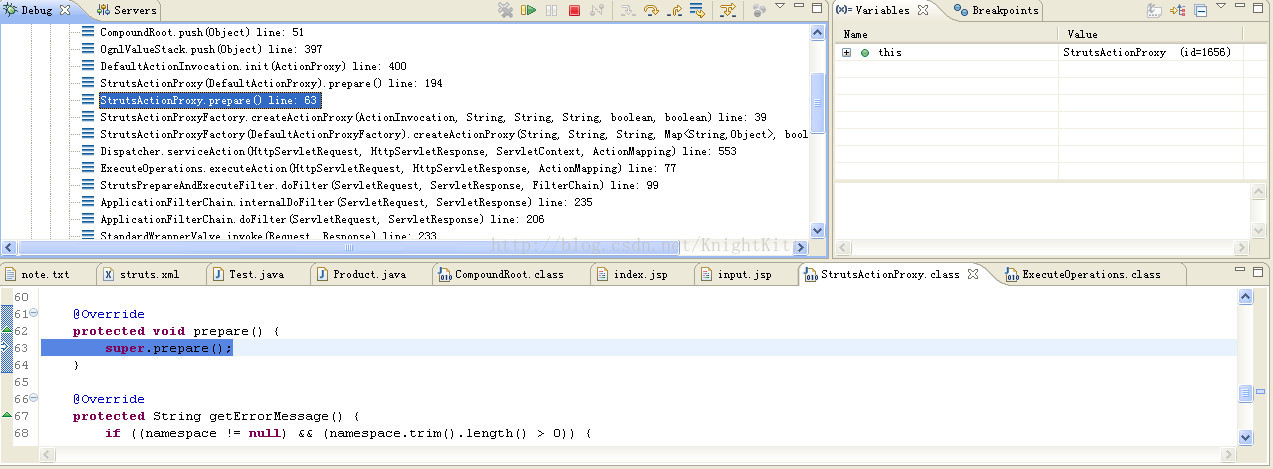
我们可以看到在上面的执行过程中,主要工作都是在创建Action的代理类对象proxy,在创建完成之后,该代理类对象proxy调用prepare()方法做了一些初始化的工作。
继续往下查看prepare()方法:
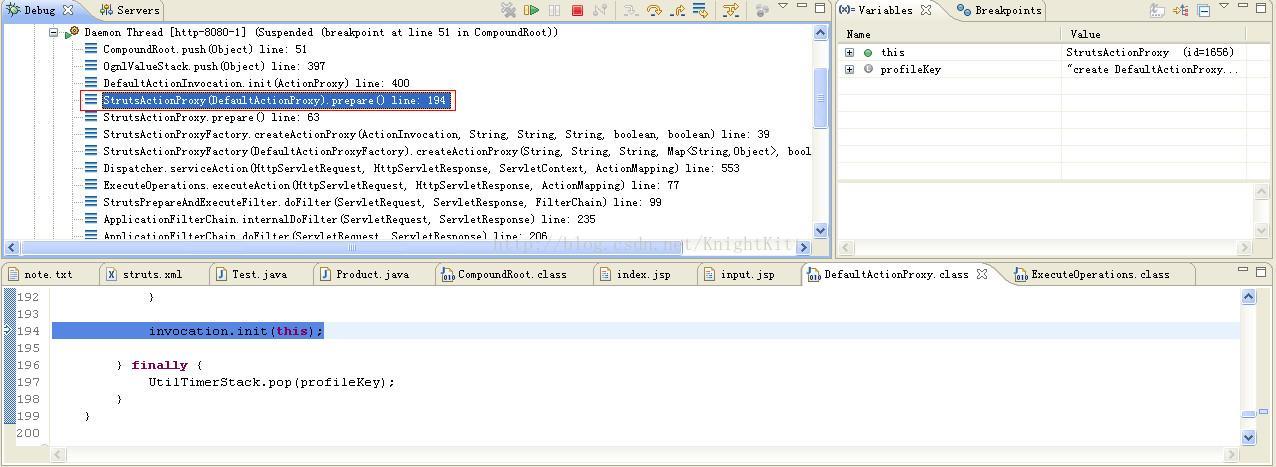
在prepare()方法(这是StrutsActionProxy的父类DefaultActionProxy的prepare()方法)中可以看到,其执行了invocation对象的init()方法,在该方法中this就是StrutsActionProxy类的对象,也即ActionProxy类的对象,就是Action的代理类。继续来看init()方法的具体实现:
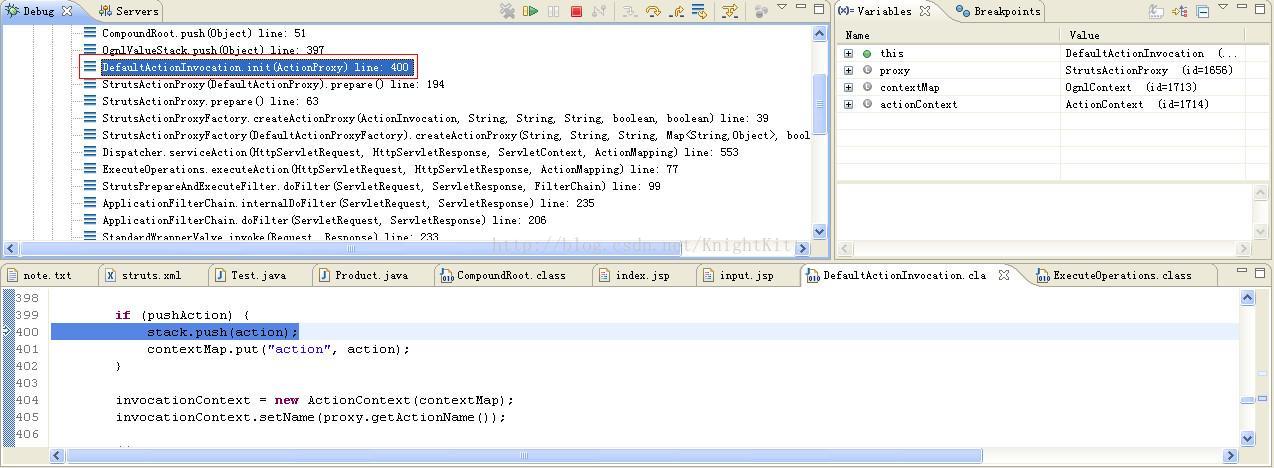
到这里我们已经能够比较清楚的看到了Struts2框架将Action对象放到值栈中。注意,这里的Action对象中的相关属性(如提交的表单中的参数)并没有被赋上值,直到真正的执行Action对象中相应的方法时,其相关属性才被赋值。
附DefaultActionInvocation类中init()方法与createAction()方法的源代码:
[java] view
plain copy
public void <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">init</span>(ActionProxy proxy) {
this.proxy = proxy;
Map<String, Object> contextMap = createContextMap();
// Setting this so that other classes, like object factories, can use the ActionProxy and other
// contextual information to operate
ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (actionContext != null) {
actionContext.setActionInvocation(this);
}
<span style="background-color: rgb(51, 255, 51);">createAction(contextMap);</span>
if (pushAction) {
<span style="background-color: rgb(51, 255, 51);">stack.push(action);</span>
<span style="background-color: rgb(51, 255, 51);">contextMap.put("action", action);</span>
}
invocationContext = new ActionContext(contextMap);
invocationContext.setName(proxy.getActionName());
// get a new List so we don't get problems with the iterator if someone changes the list
List<InterceptorMapping> interceptorList = new ArrayList<InterceptorMapping>(proxy.getConfig().getInterceptors());
interceptors = interceptorList.iterator();
}
[java] view
plain copy
protected void <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">createAction</span>(Map<String, Object> contextMap) {
// load action
String timerKey = "actionCreate: " + proxy.getActionName();
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
<span style="background-color: rgb(51, 255, 51);">action = objectFactory.buildAction(proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getNamespace(), proxy.getConfig(), contextMap);</span>
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new XWorkException("Unable to intantiate Action!", e, proxy.getConfig());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new XWorkException("Illegal access to constructor, is it public?", e, proxy.getConfig());
} catch (Exception e) {
String gripe;
if (proxy == null) {
gripe = "Whoa! No ActionProxy instance found in current ActionInvocation. This is bad ... very bad";
} else if (proxy.getConfig() == null) {
gripe = "Sheesh. Where'd that ActionProxy get to? I can't find it in the current ActionInvocation!?";
} else if (proxy.getConfig().getClassName() == null) {
gripe = "No Action defined for '" + proxy.getActionName() + "' in namespace '" + proxy.getNamespace() + "'";
} else {
gripe = "Unable to instantiate Action, " + proxy.getConfig().getClassName() + ", defined for '" + proxy.getActionName() + "' in namespace '" + proxy.getNamespace() + "'";
}
gripe += (((" -- " + e.getMessage()) != null) ? e.getMessage() : " [no message in exception]");
throw new XWorkException(gripe, e, proxy.getConfig());
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
if (actionEventListener != null) {
<span style="background-color: rgb(51, 255, 51);">action = actionEventListener.prepare(action, stack);</span>
}
}
查看值栈OgnlValueStack类的push()方法,如下图:
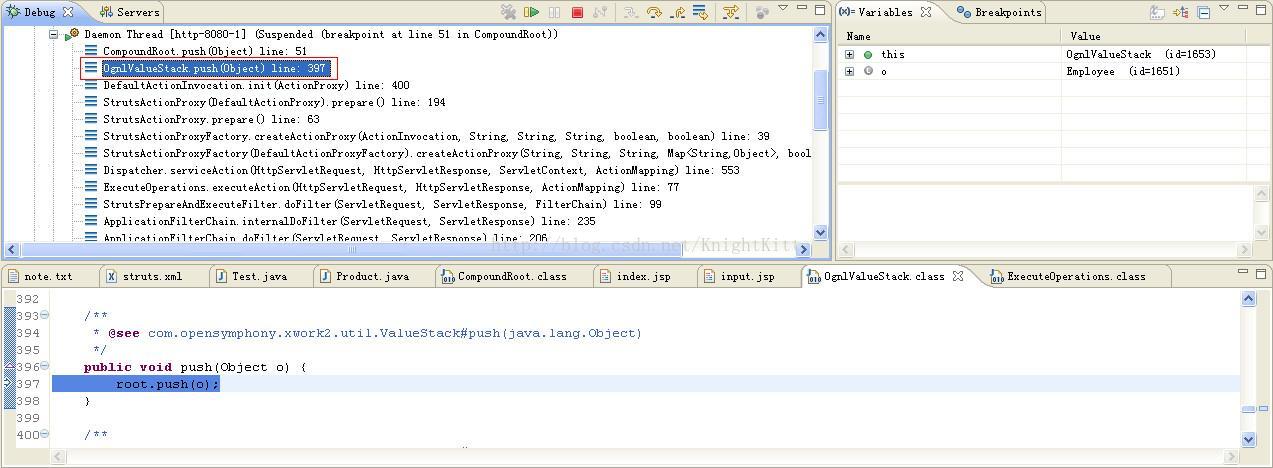
可以看到,它确实是调用了CompoundRoot对象的push()方法将Action对象放到了值栈中对象栈ObjectStack的栈顶。
收获:
1、分析问题的方法;2、通过该过程清楚了Struts2值栈的变化过程;
2、进一步学习了Eclipse的debug使用方法。
相关文章推荐
- 通过debug过程分析Struts2什么时候将Action对象放入了值栈ValueStack中
- Struts2中解耦合通过actionContext对象获取到aplication,session,request,paramter等对象
- struts2通过action返回json对象
- 通过dmesg分析linux的启动过程,几种放入dmesg文件的方法
- 通过论证:查询字段通常返回引用,该引用可以保证是原来的对象的状态的一部分。分析变量在内存中的变化过程。
- struts2的ActionContext类分析(action执行时所需对象的环境)
- Struts2 创建Action对象并放入ValueStack的时机
- 通过Android源代码分析startActivity()过程(下)
- struts2:数据校验,通过Action中的validate()方法实现校验,图解
- struts2 ActionContext获取session对象有时为null
- S5.1_Struts2_AccessWebElements action访问web对象的4种方式
- debug查看dos加载汇编源程序到内存过程分析
- ssh2 action中通过ActionContext取得HttpServletRequest对象 然后使request.getParameter("参数名")得到参数值
- Android应用程序窗口(Activity)的窗口对象(Window)的创建过程分析
- 举例分析Java对象的初始化过程
- 深入分析虚拟机在Java堆中对象分配、布局和访问的全过程
- struts2的action中获得request response session 对象
- 嵌入式软件开发培训笔记——Java第三天(方法重载、对象的构造与初始化过程分析、封装等)
- struts2请求过程源码分析(转载学习)
- struts2:数据校验,通过Action中的validate()方法实现校验,图解
