【数据结构】动态顺序表
2017-12-13 16:07
239 查看
SeqList.h
#ifndef _SEQLISTH_H_
#define _SEQLISTH_H_
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int Datatype;
typedef struct SeqList
{
Datatype* _a;
size_t _size; // 有效数据个数
size_t _capacity; // 容量
}SeqList;
void SeqPrint(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqInit(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqDestory(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqPushBack(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x);
void SeqPopBack(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqPushFront(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x);
void SeqPopFront(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqInsert(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos, Datatype x);
void SeqErase(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos);
int SeqFind(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x);
void SeqAt(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos, Datatype x);
void BubbleSort(SeqList* pSeq);
void SelectSort(SeqList* pSeq);
int BinarySearch(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x);
void test1();
#endif
SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h"
void SeqPrint(SeqList* pSeq){
int i,n = pSeq->_size;
assert(pSeq);
printf("已有数据%d 个:",pSeq->_size);
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
printf("%d ",pSeq->_a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("当前容量:%d \n",pSeq->_capacity);
}
void SeqInit(SeqList* pSeq){
assert(pSeq);
pSeq->_size=0;
pSeq->_capacity=5;
pSeq->_a=(Datatype *)malloc(sizeof(Datatype)*pSeq->_capacity);
}
void CheckCapacity(SeqList *pSeq) {
assert(pSeq);
if(pSeq->_capacity==pSeq->_size){
pSeq->_a=(Datatype *)realloc(pSeq->_a,sizeof(Datatype)*
(pSeq->_capacity+5));
pSeq->_capacity+=5;
}
}
void SeqDestory(SeqList *pSeq) {
assert(pSeq);
if (pSeq->_a)
free(pSeq->_a);
pSeq->_a = NULL;
pSeq->_size = 0;
pSeq->_capacity = 0;
}
void SeqPushBack(SeqList *pSeq, Datatype x) {
assert(pSeq);
CheckCapacity(pSeq);
pSeq->_a[pSeq->_size]=x;
++pSeq->_size;
}
void SeqPopBack(SeqList *pSeq) {
assert(pSeq);
if(pSeq->_size>0)
--pSeq->_size;
}
void SeqPushFront(SeqList *pSeq, Datatype x) {
int i=pSeq->_size;
assert(pSeq);
CheckCapacity(pSeq);
for(i;i>0;i--){
pSeq->_a[i]=pSeq->_a[i-1];
}
pSeq->_a[0]=x;
++pSeq->_size;
}
void SeqPopFront(SeqList *pSeq) {
int i=0;
assert(pSeq);
if(pSeq->_si
4000
ze>0){
for(i;i<pSeq->_size-1;i++){
pSeq->_a[i]=pSeq->_a[i+1];
}
--pSeq->_size;
}
}
void SeqInsert(SeqList *pSeq, size_t pos, Datatype x) {
size_t i=pSeq->_size;
assert(pSeq&&pos<=pSeq->_size);
CheckCapacity(pSeq);
for(i;i>pos;i--){
pSeq->_a[i]=pSeq->_a[i-1];
}
pSeq->_a[pos]=x;
++pSeq->_size;
}
void SeqErase(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos) {
int i=pos;
assert(pSeq);
if(pSeq->_size>0&&pos<pSeq->_size){
for(i;i<pSeq->_size;i++){
pSeq->_a[i]=pSeq->_a[i+1];
}
--pSeq->_size;
}
}
int SeqFind(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x){
int i=0;
assert(pSeq);
while(i<pSeq->_size){
if(pSeq->_a[i]==x)
return i;
i++;
}
return -1;
}
void SeqAt(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos, Datatype x){
assert(pSeq);
if(pos<pSeq->_size)
pSeq->_a[pos]=x;
}
void BubbleSort(SeqList* pSeq){
int i,j;
int flag = 1; //优化冒泡排序
for(i=0;i<pSeq->_size-1;i++){
flag = 1;
for(j=0;j<pSeq->_size-i-1;j++){
if(pSeq->_a[j]>pSeq->_a[j+1]){
pSeq->_a[j]^=pSeq->_a[j+1];
pSeq->_a[j+1]^=pSeq->_a[j];
pSeq->_a[j]^=pSeq->_a[j+1];
flag = 0;
}
}
if(1==flag){ //flag==1说明没有进行替换,排序已经正确
return;
}
}
}
void SelectSort(SeqList* pSeq){ //选择排序
int i,j,pos,min;
for(i=0;i<pSeq->_size-1;i++){
min=pSeq->_a[i];
for(j=i+1;j<pSeq->_size;j++){
if(min>pSeq->_a[j]){
min=pSeq->_a[j];
pos=j;
}
}
pSeq->_a[i]^=pSeq->_a[pos];
pSeq->_a[pos]^=pSeq->_a[i];
pSeq->_a[i]^=pSeq->_a[pos];
}
}
int BinarySearch(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x){ //二分查找
int left=0,right=pSeq->_size-1,mid;
while(left<=right){
mid=left+((right-left)>>1);
if(pSeq->_a[mid]>x){
right=mid-1;
}
else if(pSeq->_a[mid]<x){
left=mid+1;
}
else{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
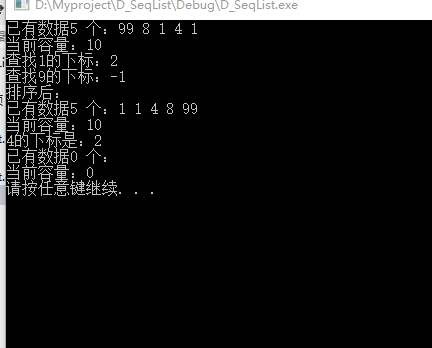
void test1(){
SeqList seq;
SeqInit(&seq);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 1);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 2);
SeqPopBack(&seq);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 3);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 4);
SeqPushFront(&seq,5);
SeqPushFront(&seq,6);
SeqPopFront(&seq);
SeqPopFront(&seq);
SeqInsert(&seq, 0, 8);
SeqInsert(&seq, 1, 8);
SeqInsert(&seq, 1, 8);
SeqErase(&seq, 2);
SeqErase(&seq, 3);
SeqAt(&seq, 0, 99);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 1);
SeqPrint(&seq);
printf("查找1的下标:%d\n",SeqFind(&seq, 1));
printf("查找9的下标:%d\n",SeqFind(&seq, 9));
printf("排序后:\n");
// BubbleSort(&seq); //冒泡排序
SelectSort(&seq); //选择排序
SeqPrint(&seq);
printf("4的下标是:%d\n",BinarySearch(&seq, 4));
SeqDestory(&seq);//清空顺序表
SeqPrint(&seq);
}
mian.c
#include"SeqList.h"
int main(){
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#ifndef _SEQLISTH_H_
#define _SEQLISTH_H_
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int Datatype;
typedef struct SeqList
{
Datatype* _a;
size_t _size; // 有效数据个数
size_t _capacity; // 容量
}SeqList;
void SeqPrint(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqInit(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqDestory(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqPushBack(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x);
void SeqPopBack(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqPushFront(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x);
void SeqPopFront(SeqList* pSeq);
void SeqInsert(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos, Datatype x);
void SeqErase(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos);
int SeqFind(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x);
void SeqAt(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos, Datatype x);
void BubbleSort(SeqList* pSeq);
void SelectSort(SeqList* pSeq);
int BinarySearch(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x);
void test1();
#endif
SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h"
void SeqPrint(SeqList* pSeq){
int i,n = pSeq->_size;
assert(pSeq);
printf("已有数据%d 个:",pSeq->_size);
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
printf("%d ",pSeq->_a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("当前容量:%d \n",pSeq->_capacity);
}
void SeqInit(SeqList* pSeq){
assert(pSeq);
pSeq->_size=0;
pSeq->_capacity=5;
pSeq->_a=(Datatype *)malloc(sizeof(Datatype)*pSeq->_capacity);
}
void CheckCapacity(SeqList *pSeq) {
assert(pSeq);
if(pSeq->_capacity==pSeq->_size){
pSeq->_a=(Datatype *)realloc(pSeq->_a,sizeof(Datatype)*
(pSeq->_capacity+5));
pSeq->_capacity+=5;
}
}
void SeqDestory(SeqList *pSeq) {
assert(pSeq);
if (pSeq->_a)
free(pSeq->_a);
pSeq->_a = NULL;
pSeq->_size = 0;
pSeq->_capacity = 0;
}
void SeqPushBack(SeqList *pSeq, Datatype x) {
assert(pSeq);
CheckCapacity(pSeq);
pSeq->_a[pSeq->_size]=x;
++pSeq->_size;
}
void SeqPopBack(SeqList *pSeq) {
assert(pSeq);
if(pSeq->_size>0)
--pSeq->_size;
}
void SeqPushFront(SeqList *pSeq, Datatype x) {
int i=pSeq->_size;
assert(pSeq);
CheckCapacity(pSeq);
for(i;i>0;i--){
pSeq->_a[i]=pSeq->_a[i-1];
}
pSeq->_a[0]=x;
++pSeq->_size;
}
void SeqPopFront(SeqList *pSeq) {
int i=0;
assert(pSeq);
if(pSeq->_si
4000
ze>0){
for(i;i<pSeq->_size-1;i++){
pSeq->_a[i]=pSeq->_a[i+1];
}
--pSeq->_size;
}
}
void SeqInsert(SeqList *pSeq, size_t pos, Datatype x) {
size_t i=pSeq->_size;
assert(pSeq&&pos<=pSeq->_size);
CheckCapacity(pSeq);
for(i;i>pos;i--){
pSeq->_a[i]=pSeq->_a[i-1];
}
pSeq->_a[pos]=x;
++pSeq->_size;
}
void SeqErase(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos) {
int i=pos;
assert(pSeq);
if(pSeq->_size>0&&pos<pSeq->_size){
for(i;i<pSeq->_size;i++){
pSeq->_a[i]=pSeq->_a[i+1];
}
--pSeq->_size;
}
}
int SeqFind(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x){
int i=0;
assert(pSeq);
while(i<pSeq->_size){
if(pSeq->_a[i]==x)
return i;
i++;
}
return -1;
}
void SeqAt(SeqList* pSeq, size_t pos, Datatype x){
assert(pSeq);
if(pos<pSeq->_size)
pSeq->_a[pos]=x;
}
void BubbleSort(SeqList* pSeq){
int i,j;
int flag = 1; //优化冒泡排序
for(i=0;i<pSeq->_size-1;i++){
flag = 1;
for(j=0;j<pSeq->_size-i-1;j++){
if(pSeq->_a[j]>pSeq->_a[j+1]){
pSeq->_a[j]^=pSeq->_a[j+1];
pSeq->_a[j+1]^=pSeq->_a[j];
pSeq->_a[j]^=pSeq->_a[j+1];
flag = 0;
}
}
if(1==flag){ //flag==1说明没有进行替换,排序已经正确
return;
}
}
}
void SelectSort(SeqList* pSeq){ //选择排序
int i,j,pos,min;
for(i=0;i<pSeq->_size-1;i++){
min=pSeq->_a[i];
for(j=i+1;j<pSeq->_size;j++){
if(min>pSeq->_a[j]){
min=pSeq->_a[j];
pos=j;
}
}
pSeq->_a[i]^=pSeq->_a[pos];
pSeq->_a[pos]^=pSeq->_a[i];
pSeq->_a[i]^=pSeq->_a[pos];
}
}
int BinarySearch(SeqList* pSeq, Datatype x){ //二分查找
int left=0,right=pSeq->_size-1,mid;
while(left<=right){
mid=left+((right-left)>>1);
if(pSeq->_a[mid]>x){
right=mid-1;
}
else if(pSeq->_a[mid]<x){
left=mid+1;
}
else{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
void test1(){
SeqList seq;
SeqInit(&seq);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 1);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 2);
SeqPopBack(&seq);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 3);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 4);
SeqPushFront(&seq,5);
SeqPushFront(&seq,6);
SeqPopFront(&seq);
SeqPopFront(&seq);
SeqInsert(&seq, 0, 8);
SeqInsert(&seq, 1, 8);
SeqInsert(&seq, 1, 8);
SeqErase(&seq, 2);
SeqErase(&seq, 3);
SeqAt(&seq, 0, 99);
SeqPushBack(&seq, 1);
SeqPrint(&seq);
printf("查找1的下标:%d\n",SeqFind(&seq, 1));
printf("查找9的下标:%d\n",SeqFind(&seq, 9));
printf("排序后:\n");
// BubbleSort(&seq); //冒泡排序
SelectSort(&seq); //选择排序
SeqPrint(&seq);
printf("4的下标是:%d\n",BinarySearch(&seq, 4));
SeqDestory(&seq);//清空顺序表
SeqPrint(&seq);
}
mian.c
#include"SeqList.h"
int main(){
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

相关文章推荐
- 老郭带你学数据结构(C语言系列)2-线性表之动态顺序表
- 数据结构_动态顺序表
- 【数据结构】C语言实现顺序表(动态顺序表)
- 数据结构:动态实现顺序表
- 【C语言基础】关于数据结构顺序表动态内存开辟的介绍
- 数据结构中的查找算法-动态查找表(2)
- c++顺序表动态版本
- 数据结构实践——顺序表:两集合的交集
- 数据结构 线性表 顺序表
- 2017C语言顺序表(动态版本)
- C语言实现通讯录—动态顺序表
- 10-12-顺序表地址排序-内部排序-第10章-《数据结构》课本源码-严蔚敏吴伟民版
- C语言简单实现动态顺序表
- 数据结构---队列---顺序表
- 数据结构 之 索引技术(线性、倒排、动态检索B+、位索引、红黑树)
- 数据结构——顺序表
- 数据结构-线性表-顺序表
- 数据结构动态申请二维数组
- C语言数据结构动态线性表的操作集
- 2015年大二上-数据结构-顺序表(1)-求集合并集
