数据库学习第二季第五集:编程语言的存储过程和函数机制及其编程语言的调用学习总结
2017-11-25 00:00
721 查看
摘要: MySQL存储过程(Stored procedure)以及函数(function)为两种MySQL编程中的常用手段,合理使用这两者可以减少重复编写查询语句的次数。此外对于MySQL查询,存储过程和函数还有安全控制以及高效实现的特点。因此有关存储过程和函数的学习也是学习MySQL编程的必修课。
书写MySQL存储过程的基本语法为:
其中,存储过程的参数列表中每一个参数需要被声明IN、OUT或者INOUT。IN表示该数据仅为传入参数,修改过程对调用该过程的程序不透明;OUT和INOUT同义,表示数据为返回参数,可能在存储过程中被修改,修改结果返回调用该过程的程序。para为参数的变量名,dataType即常用MySQL允许的数据类型。
MySQL函数可以理解为有一个OUT参数、0-多个IN参数形成的仅供查询选择单变量结果的一种特殊的存储过程,书写MySQL函数的基本语法为:
参数的理解类似存储过程。
此类存储过程在各编程语言中调用示例如下:
此类存储过程调用示例如下:
函数在各编程语言中调用示例如下:
此处的示例为采用动态SQL机制的示例。然而,无论静态还是动态SQL都可以调用存储过程以及MySQL函数。
此类存储过程调用示例如下:
“connector-cpp-en.a4.pdf.” .
“connector-odbc-en.a4.pdf.” .
tutorialspoint.com, “JDBC - Create Database Example,” www.tutorialspoint.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/jdbc/jdbc-create-database.htm. [Accessed: 16-Nov-2017].
“MySQL :: MySQL 5.7 Reference Manual :: 27.8.6 C API Function Overview.” [Online]. Available: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/c-api-function-overview.html. [Accessed: 17-Nov-2017].
王珊和萨师煊,《数据库系统概论》第5版,高等教育出版社,2016年2月,北京
程序的运行效果如图:
MySQL存储过程和函数简介
MySQL的存储过程和函数总计有四类,即不返回变量的存储过程、返回单变量或多变量的存储过程、函数和返回查询表的存储过程。对于每一类不同的存储过程或函数,不同的编程语言都有不同的调用机制。限于篇幅,本文仅选用面向对象编程语言的代表C++语言和脚本语言代表Python演示MySQL存储过程和函数的程序调用。Java代码的调用作为附录附于本文附录,欢迎Java爱好者进行参考。书写MySQL存储过程的基本语法为:
//Change the delimiter and will be changed back at end: delimiter // CREATE PROCEDURE proc_name([IN|OUT|INOUT para dataType], ...) BEGIN # Write procedure here, maybe select, insert, create, update or delete operations. END // delimiter ;
其中,存储过程的参数列表中每一个参数需要被声明IN、OUT或者INOUT。IN表示该数据仅为传入参数,修改过程对调用该过程的程序不透明;OUT和INOUT同义,表示数据为返回参数,可能在存储过程中被修改,修改结果返回调用该过程的程序。para为参数的变量名,dataType即常用MySQL允许的数据类型。
MySQL函数可以理解为有一个OUT参数、0-多个IN参数形成的仅供查询选择单变量结果的一种特殊的存储过程,书写MySQL函数的基本语法为:
delimiter // CREATE FUNCTION avgSalary([para dataType], ...) RETURNS dataType BEGIN # Put Selection operation here RETURN para; END // delimiter ;
参数的理解类似存储过程。
本文所用数据库用例结构
本文引用博文《各种编程语言从数据库中获得数据方式小结》的数据库结构,详见:https://my.oschina.net/Samyan/blog/1577680不返回变量的存储过程书写和程序调用示例:
此类存储过程往往用于程序快速调用执行简单的插入、删除以及修改操作。delimiter // CREATE PROCEDURE add_department(IN DepartmentName VARCHAR(50), IN DepartmentFloor TINYINT, IN DepartmentPhone CHAR(11), IN ManagerID SMALLINT) BEGIN SELECT MAX(DepartmentID) INTO @num_of_depts FROM department; INSERT INTO department VALUE(@num_of_depts + 1, DepartmentName, DepartmentFloor, DepartmentPhone, ManagerID); END // delimiter ;
此类存储过程在各编程语言中调用示例如下:
被Python调用:
def exec_proc_without_ret():
proc_no_ret_query = """CALL add_department('Food', 6, '3248', 2)"""
try:
cnn = connector.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123456', database='department_store')
cursor = cnn.cursor()
cursor.execute(proc_no_ret_query)
cnn.commit()
except Exception as e:
raise e
finally:
cnn.close()
cursor.close()被C++调用:
//Example of procedure returns nothing
void callNoRetProcedure() {
try {
sql::mysql::MySQL_Driver *driver;
driver = sql::mysql::get_mysql_driver_instance();
sql::Connection *con;
con = driver->connect("tcp://127.0.0.1:3306", "root", "123456");
con->setSchema("department_store");
sql::Statement *stmt;
stmt = con->createStatement();
stmt->execute("CALL add_department('Food', 6, '3248', 2)");
delete stmt;
delete con;
}
catch (sql::SQLException &e) { throw e; }
}//end function返回单或多变量的存储过程:
此类存储过程往往用于程序调用比较复杂的MySQL操作(比如既要插入又要返回关于插入的情况)。/* For creating a procedure, IN means that outer caller pass the variable to the procedure, * And the procedure deal with it without returning results. * Out means outter variable pass a variable to the procedure (possibly null) * And the procedure deal with it to return values. * INOUT is similar to OUT, except that the parameter might be initialized.*/ delimiter // CREATE PROCEDURE add_employee(IN EmployeeName VARCHAR(50), IN EmployeeSalary DECIMAL(8, 2), IN DepartmentID SMALLINT, IN BossID SMALLINT, IN HiredDate DATETIME, OUT EmpID SMALLINT) BEGIN SELECT MAX(EmployeeID) + 1 INTO EmpID FROM employee; INSERT INTO employee VALUES (EmpID, EmployeeName, EmployeeSalary, DepartmentID, BossID, HiredDate); END // delimiter ;
此类存储过程调用示例如下:
被Python调用:
def exec_proc_with_single_ret():
proc_single_ret_query = """CALL add_employee('Johney', 2500.0, 3, 1, NOW(), @id)"""
try:
cnn = connector.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123456', database='department_store')
cursor = cnn.cursor()
cursor.execute(proc_single_ret_query)
cursor.execute("SELECT @id AS employeeNum")
for eachDatum in cursor:
numEmployee = eachDatum[0]
print "Number of current employees", numEmployee
cursor.close()
cnn.commit()
except Exception as e:
raise e
finally:
cnn.close()
cursor.close()被C++调用:
//Example of procedures returns a single variable / mutiple variables
void callSingleRetProcedure() {
try {
sql::mysql::MySQL_Driver *driver;
driver = sql::mysql::get_mysql_driver_instance();
sql::Connection *con;
sql::ResultSet *retSet;
con = driver->connect("tcp://127.0.0.1:3306", "root", "123456");
con->setSchema("department_store");
sql::Statement *stmt;
stmt = con->createStatement();
stmt->execute("CALL add_employee('Johney', 2500.0, 3, 1, NOW(), @id)");
retSet = stmt->executeQuery("SELECT @id AS employeeNum");
while (retSet->next())
cout << "Number of employees now: " << retSet->getString("employeeNum") << endl;
delete stmt;
delete con;
}
catch (sql::SQLException &e) { throw e; }
}//end functionMySQL函数
MySQL函数的功能类似于返回单变量且仅实现查询功能的存储过程,例如,以下函数返回特定id的员工平均薪资:delimiter // CREATE FUNCTION `avgSalary`(EmpID1 SMALLINT, EmpID2 SMALLINT) RETURNS decimal(8,2) BEGIN SELECT AVG(EmployeeSalary) INTO @avg_salary FROM employee WHERE EmployeeID between EmpID1 AND EmpID2; RETURN @avg_salary; END // delimiter ;
函数在各编程语言中调用示例如下:
此处的示例为采用动态SQL机制的示例。然而,无论静态还是动态SQL都可以调用存储过程以及MySQL函数。
被Python调用:
def exec_func(): func_query = """SELECT avgSalary(%s, %s) AS avg_salary""" try: cnn = connector.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123456', database='department_store') cursor = cnn.cursor(prepared=True) cursor.execute(func_query, (1, 13)) for eachDatum in cursor: avg_salary = eachDatum[0] print "Avg salaries of employee whose id btw 1 and 12:", avg_salary cursor.close() except Exception: raise Exception finally: cnn.close() cursor.close()
被C++调用:
//Example of calling function, prepared statements can also be used in procedure calls and function calls.
void callFunction() {
try {
sql::mysql::MySQL_Driver *driver;
driver = sql::mysql::get_mysql_driver_instance();
sql::Connection *con;
sql::ResultSet *retSet;
con = driver->connect("tcp://127.0.0.1:3306", "root", "123456");
con->setSchema("department_store");
sql::PreparedStatement *prep_stmt;
prep_stmt = con->prepareStatement("SELECT avgSalary(1, 12) AS avg_salary");
retSet = prep_stmt->executeQuery();
while (retSet->next())
cout << "Average salary of employees from 1 to 12: " << retSet->getString("avg_salary") << endl;
delete retSet;
delete prep_stmt;
delete con;
}
catch (sql::SQLException &e) { throw e; }
}//end function返回值为单个或多个查询表的存储过程:
此类存储过程一般用于获取需要多表联合获取查询数据的数据库操作。delimiter // CREATE PROCEDURE get_emp_data() BEGIN SELECT Emp.EmployeeID, Emp.EmployeeName, Emp.EmployeeSalary, DepartmentName, Boss.EmployeeName AS Boss, Emp.HireDate FROM employee Emp NATURAL JOIN Department Dept LEFT OUTER JOIN employee Boss ON Emp.BossID = Boss.EmployeeID ORDER BY Emp.EmployeeID; END // delimiter ;
此类存储过程调用示例如下:
被Python调用:
Python调用返回查询表的存储过程机制非常特殊,需要存储结果到buffer中,而使用callproc才能启用存储该结果的buffer。def exec_proc_table_ret():
try:
cnn = connector.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='123456', database='department_store')
cursor = cnn.cursor(dictionary=True, buffered=True)
cursor.callproc('get_emp_data', args=())
for dataSet in cursor.stored_results():
for datum in dataSet.fetchall():
print datum
cursor.close()
except Exception as e:
raise e
finally:
cnn.close()
cursor.close()被C++调用:
//Example of procedures returns a table of query
void callRetSetProcedure() {
try {
sql::mysql::MySQL_Driver *driver;
driver = sql::mysql::get_mysql_driver_instance();
sql::Connection *con;
con = driver->connect("tcp://127.0.0.1:3306", "root", "123456");
sql::Statement *stmt;
sql::ResultSet *retSet;
stmt = con->createStatement();
stmt->execute("USE department_store");
retSet = stmt->executeQuery("CALL get_emp_data()");
cout << "EmployeeID " << "EmployeeName " << "EmployeeSalary " << "DepartmentName " << "Boss " << "HireDate" << endl;
while (retSet->next()) {
cout << retSet->getInt(1) << ' ' << retSet->getString(2) << ' '
<< retSet->getDouble(3) << ' ' << retSet->getString(4) << ' '
<< retSet->getString(5) << ' ' << retSet->getString(6) << endl;
}
delete retSet;
delete stmt;
delete con;
delete driver;
}
catch (sql::SQLException &e) {
throw e;
}
}//end function参考资料:
Python中MySQLConnector模块使用方法详解,URL:http://www.111cn.net/phper/python/67319.htm“connector-cpp-en.a4.pdf.” .
“connector-odbc-en.a4.pdf.” .
tutorialspoint.com, “JDBC - Create Database Example,” www.tutorialspoint.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/jdbc/jdbc-create-database.htm. [Accessed: 16-Nov-2017].
“MySQL :: MySQL 5.7 Reference Manual :: 27.8.6 C API Function Overview.” [Online]. Available: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/c-api-function-overview.html. [Accessed: 17-Nov-2017].
王珊和萨师煊,《数据库系统概论》第5版,高等教育出版社,2016年2月,北京
附录福利:MySQL Trigger机制以及Function的Java程序调用示例
//视IDE情况不同选择使用
package mysqltrigger;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class MySQLTrigger {
private Connection connect = null;
private Statement statement = null;
private ResultSet retSet = null;
private PreparedStatement prep_stmt = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO code application logic here
MySQLTrigger tg = new MySQLTrigger();
tg.callNoRetProcedure();
tg.callSingleRetProcedure();
tg.callFunction();
tg.callRetSetProcedure();
}//end main method
public void callNoRetProcedure() {
try {
// this will load the MySQL driver, each DB has its own driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// setup the connection with the DB.
connect = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost/department_store",
"root", "123456");
// statements allow to issue SQL queries to the database
statement = connect.createStatement();
// resultSet gets the result of the SQL query
statement.execute("CALL add_department('Food', 6, '3248', 2)");
statement.close();
connect.close();
} catch (SQLException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}//end try-catch
}
public void callSingleRetProcedure() {
try {
// this will load the MySQL driver, each DB has its own driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// setup the connection with the DB.
connect = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost/department_store",
"root", "123456");
// statements allow to issue SQL queries to the database
statement = connect.createStatement();
// resultSet gets the result of the SQL query
statement.executeQuery("CALL add_employee('Johney', 2500.0, 3, 1, NOW(), @id)");
retSet = statement.executeQuery("SELECT @id AS employeeNum");
while (retSet.next()) {
System.out.println("Number of current employees: " + retSet.getInt(1));
}
statement.close();
connect.close();
} catch (SQLException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}//end try-catch
}//end method
public void callFunction() {
try {
// this will load the MySQL driver, each DB has its own driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// setup the connection with the DB.
connect = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost/department_store",
"root", "123456");
// resultSet gets the result of the SQL query
prep_stmt = connect.prepareStatement("SELECT avgSalary(?, ?) AS avg_salary");
prep_stmt.setInt(1, 1);
prep_stmt.setInt(2, 12);
retSet = prep_stmt.executeQuery();
if (retSet.next()) {
System.out.println("Average salary of employees id from 1 to 12: "
+ retSet.getDouble(1));
}
retSet.close();
prep_stmt.close();
connect.close();
} catch (SQLException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}//end try-catch
}//end method
public void callRetSetProcedure() {
try {
// this will load the MySQL driver, each DB has its own driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// setup the connection with the DB.
connect = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost/department_store",
"root", "123456");
// statements allow to issue SQL queries to the database
statement = connect.createStatement();
// resultSet gets the result of the SQL query
retSet = statement.executeQuery("CALL get_emp_data()");
System.out.println("ID EmployeeName Salary Department Boss HiredDate");
while (retSet.next()) {
System.out.print(retSet.getInt(1) + " ");
System.out.print(retSet.getString(2) + " ");
System.out.print(retSet.getDouble(3) + " ");
System.out.print(retSet.getString(4) + " ");
System.out.print(retSet.getString(5) + " ");
System.out.println(retSet.getTimestamp(6));
/*//Or this is also ok, but returns Date only:
//System.out.println(retSet.getDate(6));*/
}
retSet.close();
statement.close();
connect.close();
} catch (SQLException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}//end try-catch
}//end method
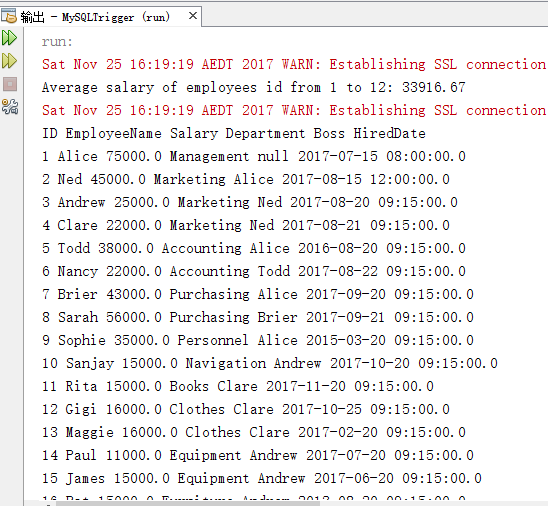
}//end class程序的运行效果如图:

相关文章推荐
- 数据库学习四:c#调用存储过程
- 数据库学习之存储过程及函数。
- MyBatis学习总结(六)——调用存储过程
- java中用事物控制语言调用数据库中的数据,以及调用存储过程或函数
- 数据库复习总结(20)-存储过程以及.net调用存储过程
- Mysql学习总结(11)——MySql存储过程与函数
- java中调用数据库中的存储过程和函数
- MyBatis学习总结(六)——调用存储过程
- MyBatis学习总结(六)——调用存储过程
- 【学习】java下实现调用oracle的存储过程和函数
- 运用ORACLE的OO4O类库函数解决调用存储过程向远程数据库上传超过32K图片失败的问题
- 数据库存储过程及其与函数区别
- Mybatis 学习总结(八)——调用存储过程
- 数据库存储过程及其调用
- MyBatis学习总结(六)调用存储过程
- java中使用jdbc和mybatis调用数据库中的存储过程和函数
- Java中调用数据库的存储过程存储函数和包体
- Mysql学习总结(11)——MySql存储过程与函数
- Java学习笔记之数据库(触发器、事物、索引、投影和除、视图、存储过程和函数 )含各种链)___ 一直补充
- .net学习总结(6)之sqlserver 自定义函数与存储过程
