数据结构——链式队列模板类实现
2017-10-14 21:24
666 查看
数据结构笔记3.3.3 Queue
与栈类似,队列也分成顺序队列和链式队列。用单链表表示的链式队列特别适合于元素变动比较大的情形,而且不存在队列FULL而溢出的情况。另外,假若程序中需要多个队列,与多个栈的情形一样,最好使用链式队列。这样不会出现存储分配不合理的问题,也不需要考虑存储的移动。下面就给出相应的代码。
链式队列模板类代码:
Main函数测试代码:
运行效果:
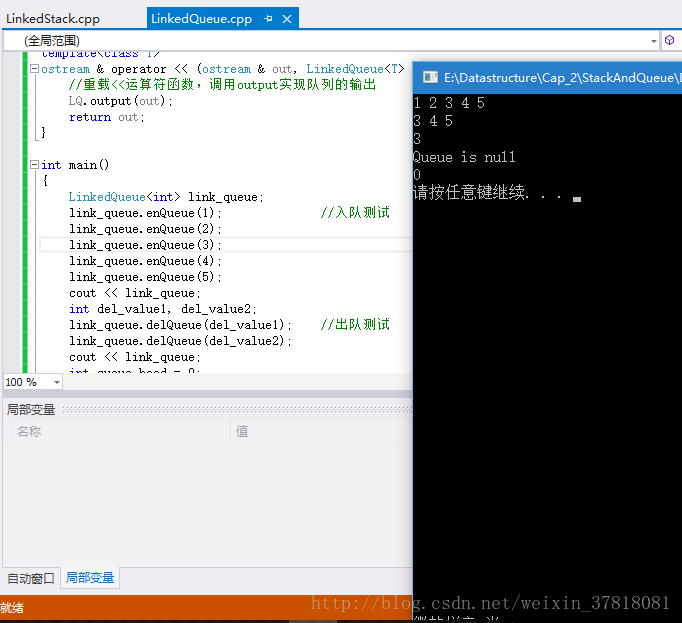
与栈类似,队列也分成顺序队列和链式队列。用单链表表示的链式队列特别适合于元素变动比较大的情形,而且不存在队列FULL而溢出的情况。另外,假若程序中需要多个队列,与多个栈的情形一样,最好使用链式队列。这样不会出现存储分配不合理的问题,也不需要考虑存储的移动。下面就给出相应的代码。
链式队列模板类代码:
//数据结构——链式队列模板类
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct LinkNode {
T data; //队列每个节点的数据域
LinkNode<T> *next; //队列每个节点的指针域
//构造函数
LinkNode(T x, LinkNode<T> *p = NULL) {
data = x;
next = p;
}
};
template<class T>
class LinkedQueue {
public:
LinkedQueue(); //构造函数
~LinkedQueue(); //析构函数
bool enQueue(const T & x); //将x加入队列当中
bool delQueue(T & x); //删除队头元素,x返回其值
bool getFront(T & x) const; //查看队头元素的值
void makeEmpty(); //将队列清空
bool isEmpty() const; //判断队列是否为NULL
int getSize() const; //返回队列元素的个
4000
数
void output(ostream & out); //输出队列元素,由重载运算符函数调用
private:
LinkNode<T> *front, *rear; //队头、队尾指针
};
//函数定义
template<class T>
LinkedQueue<T>::LinkedQueue() {
//构造函数,初始化队头和队尾指针
front = rear = NULL;
}
template<class T>
void LinkedQueue<T>::makeEmpty() {
//置空队列,释放链表中的所有节点
LinkNode<T> *current;
while (front != NULL) {
current = front;
front = front->next;
delete current;
}
}
template<class T>
bool LinkedQueue<T>::enQueue(const T & x) {
//元素x进入队尾
if (NULL == front) {
//如果是空队列,直接用指针开辟节点
front = rear = new LinkNode<T>(x);
if (NULL == front) {
//分配内存失败返回false
return false;
}
}
else {
rear->next = new LinkNode<T>(x);
if (NULL == rear->next) { //直接用rear的next开辟新节点
return false;
}
rear = rear->next; //更新尾指针
}
return true;
}
template<class T>
bool LinkedQueue<T>::delQueue(T & x) {
//如果队列不是NULL,删除队头节点,函数返回true,否则返回false
if (isEmpty()) { //队列为空,出队失败
return false;
}
LinkNode<T> *Del = front;
x = front->data;
front = front->next;
delete Del;
return true;
}
template<class T>
bool LinkedQueue<T>::getFront(T & x)const {
//若队列不为NULL,函数返回队头元素的值和true,否则返回false
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
x = front->data;
return true;
}
template<class T>
int LinkedQueue<T>::getSize()const {
//函数返回队列元素的个数
LinkNode<T> *p = front;
int queueEleAmount = 0;
while (p != NULL) {
queueEleAmount++;
p = p->next;
}
return queueEleAmount;
}
template<class T>
bool LinkedQueue<T>::isEmpty() const {
//判断队列是否为NULL并返回true,否则返回false
if (front == NULL) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
template<class T>
LinkedQueue<T>::~LinkedQueue() {
//析构函数,释放程序中的资源
makeEmpty();
}
template<class T>
void LinkedQueue<T>::output(ostream & out) {
//输出队列中的元素,被重载<<函数调用
LinkNode<T> *current = front;
while (current != NULL) {
out << current->data << " ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
template<class T>
ostream & operator << (ostream & out, LinkedQueue<T> &LQ) {
//重载<<运算符函数,调用output实现队列的输出
LQ.output(out);
return out;
}Main函数测试代码:
int main()
{
LinkedQueue<int> link_queue;
link_queue.enQueue(1); //入队测试
link_queue.enQueue(2);
link_queue.enQueue(3);
link_queue.enQueue(4);
link_queue.enQueue(5);
cout << link_queue;
int del_value1, del_value2;
link_queue.delQueue(del_value1); //出队测试
link_queue.delQueue(del_value2);
cout << link_queue;
int queue_head = 0;
link_queue.getFront(queue_head); //读取队头测试
cout << queue_head << endl;
link_queue.makeEmpty(); //set NULL test
if (link_queue.isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is null" << endl;
}
cout << link_queue.getSize() << endl;//返回队列元素个数测试
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行效果:

相关文章推荐
- 数据结构单链队列——链式存储实现
- 数据结构基础(14) --链式队列的设计与实现
- 看数据结构写代码(15)链式队列的实现(总结篇)
- 数据结构基础(14) --链式队列的设计与实现
- 数据结构基础(14) --链式队列的设计与实现
- 数据结构(6): 链队——队列的链式表示和实现
- 数据结构基础(14) --链式队列的设计与实现
- 数据结构之---C语言实现链式队列
- 数据结构——循环队列(顺序队列)模板类实现
- 数据结构与算 5:C++ 顺序/链式存储,栈 模板类实现,编译模板类问题解决
- 【数据结构】顺序表与链式实现队列并测试
- 数据结构(三)——双链表、链式栈、链式队列 及实现
- 数据结构(六)---队列的链式存储的实现---java版
- 数据结构之C/C++实现链式队列
- 数据结构之循环队列(顺序表存储)——C++模板类实现
- 数据结构(五)——双链表、链式栈、链式队列 及实现
- 数据结构(严蔚敏)之六——链式队列c语言实现
- 数据结构:实验六(单循环链表实现链式队列)
- 数据结构之队列的链式表示及其实现
- 数据结构——队列的链式实现(C语言)
