C++设计模式实例讲解
2017-11-14 15:22
309 查看
感言
本文很长,但文中近乎有十之八九只能算是我在拜读各位大神大牛们分享的作品的笔记,这里只是我第一遍学习,我知道过了几天我肯定又会把看过的东西给忘记,所以就索性把各位大牛们的东西整理到了一起,方便以后的学习。
1.(Strategy策略模式)
一个策略放到一个锦囊里。当用的时候,找到这个锦囊,从锦囊里拿出策略来使用。
注意:锦囊只是简单的装载和调用策略,锦囊里没有逻辑。策略会有更大的自主权,运行更多的逻辑。
策略接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[/code]
实际策略BackDoor
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
实际策略GivenGreenLigh
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
使用锦囊包装策略CContext
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
{
this->m_strategy = mStrategy;
}
Context::~Context(void)
{
delete this->m_strategy;
}
void Context::Operator()
{
this->m_strategy->Operator();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
结果测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:

一个锦囊只能装一个妙计,可以有多个锦囊。属于对象行为型模式
2.(Proxy代理模式)
所谓代理,一看名字就知道这只是个中介而已,真实的执行者在代理的后面。
代理和实际执行者派生于共同的接口,代理拥有实际执行者的实例。代理的每一个函数(接口的实现函数),直接调用实际执行者的对应接口函数。
注意:代理只是简单的装载,然后调用实际执行者的函数
代理和实际执行者派生于共同的接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
实际执行者的代理者
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
实际执行者PanJinLian
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
实际执行者JiaShi
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
实际测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:

看起来代理模式的结构和策略模式类似,都是由一个类来装载接口的一个实例,策略模式是CContext来装载,代理模式是CWangPo来装载。CContext不是从IStrategy派生,所以不需要实现IStrategy接口函数,而CWangPo是从IKindWomen派生的所以CWangPo很清楚CPanJinLian和CJiaShi的接口函数。这就是代理,代理人知道被代理人能干的事情即函数,所以代理人可以成为中介。
代理模式可以很好的将前后端分开,实现了松散耦合。代理模式属于结构型模式
3.(Singleton单例模式)
单例模式顾名思义,就是在系统中只允许产生这个类的一个实例。
实例说明:很多大臣拜见的皇帝,只有一个。体现在面向对象方面,CEmperor定义一个静态指针,和一个静态函数,私有化构造函数、析构函数、构造函数复制、重载赋值语句。
注意:线程安全,采用互斥体的方式实现
用单例的方式实现Emperor,不论在使用过程中new多少次均只会有一个实例
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
[/code]
实例测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:
单例模式比较简单,但在项目中使用的时候,需要明确只调用CEmperor的GetInstance函数来获取实例
4.(Multition多例模式)
和单例基本一样,是有个数限制的单例。如果对于产生的实例个数没有限制,那就不是多例了,和普通的类没有区别
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
[/code]
测试使用:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
代码结构图:
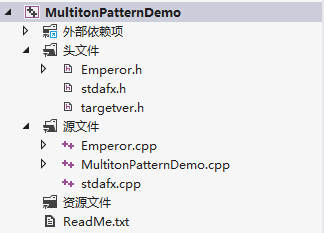
运行结果:
5.(Factory Method工厂方法模式)
工厂方法模式的意义是定义一个创建产品对象的工厂接口,将实际创建工作推迟到子类当中。核心工厂类不再负责产品的创建,这样核心类成为一个抽象工厂角色,仅负责具体工厂子类必须实现的接口,这样进一步抽象化的好处是使得工厂方法模式可以使系统在不修改具体工厂角色的情况下引进新的产品。
抽象基类IHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
实例类YellowHuman,继承自IHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
实例类WhiteHuman,继承自IHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
实例类BlackHuman,继承自IHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
简单工厂实现
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:

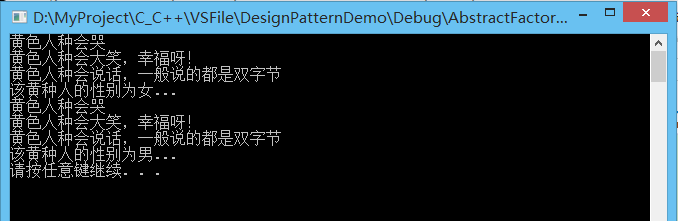
6.(AbstractFactory抽象工厂模式)
抽象工厂,提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。对于工厂方法来说,抽象工厂可实现一系列产品的生产,抽象工厂更注重产品的组合。
产品接口IHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
抽象产品之一YellowHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[/code]
具体产品之一,继承自YellowHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
具体产品,继承自YellowHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
抽象产品之二WhiteHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[/code]
具体产品,继承自CWhiteHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
具体产品,继承自CWhiteHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
抽象产品之三
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
具体产品,继承自CBlackHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
具体产品,继承自CBlackHuman
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
抽象工厂
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
抽象工厂基类(此类可有可无)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
男人工厂
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "MaleHumanFactory.h"
template<class T>
CMaleHumanFactory<T>::CMaleHumanFactory(void)
{
}
template<class T>
CMaleHumanFactory<T>::~CMaleHumanFactory(void)
{
}
template<class T>
IHuman * CMaleHumanFactory<T>::CreateYellowHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}
template<class T>
IHuman * CMaleHumanFactory<T>::CreateWhiteHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}
template<class T>
IHuman * CMaleHumanFactory<T>::CreateBlackHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
女人工厂
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
[/code]
测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:
7.(Facade门面模式)
Facade门面模式,也是比较常用的一种模式,其含义是为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面, Facade 模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。简单说,就是将复杂的逻辑封装起来,对外公开简单的接口,由客户程序调用。
以收发信件和警察检查实例为例
说明:邮局对外只有一个窗口,接收信件内容和邮件地址。对内调用邮件处理的4个函数。将复杂逻辑封装在邮局的里面,当需要增加警察来检查信件时,只需在邮局内增加警察检查信件的方法。
注意:将复杂逻辑封装起来,对外只有一个简单的接口。
抽象信件处理类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
信件处理实现类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
[/code]
邮局处理信件类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
警察检查信件
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:

8.(Adapter适配器模式)
适配器模式,使用之处比较特殊,不属于常规设计模式,主要用于不同系统之间的处理。是将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口。Adapter模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。
系统内部的实体接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
系统内部实体类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
[/code]
外部系统实体接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
外部系统实体类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
外部系统实体基本信息类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
外部系统实体家庭信息类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
外部系统实体办公信息类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
由IUserInfo接口派生的实体类,并引入外部系统实体的实例,起适配作用
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:
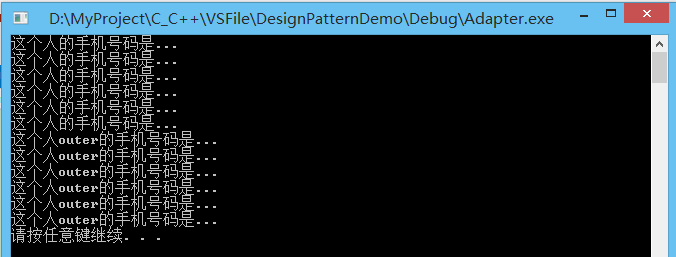
适配器模式属于结构型模式,当出现数据接口不一致的情况下,才会使用到。
9.(Template Method模板方法模式)
模板模式也是相当简单的一种模式,而且是比较常用的。模板模式是定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。TemplateMethod使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
说明:在CHummerModel声明Start、Engineboom、Alarm、Stop虚函数,由派生类实现。基类的Run负责组织逻辑,分别调用这几个派生类实现的函数。
注意:基类中的Run应该禁止派生类覆盖。
Model抽象基类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[/code]
Model衍生类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
[/code]
Model衍生类2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
[/code]
代码结构图:
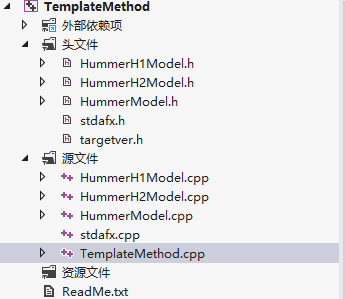
运行结果:
10. (Builder建造者模式)
建造者模式,将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。一段晦涩难懂的文字,实现创建不同表示的方法就是给创建的过程传入创建的参数。
CCarModel实现模板方法,Builder负责开始建造产品。建造产品时,构建的顺序由Director或main决定。
建造者模式和抽象工厂非常类似。建造者更重视产品建造时的逻辑顺序,而抽象工厂更重视生产出不同型号的产品,抽象工厂不关心顺序。
CarModel抽象基类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
[/code]
实际模型1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
[/code]
实际模型2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
[/code]
建造者基类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
实际建造者1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
实际建造者2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
指导者
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
[/code]
使用实例
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:
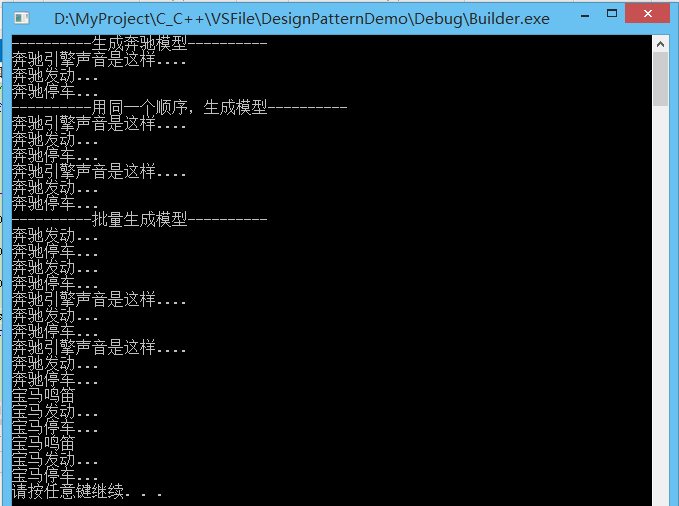
建造者模式属于创建型模式,主要关注创建的顺序,不同的顺序,生产的产品略有不同。
11. (Bridge桥接模式)
桥接模式,将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化。实现分离的办法就是增加一个类。
说明:客户直接使用CNewHouseCorp和CShanZhaiCorp类,在main()函数里构造产品,然后传到这两个类里。这两个类的MakeMoney()函数,先调用基类的MakeMoney(),然后分别执行各自的逻辑。
注意:CNewCorp起到了桥梁的作用。可以分别增加产品和公司。
产品基类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
产品——房子
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
产品——衣服
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
产品——ipod
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
桥梁类,其中MakeMoney()是桥梁方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
只生产房子的类,靠卖房子挣钱
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
靠生产山寨产品挣钱
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
[/code]
代码结构图:
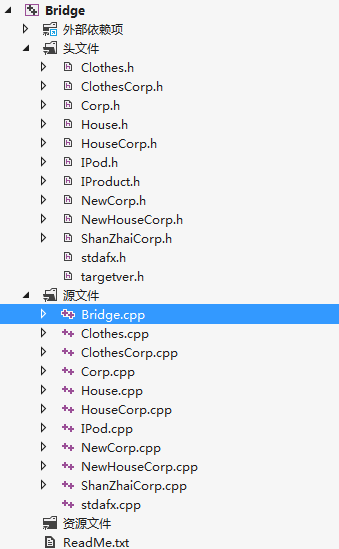
运行结果:
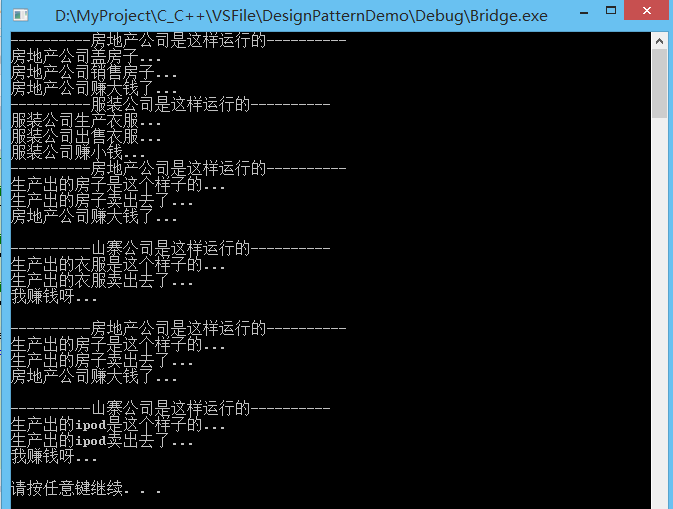
12.(Command命令模式)
命令模式,将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤消的操作。
说明:客户只需要知道向Invoker发出命令(多个命令),而不是将命令直接传达给具体的执行者。当然,客户是需要知道都有什么命令的。
注意:客户只发命令,不需要知道由谁来执行和怎么执行,体现出高内聚的特点。用户在发出命令后,是允许撤回的,所以可以增加一个命令“Undo ”,Undo是状态的变更。
命令接收者
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
执行都抽象基类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
实际执行者1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
实际执行者2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
实际执行者3
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
命令接口抽象基类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[/code]
添加执行命令
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
删除撤消命令
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
[/code]
代码结构图:
运行结果:
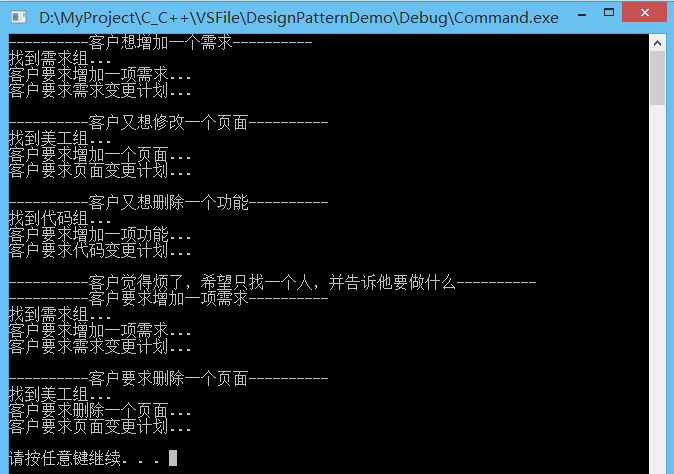
缺点:因为一个命令就定义为一个ICommand实现类,这样的话,对ICommand派生类的数量增长可能会难以控制。
13.(Decorator装饰模式)
装饰模式,动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,Decorator模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
成绩单抽象基类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
四年级成绩单
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[/code]
成绩单装饰基类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
最高分装饰者
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
成绩排名装饰者
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
[/code]
代码结构图:
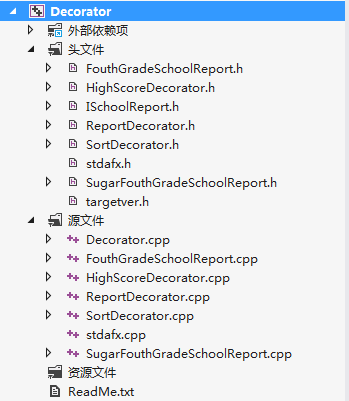
运行结果:
14.(Iterator迭代器模式)
所谓迭代器模式是提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部表示。
说明:CProject实现产品类,能够返回一个迭代器的指针。这个迭代器将封装产品类里的一个数组。所以迭代器在运行Next函数时,可以遍历这个数组的所有元素。
简单来说,就是用代码实现vector::iterator或vector::const_iterator。
产品接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
产品类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
[/code]
迭代器接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
产品迭代器接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
产品迭代器实现类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
[/code]
代码结构:
运行结果:
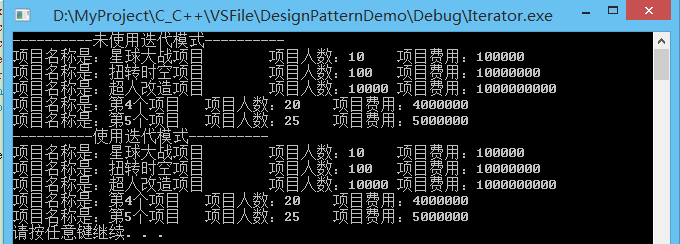
15.(Composite组合模式)
将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构。Composite使得用户对单个对象和组合的使用具有一致性。
说明:组合模式主要是实现在CBranchNode对象里增加对其它对象的数组,如vector
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
[/code]
树枝节点,实现Addordinate()函数和GetSubordinate()函数
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
[/code]
叶子节点
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
[/code]
代码结构图:
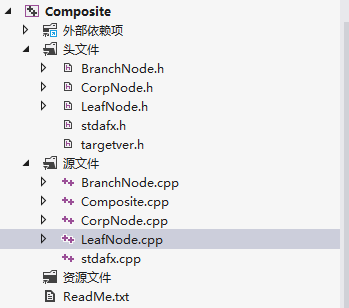
运行结果:
**16.(Observer观察者模式)
定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并被自动更新。
说明:将观察者聚集到被观察者韩非子身边,韩非子的每一个举动都会通知给观察者,如李斯或周斯。
注意:最多允许一个对象既是观察者也是被观察者。就像数据库中的触发器一样,成为一个复杂的链就很难维护了。观察者类似于委托的处理方式。
被观察者接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
被观察者1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
[/code]
观察者接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
观察者1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
[/code]
观察者2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
[/code]
代码结构:
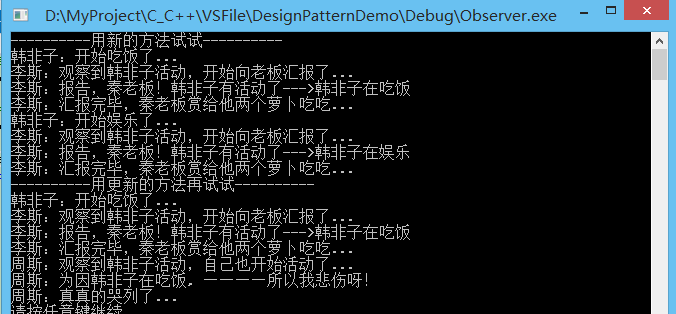
运行结果:
17.(Chain of Responsibility责任链模式)
使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系。将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止。
说明:CHandler抽象类负责聚合责任链之中的其它处理对象,用SetNext来建立这个责任链。HandleMessage在处理请求时,会判断是否是自己要处理的请求,如果是则直接处理。如果不是,则查找下一个责任链上的处理对象,找到了则由下一个处理。
发出请求者接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
请求者实现类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
[/code]
处理请求抽象类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
处理请求实现类,责任链1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
处理请求实现类,责任链2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
处理请求实现类,责任链3
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
[/code]
代码结构:
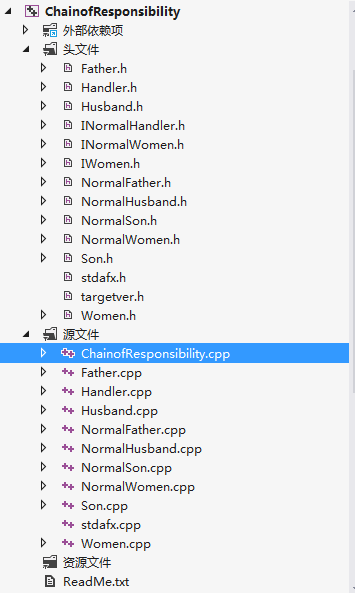
运行结果:

18.(Visitor访问者模式)
表示一个作用于某对象结构中的各元素的操作。它使你可以在不改变各元素的类的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新操作。
说明:A接受B的访问,B主动的执行访问动作。
注意:和观察者的区别是,被观察者要执行一个动作,然后主动发送通知给观察者。访问者模式是由访问者主动发出的动作。
访问者接口
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
访问者实现类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
[/code]
被访问者抽象类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
[/code]
被访问者实现类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
[/code]
被访问者实现类2 CCommonEmployee
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[/code]
使用测试
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
[/code]
代码结构:
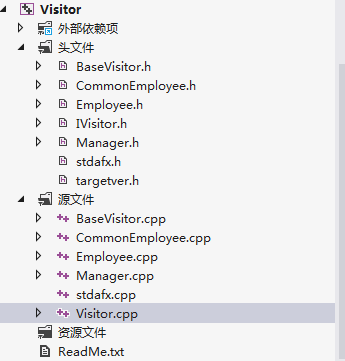
运行结果:
19.(State状态模式)
允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为。对象看起来似乎修改了它的类。
说明:CContext保持电梯的状态,并提供操作的接口函数。当函数被调用时,CContext直接调用当前状态的相应函数。由状态的接口函数来确定是否可以执行这个动作,以及修改状态为执行这个动作后的状态。
电梯实体抽象类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[/code]
电梯实体类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
[/code]
不用设计模式情况下测试使用
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
电梯状态抽象类
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
电梯门关闭
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
[/code]
电梯门打开
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
[/code]
电梯运行
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
[/code]
电梯停止
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
[/code]
电梯的控制面板
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Context.h"
COpenningState* CContext::pOpenningState = NULL;
CCloseingState* CContext::pCloseingState = NULL;
CRunningState* CContext::pRunningState = NULL;
CStoppingState* CContext::pStoppingState = NULL;
CContext::CContext(void)
{
m_pLiftState = NULL;
pOpenningState = new COpenningState();
pCloseingState = new CCloseingState();
pRunningState = new CRunningState();
pStoppingState = new CStoppingState();
}
CContext::~CContext(void)
{
delete pOpenningState;
pOpenningState = NULL;
delete pCloseingState;
pCloseingState = NULL;
delete pRunningState;
pRunningState = NULL;
delete pStoppingState;
pStoppingState = NULL;
}
CLiftState * CContext::GetLiftState()
{
return m_pLiftState;
}
void CContext::SetLiftState(CLiftState *pLiftState)
{
this->m_pLiftState = pLiftState;
this->m_pLiftState->SetContext(this);
}
void CContext::Open()
{
this->m_pLiftState->Open();
}
void CContext::Close()
{
this->m_pLiftState->Close();
}
void CContext::Run()
{
this->m_pLiftState->Run();
}
void CContext::Stop()
{
this->m_pLiftState->Stop();
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
测试使用
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
[/code]
代码结构:
运行结果:
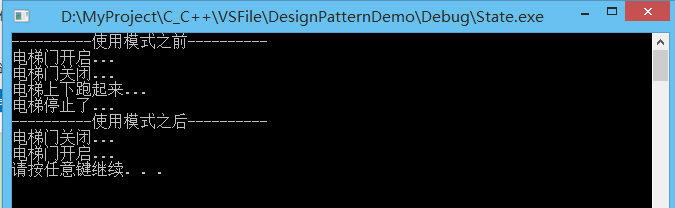
参考资料
http://www.cnblogs.com/wanggary/category/294620.html
《24种设计模式介绍与6大设计原则》
致谢
感谢博主wang_gary的博客分享,在今年3月份第一次看到关于设计模式的分享时就备感激动,而且是C++版本的,正好方便了我个人理解设计模式的精妙,以方便了我的C++学习。
本文很长,但文中近乎有十之八九只能算是我在拜读各位大神大牛们分享的作品的笔记,这里只是我第一遍学习,我知道过了几天我肯定又会把看过的东西给忘记,所以就索性把各位大牛们的东西整理到了一起,方便以后的学习。
1.(Strategy策略模式)
一个策略放到一个锦囊里。当用的时候,找到这个锦囊,从锦囊里拿出策略来使用。
注意:锦囊只是简单的装载和调用策略,锦囊里没有逻辑。策略会有更大的自主权,运行更多的逻辑。
策略接口
//IStrategy.h
#pragma once
class IStrategy
{
public:
IStrategy(void);
virtual ~IStrategy(void);
virtual void Operator(void) = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[/code]
实际策略BackDoor
//BackDoor.h
#pragma once
#include "IStrategy.h"
class CBackDoor : public IStrategy
{
public:
CBackDoor(void);
~CBackDoor(void);
void Operator(void);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
//BackDoor.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "BackDoor.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CBackDoor::CBackDoor(void)
{
}
CBackDoor::~CBackDoor(void)
{
}
void CBackDoor::Operator(void)
{
cout << "找乔国老帮忙,让吴国太给孙权施压" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
实际策略GivenGreenLigh
//GivenGreenLight.h
#pragma once
#include "IStrategy.h"
class GivenGreenLight : public IStrategy
{
public:
GivenGreenLight(void);
~GivenGreenLight(void);
void Operator(void);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
//GivenGreenList.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "GivenGreenLight.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
GivenGreenLight::GivenGreenLight(void)
{
}
GivenGreenLight::~GivenGreenLight(void)
{
}
void GivenGreenLight::Operator(void)
{
cout << "求吴国太给绿灯,放行" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
使用锦囊包装策略CContext
#pragma once
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "IStrategy.h"
class Context
{
public:
Context(IStrategy *strategy);
~Context();
void Operator(void);
private:
IStrategy *m_strategy;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
//Context.cpp
include “stdafx.h”
include “Context.h”
Context::Context(IStrategy *mStrategy){
this->m_strategy = mStrategy;
}
Context::~Context(void)
{
delete this->m_strategy;
}
void Context::Operator()
{
this->m_strategy->Operator();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
结果测试
//Strategy.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "BackDoor.h"
#include "GivenGreenLight.h"
#include "BlockEnemy.h"
#include "Context.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Context *p_context;
p_context = new Context(new CBackDoor());
p_context->Operator();
p_context = new Context(new GivenGreenLight());
p_context->Operator();
system(“pause”);
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

一个锦囊只能装一个妙计,可以有多个锦囊。属于对象行为型模式
2.(Proxy代理模式)
所谓代理,一看名字就知道这只是个中介而已,真实的执行者在代理的后面。
代理和实际执行者派生于共同的接口,代理拥有实际执行者的实例。代理的每一个函数(接口的实现函数),直接调用实际执行者的对应接口函数。
注意:代理只是简单的装载,然后调用实际执行者的函数
代理和实际执行者派生于共同的接口
//IKindWomen.h
#pragma once
class IKindWomen
{
public:
IKindWomen(void) {};
virtual ~IKindWomen(void) {};
virtual void MakeEyesWithMan() = 0;
virtual void HappyWithMan() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
实际执行者的代理者
//WangPo.h
#pragma once
#include "IKindWomen.h"
class WangPo : public IKindWomen
{
public:
WangPo(IKindWomen *pKindWomen);
~WangPo(void);
void HappyWithMan(void);
void MakeEyesWithMan(void);
private:
IKindWomen *m_kindwomen;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//WangPo.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "WangPo.h"
WangPo::WangPo(IKindWomen *pIKindWomen)
{
this->m_kindwomen = pIKindWomen;
}
WangPo::~WangPo(void)
{
delete this->m_kindwomen;
}
void WangPo::HappyWithMan()
{
this->m_kindwomen->HappyWithMan();
}
void WangPo::MakeEyesWithMan()
{
this->m_kindwomen->MakeEyesWithMan();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
实际执行者PanJinLian
//PanJinLian.h
#pragma once
#include "IKindWomen.h"
class PanJinLian : public IKindWomen
{
public:
PanJinLian(void);
~PanJinLian(void);
void HappyWithMan();
void MakeEyesWithMan();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
//PanJinLian.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "PanJinLian.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
PanJinLian::PanJinLian(void)
{
}
PanJinLian::~PanJinLian(void)
{
}
void PanJinLian::HappyWithMan()
{
cout << "潘金莲和男人做那个..." << endl;
}
void PanJinLian::MakeEyesWithMan(void)
{
cout << "潘金莲抛媚眼" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
实际执行者JiaShi
//JiaShi.h
#pragma once
#include "IKindWomen.h"
class JiaShi : public IKindWomen
{
public:
JiaShi(void);
~JiaShi(void);
void HappyWithMan();
void MakeEyesWithMan();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
//JiaShi.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "JiaShi.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
JiaShi::JiaShi(void)
{
}
JiaShi::~JiaShi(void)
{
}
void JiaShi::HappyWithMan()
{
cout << "贾氏和男人做那个..." << endl;
}
void JiaShi::MakeEyesWithMan(void)
{
cout << "贾氏抛媚眼" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
实际测试
// PoxyPatternDemo.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "WangPo.h"
#include "PanJinLian.h"
#include "JiaShi.h"
void doPanJinLian()
{
WangPo *pWangPo;
pWangPo = new WangPo(new PanJinLian());
pWangPo->MakeEyesWithMan();
pWangPo->HappyWithMan();
delete pWangPo;
}
void doJiaShi()
{
WangPo *pWangPo;
pWangPo = new WangPo(new JiaShi());
pWangPo->MakeEyesWithMan();
pWangPo->HappyWithMan();
delete pWangPo;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
doPanJinLian();
doJiaShi();
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

看起来代理模式的结构和策略模式类似,都是由一个类来装载接口的一个实例,策略模式是CContext来装载,代理模式是CWangPo来装载。CContext不是从IStrategy派生,所以不需要实现IStrategy接口函数,而CWangPo是从IKindWomen派生的所以CWangPo很清楚CPanJinLian和CJiaShi的接口函数。这就是代理,代理人知道被代理人能干的事情即函数,所以代理人可以成为中介。
代理模式可以很好的将前后端分开,实现了松散耦合。代理模式属于结构型模式
3.(Singleton单例模式)
单例模式顾名思义,就是在系统中只允许产生这个类的一个实例。
实例说明:很多大臣拜见的皇帝,只有一个。体现在面向对象方面,CEmperor定义一个静态指针,和一个静态函数,私有化构造函数、析构函数、构造函数复制、重载赋值语句。
注意:线程安全,采用互斥体的方式实现
用单例的方式实现Emperor,不论在使用过程中new多少次均只会有一个实例
//Emperor.h
#pragma once
#include <Windows.h>
#include <winnt.h>
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
class Emperor
{
public:
static Emperor* getInstance();
static void releaseInstance();
void emperorInfo(void);
void setEmperorTag(string tag);
private:
Emperor(void);
virtual ~Emperor(void);
Emperor(const Emperor&);
Emperor& operator=(const Emperor&);
static Emperor *m_emperor;
static HANDLE m_mutex;
string m_emperor_tag;
class Garbo
{
public:
Garbo()
{
cout << "create garbo" << endl;
}
~Garbo()
{
cout << "destrory garbo" << endl;
getchar();
if(NULL != m_emperor)
{
WaitForSingleObject(m_mutex, INFINITE);
if(NULL != m_emperor)
{
cout << "remove instance" << endl;
delete m_emperor;
m_emperor = NULL;
}
ReleaseMutex(m_mutex);
}
if(NULL != m_mutex)
{
cout << "delete mutex" << endl;
CloseHandle(m_mutex);
m_mutex = NULL;
}
}
};
static Garbo m_garbo;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
[/code]
//Emperor.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Emperor.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
Emperor *Emperor::m_emperor = NULL;
HANDLE Emperor::m_mutex = CreateMutex(NULL, FALSE, NULL);
Emperor::Garbo Emperor::m_garbo;
Emperor::Emperor(void)
{
cout << "create emperor instance" << endl;
}
Emperor::~Emperor(void)
{
cout << "destroy emperor instance and release its resources" << endl;
}
void Emperor::emperorInfo(void)
{
char msg_buf[50] = {0};
sprintf_s(msg_buf, 50, "the emperor's name is (%s)", m_emperor_tag.c_str());
string msg(msg_buf);
cout << msg.c_str() << endl;
}
Emperor *Emperor::getInstance()
{
if(NULL == m_emperor)
{
WaitForSingleObject(m_mutex, INFINITE);
if(NULL == m_emperor)
m_emperor = new Emperor();
ReleaseMutex(m_mutex);
}
return m_emperor;
}
void Emperor::releaseInstance()
{
if(NULL != m_emperor)
{
WaitForSingleObject(m_mutex, INFINITE);
if(NULL != m_emperor)
{
delete m_emperor;
m_emperor = NULL;
}
ReleaseMutex(m_mutex);
}
}
void Emperor::setEmperorTag(string tag)
{
m_emperor_tag = tag;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
[/code]
实例测试
// SingletoPatternDemo.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Emperor.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Emperor *pEmperor1 = Emperor::getInstance();
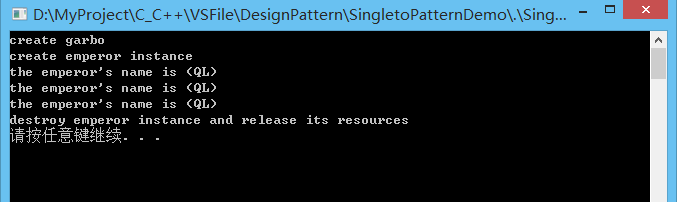
pEmperor1->setEmperorTag("QL");
pEmperor1->emperorInfo();
Emperor *pEmperor2 = Emperor::getInstance();
pEmperor2->emperorInfo();
Emperor *pEmperor3 = Emperor::getInstance();
pEmperor3->emperorInfo();
Emperor::releaseInstance();
getchar();
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

单例模式比较简单,但在项目中使用的时候,需要明确只调用CEmperor的GetInstance函数来获取实例
4.(Multition多例模式)
和单例基本一样,是有个数限制的单例。如果对于产生的实例个数没有限制,那就不是多例了,和普通的类没有区别
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Emperor
{
private:
string info;
static int maxNumOfEmperor;
static vector<Emperor*> emperor_list;
Emperor();
Emperor(string info);
~Emperor();
public:
static Emperor* getInstance(int idx);
void emperorInfo();
static void releaseInstance();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Emperor.h"
#include <iostream>
int Emperor::maxNumOfEmperor = 3;
vector<Emperor*> Emperor::emperor_list;
Emperor::Emperor(void)
{
cout << "create emperor instance" << endl;
}
Emperor::Emperor(string info)
{
cout << "create emperor instance with info " << endl;
this->info = info;
}
Emperor::~Emperor(void)
{
cout << "destroy emperor instance and release its resources" << endl;
}
void Emperor::emperorInfo()
{
char msg_buf[50] = {0};
sprintf_s(msg_buf, 50, "the emperor's name is (%s)", this->info.c_str());
string msg(msg_buf);
cout << msg.c_str() << endl;
}
Emperor *Emperor::getInstance(int idx)
{
if(emperor_list.empty())
{
for(int i = 0; i < maxNumOfEmperor; ++ i)
{
char name[10] = {0};
sprintf_s(name, 10, "emperor %d", i);
string tmp(name);
Emperor *emp = new Emperor(tmp);
emperor_list.push_back(emp);
}
}
if(idx > -1 && idx < maxNumOfEmperor)
return emperor_list.at(idx);
return NULL;
}
void Emperor::releaseInstance()
{
emperor_list.clear();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
[/code]
测试使用:
// MultitonPatternDemo.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Emperor.h"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Emperor *emperor1 = Emperor::getInstance(0);
emperor1->emperorInfo();
Emperor *emperor2 = Emperor::getInstance(1);
emperor2->emperorInfo();
Emperor *emperor3 = Emperor::getInstance(2);
emperor3->emperorInfo();
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

5.(Factory Method工厂方法模式)
工厂方法模式的意义是定义一个创建产品对象的工厂接口,将实际创建工作推迟到子类当中。核心工厂类不再负责产品的创建,这样核心类成为一个抽象工厂角色,仅负责具体工厂子类必须实现的接口,这样进一步抽象化的好处是使得工厂方法模式可以使系统在不修改具体工厂角色的情况下引进新的产品。
抽象基类IHuman
//IHuman.h
#pragma once
class IHuman
{
public:
IHuman(void)
{
}
virtual ~IHuman(void)
{
}
virtual void Laugh() = 0;
virtual void Cry() = 0;
virtual void Talk() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
实例类YellowHuman,继承自IHuman
//YellowHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "ihuman.h"
class CYellowHuman :
public IHuman
{
public:
CYellowHuman(void);
~CYellowHuman(void);
void Laugh();
void Cry();
void Talk();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
//YellowHuman.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "YellowHuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CYellowHuman::CYellowHuman(void)
{
}
CYellowHuman::~CYellowHuman(void)
{
}
void CYellowHuman::Cry()
{
cout << "黄色人种会哭" << endl;
}
void CYellowHuman::Laugh()
{
cout << "黄色人种会大笑,幸福呀!" << endl;
}
void CYellowHuman::Talk()
{
cout << "黄色人种会说话,一般说的都是双字节" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
实例类WhiteHuman,继承自IHuman
//WhiteHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "ihuman.h"
class CWhiteHuman :
public IHuman
{
public:
CWhiteHuman(void);
~CWhiteHuman(void);
void Laugh();
void Cry();
void Talk();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
//WhiteHuman.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "WhiteHuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CWhiteHuman::CWhiteHuman(void)
{
}
CWhiteHuman::~CWhiteHuman(void)
{
}
void CWhiteHuman::Cry()
{
cout << "白色人种会哭" << endl;
}
void CWhiteHuman::Laugh()
{
cout << "白色人种会大笑,侵略的笑声" << endl;
}
void CWhiteHuman::Talk()
{
cout << "白色人种会说话,一般都是单字节" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
实例类BlackHuman,继承自IHuman
//BlackHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "ihuman.h"
class CBlackHuman :
public IHuman
{
public:
CBlackHuman(void);
~CBlackHuman(void);
void Laugh();
void Cry();
void Talk();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
//BlackHuman.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "BlackHuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CBlackHuman::CBlackHuman(void)
{
}
CBlackHuman::~CBlackHuman(void)
{
}
void CBlackHuman::Cry()
{
cout << "黑人会哭" << endl;
}
void CBlackHuman::Laugh()
{
cout << "黑人会笑" << endl;
}
void CBlackHuman::Talk()
{
cout << "黑人可以说话,一般人听不懂" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
简单工厂实现
//SimpleHumanFactory.h
#pragma once
#include "IHuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CSimpleHumanFactory
{
public:
CSimpleHumanFactory(void);
virtual ~CSimpleHumanFactory(void);
virtual IHuman * CreateHuman(string classType);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
// SimpleHumanFactory.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "SimpleHumanFactory.h"
#include "YellowHuman.h"
#include "WhiteHuman.h"
#include "BlackHuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
CSimpleHumanFactory::CSimpleHumanFactory(void)
{
}
CSimpleHumanFactory::~CSimpleHumanFactory(void)
{
}
IHuman * CSimpleHumanFactory::CreateHuman( string classType )
{
if (classType.compare("CYellowHuman") == 0)
{
return new CYellowHuman();
}
else if(classType.compare("CWhiteHuman") == 0)
{
return new CWhiteHuman();
}
else if(classType.compare("CBlackHuman") == 0)
{
return new CBlackHuman();
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
[/code]
使用测试
// FactoryMethod.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "IHuman.h"
#include "YellowHuman.h"
#include "WhiteHuman.h"
#include "BlackHuman.h"
#include "SimpleHumanFactory.h"
#include "StandardHumanFactory.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
void DoSimpleFactory()
{
CSimpleHumanFactory *pSimpleHumanFactory = new CSimpleHumanFactory();
cout << "----------第一批人是这样的:黄种人" << endl;
IHuman *pYellowHuman = pSimpleHumanFactory->CreateHuman("CYellowHuman");
pYellowHuman->Cry();
pYellowHuman->Laugh();
pYellowHuman->Talk();
delete pYellowHuman;
cout << "----------第二批人是这样的:白种人" << endl;
IHuman *pWhiteHuman = pSimpleHumanFactory->CreateHuman("CWhiteHuman");
pWhiteHuman->Cry();
pWhiteHuman->Laugh();
pWhiteHuman->Talk();
delete pWhiteHuman;
cout << "----------第三批人是这样的:黑种人" << endl;
IHuman *pBlackHuman = pSimpleHumanFactory->CreateHuman("CBlackHuman");
pBlackHuman->Cry();
pBlackHuman->Laugh();
pBlackHuman->Talk();
delete pBlackHuman;
cout << "----------第四批人是这样的:生产黄种人的工厂,采用了模板的方式。" << endl;
CStandardHumanFactory<CYellowHuman> standardHumanFactory;
pYellowHuman = standardHumanFactory.CreateHuman();
pYellowHuman->Cry();
pYellowHuman->Laugh();
pYellowHuman->Talk();
delete pYellowHuman;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
DoSimpleFactory();
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

6.(AbstractFactory抽象工厂模式)
抽象工厂,提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。对于工厂方法来说,抽象工厂可实现一系列产品的生产,抽象工厂更注重产品的组合。
产品接口IHuman
//IHuman.h
#pragma once
class IHuman
{
public:
IHuman(void)
{
}
virtual ~IHuman(void)
{
}
virtual void Laugh() = 0;
virtual void Cry() = 0;
virtual void Talk() = 0;
virtual void Sex() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
抽象产品之一YellowHuman
//YellowHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "ihuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CYellowHuman :
public IHuman
{
public:
CYellowHuman(void)
{
}
~CYellowHuman(void)
{
}
void Laugh()
{
cout << "黄色人种会大笑,幸福呀!" << endl;
}
void Cry()
{
cout << "黄色人种会哭" << endl;
}
void Talk()
{
cout << "黄色人种会说话,一般说的都是双字节" << endl;
}
virtual void Sex() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[/code]
具体产品之一,继承自YellowHuman
//YellowFemaleHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "yellowhuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CYellowFemaleHuman :
public CYellowHuman
{
public:
CYellowFemaleHuman(void)
{
}
~CYellowFemaleHuman(void)
{
}
void Sex()
{
cout << "该黄种人的性别为女..." << endl;
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
具体产品,继承自YellowHuman
//YellowMaleHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "yellowhuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CYellowMaleHuman :
public CYellowHuman
{
public:
CYellowMaleHuman(void)
{
}
~CYellowMaleHuman(void)
{
}
void Sex()
{
cout << "该黄种人的性别为男..." << endl;
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
抽象产品之二WhiteHuman
//WhiteHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "ihuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CWhiteHuman :
public IHuman
{
public:
CWhiteHuman(void)
{
}
~CWhiteHuman(void)
{
}
void Laugh()
{
cout << "白色人种会大笑,侵略的笑声" << endl;
}
void Cry()
{
cout << "白色人种会哭" << endl;
}
void Talk()
{
cout << "白色人种会说话,一般都是单字节" << endl;
}
virtual void Sex() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[/code]
具体产品,继承自CWhiteHuman
//WhiteFemaleHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "whitehuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CWhiteFemaleHuman :
public CWhiteHuman
{
public:
CWhiteFemaleHuman(void)
{
}
~CWhiteFemaleHuman(void)
{
}
void Sex()
{
cout << "该白种人的性别为女..." << endl;
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
具体产品,继承自CWhiteHuman
//WhiteMaleHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "whitehuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CWhiteMaleHuman :
public CWhiteHuman
{
public:
CWhiteMaleHuman(void)
{
}
~CWhiteMaleHuman(void)
{
}
void Sex()
{
cout << "该白种人的性别为男..." << endl;
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
抽象产品之三
//BlackHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "ihuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CBlackHuman :
public IHuman
{
public:
CBlackHuman(void)
{
}
~CBlackHuman(void)
{
}
void Laugh()
{
cout << "黑人会笑" << endl;
}
void Cry()
{
cout << "黑人会哭" << endl;
}
void Talk()
{
cout << "黑人可以说话,一般人听不懂" << endl;
}
virtual void Sex() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
具体产品,继承自CBlackHuman
//BlackFemaleHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "blackhuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CBlackFemaleHuman :
public CBlackHuman
{
public:
CBlackFemaleHuman(void)
{
}
~CBlackFemaleHuman(void)
{
}
void Sex()
{
cout << "该黑种人的性别为女..." << endl;
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
具体产品,继承自CBlackHuman
//BlackMaleHuman.h
#pragma once
#include "blackhuman.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class CBlackMaleHuman :
public CBlackHuman
{
public:
CBlackMaleHuman(void)
{
}
~CBlackMaleHuman(void)
{
}
void Sex()
{
cout << "该黑种人的性别为男..." << endl;
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
抽象工厂
//IHumanFactory.h
#pragma once
#include "IHuman.h"
class IHumanFactory
{
public:
IHumanFactory(void)
{
}
virtual ~IHumanFactory(void)
{
}
virtual IHuman * CreateYellowHuman() = 0;
virtual IHuman * CreateWhiteHuman() = 0;
virtual IHuman * CreateBlackHuman() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
抽象工厂基类(此类可有可无)
//StandardHumanFactory.h
#pragma once
#include "ihumanfactory.h"
#include "IHuman.h"
template<class T>
class CStandardHumanFactory :
public IHumanFactory
{
public:
CStandardHumanFactory(void)
{
}
~CStandardHumanFactory(void)
{
}
IHuman * CreateHuman()
{
return new T;
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
男人工厂
//MaleHumanFactory.h
#pragma once
#include "standardhumanfactory.h"
#include "IHumanFactory.h"
template<class T>
class CMaleHumanFactory :
public CStandardHumanFactory<T>
{
public:
CMaleHumanFactory(void);
~CMaleHumanFactory(void);
IHuman * CreateYellowHuman();
IHuman * CreateWhiteHuman();
IHuman * CreateBlackHuman();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
//MaleHumanFactory.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "MaleHumanFactory.h"
template<class T>
CMaleHumanFactory<T>::CMaleHumanFactory(void)
{
}
template<class T>
CMaleHumanFactory<T>::~CMaleHumanFactory(void)
{
}
template<class T>
IHuman * CMaleHumanFactory<T>::CreateYellowHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}
template<class T>
IHuman * CMaleHumanFactory<T>::CreateWhiteHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}
template<class T>
IHuman * CMaleHumanFactory<T>::CreateBlackHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
女人工厂
//FemaleHumanFactory.h
#pragma once
#include "standardhumanfactory.h"
template<class T>
class CFemaleHumanFactory :
public CStandardHumanFactory<T>
{
public:
CFemaleHumanFactory(void)
{
}
~CFemaleHumanFactory(void)
{
}
IHuman * CreateYellowHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}
IHuman * CreateWhiteHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}
IHuman * CreateBlackHuman()
{
return CreateHuman();
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
[/code]
测试
//AbstractFactory.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "IHuman.h"
#include "IHumanFactory.h"
#include "FemaleHumanFactory.h"
#include "MaleHumanFactory.h"
#include "MaleHumanFactory.cpp"
#include "YellowFemaleHuman.h"
#include "YellowMaleHuman.h"
#include "WhiteFemaleHuman.h"
#include "WhiteMaleHuman.h"
#include "BlackFemaleHuman.h"
#include "BlackMaleHuman.h"
void DoIt()
{
IHumanFactory *pFemaleHumanFactory = new CFemaleHumanFactory<CYellowFemaleHuman>();
IHuman *pYellowFemaleHuman = pFemaleHumanFactory->CreateYellowHuman();
pYellowFemaleHuman->Cry();
pYellowFemaleHuman->Laugh();
pYellowFemaleHuman->Talk();
pYellowFemaleHuman->Sex();
delete pYellowFemaleHuman;
delete pFemaleHumanFactory;
IHumanFactory *pMaleHumanFactory = new CMaleHumanFactory<CYellowMaleHuman>();
IHuman *pYellowMaleHuman = pMaleHumanFactory->CreateYellowHuman();
pYellowMaleHuman->Cry();
pYellowMaleHuman->Laugh();
pYellowMaleHuman->Talk();
pYellowMaleHuman->Sex();
delete pYellowMaleHuman;
delete pMaleHumanFactory;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
DoIt();
system(“pause”);
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

7.(Facade门面模式)
Facade门面模式,也是比较常用的一种模式,其含义是为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面, Facade 模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。简单说,就是将复杂的逻辑封装起来,对外公开简单的接口,由客户程序调用。
以收发信件和警察检查实例为例
说明:邮局对外只有一个窗口,接收信件内容和邮件地址。对内调用邮件处理的4个函数。将复杂逻辑封装在邮局的里面,当需要增加警察来检查信件时,只需在邮局内增加警察检查信件的方法。
注意:将复杂逻辑封装起来,对外只有一个简单的接口。
抽象信件处理类
//ILetterProcess.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class ILetterProcess
{
public:
ILetterProcess(void);
virtual ~ILetterProcess(void);
virtual void WriteContext(string context) = 0;
virtual void FillEnvelope(string address) = 0;
virtual void LetterIntoEnvelope() = 0;
virtual void SendLetter() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
//ILetterProcess.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "ILetterProcess.h"
ILetterProcess::ILetterProcess(void)
{
}
ILetterProcess::~ILetterProcess(void)
{
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[/code]
信件处理实现类
//LetterprocessImpl.h
#pragma once
#include "iletterprocess.h"
class CLetterProcessImpl :
public ILetterProcess
{
public:
CLetterProcessImpl(void);
~CLetterProcessImpl(void);
void WriteContext(string context);
void FillEnvelope(string address);
void LetterIntoEnvelope();
void SendLetter();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
//LetterProcessImpl.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "LetterProcessImpl.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CLetterProcessImpl::CLetterProcessImpl(void)
{
}
CLetterProcessImpl::~CLetterProcessImpl(void)
{
}
void CLetterProcessImpl::WriteContext(string context)
{
cout << "填写信的内容... ..." << endl;
}
void CLetterProcessImpl::FillEnvelope(string address)
{
cout << "填写收件人地址及姓名... ..." << endl;
}
void CLetterProcessImpl::LetterIntoEnvelope()
{
cout << "把信放到信封中..." << endl;
}
void CLetterProcessImpl::SendLetter()
{
cout << "邮递信件..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
[/code]
邮局处理信件类
//ModenPostOffice.h
#pragma once
#include "ILetterProcess.h"
#include "LetterProcessImpl.h"
#include "LetterPolice.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CModenPostOffice
{
public:
CModenPostOffice(void);
~CModenPostOffice(void);
void SendLetter(string context, string address);
private:
ILetterProcess *m_pLetterProcess;
CLetterPolice *m_pLetterPolice;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
//ModenPostOffice.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "ModenPostOffice.h"
CModenPostOffice::CModenPostOffice(void)
{
this->m_pLetterProcess = new CLetterProcessImpl();
this->m_pLetterPolice = new CLetterPolice();
}
CModenPostOffice::~CModenPostOffice(void)
{
delete m_pLetterProcess;
delete m_pLetterPolice;
}
void CModenPostOffice::SendLetter( string context, string address )
{
//帮忙写信
m_pLetterProcess->WriteContext(context);
//写好信封
m_pLetterProcess->FillEnvelope(address);
//警察要检查信件了
m_pLetterPolice->CheckLetter(m_pLetterProcess);
//把信放到信封中
m_pLetterProcess->LetterIntoEnvelope();
//邮递信件
m_pLetterProcess->SendLetter();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
警察检查信件
//LetterPolice.h
#pragma once
#include "ILetterProcess.h"
class CLetterPolice
{
public:
CLetterPolice(void);
~CLetterPolice(void);
void CheckLetter(ILetterProcess *pLetterProcess);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
//LetterPolice.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "LetterPolice.h"
CLetterPolice::CLetterPolice(void)
{
}
CLetterPolice::~CLetterPolice(void)
{
}
void CLetterPolice::CheckLetter( ILetterProcess *pLetterProcess )
{
cout << “检查信件,此处省略一万字。” << endl;
return;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
测试
//Facade.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "ILetterProcess.h"
#include "LetterProcessImpl.h"
#include "ModenPostOffice.h"
#include<iostream>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void DoItByPostOffice()
{
CModenPostOffice modenPostOffice;
string context = "Hello, It's me, do you know who I am? I'm your old lover. I'd like to ... ...";
string address = "Happy Road No. 666, Beijing City, China";
modenPostOffice.SendLetter(context, address);
}
void DoItYourself()
{
ILetterProcess *pLetterProcess = new CLetterProcessImpl();
pLetterProcess->WriteContext("Hello, It's me, do you know who I am? I'm your old lover. I'd like to ... ...");
pLetterProcess->FillEnvelope("Happy Road No. 666, Beijing City, China");
pLetterProcess->LetterIntoEnvelope();
pLetterProcess->SendLetter();
delete pLetterProcess;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//现在的调用方式。对于客户来说确实简单多了。
//如需要增加逻辑,例如让警察来检查邮件。可以在邮局里完成这项工作。
DoItByPostOffice();
//原来的调用方式。
DoItYourself();
system(“pause”);
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

8.(Adapter适配器模式)
适配器模式,使用之处比较特殊,不属于常规设计模式,主要用于不同系统之间的处理。是将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口。Adapter模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作。
系统内部的实体接口
//IUserInfo.h//
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class IUserInfo
{
public:
IUserInfo(void)
{
}
virtual ~IUserInfo(void)
{
}
virtual string GetUserName() = 0;
virtual string GetHomeAddress() = 0;
virtual string GetMobileNumber() = 0;
virtual string GetOfficeTelNumber() = 0;
virtual string GetJobPosition() = 0;
virtual string GetHomeTelNumber() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
系统内部实体类
//UserInfo.h//
#pragma once
#include "iuserinfo.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CUserInfo :
public IUserInfo
{
public:
CUserInfo(void);
~CUserInfo(void);
string GetUserName();
string GetHomeAddress();
string GetMobileNumber();
string GetOfficeTelNumber();
string GetJobPosition();
string GetHomeTelNumber();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
//UserInfo.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "UserInfo.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
CUserInfo::CUserInfo(void)
{
}
CUserInfo::~CUserInfo(void)
{
}
string CUserInfo::GetUserName()
{
cout << "姓名叫做..." << endl;
return "0";
}
string CUserInfo::GetHomeAddress()
{
cout << "这里是员工的家庭地址..." << endl;
return "0";
}
string CUserInfo::GetMobileNumber()
{
cout << "这个人的手机号码是..." << endl;
return "0";
}
string CUserInfo::GetOfficeTelNumber()
{
cout << "办公室电话是..." << endl;
return "0";
}
string CUserInfo::GetJobPosition()
{
cout << "这个人的职位是BOSS..." << endl;
return "0";
}
string CUserInfo::GetHomeTelNumber()
{
cout << "员工的家庭电话是..." << endl;
return "0";
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
[/code]
外部系统实体接口
//IOuterUser.h//
#pragma once
#include "OuterUserBaseInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserHomeInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserOfficeInfo.h"
class IOuterUser
{
public:
IOuterUser(void)
{
}
~IOuterUser(void)
{
}
COuterUserBaseInfo * GetUserBaseInfo();
COuterUserHomeInfo * GetUserHomeInfo();
COuterUserOfficeInfo * GetUserOfficeInfo();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
外部系统实体类
//OuterUser.h//
#pragma once
#include "OuterUserBaseInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserHomeInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserOfficeInfo.h"
class IOuterUser
{
public:
IOuterUser(void)
{
}
~IOuterUser(void)
{
}
COuterUserBaseInfo * GetUserBaseInfo();
COuterUserHomeInfo * GetUserHomeInfo();
COuterUserOfficeInfo * GetUserOfficeInfo();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
//OuterUser.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "OuterUser.h"
#include "OuterUserBaseInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserHomeInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserOfficeInfo.h"
COuterUser::COuterUser(void)
{
}
COuterUser::~COuterUser(void)
{
}
COuterUserBaseInfo * COuterUser::GetUserBaseInfo()
{
return new COuterUserBaseInfo();
}
COuterUserHomeInfo * COuterUser::GetUserHomeInfo()
{
return new COuterUserHomeInfo();
}
COuterUserOfficeInfo * COuterUser::GetUserOfficeInfo()
{
return new COuterUserOfficeInfo();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
外部系统实体基本信息类
//OuterUserBaseInfo.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
class COuterUserBaseInfo
{
public:
COuterUserBaseInfo(void)
{
}
~COuterUserBaseInfo(void)
{
}
string GetUserName()
{
cout << "姓名叫做..." << endl;
return "0";
}
string GetMobileNumber()
{
cout << "这个人outer的手机号码是... " << endl;
return "0";
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
外部系统实体家庭信息类
//OuterUserHomeInfo.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
class COuterUserHomeInfo
{
public:
COuterUserHomeInfo(void)
{
}
~COuterUserHomeInfo(void)
{
}
string GetHomeAddress()
{
cout << "这里是员工的家庭地址..." << endl;
return "0";
}
string GetHomeTelNumber()
{
cout << "员工的家庭电话是..." << endl;
return "0";
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
外部系统实体办公信息类
//OuterUserOfficeInfo.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
class COuterUserOfficeInfo
{
public:
COuterUserOfficeInfo(void)
{
}
~COuterUserOfficeInfo(void)
{
}
string GetOfficeTelNumber()
{
cout << "办公室电话是..." << endl;
return "0";
}
string GetJobPosition()
{
cout << "这个人的职位是BOSS..." << endl;
return "0";
}
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
由IUserInfo接口派生的实体类,并引入外部系统实体的实例,起适配作用
//OuterUserInfo.h//
#pragma once
#include "iuserinfo.h"
#include "OuterUser.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class COuterUserInfo :
public IUserInfo
{
public:
COuterUserInfo(void);
~COuterUserInfo(void);
string GetUserNa
65a9b
me();
string GetHomeAddress();
string GetMobileNumber();
string GetOfficeTelNumber();
string GetJobPosition();
string GetHomeTelNumber();
private:
COuterUser *m_pOuterUser;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
//OuterUserInfo.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "OuterUserInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserBaseInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserHomeInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserOfficeInfo.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
COuterUserInfo::COuterUserInfo(void)
{
m_pOuterUser = new COuterUser();
}
COuterUserInfo::~COuterUserInfo(void)
{
delete m_pOuterUser;
}
string COuterUserInfo::GetUserName()
{
COuterUserBaseInfo *pBaseInfo = m_pOuterUser->GetUserBaseInfo();
string name = pBaseInfo->GetUserName();
delete pBaseInfo;
pBaseInfo = NULL;
return name;
}
string COuterUserInfo::GetHomeAddress()
{
COuterUserHomeInfo *pHomeInfo = m_pOuterUser->GetUserHomeInfo();
pHomeInfo->GetHomeAddress();
delete pHomeInfo;
pHomeInfo = NULL;
return "0";
}
string COuterUserInfo::GetMobileNumber()
{
COuterUserBaseInfo *pBaseInfo = m_pOuterUser->GetUserBaseInfo();
string number = pBaseInfo->GetMobileNumber();
delete pBaseInfo;
pBaseInfo = NULL;
return number;
}
string COuterUserInfo::GetOfficeTelNumber()
{
COuterUserOfficeInfo *pOfficeInfo = m_pOuterUser->GetUserOfficeInfo();
string num = pOfficeInfo->GetOfficeTelNumber();
delete pOfficeInfo;
pOfficeInfo = NULL;
return num;
}
string COuterUserInfo::GetJobPosition()
{
COuterUserOfficeInfo *pOfficeInfo = m_pOuterUser->GetUserOfficeInfo();
string ret = pOfficeInfo->GetJobPosition();
delete pOfficeInfo;
pOfficeInfo = NULL;
return ret;
}
string COuterUserInfo::GetHomeTelNumber()
{
COuterUserHomeInfo *pHomeInfo = m_pOuterUser->GetUserHomeInfo();
string ret = pHomeInfo->GetHomeTelNumber();
delete pHomeInfo;
pHomeInfo = NULL;
return ret;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
[/code]
使用测试
//Adapter.cpp//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "IOuterUser.h"
#include "IUserInfo.h"
#include "UserInfo.h"
#include "OuterUserInfo.h"
void DoIt()
{
IUserInfo *pYourGirl = new CUserInfo();
for(int i = 0; i < 101; i += 20)
{
pYourGirl->GetMobileNumber();
}
delete pYourGirl;
}
void NowDoIt()
{
IUserInfo *pYourGirl = new COuterUserInfo();
for(int i = 0; i < 101; i += 20)
{
pYourGirl->GetMobileNumber();
}
delete pYourGirl;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
DoIt();
NowDoIt();
system(“pause”)
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

适配器模式属于结构型模式,当出现数据接口不一致的情况下,才会使用到。
9.(Template Method模板方法模式)
模板模式也是相当简单的一种模式,而且是比较常用的。模板模式是定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。TemplateMethod使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
说明:在CHummerModel声明Start、Engineboom、Alarm、Stop虚函数,由派生类实现。基类的Run负责组织逻辑,分别调用这几个派生类实现的函数。
注意:基类中的Run应该禁止派生类覆盖。
Model抽象基类
//HummerModel.h
#pragma once
class CHummerModel
{
public:
CHummerModel(void);
virtual ~CHummerModel(void);
void Run();
protected:
virtual void Start() = 0;
virtual void Stop() = 0;
virtual void Alarm() = 0;
virtual void EngineBoom() = 0;
virtual bool IsAlarm();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
//HummerModel.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "HummerModel.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CHummerModel::CHummerModel(void)
{
}
CHummerModel::~CHummerModel(void)
{
}
void CHummerModel::Run()
{
//先发动汽车
Start();
//引擎开始轰鸣
EngineBoom();
//然后就开始跑了,跑的过程中遇到一条狗挡路,就按喇叭
if (IsAlarm())
Alarm();
//到达目的地就停车
Stop();
}
bool CHummerModel::IsAlarm()
{
//钩子方法,默认喇叭是会响的
return true;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[/code]
Model衍生类1
//HummerH1Model.h
#pragma once
#include "hummermodel.h"
class CHummerH1Model :
public CHummerModel
{
public:
CHummerH1Model(void);
~CHummerH1Model(void);
void SetAlarm(bool tag);
void Start();
void Stop();
void Alarm();
void EngineBoom();
bool IsAlarm();
private:
bool m_isAlarm;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
//HummerH1Model.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "HummerH1Model.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CHummerH1Model::CHummerH1Model(void)
{
m_isAlarm = true;
}
CHummerH1Model::~CHummerH1Model(void)
{
}
void CHummerH1Model::Start()
{
cout << "悍马H1发动..." << endl;
}
void CHummerH1Model::Stop()
{
cout << "悍马H1停车..." << endl;
}
void CHummerH1Model::Alarm()
{
cout << "悍马H1鸣笛" << endl;
}
void CHummerH1Model::EngineBoom()
{
cout << "悍马H1引擎声音是这样...." << endl;
}
bool CHummerH1Model::IsAlarm()
{
return this->m_isAlarm;
}
void CHummerH1Model::SetAlarm( bool tag )
{
this->m_isAlarm = tag;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
[/code]
Model衍生类2
//HummerH2Model.h
#pragma once
#include "hummermodel.h"
class CHummerH2Model :
public CHummerModel
{
public:
CHummerH2Model(void);
~CHummerH2Model(void);
void Start();
void Stop();
void Alarm();
void EngineBoom();
bool IsAlarm();
};
//HummerH2Model.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "HummerH2Model.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CHummerH2Model::CHummerH2Model(void)
{
}
CHummerH2Model::~CHummerH2Model(void)
{
}
void CHummerH2Model::Start()
{
cout << "悍马H2发动..." << endl;
}
void CHummerH2Model::Stop()
{
cout << "悍马H2停车..." << endl;
}
void CHummerH2Model::Alarm()
{
cout << "悍马H2鸣笛" << endl;
}
void CHummerH2Model::EngineBoom()
{
cout << "悍马H2引擎声音是这样...." << endl;
}
bool CHummerH2Model::IsAlarm()
{
return false;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
[/code]
使用测试
//TemplateMethod.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "HummerModel.h"
#include "HummerH1Model.h"
#include "HummerH2Model.h"
#include <crtdbg.h>
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//客户开着H1型号,出去遛弯了
CHummerModel *ph1 = new CHummerH1Model();
ph1->Run();
delete ph1;
//客户开H2型号,出去玩耍了
CHummerModel *ph2 = new CHummerH2Model();
ph2->Run();
delete ph2;
//客户开着H1型号,出去遛弯了,并且不让喇叭响
CHummerH1Model *ph11 = new CHummerH1Model();
ph11->SetAlarm(false);
ph11->Run();
delete ph11;
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

10. (Builder建造者模式)
建造者模式,将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。一段晦涩难懂的文字,实现创建不同表示的方法就是给创建的过程传入创建的参数。
CCarModel实现模板方法,Builder负责开始建造产品。建造产品时,构建的顺序由Director或main决定。
建造者模式和抽象工厂非常类似。建造者更重视产品建造时的逻辑顺序,而抽象工厂更重视生产出不同型号的产品,抽象工厂不关心顺序。
CarModel抽象基类
//CarModel.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
class CCarModel
{
public:
CCarModel(void);
virtual ~CCarModel(void);
void Run();
void SetSequence(vector<string> *pSeq);
protected:
virtual void Start() = 0;
virtual void Stop() = 0;
virtual void Alarm() = 0;
virtual void EngineBoom() = 0;
private:
vector<string> * m_pSequence;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
//CarModel.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "CarModel.h"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
CCarModel::CCarModel(void)
{
}
CCarModel::~CCarModel(void)
{
}
void CCarModel::SetSequence(vector<string> *pSeq)
{
m_pSequence = pSeq;
}
void CCarModel::Run()
{
vector<string>::const_iterator it = m_pSequence->begin();
for (; it < m_pSequence->end(); ++it)
{
string actionName = *it;
if(actionName.compare("start") == 0)
{
Start();
}
else if(actionName.compare("stop") == 0)
{
Stop();
}
else if(actionName.compare("alarm") == 0)
{
Alarm();
}
else if(actionName.compare("engine boom") == 0)
{
EngineBoom();
}
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
[/code]
实际模型1
//BenzModel.h
#pragma once
#include "carmodel.h"
class CBenzModel :
public CCarModel
{
public:
CBenzModel(void);
~CBenzModel(void);
protected:
void Start();
void Stop();
void Alarm();
void EngineBoom();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
//BenzModel.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "BenzModel.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CBenzModel::CBenzModel(void)
{
}
CBenzModel::~CBenzModel(void)
{
}
void CBenzModel::Start()
{
cout << "奔驰发动..." << endl;
}
void CBenzModel::Stop()
{
cout << "奔驰停车..." << endl;
}
void CBenzModel::Alarm()
{
cout << "奔驰鸣笛" << endl;
}
void CBenzModel::EngineBoom()
{
cout << "奔驰引擎声音是这样...." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
[/code]
实际模型2
//BMWModel.h
#pragma once
#include "carmodel.h"
class CBMWModel :
public CCarModel
{
public:
CBMWModel(void);
~CBMWModel(void);
protected:
void Start();
void Stop();
void Alarm();
void EngineBoom();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
//BMWModel.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "BMWModel.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CBMWModel::CBMWModel(void)
{
}
CBMWModel::~CBMWModel(void)
{
}
void CBMWModel::Start()
{
cout << "宝马发动..." << endl;
}
void CBMWModel::Stop()
{
cout << "宝马停车..." << endl;
}
void CBMWModel::Alarm()
{
cout << "宝马鸣笛" << endl;
}
void CBMWModel::EngineBoom()
{
cout << "宝马引擎声音是这样...." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
[/code]
建造者基类
//ICarBuilder.h
#pragma once
#include "CarModel.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::string;
using std::vector;
class ICarBuilder
{
public:
ICarBuilder(void)
{
}
virtual ~ICarBuilder(void)
{
}
virtual void SetSequence(vector<string> *pseq) = 0;
virtual CCarModel * GetCarModel() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
实际建造者1
//BenzBuilder.h
#pragma once
#include "icarbuilder.h"
#include "CarModel.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::string;
using std::vector;
class CBenzBuilder :
public ICarBuilder
{
public:
CBenzBuilder(void);
~CBenzBuilder(void);
void SetSequence(vector<string> *pSeq);
CCarModel * GetCarModel();
private:
CCarModel *m_pBenz;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
//BenzBuilder.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "BenzBuilder.h"
#include "BenzModel.h"
CBenzBuilder::CBenzBuilder(void)
{
m_pBenz = new CBenzModel();
}
CBenzBuilder::~CBenzBuilder(void)
{
delete m_pBenz;
}
void CBenzBuilder::SetSequence(vector<string> *pSeq)
{
m_pBenz->SetSequence(pSeq);
}
CCarModel * CBenzBuilder::GetCarModel()
{
return m_pBenz;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
实际建造者2
//BMWBuilder.h
#pragma once
#include "icarbuilder.h"
#include "CarModel.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::string;
using std::vector;
class CBMWBuilder :
public ICarBuilder
{
public:
CBMWBuilder(void);
~CBMWBuilder(void);
void SetSequence(vector<string> *pSeq);
CCarModel * GetCarModel();
private:
CCarModel *m_pBMW;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
//BMWBuilder.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "BMWBuilder.h"
#include "BMWModel.h"
CBMWBuilder::CBMWBuilder(void)
{
m_pBMW = new CBMWModel();
}
CBMWBuilder::~CBMWBuilder(void)
{
delete m_pBMW;
}
void CBMWBuilder::SetSequence( vector<string> *pSeq )
{
m_pBMW->SetSequence(pSeq);
}
CCarModel * CBMWBuilder::GetCarModel()
{
return m_pBMW;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
指导者
//Director.h
#pragma once
#include "BenzModel.h"
#include "BMWModel.h"
#include "BenzBuilder.h"
#include "BMWBuilder.h"
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
class CDirector
{
public:
CDirector(void);
~CDirector(void);
CBenzModel * GetABenzModel();
CBenzModel * GetBBenzModel();
CBMWModel * GetCBMWModel();
CBMWModel * GetDBMWModel();
private:
vector<string> * m_pSeqence;
CBenzBuilder * m_pBenzBuilder;
CBMWBuilder * m_pBMWBuilder;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[/code]
//Director.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Director.h"
CDirector::CDirector(void)
{
m_pBenzBuilder = new CBenzBuilder();
m_pBMWBuilder = new CBMWBuilder();
m_pSeqence = new vector<string>();
}
CDirector::~CDirector(void)
{
delete m_pBenzBuilder;
delete m_pBMWBuilder;
delete m_pSeqence;
}
CBenzModel * CDirector::GetABenzModel()
{
m_pSeqence->clear();
m_pSeqence->push_back("start");
m_pSeqence->push_back("stop");
m_pBenzBuilder->SetSequence(m_pSeqence);
return dynamic_cast<CBenzModel*>(m_pBenzBuilder->GetCarModel());
}
CBenzModel * CDirector::GetBBenzModel()
{
m_pSeqence->clear();
m_pSeqence->push_back("engine boom");
m_pSeqence->push_back("start");
m_pSeqence->push_back("stop");
m_pBenzBuilder->SetSequence(m_pSeqence);
return dynamic_cast<CBenzModel*>(m_pBenzBuilder->GetCarModel());
}
CBMWModel * CDirector::GetCBMWModel()
{
m_pSeqence->clear();
m_pSeqence->push_back("alarm");
m_pSeqence->push_back("start");
m_pSeqence->push_back("stop");
m_pBMWBuilder->SetSequence(m_pSeqence);
return static_cast<CBMWModel*>(m_pBMWBuilder->GetCarModel());
}
CBMWModel * CDirector::GetDBMWModel()
{
m_pSeqence->clear();
m_pSeqence->push_back("start");
m_pBenzBuilder->SetSequence(m_pSeqence);
return dynamic_cast<CBMWModel*>(m_pBMWBuilder->GetCarModel());
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
[/code]
使用实例
// Builder.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CarModel.h"
#include "BenzModel.h"
#include "BMWModel.h"
#include "BenzBuilder.h"
#include "BMWBuilder.h"
#include "Director.h"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void DoBenzRun() //没有使用模式时,需要把步骤一条一条的传入模型。
{
cout << "----------生成奔驰模型----------" << endl;
CBenzModel *pBenz = new CBenzModel();
vector<string> seq;
seq.push_back("engine boom");//客户要求run的时候先发动引擎
seq.push_back("start");//启动起来
seq.push_back("stop");//开了一段就停下来
pBenz->SetSequence(&seq);
pBenz->Run();
delete pBenz;
}
//使用模式后,由benzBuilder和bmwBuilder来生成,并且使用同样的创建顺序。
void DoBuilder()
{
cout << "----------用同一个顺序,生成模型----------" << endl;
vector<string> seq;
seq.push_back("engine boom");
seq.push_back("start");
seq.push_back("stop");
CBenzBuilder benzBuilder;
benzBuilder.SetSequence(&seq);
CBenzModel *pBenz = dynamic_cast<CBenzModel*>(benzBuilder.GetCarModel());
pBenz->Run();
CBMWBuilder bmwBuilder;
bmwBuilder.SetSequence(&seq);
CBMWModel *pBmw = dynamic_cast<CBMWModel*>(bmwBuilder.GetCarModel());
pBenz->Run();
}
void DoDirector() //使用指导者来封装创建的逻辑,把创建的顺序内聚在指导者类里面。
{
cout << "----------批量生成模型----------" << endl;
CDirector director;
//1W辆A类型的奔驰车
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
director.GetABenzModel()->Run();
//100W辆B类型的奔驰车
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
director.GetBBenzModel()->Run();
//1000W辆C类型的宝马车
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
director.GetCBMWModel()->Run();
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
DoBenzRun();
DoBuilder();
DoDirector();
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

建造者模式属于创建型模式,主要关注创建的顺序,不同的顺序,生产的产品略有不同。
11. (Bridge桥接模式)
桥接模式,将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化。实现分离的办法就是增加一个类。
说明:客户直接使用CNewHouseCorp和CShanZhaiCorp类,在main()函数里构造产品,然后传到这两个类里。这两个类的MakeMoney()函数,先调用基类的MakeMoney(),然后分别执行各自的逻辑。
注意:CNewCorp起到了桥梁的作用。可以分别增加产品和公司。
产品基类
//IProduct.h
#pragma once
class IProduct
{
public:
IProduct(void)
{
}
virtual ~IProduct(void)
{
}
virtual void BeProducted() = 0;
virtual void BeSelled() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
产品——房子
//House.h
#pragma once
#include "iproduct.h"
class CHouse :
public IProduct
{
public:
CHouse(void);
~CHouse(void);
void BeProducted();
void BeSelled();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//House.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "House.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CHouse::CHouse(void)
{
}
CHouse::~CHouse(void)
{
}
void CHouse::BeProducted()
{
cout << "生产出的房子是这个样子的..." << endl;
}
void CHouse::BeSelled()
{
cout << "生产出的房子卖出去了..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
产品——衣服
//Clothes.h
#pragma once
#include "iproduct.h"
class CClothes :
public IProduct
{
public:
CClothes(void);
~CClothes(void);
void BeProducted();
void BeSelled();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//Clothes.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Clothes.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CClothes::CClothes(void)
{
}
CClothes::~CClothes(void)
{
}
void CClothes::BeProducted()
{
cout << "生产出的衣服是这个样子的..." << endl;
}
void CClothes::BeSelled()
{
cout << "生产出的衣服卖出去了..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
产品——ipod
//IPod.h
#pragma once
#include "iproduct.h"
class CIPod :
public IProduct
{
public:
CIPod(void);
~CIPod(void);
void BeProducted();
void BeSelled();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//IPod.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "IPod.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CIPod::CIPod(void)
{
}
CIPod::~CIPod(void)
{
}
void CIPod::BeProducted()
{
cout << "生产出的ipod是这个样子的..." << endl;
}
void CIPod::BeSelled()
{
cout << "生产出的ipod卖出去了..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
桥梁类,其中MakeMoney()是桥梁方法
//NewCorp.h
#pragma once
#include "IProduct.h"
class CNewCorp
{
public:
CNewCorp(IProduct *pproduct);
virtual ~CNewCorp(void);
void MakeMoney();
private:
IProduct *m_pProduct;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//NewCorp.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "NewCorp.h"
CNewCorp::CNewCorp( IProduct *pproduct )
{
this->m_pProduct = pproduct;
}
CNewCorp::~CNewCorp(void)
{
}
void CNewCorp::MakeMoney()
{
//每个公司都是一样,先生产
this->m_pProduct->BeProducted();
//然后销售
this->m_pProduct->BeSelled();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
只生产房子的类,靠卖房子挣钱
//NewHouseCorp.h
#pragma once
#include "newcorp.h"
#include "House.h"
class CNewHouseCorp :
public CNewCorp
{
public:
CNewHouseCorp(CHouse *pHouse);
~CNewHouseCorp(void);
void MakeMoney();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//NewHouseCorp.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "NewHouseCorp.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CNewHouseCorp::CNewHouseCorp(CHouse *pHouse) : CNewCorp(pHouse)
{
}
CNewHouseCorp::~CNewHouseCorp(void)
{
}
void CNewHouseCorp::MakeMoney()
{
this->CNewCorp::MakeMoney();
cout << "房地产公司赚大钱了..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
靠生产山寨产品挣钱
//ShanZhaiCorp.h
#pragma once
#include "newcorp.h"
#include "IProduct.h"
class CShanZhaiCorp :
public CNewCorp
{
public:
CShanZhaiCorp(IProduct *pproduct);
~CShanZhaiCorp(void);
void MakeMoney();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//ShanZhaiCorp.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "ShanZhaiCorp.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CShanZhaiCorp::CShanZhaiCorp(IProduct *pproduct) : CNewCorp(pproduct)
{
}
CShanZhaiCorp::~CShanZhaiCorp(void)
{
}
void CShanZhaiCorp::MakeMoney()
{
this->CNewCorp::MakeMoney();
cout << "我赚钱呀..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
使用测试
// Bridge.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "ClothesCorp.h"
#include "NewHouseCorp.h"
#include "Clothes.h"
#include "IPod.h"
#include "ShanZhaiCorp.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void DoNewRun1()
{
cout << "----------房地产公司是这样运行的----------" << endl;
CHouse house;
CNewHouseCorp newHouseCorp(&house);
newHouseCorp.MakeMoney();
cout << endl;
cout << "----------山寨公司是这样运行的----------" << endl;
CClothes clothes;
CShanZhaiCorp shanZhaiCorp(&clothes);
shanZhaiCorp.MakeMoney();
cout << endl;
}
void DoNewRun2()
{
cout << "----------房地产公司是这样运行的----------" << endl;
CHouse house;
CNewHouseCorp newHouseCorp(&house);
newHouseCorp.MakeMoney();
cout << endl;
cout << "----------山寨公司是这样运行的----------" << endl;
CIPod ipod;
CShanZhaiCorp shanZhaiCorp(&ipod);
shanZhaiCorp.MakeMoney();
cout << endl;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//只有两家公司,一家是房地产公司,另一家公司是衣服赚钱就生产衣服
DoNewRun1();
//只有两家公司,一家是房地产公司,另一家公司是ipod赚钱就生产ipod
DoNewRun2();
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

12.(Command命令模式)
命令模式,将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤消的操作。
说明:客户只需要知道向Invoker发出命令(多个命令),而不是将命令直接传达给具体的执行者。当然,客户是需要知道都有什么命令的。
注意:客户只发命令,不需要知道由谁来执行和怎么执行,体现出高内聚的特点。用户在发出命令后,是允许撤回的,所以可以增加一个命令“Undo ”,Undo是状态的变更。
命令接收者
//Invoker.h
#pragma once
#include "ICommand.h"
class CInvoker
{
public:
CInvoker(void);
~CInvoker(void);
void SetCommand(ICommand *pcommand);
void Action();
private:
ICommand *m_pCommand;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//Invoker.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Invoker.h"
CInvoker::CInvoker(void)
{
}
CInvoker::~CInvoker(void)
{
}
void CInvoker::SetCommand( ICommand *pcommand )
{
this->m_pCommand = pcommand;
}
void CInvoker::Action()
{
this->m_pCommand->Execute();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
执行都抽象基类
//IGroup.h
#pragma once
class IGroup
{
public:
IGroup(void)
{
}
virtual ~IGroup(void)
{
}
virtual void Find() = 0;
virtual void Add() = 0;
virtual void Delete() = 0;
virtual void Change() = 0;
virtual void Plan() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
实际执行者1
//RequirementGroup.h
#pragma once
#include "igroup.h"
class CRequirementGroup :
public IGroup
{
public:
CRequirementGroup(void);
~CRequirementGroup(void);
void Find();
void Add();
void Delete();
void Change();
void Plan();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
//RequirementGroup.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "RequirementGroup.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CRequirementGroup::CRequirementGroup(void)
{
}
CRequirementGroup::~CRequirementGroup(void)
{
}
void CRequirementGroup::Find()
{
cout << "找到需求组..." << endl;
}
void CRequirementGroup::Add()
{
cout << "客户要求增加一项需求..." << endl;
}
void CRequirementGroup::Delete()
{
cout << "要求删除一项需求..." << endl;
}
void CRequirementGroup::Change()
{
cout << "客户要求修改一项需求..." << endl;
}
void CRequirementGroup::Plan()
{
cout << "客户要求需求变更计划..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
实际执行者2
//PageGroup.h
#pragma once
#include "igroup.h"
class CPageGroup :
public IGroup
{
public:
CPageGroup(void);
~CPageGroup(void);
void Find();
void Add();
void Delete();
void Change();
void Plan();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
//PageGroup.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "PageGroup.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CPageGroup::CPageGroup(void)
{
}
CPageGroup::~CPageGroup(void)
{
}
void CPageGroup::Find()
{
cout << "找到美工组..." << endl;
}
void CPageGroup::Add()
{
cout << "客户要求增加一个页面..." << endl;
}
void CPageGroup::Delete()
{
cout << "客户要求删除一个页面..." << endl;
}
void CPageGroup::Change()
{
cout << "客户要求修改一个页面..." << endl;
}
void CPageGroup::Plan()
{
cout << "客户要求页面变更计划..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
实际执行者3
//CodeGroup.h
#pragma once
#include "igroup.h"
class CCodeGroup :
public IGroup
{
public:
CCodeGroup(void);
~CCodeGroup(void);
void Find();
void Add();
void Delete();
void Change();
void Plan();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
//CodeGroup.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "CodeGroup.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CCodeGroup::CCodeGroup(void)
{
}
CCodeGroup::~CCodeGroup(void)
{
}
void CCodeGroup::Find()
{
cout << "找到代码组..." << endl;
}
void CCodeGroup::Add()
{
cout << "客户要求增加一项功能..." << endl;
}
void CCodeGroup::Delete()
{
cout << "客户要求删除一项功能..." << endl;
}
void CCodeGroup::Change()
{
cout << "客户要求修改一项功能..." << endl;
}
void CCodeGroup::Plan()
{
cout << "客户要求代码变更计划..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
命令接口抽象基类
//ICommand.h
#pragma once
#include "RequirementGroup.h"
#include "PageGroup.h"
#include "CodeGroup.h"
class ICommand
{
public:
ICommand(void)
{
m_prg = new CRequirementGroup();
m_ppg = new CPageGroup();
m_pcg = new CCodeGroup();
}
virtual ~ICommand(void)
{
delete m_prg;
delete m_ppg;
delete m_pcg;
}
virtual void Execute() = 0;
protected:
CRequirementGroup *m_prg;
CPageGroup *m_ppg;
CCodeGroup *m_pcg;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[/code]
添加执行命令
//AddRequirementCommand.h
#pragma once
#include "icommand.h"
class CAddRequirementCommand :
public ICommand
{
public:
CAddRequirementCommand(void);
~CAddRequirementCommand(void);
void Execute();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
//AddRequirementCommand.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "AddRequirementCommand.h"
CAddRequirementCommand::CAddRequirementCommand(void)
{
}
CAddRequirementCommand::~CAddRequirementCommand(void)
{
}
void CAddRequirementCommand::Execute()
{
//执行增另一项需求的命令
this->ICommand::m_prg->Find();
//增加一份需求
this->ICommand::m_prg->Add();
//给出计划
this->ICommand::m_prg->Plan();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
删除撤消命令
//DeletePageCommand.h
#pragma once
#include "icommand.h"
class CDeletePageCommand :
public ICommand
{
public:
CDeletePageCommand(void);
~CDeletePageCommand(void);
void Execute();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
//DeletePageCommand.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "DeletePageCommand.h"
CDeletePageCommand::CDeletePageCommand(void)
{
}
CDeletePageCommand::~CDeletePageCommand(void)
{
}
void CDeletePageCommand::Execute()
{
//执行增另一项需求的命令
this->ICommand::m_ppg->Find();
//增加一份需求
this->ICommand::m_ppg->Delete();
//给出计划
this->ICommand::m_ppg->Plan();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
使用测试
//Command.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "IGroup.h"
#include "CodeGroup.h"
#include "PageGroup.h"
#include "RequirementGroup.h"
#include "Invoker.h"
#include "AddRequirementCommand.h"
#include "DeletePageCommand.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void DoIt()
{
cout << "----------客户想增加一个需求----------" << endl;
IGroup *rg = new CRequirementGroup();
rg->Find();
rg->Add();
rg->Plan();
delete rg;
cout << endl;
cout << "----------客户又想修改一个页面----------" << endl;
IGroup *pg = new CPageGroup();
pg->Find();
pg->Add();
pg->Plan();
delete pg;
cout << endl;
cout << "----------客户又想删除一个功能----------" << endl;
IGroup *cg = new CCodeGroup();
cg->Find();
cg->Add();
cg->Plan();
delete cg;
cout << endl;
}
void DoNew()
{
cout << "----------客户觉得烦了,希望只找一个人,并告诉他要做什么----------" << endl;
cout << "----------客户要求增加一项需求----------" << endl;
CInvoker gary;
ICommand *pcommand = new CAddRequirementCommand();
gary.SetCommand(pcommand);
gary.Action();
delete pcommand;
cout << endl;
//客户想要改动只需要找CInvoker就可以了。
cout << "----------客户要求删除一个页面----------" << endl;
CInvoker ricky;
ICommand *pcommand2 = new CDeletePageCommand();
ricky.SetCommand(pcommand2);
ricky.Action();
delete pcommand2;
cout << endl;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//客户原来的运行流程
DoIt();
//客户觉得麻烦了,每次改动都要找不同的组,谈不同的事
//客户只想找一个人,告诉他要做什么就可以,不想关心由哪几个组来做和怎么做
DoNew();
system(“pause”)
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

缺点:因为一个命令就定义为一个ICommand实现类,这样的话,对ICommand派生类的数量增长可能会难以控制。
13.(Decorator装饰模式)
装饰模式,动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,Decorator模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
成绩单抽象基类
//ISchoolReport.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class ISchoolReport
{
public:
ISchoolReport(void)
{
}
virtual ~ISchoolReport(void)
{
}
virtual void Report() = 0;
virtual void Sign(string name) = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
四年级成绩单
//FouthGradeSchoolReport.h
#pragma once
#include "ischoolreport.h"
class CFouthGradeSchoolReport :
public ISchoolReport
{
public:
CFouthGradeSchoolReport(void);
~CFouthGradeSchoolReport(void);
void Report();
void Sign(string name);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//FouthGradeSchoolReport.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "FouthGradeSchoolReport.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
CFouthGradeSchoolReport::CFouthGradeSchoolReport(void)
{
}
CFouthGradeSchoolReport::~CFouthGradeSchoolReport(void)
{
}
void CFouthGradeSchoolReport::Report()
{
cout << "尊敬的XXX家长:" << endl;
cout << "......" << endl;
cout << "语文62 数学65 体育98 自然63" << endl;
cout << "......" << endl;
cout << " 家长签名:" << endl;
}
void CFouthGradeSchoolReport::Sign(string name)
{
cout << "家长签名为:" << name.c_str() << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[/code]
成绩单装饰基类
//ReportDecorator.h
#pragma once
#include "ischoolreport.h"
class CReportDecorator :
public ISchoolReport
{
public:
CReportDecorator(ISchoolReport *psr);
virtual ~CReportDecorator(void);
void Report();
void Sign(string name);
private:
ISchoolReport *m_pSchoolReport;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
//ReportDecorator.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "ReportDecorator.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
CReportDecorator::CReportDecorator(ISchoolReport *psr)
{
this->m_pSchoolReport = psr;
}
CReportDecorator::~CReportDecorator(void)
{
}
void CReportDecorator::Report()
{
this->m_pSchoolReport->Report();
}
void CReportDecorator::Sign( string name )
{
this->m_pSchoolReport->Sign(name);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
最高分装饰者
//HighScoreDecorator.h
#pragma once
#include "reportdecorator.h"
#include "ISchoolReport.h"
class CHighScoreDecorator :
public CReportDecorator
{
public:
CHighScoreDecorator(ISchoolReport *psr);
~CHighScoreDecorator(void);
void Report();
private:
void ReportHighScore();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
//HighScoreDecorator.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "HighScoreDecorator.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CHighScoreDecorator::CHighScoreDecorator( ISchoolReport *psr ) : CReportDecorator(psr)
{
}
CHighScoreDecorator::~CHighScoreDecorator(void)
{
}
void CHighScoreDecorator::Report()
{
this->ReportHighScore();
this->CReportDecorator::Report();
}
void CHighScoreDecorator::ReportHighScore()
{
cout << "这次考试语文最高是75, 数学是78, 自然是80" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
成绩排名装饰者
//SortDecorator.h
#pragma once
#include "reportdecorator.h"
#include "ISchoolReport.h"
class CSortDecorator :
public CReportDecorator
{
public:
CSortDecorator(ISchoolReport *psr);
~CSortDecorator(void);
void Report();
private:
void ReportSort();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
//SortDecorator.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "SortDecorator.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CSortDecorator::CSortDecorator( ISchoolReport *psr ) : CReportDecorator(psr)
{
}
CSortDecorator::~CSortDecorator(void)
{
}
void CSortDecorator::ReportSort()
{
cout << "我是排名第38名..." << endl;
}
void CSortDecorator::Report()
{
this->CReportDecorator::Report();
this->ReportSort();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
使用测试
// Decorator.cpp//主程序
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "ISchoolReport.h"
#include "FouthGradeSchoolReport.h"
#include "SugarFouthGradeSchoolReport.h"
#include "HighScoreDecorator.h"
#include "SortDecorator.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void DoIt()
{
ISchoolReport *psr = new CSugarFouthGradeSchoolReport();
psr->Report();//看成绩单
psr->Sign("老三");//很开心,就签字了
delete psr;
}
void DoNew()
{
cout << "----------分部分进行装饰----------" << endl;
ISchoolReport *psr = new CFouthGradeSchoolReport();//原装成绩单
//
ISchoolReport *pssr = new CSortDecorator(psr);//又加了成绩排名的说明
ISchoolReport *phsr = new CHighScoreDecorator(pssr);//加了最高分说明的成绩单
phsr->Report();//看成绩单
phsr->Sign("老三");//很开心,就签字了
//先装饰哪个不重要,顺序已经在装饰内部确定好,但一定要调用最后一个装饰器的接口。
//ISchoolReport *phsr = new CHighScoreDecorator(psr);//加了最高分说明的成绩单
//ISchoolReport *pssr = new CSortDecorator(phsr);//又加了成绩排名的说明
//pssr->Report();//看成绩单
//pssr->Sign("老三");//很开心,就签字了
delete pssr;
delete phsr;
delete psr;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//在装饰之前,可以用继承的办法,来进行简单的修饰
DoIt();
//但如果需要修饰的项目太多呢?或者装饰的项目不是固定的,继承显然会变得更复杂
DoNew();
system(“pause”)
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

14.(Iterator迭代器模式)
所谓迭代器模式是提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部表示。
说明:CProject实现产品类,能够返回一个迭代器的指针。这个迭代器将封装产品类里的一个数组。所以迭代器在运行Next函数时,可以遍历这个数组的所有元素。
简单来说,就是用代码实现vector::iterator或vector::const_iterator。
产品接口
//IProject.h
#pragma once
#include "IProjectIterator.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class IProject
{
public:
IProject(void)
{
}
virtual ~IProject(void)
{
}
virtual void Add(string name, int num, int cost) = 0;
virtual string GetProjectInfo() = 0;
virtual IProjectIterator* GetIterator() = 0;
virtual void Erase() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
产品类
//Project.h
#pragma once
#include "iproject.h"
#include "IProjectIterator.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::string;
using std::vector;
class CProject :
public IProject
{
public:
CProject(void);
CProject(string name, int num, int cost);
~CProject(void);
string GetProjectInfo();
void Add(string name, int num, int cost);
IProjectIterator * GetIterator();
void Erase();
private:
string m_name;
int m_num;
int m_cost;
vector<IProject*> m_projectList;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[/code]
//Project.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Project.h"
#include "ProjectIterator.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::string;
using std::vector;
CProject::CProject( void )
{
m_name = "";
m_num = 0;
m_cost = 0;
}
CProject::CProject(string name, int num, int cost) :m_name(name), m_num(num), m_cost(cost)
{
}
CProject::~CProject(void)
{
}
string CProject::GetProjectInfo()
{
string info = "";
info.append("项目名称是:");
info.append(this->m_name);
info.append("\t项目人数:");
char buf1[20] = {0}, buf2[20] = {0};
sprintf_s(buf1, "%d", m_num);
info.append(buf1);
info.append("\t项目费用:");
sprintf_s(buf2, "%d", m_cost);
info.append(buf2);
return info;
}
void CProject::Add( string name, int num, int cost )
{
this->m_projectList.push_back(new CProject(name, num, cost));
}
IProjectIterator * CProject::GetIterator()
{
return new CProjectIterator(this->m_projectList);
}
void CProject::Erase()
{
vector<IProject*>::reverse_iterator projectDelIt = m_projectList.rbegin();
for (; projectDelIt != m_projectList.rend(); projectDelIt++)
{
delete (*projectDelIt);
(*projectDelIt) = NULL;
}
m_projectList.clear();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
[/code]
迭代器接口
//IIterator.h
#pragma once
class IProject;
class IIterator
{
public:
IIterator(void)
{
}
virtual ~IIterator(void)
{
}
virtual bool HasNext() = 0;
virtual IProject * Next() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
产品迭代器接口
//IProjectIterator.h
#pragma once
#include "iiterator.h"
class IProject;
class IProjectIterator :
public IIterator
{
public:
IProjectIterator(void)
{
}
virtual ~IProjectIterator(void)
{
}
virtual bool HasNext() = 0;
virtual IProject * Next() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
产品迭代器实现类
//ProjectIterator.h
#pragma once
#include "iprojectiterator.h"
#include "IProject.h"
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
class CProjectIterator :
public IProjectIterator
{
public:
CProjectIterator(vector<IProject *> pl);
~CProjectIterator(void);
bool HasNext();
IProject * Next();
private:
vector<IProject *> m_projectList;
size_t m_currentItem;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
//ProjectIterator.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "ProjectIterator.h"
CProjectIterator::CProjectIterator(vector<IProject *> pl) : m_projectList(pl)
{
m_currentItem = 0;
}
CProjectIterator::~CProjectIterator(void)
{
}
bool CProjectIterator::HasNext()
{
bool b = true;
if (m_currentItem >= m_projectList.size())
b = false;
return b;
}
IProject * CProjectIterator::Next()
{
IProject *pp = m_projectList.at(m_currentItem ++);
return pp;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[/code]
使用测试
// Iterator.cpp
// Iterator.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "IProject.h"
#include "Project.h"
#include "ProjectIterator.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void DoIt()
{
cout << "----------未使用迭代模式----------" << endl;
vector<IProject*> projectList;
projectList.push_back(new CProject("星球大战项目", 10, 100000));
projectList.push_back(new CProject("扭转时空项目", 100, 10000000));
projectList.push_back(new CProject("超人改造项目", 10000, 1000000000));
for (int i = 4; i < 6; i ++)
{
string name = "";
name.append("第");
char buf[10] = {0};
sprintf_s(buf, "%d", i);
name.append(buf);
name.append("个项目");
projectList.push_back(new CProject(name, i * 5, i * 1000000));
}
vector<IProject*>::const_iterator projectIt = projectList.begin();
for (; projectIt != projectList.end(); projectIt++)
cout << (*projectIt)->GetProjectInfo().c_str() << endl;
vector<IProject*>::reverse_iterator projectDelIt = projectList.rbegin();
for (; projectDelIt != projectList.rend(); projectDelIt++)
{
delete (*projectDelIt);
(*projectDelIt) = NULL;
}
projectList.clear();
}
void DoNew()
{
cout << "----------使用迭代模式----------" << endl;
IProject *pproject = new CProject();
pproject->Add("星球大战项目", 10, 100000);
pproject->Add("扭转时空项目", 100, 10000000);
pproject->Add("超人改造项目", 10000, 1000000000);
for (int i = 4; i < 6; i ++)
{
string name = "";
name.append("第");
char buf[10] = {0};
sprintf_s(buf, "%d", i);
name.append(buf);
name.append("个项目");
pproject->Add(name, i * 5, i * 1000000);
}
IProjectIterator *pprojectIt = pproject->GetIterator();
while(pprojectIt->HasNext())
{
IProject *p = dynamic_cast<IProject*>(pprojectIt->Next());
cout << p->GetProjectInfo().c_str() << endl;
}
delete pprojectIt;
pprojectIt = NULL;
pproject->Erase();
delete pproject;
pproject = NULL;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//使用Iterator模式之前
DoIt();
//使用Iterator
DoNew();
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
[/code]
代码结构:

运行结果:

15.(Composite组合模式)
将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构。Composite使得用户对单个对象和组合的使用具有一致性。
说明:组合模式主要是实现在CBranchNode对象里增加对其它对象的数组,如vector
//CorpNode.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CCorpNode
{
public:
CCorpNode();
CCorpNode(string _name, string _pos, int _salary);
virtual ~CCorpNode(void);
virtual string GetInfo();
void SetParent(CCorpNode *_pParent);
CCorpNode * GetParent();
virtual bool IsLeaf() = 0;
private:
string m_name;
string m_position;
int m_salary;
protected:
bool m_isLeaf;
CCorpNode *m_pParent;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[/code]
//CorpNode.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "CorpNode.h"
CCorpNode::CCorpNode(void)
{
m_name = "";
m_position = "";
m_salary = 0;
}
CCorpNode::CCorpNode(string _name, string _pos, int _salary) : m_name(_name), m_position(_pos), m_salary(_salary)
{
}
CCorpNode::~CCorpNode(void)
{
}
string CCorpNode::GetInfo()
{
string info = "";
info.append("姓名:");
info.append(this->m_name);
info.append("\t职位:");
info.append(this->m_position);
info.append("\t薪水:");
char buf[50] = {0};
sprintf_s(buf, "%d", this->m_salary);
info.append(buf);
return info;
}
void CCorpNode::SetParent( CCorpNode *_parent )
{
this->m_pParent = _parent;
}
CCorpNode * CCorpNode::GetParent()
{
return this->m_pParent;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
[/code]
树枝节点,实现Addordinate()函数和GetSubordinate()函数
//BranchNode.h
#pragma once
#include "corpnode.h"
#include "CorpNode.h"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
class CBranchNode :
public CCorpNode
{
public:
CBranchNode(void);
CBranchNode(string name, string pos, int salary);
~CBranchNode(void);
void Add(CCorpNode *pcorpNode);
vector<CCorpNode*> GetSubordinateInfo();
bool IsLeaf();
private:
vector<CCorpNode*> m_subordinateList;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
//BranchNode.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "BranchNode.h"
CBranchNode::CBranchNode(void)
{
m_isLeaf = false;
}
CBranchNode::CBranchNode( string name, string pos, int salary ) : CCorpNode(name, pos, salary)
{
m_isLeaf = false;
}
CBranchNode::~CBranchNode(void)
{
}
void CBranchNode::Add( CCorpNode *pcorpNode )
{
pcorpNode->SetParent(this);
m_subordinateList.push_back(pcorpNode);
}
vector<CCorpNode*> CBranchNode::GetSubordinateInfo()
{
return this->m_subordinateList;
}
bool CBranchNode::IsLeaf()
{
return m_isLeaf;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
[/code]
叶子节点
//LeafNode.h
#pragma once
#include "corpnode.h"
class CLeafNode :
public CCorpNode
{
public:
CLeafNode(void);
CLeafNode(string name, string pos, int salary);
~CLeafNode(void);
bool IsLeaf();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//LeafNode.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "LeafNode.h"
CLeafNode::CLeafNode(void)
{
m_isLeaf = true;
}
CLeafNode::CLeafNode( string name, string pos, int salary ) : CCorpNode(name, pos, salary)
{
m_isLeaf = true;
}
CLeafNode::~CLeafNode(void)
{
}
bool CLeafNode::IsLeaf()
{
return m_isLeaf;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
使用测试
// Composite.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "BranchNode.h"
#include "LeafNode.h"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
string GetTreeInfo(CBranchNode * proot)
{
vector<CCorpNode*> subordinateList = proot->GetSubordinateInfo();
string info = "";
vector<CCorpNode*>::const_iterator it = subordinateList.begin();
for (; it != subordinateList.end(); it++)
{
if ((*it)->IsLeaf())
{
info.append((*it)->GetInfo());
info.append("\n");
}
else
{
info.append((*it)->GetInfo());
info.append("\n");
info.append(GetTreeInfo(dynamic_cast<CBranchNode*>(*it)));
}
}
return info;
}
void DoNew()
{
CBranchNode root("赵大", "总经理", 100000);
CBranchNode devDep("钱大", "研发部门经理", 10000);
CBranchNode saleDep("孙大", "销售部门经理", 20000);
CBranchNode financeDep("李大", "财务部门经理", 30000);
CBranchNode firstDevGroup("周三也斜", "开发一组组长", 5000);
CBranchNode secondDevGroup("吴大棒槌", "开发二组组长", 6000);
CLeafNode a("a", "开发人员", 2000);
CLeafNode b("b", "开发人员", 2000);
CLeafNode c("c", "开发人员", 2000);
CLeafNode d("d", "开发人员", 2000);
CLeafNode e("e", "开发人员", 2000);
CLeafNode f("f", "开发人员", 2000);
CLeafNode g("g", "开发人员", 2000);
CLeafNode h("h", "开发人员", 5000);
CLeafNode i("i", "开发人员", 4000);
CLeafNode j("j", "开发人员", 5000);
CLeafNode k("k", "CEO秘书", 8000);
CLeafNode zheng("郑老六", "研发部副经理", 20000);
root.Add(&k);//CEO有三个部门经理和一个秘书
root.Add(&devDep);
root.Add(&saleDep);
root.Add(&financeDep);
devDep.Add(&zheng);//开发部有一个副经理和两个小组
devDep.Add(&firstDevGroup);
devDep.Add(&secondDevGroup);
firstDevGroup.Add(&a);
firstDevGroup.Add(&b);
firstDevGroup.Add(&c);
secondDevGroup.Add(&d);
secondDevGroup.Add(&e);
secondDevGroup.Add(&f);
saleDep.Add(&g);
saleDep.Add(&h);
financeDep.Add(&i);
financeDep.Add(&j);
cout << root.GetInfo().c_str() << endl;
cout << GetTreeInfo(&root).c_str() << endl;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//使用组合模式后的调用。
DoNew();
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
[/code]
代码结构图:

运行结果:

**16.(Observer观察者模式)
定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并被自动更新。
说明:将观察者聚集到被观察者韩非子身边,韩非子的每一个举动都会通知给观察者,如李斯或周斯。
注意:最多允许一个对象既是观察者也是被观察者。就像数据库中的触发器一样,成为一个复杂的链就很难维护了。观察者类似于委托的处理方式。
被观察者接口
//IObservable.h
#pragma once
#include "IObserver.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class IObservable
{
public:
IObservable(void)
{
}
virtual ~IObservable(void)
{
}
virtual void AddObserver(IObserver *pObserver) = 0;
virtual void DeleteObserver(IObserver *pObserver) = 0;
virtual void NotifyObservers(string context) = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
被观察者1
//HanFeiziObservable.h
#pragma once
#include "iobservable.h"
#include "IObserver.h"
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
class CHanFeiziObservable :
public IObservable
{
public:
CHanFeiziObservable(void);
~CHanFeiziObservable(void);
void AddObserver(IObserver *pObserver);
void DeleteObserver(IObserver *pObserver);
void NotifyObservers(string context);
void HaveBreakfast();
void HaveFun();
private:
vector<IObserver*> m_observerList;
typedef vector<IObserver*>::const_iterator ObserverList_C_iterator;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[/code]
//HanFeiziObservable.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "HanFeiziObservable.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CHanFeiziObservable::CHanFeiziObservable(void)
{
}
CHanFeiziObservable::~CHanFeiziObservable(void)
{
}
void CHanFeiziObservable::AddObserver( IObserver *pObserver )
{
m_observerList.push_back(pObserver);
}
void CHanFeiziObservable::DeleteObserver( IObserver *pObserver )
{
ObserverList_C_iterator it = m_observerList.begin();
for (; it != m_observerList.end(); it++)
{
string name = (*it)->GetName();
if (name.compare(pObserver->GetName()) == 0)
{
//找到了删除。
}
}
}
void CHanFeiziObservable::NotifyObservers( string context )
{
ObserverList_C_iterator it = m_observerList.begin();
for (; it != m_observerList.end(); it ++)
{
(*it)->Update(context);
}
}
void CHanFeiziObservable::HaveBreakfast()
{
cout << "韩非子:开始吃饭了..." << endl;
this->NotifyObservers("韩非子在吃饭");
}
void CHanFeiziObservable::HaveFun()
{
cout << "韩非子:开始娱乐了..." << endl;
this->NotifyObservers("韩非子在娱乐");
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
[/code]
观察者接口
//IObserver.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class IObserver
{
public:
IObserver(string _name)
{
this->m_name = _name;
}
virtual ~IObserver(void)
{
}
virtual void Update(string context) = 0;
virtual string GetName() = 0;//为c++单独增加的函数,用于删除时查找观察者。
protected:
string m_name;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
观察者1
//LiSiObserver.h
#pragma once
#include "iobserver.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CLiSiObserver :
public IObserver
{
public:
CLiSiObserver(void);
~CLiSiObserver(void);
void Update(string context);
string GetName();
private:
void ReportToQinShiHuang(string report);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
//LiSiObserver.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "LiSiObserver.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
CLiSiObserver::CLiSiObserver(void) : IObserver("李斯")
{
}
CLiSiObserver::~CLiSiObserver(void)
{
}
void CLiSiObserver::Update( string context )
{
cout << "李斯:观察到韩非子活动,开始向老板汇报了..." << endl;
this->ReportToQinShiHuang(context);
cout << "李斯:汇报完毕,秦老板赏给他两个萝卜吃吃..." << endl;
}
void CLiSiObserver::ReportToQinShiHuang( string report )
{
cout << "李斯:报告,秦老板!韩非子有活动了--->" << report.c_str() << endl;
}
string CLiSiObserver::GetName()
{
return m_name;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
[/code]
观察者2
//ZhouSiObserver.h
#pragma once
#include "iobserver.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CZhouSiObserver :
public IObserver
{
public:
CZhouSiObserver(void);
~CZhouSiObserver(void);
void Update(string context);
string GetName();
private:
void Cry(string report);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
//ZhouSiObserver.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "ZhouSiObserver.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
CZhouSiObserver::CZhouSiObserver(void) : IObserver("周斯")
{
}
CZhouSiObserver::~CZhouSiObserver(void)
{
}
void CZhouSiObserver::Update( string context )
{
cout << "周斯:观察到韩非子活动,自己也开始活动了..." << endl;
this->Cry(context);
cout << "周斯:真真的哭列了..." << endl;
}
void CZhouSiObserver::Cry( string report )
{
cout << "周斯:为因" << report.c_str() << ", ————所以我悲伤呀!" << endl;
}
string CZhouSiObserver::GetName()
{
return m_name;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
[/code]
使用测试
// Observer.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "HanFeiZi.h"
#include "LiSi.h"
#include "HanFeiZiNew.h"
#include "HanFeiziObservable.h"
#include "LiSiObserver.h"
#include "ZhouSiObserver.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
void DoNew()
{
//IHanFeiZi.h, HanFeiZiNew.h, ILiSi.h, LiSi.h
// cout << "----------用新的方法试试----------" << endl;
//CHanFeiZiNew hanfeizi;
//hanfeizi.HaveBreakfast();
//hanfeizi.HaveFun();
}
void DoNewNew()
{
//IObservable.h, HanfeiziObservable.h, IObserver.h, LiSiObserver.h
cout << "----------用更新的方法再试试----------" << endl;
IObserver *pLiSi = new CLiSiObserver();
IObserver *pZhouSi = new CZhouSiObserver();
CHanFeiziObservable *pHanFeiZi = new CHanFeiziObservable();
pHanFeiZi->AddObserver(pLiSi);
pHanFeiZi->AddObserver(pZhouSi);
pHanFeiZi->HaveBreakfast();
delete pLiSi;
pLiSi = NULL;
delete pHanFeiZi;
pHanFeiZi = NULL;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//比较原始的方法,用线程来观察。
//DoIt();
//把李斯这个类聚集到韩非子这个类上,这样的话耦合度太高了,还是用更抽象的方式。
DoNew();
//更抽象的方式,想要观察韩非子的人多了去了,不可能只允许李斯观察。
DoNewNew();
system(“pause”)
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
[/code]
代码结构:

运行结果:

17.(Chain of Responsibility责任链模式)
使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系。将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止。
说明:CHandler抽象类负责聚合责任链之中的其它处理对象,用SetNext来建立这个责任链。HandleMessage在处理请求时,会判断是否是自己要处理的请求,如果是则直接处理。如果不是,则查找下一个责任链上的处理对象,找到了则由下一个处理。
发出请求者接口
//IWomen.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class IWomen
{
public:
IWomen(void)
{
}
virtual ~IWomen(void)
{
}
virtual int GetType() = 0;
virtual string GetRequest() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
[/code]
请求者实现类
//Women.h
#pragma once
#include "iwomen.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CWomen :
public IWomen
{
public:
CWomen(int _type, string _request);
~CWomen(void);
int GetType();
string GetRequest();
private:
int m_type;
string m_request;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
//Women.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Women.h"
CWomen::CWomen( int _type, string _request )
{
this->m_type = _type;
switch (this->m_type)
{
case 1:
this->m_request.append("女儿的请求是:");
this->m_request.append(_request);
break;
case 2:
this->m_request.append("妻子的请求是:");
this->m_request.append(_request);
break;
case 3:
this->m_request.append("母亲的请求是:");
this->m_request.append(_request);
break;
}
}
CWomen::~CWomen(void)
{
}
int CWomen::GetType()
{
return m_type;
}
string CWomen::GetRequest()
{
return m_request;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
[/code]
处理请求抽象类
//Handler.h
#pragma once
#include "IWomen.h"
class CHandler
{
public:
CHandler(int _level);
virtual ~CHandler(void);
void HandleMessage(IWomen *pwomen);
void SetNext(CHandler *phandler);
virtual void Response(IWomen *pwomen) = 0;
private:
int m_level;
CHandler *m_pNextHandler;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
//Handler.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Handler.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CHandler::CHandler(int _level ) : m_level(_level)
{
m_pNextHandler = NULL;
}
CHandler::~CHandler(void)
{
}
void CHandler::HandleMessage( IWomen *pwomen )
{
if (pwomen->GetType() == this->m_level)
{
this->Response(pwomen);
}
else
{
if(this->m_pNextHandler != NULL)
this->m_pNextHandler->HandleMessage(pwomen);
else
cout << "----------没地方请示了,不做处理!----------" << endl;
}
}
void CHandler::SetNext( CHandler *phandler )
{
m_pNextHandler = phandler;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
[/code]
处理请求实现类,责任链1
//Father.h
#pragma once
#include "handler.h"
#include "IWomen.h"
class CFather :
public CHandler
{
public:
CFather(void);
~CFather(void);
void Response(IWomen *pwomen);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//Father.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Father.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CFather::CFather(void) : CHandler(1)
{
}
CFather::~CFather(void)
{
}
void CFather::Response( IWomen *pwomen )
{
cout << "女儿向父亲请示:" << endl;
cout << pwomen->GetRequest().c_str() << endl;
cout << "父亲的答复是:同意" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
处理请求实现类,责任链2
//Husband.h
#pragma once
#include "handler.h"
#include "IWomen.h"
class CHusband :
public CHandler
{
public:
CHusband(void);
~CHusband(void);
void Response(IWomen *pwomen);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//Husband.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Husband.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CHusband::CHusband(void) : CHandler(2)
{
}
CHusband::~CHusband(void)
{
}
void CHusband::Response( IWomen *pwomen )
{
cout << "妻子向丈夫请示:" << endl;
cout << pwomen->GetRequest().c_str() << endl;
cout << "丈夫的答复是:同意" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
处理请求实现类,责任链3
//Son.h
#pragma once
#include "handler.h"
#include "IWomen.h"
class CSon :
public CHandler
{
public:
CSon(void);
~CSon(void);
void Response(IWomen *pwomen);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
//Son.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Son.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CSon::CSon(void) : CHandler(3)
{
}
CSon::~CSon(void)
{
}
void CSon::Response( IWomen *pwomen )
{
cout << "母亲向儿子请示:" << endl;
cout << pwomen->GetRequest().c_str() << endl;
cout << "儿子的答复是:同意" << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
使用测试
// ChainofResponsibility.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "INormalWomen.h"
#include "NormalWomen.h"
#include "INormalHandler.h"
#include "NormalFather.h"
#include "NormalHusband.h"
#include "NormalSon.h"
#include "IWomen.h"
#include "Women.h"
#include "Handler.h"
#include "Father.h"
#include "Husband.h"
#include "Son.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void DoIt()
{
cout << "----------原来的处理方式----------" << endl;
//INormalWomen.h, NormalWomen.h, INormalHandler.h, NormalFather.h, NormalHusband.h, NormalSon.h
INormalWomen *pwomen = new CNormalWomen(1, "我要出去逛街");
INormalHandler *pfather = new CNormalFather();
INormalHandler *phusband = new CNormalHusband();
INormalHandler *pson = new CNormalSon();
if (pwomen->GetType() == 1)
{
cout << "女儿向父亲请示:" << endl;
pfather->HandleMessage(pwomen);
}
else if (pwomen->GetType() == 2)
{
cout << "妻子向丈夫请示:" << endl;
phusband->HandleMessage(pwomen);
}
else if (pwomen->GetType() == 3)
{
cout << "母亲向儿子请示:" << endl;
pson->HandleMessage(pwomen);
}
else
{
//什么也不做
}
delete pwomen;
delete pfather;
delete phusband;
delete pson;
}
void DoNew()
{
cout << "----------使用模式后的处理方式----------" << endl;
//Handler.h, Handler.cpp, IWomen.h, Women.h, Women.cpp, Father.h, Father,cpp, Husband.h, Husband.cpp, Son.h, Son.cpp
IWomen *pwomen1 = new CWomen(1, "我要出去逛街");
IWomen *pwomen2 = new CWomen(2, "我要出去吃饭");
IWomen *pwomen3 = new CWomen(3, "我也要出去吃饭");
IWomen *pwomen4 = new CWomen(4, "我也要出去逛街");
CHandler *pfather = new CFather();
CHandler *phusband = new CHusband();
CHandler *pson = new CSon();
pfather->SetNext(phusband);
phusband->SetNext(pson);
pfather->HandleMessage(pwomen1);
pfather->HandleMessage(pwomen2);
pfather->HandleMessage(pwomen3);
pfather->HandleMessage(pwomen4);
delete pfather;
delete phusband;
delete pson;
delete pwomen1;
delete pwomen2;
delete pwomen3;
delete pwomen4;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//反面
DoIt();
//要实现逻辑判断,即女性的请求先发送到父亲类,父亲类一看是自己要处理的,就回应进行处理。如果女儿已经出嫁了,那就把这个请求转发到女婿类来处理。依此类推,形成了一个责任链。
DoNew();
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
[/code]
代码结构:

运行结果:

18.(Visitor访问者模式)
表示一个作用于某对象结构中的各元素的操作。它使你可以在不改变各元素的类的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新操作。
说明:A接受B的访问,B主动的执行访问动作。
注意:和观察者的区别是,被观察者要执行一个动作,然后主动发送通知给观察者。访问者模式是由访问者主动发出的动作。
访问者接口
//IVisitor.h
#pragma once
class CCommonEmployee;
class CManager;
class IVisitor
{
public:
IVisitor(void)
{
}
virtual ~IVisitor(void)
{
}
virtual void Visit(CCommonEmployee commonEmployee) = 0;
virtual void Visit(CManager manager) = 0;
virtual int GetTotalSalary() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
访问者实现类
//BaseVisitor.h
#pragma once
#include "ivisitor.h"
#include "CommonEmployee.h"
#include "Manager.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CBaseVisitor :
public IVisitor
{
public:
CBaseVisitor(void);
~CBaseVisitor(void);
void Visit(CCommonEmployee commonEmployee);
void Visit(CManager manager);
int GetTotalSalary();
private:
string GetBasicInfo(CEmployee *pemployee);
string GetManagerInfo(CManager manager);
string GetCommonEmployee(CCommonEmployee employee);
static const int MANAGER_COEFFICENT = 5;
static const int COMMONEMPLOYEE_COEFFICENT = 2;
int m_commonTotal;
int m_managerTotal;
void CalCommonSalary(int salary);
void CalManagerSalary(int salary);
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
[/code]
//BaseVisitor.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "..\CommonDeclare\Convert.h"
#include "BaseVisitor.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CBaseVisitor::CBaseVisitor(void)
{
m_commonTotal = 0;
m_managerTotal = 0;
}
CBaseVisitor::~CBaseVisitor(void)
{
}
void CBaseVisitor::Visit(CCommonEmployee commonEmployee)
{
cout << this->GetCommonEmployee(commonEmployee).c_str() << endl;
this->CalCommonSalary(commonEmployee.GetSalary());
}
void CBaseVisitor::Visit(CManager manager)
{
cout << this->GetManagerInfo(manager).c_str() << endl;
this->CalManagerSalary(manager.GetSalary());
}
string CBaseVisitor::GetBasicInfo(CEmployee *pemployee)
{
string info = "";
info.append("姓名:");
info.append(pemployee->GetName());
info.append("\t");
info.append("性别:");
info.append(CConvert::ToString(pemployee->GetSex()));
info.append("\t");
info.append("薪水:");
info.append(CConvert::ToString(pemployee->GetSalary()));
info.append("\t");
return info;
}
string CBaseVisitor::GetManagerInfo(CManager manager)
{
string basicInfo = this->GetBasicInfo(&manager);
string otherInfo = "";
otherInfo.append("业绩:");
otherInfo.append(manager.GetPerformance());
otherInfo.append("\t");
basicInfo.append(otherInfo);
return basicInfo;
}
string CBaseVisitor::GetCommonEmployee(CCommonEmployee employee)
{
string basicInfo = this->GetBasicInfo(&employee);
string otherInfo = "";
otherInfo.append("工作:");
otherInfo.append(employee.GetJob());
otherInfo.append("\t");
basicInfo.append(otherInfo);
return basicInfo;
}
int CBaseVisitor::GetTotalSalary()
{
return this->m_commonTotal + this->m_managerTotal;
}
void CBaseVisitor::CalCommonSalary(int salary)
{
this->m_commonTotal += salary;
}
void CBaseVisitor::CalManagerSalary(int salary)
{
this->m_managerTotal += salary;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
[/code]
被访问者抽象类
//Employee.h
#pragma once
#include "IVisitor.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CEmployee
{
public:
static int MALE;
static int FEMALE;
CEmployee(void);
virtual ~CEmployee(void);
string GetName();
void SetName(string name);
int GetSalary();
void SetSalary(int v);
int GetSex();
void SetSex(int v);
virtual void Accept(IVisitor *pVisitor) = 0;
private:
string m_name;
int m_salary;
int m_sex;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
[/code]
//Employee.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Employee.h"
int CEmployee::MALE = 0;
int CEmployee::FEMALE = 1;
CEmployee::CEmployee(void)
{
}
CEmployee::~CEmployee(void)
{
}
string CEmployee::GetName()
{
return m_name;
}
void CEmployee::SetName( string name )
{
m_name = name;
}
int CEmployee::GetSalary()
{
return m_salary;
}
void CEmployee::SetSalary( int v )
{
m_salary = v;
}
int CEmployee::GetSex()
{
return m_sex;
}
void CEmployee::SetSex( int v )
{
m_sex = v;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
[/code]
被访问者实现类1
//Manager.h
#pragma once
#include "employee.h"
#include "IVisitor.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CManager :
public CEmployee
{
public:
CManager(void);
~CManager(void);
string GetPerformance();
void SetPerformance(string per);
void Accept(IVisitor *pVisitor);
protected:
string GetOtherInfo();
private:
string m_performance;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
//Manager.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Manager.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
CManager::CManager(void)
{
this->m_performance = "";
}
CManager::~CManager(void)
{
}
string CManager::GetPerformance()
{
return m_performance;
}
void CManager::SetPerformance(string per)
{
this->m_performance = per;
}
string CManager::GetOtherInfo()
{
string info = "";
info.append("业绩:");
info.append(this->m_performance);
info.append("\t");
return info;
}
void CManager::Accept(IVisitor *pVisitor)
{
pVisitor->Visit(*this);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
[/code]
被访问者实现类2 CCommonEmployee
#pragma once
#include "employee.h"
#include "IVisitor.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
class CCommonEmployee :
public CEmployee
{
public:
CCommonEmployee(void);
~CCommonEmployee(void);
string GetJob();
void SetJob(string job);
void Accept(IVisitor *pVisitor);
protected:
string GetOtherInfo();
private:
string m_job;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "CommonEmployee.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::string;
CCommonEmployee::CCommonEmployee(void)
{
this->m_job = "";
}
CCommonEmployee::~CCommonEmployee(void)
{
}
string CCommonEmployee::GetJob()
{
return this->m_job;
}
void CCommonEmployee::SetJob(string job)
{
this->m_job = job;
}
string CCommonEmployee::GetOtherInfo()
{
string job = "";
job.append("工作:");
job.append(this->m_job);
job.append("\t");
return job;
}
void CCommonEmployee::Accept(IVisitor *pVisitor)
{
pVisitor->Visit(*this);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
[/code]
使用测试
// Visitor.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Employee.h"
#include "CommonEmployee.h"
#include "Manager.h"
#include "BaseVisitor.h"
#include "..\CommonDeclare\Convert.h"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void MockEmployee(vector<CEmployee*> *pvce)
{
CCommonEmployee *pZhangSan = new CCommonEmployee();
pZhangSan->SetJob("编写Java程序,绝对的蓝领、苦工加搬运工");
pZhangSan->SetName("张三");
pZhangSan->SetSalary(1800);
pZhangSan->SetSex(CEmployee::MALE);
pvce->push_back(pZhangSan);
CCommonEmployee *pLiSi = new CCommonEmployee();
pLiSi->SetJob("页面美工,审美素质太不流行了!");
pLiSi->SetName("李四");
pLiSi->SetSalary(1900);
pLiSi->SetSex(CEmployee::FEMALE);
pvce->push_back(pLiSi);
CManager *pWangWu = new CManager();
pWangWu->SetPerformance("基本上是负值,但是我会拍马屁呀");
pWangWu->SetName("王五");
pWangWu->SetSalary(1900);
pWangWu->SetSex(CEmployee::FEMALE);
pvce->push_back(pWangWu);
}
void DoIt()
{
vector<CEmployee*> vce;
MockEmployee(&vce);
vector<CEmployee*>::const_iterator readIt = vce.begin();
CBaseVisitor visitor;
for (; readIt != vce.end(); readIt ++)
{
(*readIt)->Accept(&visitor);
}
cout << "本公司的月工资总额是:" << CConvert::ToString(visitor.GetTotalSalary()).c_str() << endl;
vector<CEmployee*>::reverse_iterator delIt = vce.rbegin();
for (; delIt != vce.rend(); delIt++)
{
delete (*delIt);
(*delIt) = NULL;
}
vce.clear();
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
DoIt();
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
[/code]
代码结构:

运行结果:

19.(State状态模式)
允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为。对象看起来似乎修改了它的类。
说明:CContext保持电梯的状态,并提供操作的接口函数。当函数被调用时,CContext直接调用当前状态的相应函数。由状态的接口函数来确定是否可以执行这个动作,以及修改状态为执行这个动作后的状态。
电梯实体抽象类
//ILift.h
#pragma once
class ILift
{
public:
ILift(void)
{
}
virtual ~ILift(void)
{
}
static const int OPENING_STATE = 1;
static const int CLOSING_STATE = 2;
static const int RUNNING_STATE = 3;
static const int STOPPING_STATE = 4;
virtual void SetState(int state) = 0;
virtual void Open() = 0;
virtual void Close() = 0;
virtual void Run() = 0;
virtual void Stop() = 0;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[/code]
电梯实体类
//Lift.h
#pragma once
#include "ilift.h"
class CLift :
public ILift
{
public:
CLift(void);
~CLift(void);
void SetState(int state);
void Open();
void Close();
void Run();
void Stop();
private:
int m_state;
void OpenWithoutLogic();
void CloseWithoutLogic();
void RunWithoutLogic();
void StopWithoutLogic();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
//Lift.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Lift.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CLift::CLift(void)
{
this->m_state = 0;
}
CLift::~CLift(void)
{
}
void CLift::SetState(int state)
{
this->m_state = state;
}
void CLift::Open()
{
switch(this->m_state)
{
case OPENING_STATE:
break;
case CLOSING_STATE:
this->OpenWithoutLogic();
this->SetState(OPENING_STATE);
break;
case RUNNING_STATE:
break;
case STOPPING_STATE:
this->OpenWithoutLogic();
this->SetState(OPENING_STATE);
break;
}
}
void CLift::Close()
{
switch(this->m_state)
{
case OPENING_STATE:
this->CloseWithoutLogic();
this->SetState(CLOSING_STATE);
break;
case CLOSING_STATE:
break;
case RUNNING_STATE:
break;
case STOPPING_STATE:
break;
}
}
void CLift::Run()
{
switch(this->m_state)
{
case OPENING_STATE:
break;
case CLOSING_STATE:
this->RunWithoutLogic();
this->SetState(RUNNING_STATE);
break;
case RUNNING_STATE:
break;
case STOPPING_STATE:
this->RunWithoutLogic();
this->SetState(RUNNING_STATE);
break;
}
}
void CLift::Stop()
{
switch(this->m_state)
{
case OPENING_STATE:
break;
case CLOSING_STATE:
this->StopWithoutLogic();
this->SetState(CLOSING_STATE);
break;
case RUNNING_STATE:
this->StopWithoutLogic();
this->SetState(CLOSING_STATE);
break;
case STOPPING_STATE:
break;
}
}
void CLift::OpenWithoutLogic()
{
cout << "电梯门开启..." << endl;
}
void CLift::CloseWithoutLogic()
{
cout << "电梯门关闭..." << endl;
}
void CLift::RunWithoutLogic()
{
cout << "电梯上下跑起来..." << endl;
}
void CLift::StopWithoutLogic()
{
cout << "电梯停止了..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
[/code]
不用设计模式情况下测试使用
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
#include <new>
#include <cstddef>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <climits>
namespace simple_alloctor
{
template <class T>
inline T*
}
int main()
{
system("pause");
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
电梯状态抽象类
//LiftState.h
#pragma once
class CContext;
class CLiftState
{
public:
CLiftState(void);
virtual ~CLiftState(void);
void SetContext(CContext *pContext);
virtual void Open() = 0;
virtual void Close() = 0;
virtual void Run() = 0;
virtual void Stop() = 0;
protected:
CContext *m_pContext;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
//LiftState.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "LiftState.h"
CLiftState::CLiftState(void)
{
}
CLiftState::~CLiftState(void)
{
}
void CLiftState::SetContext( CContext *pContext )
{
m_pContext = pContext;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[/code]
电梯门关闭
//CloseingState.h
#pragma once
#include "liftstate.h"
class CCloseingState :
public CLiftState
{
public:
CCloseingState(void);
~CCloseingState(void);
void Open();
void Close();
void Run();
void Stop();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
//CloseingState.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "CloseingState.h"
#include "Context.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CCloseingState::CCloseingState(void)
{
}
CCloseingState::~CCloseingState(void)
{
}
void CCloseingState::Open()
{
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->SetLiftState(CContext::pOpenningState);
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->GetLiftState()->Open();
}
void CCloseingState::Close()
{
cout << "电梯门关闭..." << endl;
}
void CCloseingState::Run()
{
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->SetLiftState(CContext::pRunningState);
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->GetLiftState()->Run();
}
void CCloseingState::Stop()
{
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->SetLiftState(CContext::pStoppingState);
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->GetLiftState()->Stop();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
[/code]
电梯门打开
//OpenningState.h
#pragma once
#include "liftstate.h"
class COpenningState :
public CLiftState
{
public:
COpenningState(void);
~COpenningState(void);
void Open();
void Close();
void Run();
void Stop();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
//OpenningState.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "OpenningState.h"
#include "Context.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
COpenningState::COpenningState(void)
{
}
COpenningState::~COpenningState(void)
{
}
void COpenningState::Open()
{
cout << "电梯门开启..." << endl;
}
void COpenningState::Close()
{
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->SetLiftState(CContext::pCloseingState);
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->GetLiftState()->Close();
}
void COpenningState::Run()
{
//do nothing
}
void COpenningState::Stop()
{
//do nothing
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
[/code]
电梯运行
//RunningState.h
#pragma once
#include "liftstate.h"
class CRunningState :
public CLiftState
{
public:
CRunningState(void);
~CRunningState(void);
void Open();
void Close();
void Run();
void Stop();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
//RunningState.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "RunningState.h"
#include "Context.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CRunningState::CRunningState(void)
{
}
CRunningState::~CRunningState(void)
{
}
void CRunningState::Open()
{
//do nothing
}
void CRunningState::Close()
{
//do nothing
}
void CRunningState::Run()
{
cout << "电梯上下跑..." << endl;
}
void CRunningState::Stop()
{
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->SetLiftState(CContext::pStoppingState);
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->GetLiftState()->Stop();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
[/code]
电梯停止
//StoppingState.h
#pragma once
#include "liftstate.h"
class CStoppingState :
public CLiftState
{
public:
CStoppingState(void);
~CStoppingState(void);
void Open();
void Close();
void Run();
void Stop();
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
//StoppingState.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "StoppingState.h"
#include "Context.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
CStoppingState::CStoppingState(void)
{
}
CStoppingState::~CStoppingState(void)
{
}
void CStoppingState::Open()
{
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->SetLiftState(CContext::pOpenningState);
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->GetLiftState()->Open();
}
void CStoppingState::Close()
{
//do nothing
}
void CStoppingState::Run()
{
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->SetLiftState(CContext::pRunningState);
this->CLiftState::m_pContext->GetLiftState()->Run();
}
void CStoppingState::Stop()
{
cout << "电梯停止了..." << endl;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
[/code]
电梯的控制面板
//Contex.h
#pragma once
#include "LiftState.h"
#include "OpenningState.h"
#include "CloseingState.h"
#include "RunningState.h"
#include "StoppingState.h"
class CContext
{
public:
CContext(void);
~CContext(void);
static COpenningState *pOpenningState;
static CCloseingState *pCloseingState;
static CRunningState *pRunningState;
static CStoppingState *pStoppingState;
CLiftState * GetLiftState();
void SetLiftState(CLiftState *pLiftState);
void Open();
void Close();
void Run();
void Stop();
private:
CLiftState *m_pLiftState;
};12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[/code]
//Context.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Context.h"
COpenningState* CContext::pOpenningState = NULL;
CCloseingState* CContext::pCloseingState = NULL;
CRunningState* CContext::pRunningState = NULL;
CStoppingState* CContext::pStoppingState = NULL;
CContext::CContext(void)
{
m_pLiftState = NULL;
pOpenningState = new COpenningState();
pCloseingState = new CCloseingState();
pRunningState = new CRunningState();
pStoppingState = new CStoppingState();
}
CContext::~CContext(void)
{
delete pOpenningState;
pOpenningState = NULL;
delete pCloseingState;
pCloseingState = NULL;
delete pRunningState;
pRunningState = NULL;
delete pStoppingState;
pStoppingState = NULL;
}
CLiftState * CContext::GetLiftState()
{
return m_pLiftState;
}
void CContext::SetLiftState(CLiftState *pLiftState)
{
this->m_pLiftState = pLiftState;
this->m_pLiftState->SetContext(this);
}
void CContext::Open()
{
this->m_pLiftState->Open();
}
void CContext::Close()
{
this->m_pLiftState->Close();
}
void CContext::Run()
{
this->m_pLiftState->Run();
}
void CContext::Stop()
{
this->m_pLiftState->Stop();
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
测试使用
// State.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "ILift.h"
#include "Lift.h"
#include "Context.h"
#include "OpenningState.h"
#include "CloseingState.h"
#include "RunningState.h"
#include "StoppingState.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void DoIt()
{
//ILift.h, Lift.h, Lift.cpp
ILift *pLift = new CLift();
pLift->SetState(ILift::STOPPING_STATE);//电梯的初始条件是停止状态。
pLift->Open();//首先是电梯门开启,人进去
pLift->Close();//然后电梯门关闭
pLift->Run();//再然后,电梯跑起来,向上或者向下
pLift->Stop();//最后到达目的地,电梯停下来
delete pLift;
}
void DoNew()
{
//LiftState.h, LiftState.cpp, OpenningState.h, CloseingState.h, RunningState.h, StoppingState.h
//Context.h, Context.cpp
CContext context;
CCloseingState closeingState;
context.SetLiftState(&closeingState);
context.Close();
context.Open();
context.Run();
context.Stop();
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
cout << "----------使用模式之前----------" << endl;
DoIt();
cout << "----------使用模式之后----------" << endl;
DoNew();
system(“pause”)
return 0;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
[/code]
代码结构:

运行结果:

参考资料
http://www.cnblogs.com/wanggary/category/294620.html
《24种设计模式介绍与6大设计原则》
致谢
感谢博主wang_gary的博客分享,在今年3月份第一次看到关于设计模式的分享时就备感激动,而且是C++版本的,正好方便了我个人理解设计模式的精妙,以方便了我的C++学习。
相关文章推荐
- C++设计模式之简单工厂模式实例
- 实例讲解设计模式中的命令模式在iOS App开发中的运用
- C++编程中使用设计模式中的policy策略模式的实例讲解
- 23种常用设计模式详细讲解及实例
- 23种设计模式C++实例之备忘录模式
- C#设计模式之单例模式实例讲解
- PHP设计模式之 单例模式 工厂模式 实例讲解
- 23种设计模式C++实例之迭代器模式
- C++设计模式之 简单工厂模式讲解(历史上最简单明白的例子)
- java设计模式-代理模式(实例讲解)
- 23种设计模式C++实例之桥接模式
- 实例讲解Java的设计模式编程中责任链模式的运用
- 23种设计模式C++实例之创建者模式
- 23种设计模式C++实例之解释器模式
- 通过C++和python场景实例理解装饰器设计模式。
- 23种设计模式C++实例之原型模式
- 实例讲解Java设计模式编程中的OCP开闭原则
- c++设计模式之单例模式下的实例自动销毁(垃圾自动回收器)
- 安卓设计模式-策略模式实例讲解
- java语言讲解singleton的编程思想---深入浅出单实例Singleton设计模式
