关于Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析
2017-10-13 11:22
417 查看
本篇文章是由朋友的一篇博客引出的,博客原文地址:http://jinnianshilongnian.iteye.com/blog/1416322
他这篇博客比较细的讲解了classpath与classpath*,以及通配符的使用,那些配置能成功加载到资源,那些配置加载不了资源。但是我相信仍然有很多同学不明白,为什么是这样的,知其然,不知其所以然,那么本篇文章将慢慢为你揭开神秘的面纱,让你知其然,更知其所以然。
关于Spring Resource的资源类型以及继承体系我们已经在上一篇文件粗略的说了一下。Spring加载Resource文件是通过ResourceLoader来进行的,那么我们就先来看看ResourceLoader的继承体系,让我们对这个模块有一个比较系统的认知。
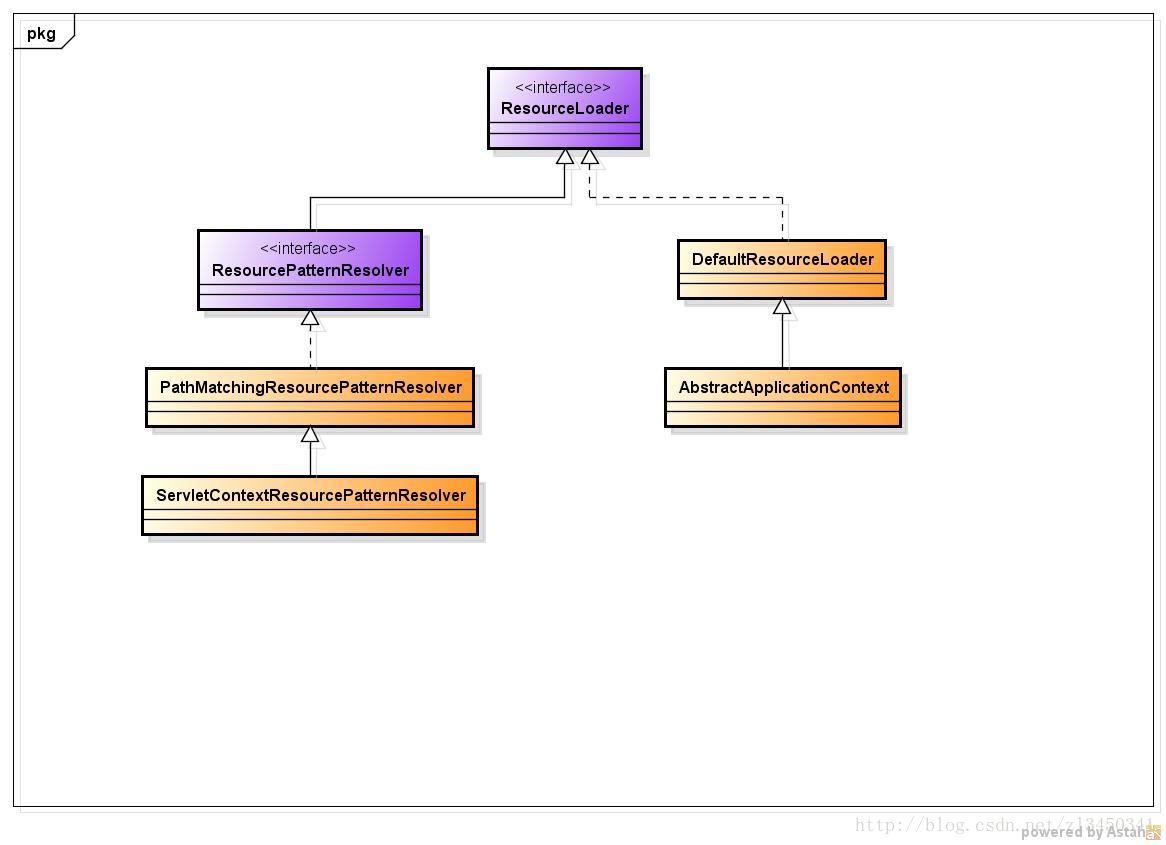
上图仅右边的继承体系,仅画至AbstractApplicationContext,由于ApplicationContext的继承体系,我们已经在前面章节给出,所以为了避免不必要的复杂性,本章继承体系就不引入ApplicationContext。
我们还是来关注本章的重点————classpath 与 classpath*以及通配符是怎么处理的
首先,我们来看下ResourceLoader的源码
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


public interface ResourceLoader
{
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from
the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
Resource getResource(String location);
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
Resource getResource(String location);
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
我们发现,其实ResourceLoader接口只提供了classpath前缀的支持。而classpath*的前缀支持是在它的子接口ResourcePatternResolver中。
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


public interface ResourcePatternResolverextends ResourceLoader
{
/**
* Pseudo URL prefix for all matching
resources from the class path: "classpath*:"
* This differs from ResourceLoader's
classpath URL prefix in that it
* retrieves all matching resources
for a given name (e.g. "/beans.xml"),
* for example in the root of all deployed
JAR files.
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader#CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX
*/
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
/**
* Pseudo URL prefix for all matching resources from the class path: "classpath*:"
* This differs from ResourceLoader's classpath URL prefix in that it
* retrieves all matching resources for a given name (e.g. "/beans.xml"),
* for example in the root of all deployed JAR files.
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader#CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX
*/
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
通过2个接口的源码对比,我们发现ResourceLoader提供 classpath下单资源文件的载入,而ResourcePatternResolver提供了多资源文件的载入。
ResourcePatternResolver有一个实现类:PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver,那我们直奔主题,查看PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver的getResources()
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


public Resource[]
getResources(String locationPattern)throws IOException
{
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location
pattern must not be null");
//是否以classpath*开头
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX))
{
//是否包含?或者*
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length())))
{
// a class path resource
pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// all class path resources
with the given name
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// Only look for a pattern
after a prefix here
// (to not get fooled by a
pattern symbol in a strange prefix).
int prefixEnd
= locationPattern.indexOf(":") +1;
//是否包含?或者*
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd)))
{
// a file pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// a single resource with
the given name
return new Resource[]
{getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
//是否以classpath*开头
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {
//是否包含?或者*
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {
// a class path resource pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// all class path resources with the given name
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// Only look for a pattern after a prefix here
// (to not get fooled by a pattern symbol in a strange prefix).
int prefixEnd = locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1;
//是否包含?或者*
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
// a file pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// a single resource with the given name
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
由此我们可以看出在加载配置文件时,以是否是以classpath*开头分为2大类处理场景,每大类在又根据路径中是否包括通配符分为2小类进行处理,
处理的流程图如下:
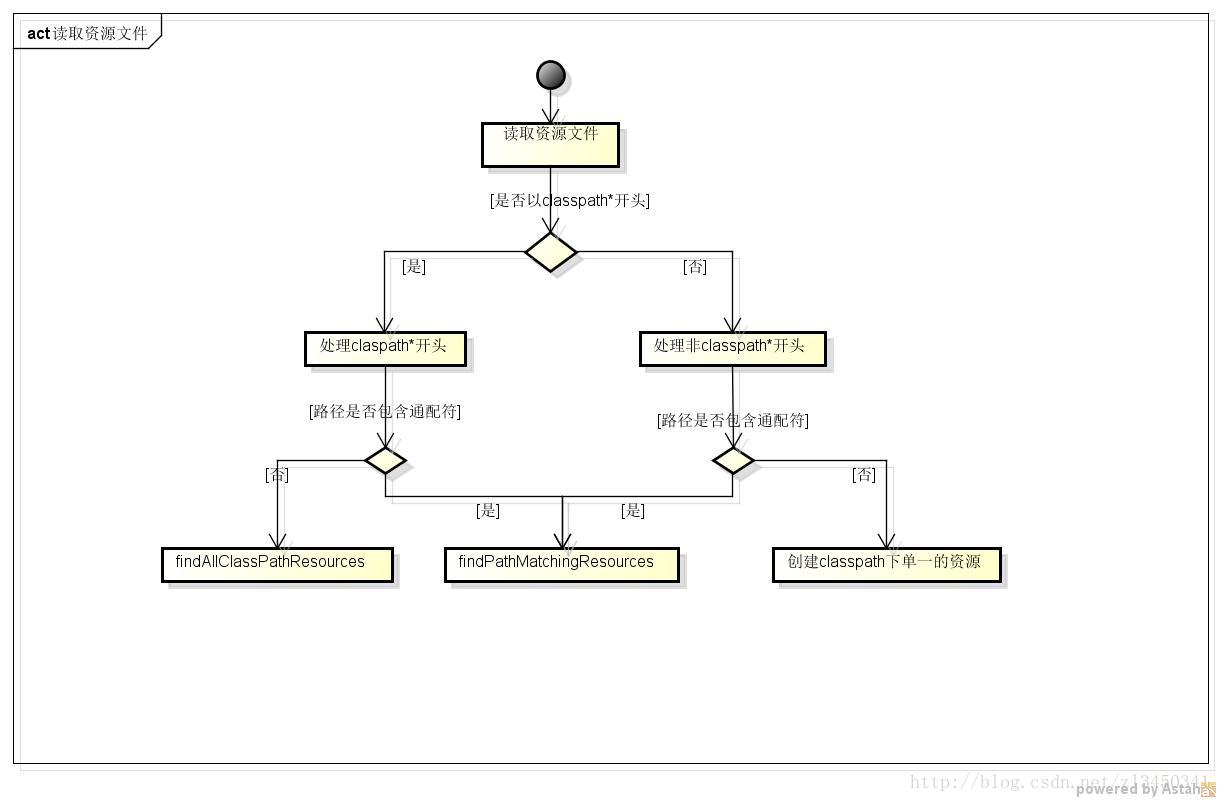
从上图看,整个加载资源的场景有三条处理流程
以classpath*开头,但路径不包含通配符的
让我们来看看findAllClassPathResources是怎么处理的
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


protected Resource[]
findAllClassPathResources(String location)throws IOException
{
String path = location;
if (path.startsWith("/"))
{
path = path.substring(1);
}
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = getClassLoader().getResources(path);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements())
{
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
String path = location;
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = getClassLoader().getResources(path);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
我们可以看到,最关键的一句代码是:Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = getClassLoader().getResources(path);
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


public ClassLoader
getClassLoader() {
return getResourceLoader().getClassLoader();
}
public ResourceLoader
getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
//默认情况下
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver()
{
this.resourceLoader
= new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return getResourceLoader().getClassLoader();
}
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
//默认情况下
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
其实上面这3个方法不是最关键的,之所以贴出来,是让大家清楚整个调用链,其实这种情况最关键的代码在于ClassLoader的getResources()方法。那么我们同样跟进去,看看源码
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


public Enumeration<URL>
getResources(String name)throws IOException
{
Enumeration[] tmp = new Enumeration[2];
if (parent
!= null) {
tmp[0]
= parent.getResources(name);
} else {
tmp[0]
= getBootstrapResources(name);
}
tmp[1]
= findResources(name);
return new CompoundEnumeration(tmp);
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public Enumeration<URL> getResources(String name) throws IOException {
Enumeration[] tmp = new Enumeration[2];
if (parent != null) {
tmp[0] = parent.getResources(name);
} else {
tmp[0] = getBootstrapResources(name);
}
tmp[1] = findResources(name);
return new CompoundEnumeration(tmp);
}
是不是一目了然了?当前类加载器,如果存在父加载器,则向上迭代获取资源, 因此能加到jar包里面的资源文件。
不以classpath*开头,且路径不包含通配符的
处理逻辑如下
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


return new Resource[]
{getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
[java] view
plain copy
print?
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
上面我们已经贴过getResourceLoader()的逻辑了, 即默认是DefaultResourceLoader(),那我们进去看看getResouce()的实现
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


public Resource
getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must
not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX))
{
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()),
getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location
as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException
ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource
path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
其实很简单,如果以classpath开头,则创建为一个ClassPathResource,否则则试图以URL的方式加载资源,创建一个UrlResource.
路径包含通配符的
这种情况是最复杂的,涉及到层层递归,那我把加了注释的代码发出来大家看一下,其实主要的思想就是
1.先获取目录,加载目录里面的所有资源
2.在所有资源里面进行查找匹配,找出我们需要的资源
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


protected Resource[]
findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern)throws IOException
{
//拿到能确定的目录,即拿到不包括通配符的能确定的路径 比如classpath*:/aaa/bbb/spring-*.xml
则返回classpath*:/aaa/bbb/ //如果是classpath*:/aaa/*/spring-*.xml,则返回 classpath*:/aaa/
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
//得到spring-*.xml
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
//递归加载所有的根目录资源,要注意的是递归的时候又得考虑classpath,与classpath*的情况,而且还得考虑根路径中是否又包含通配符,参考上面那张流程图
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
//将根目录所有资源中所有匹配我们需要的资源(如spring-*)加载result中
for (Resource
rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
if (isJarResource(rootDirResource))
{
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
else if (rootDirResource.getURL().getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS))
{
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirResource, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
{
logger.debug("Resolved location
pattern [" + locationPattern +"] to resources " +
result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
//拿到能确定的目录,即拿到不包括通配符的能确定的路径 比如classpath*:/aaa/bbb/spring-*.xml 则返回classpath*:/aaa/bbb/ //如果是classpath*:/aaa/*/spring-*.xml,则返回 classpath*:/aaa/
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
//得到spring-*.xml
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
//递归加载所有的根目录资源,要注意的是递归的时候又得考虑classpath,与classpath*的情况,而且还得考虑根路径中是否又包含通配符,参考上面那张流程图
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
//将根目录所有资源中所有匹配我们需要的资源(如spring-*)加载result中
for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
if (isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
else if (rootDirResource.getURL().getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirResource, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
值得注解一下的是determineRootDir()方法的作用,是确定根目录,这个根目录必须是一个能确定的路径,不会包含通配符。如果classpath*:aa/bb*/spring-*.xml,得到的将是classpath*:aa/ 可以看下他的源码
[java] view
plaincopyprint?


protected String
determineRootDir(String location) {
int prefixEnd
= location.indexOf(":") +1;
int rootDirEnd
= location.length();
while (rootDirEnd
> prefixEnd && getPathMatcher().isPattern(location.substring(prefixEnd, rootDirEnd))) {
rootDirEnd = location.lastIndexOf('/',
rootDirEnd -2) + 1;
}
if (rootDirEnd
== 0) {
rootDirEnd = prefixEnd;
}
return location.substring(0,
rootDirEnd);
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
protected String determineRootDir(String location) {
int prefixEnd = location.indexOf(":") + 1;
int rootDirEnd = location.length();
while (rootDirEnd > prefixEnd && getPathMatcher().isPattern(location.substring(prefixEnd, rootDirEnd))) {
rootDirEnd = location.lastIndexOf('/', rootDirEnd - 2) + 1;
}
if (rootDirEnd == 0) {
rootDirEnd = prefixEnd;
}
return location.substring(0, rootDirEnd);
}
分析到这,结合测试我们可以总结一下:
1.无论是classpath还是classpath*都可以加载整个classpath下(包括jar包里面)的资源文件。
2.classpath只会返回第一个匹配的资源,查找路径是优先在项目中存在资源文件,再查找jar包。
3.文件名字包含通配符资源(如果spring-*.xml,spring*.xml), 如果根目录为"", classpath加载不到任何资源, 而classpath*则可以加载到classpath中可以匹配的目录中的资源,但是不能加载到jar包中的资源
第1,2点比较好表理解,大家可以自行测试,第三点表述有点绕,举个例,现在有资源文件结构如下:
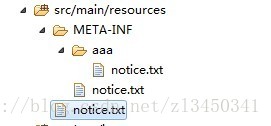
classpath:notice*.txt 加载不到资源
classpath*:notice*.txt 加载到resource根目录下notice.txt
classpath:META-INF/notice*.txt 加载到META-INF下的一个资源(classpath是加载到匹配的第一个资源,就算删除classpath下的notice.txt,他仍然可以
加载jar包中的notice.txt)
classpath:META-*/notice*.txt 加载不到任何资源
classpath*:META-INF/notice*.txt 加载到classpath以及所有jar包中META-INF目录下以notice开头的txt文件
classpath*:META-*/notice*.txt 只能加载到classpath下 META-INF目录的notice.txt
他这篇博客比较细的讲解了classpath与classpath*,以及通配符的使用,那些配置能成功加载到资源,那些配置加载不了资源。但是我相信仍然有很多同学不明白,为什么是这样的,知其然,不知其所以然,那么本篇文章将慢慢为你揭开神秘的面纱,让你知其然,更知其所以然。
关于Spring Resource的资源类型以及继承体系我们已经在上一篇文件粗略的说了一下。Spring加载Resource文件是通过ResourceLoader来进行的,那么我们就先来看看ResourceLoader的继承体系,让我们对这个模块有一个比较系统的认知。

上图仅右边的继承体系,仅画至AbstractApplicationContext,由于ApplicationContext的继承体系,我们已经在前面章节给出,所以为了避免不必要的复杂性,本章继承体系就不引入ApplicationContext。
我们还是来关注本章的重点————classpath 与 classpath*以及通配符是怎么处理的
首先,我们来看下ResourceLoader的源码
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

public interface ResourceLoader
{
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from
the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
Resource getResource(String location);
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
Resource getResource(String location);
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
我们发现,其实ResourceLoader接口只提供了classpath前缀的支持。而classpath*的前缀支持是在它的子接口ResourcePatternResolver中。
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

public interface ResourcePatternResolverextends ResourceLoader
{
/**
* Pseudo URL prefix for all matching
resources from the class path: "classpath*:"
* This differs from ResourceLoader's
classpath URL prefix in that it
* retrieves all matching resources
for a given name (e.g. "/beans.xml"),
* for example in the root of all deployed
JAR files.
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader#CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX
*/
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
/**
* Pseudo URL prefix for all matching resources from the class path: "classpath*:"
* This differs from ResourceLoader's classpath URL prefix in that it
* retrieves all matching resources for a given name (e.g. "/beans.xml"),
* for example in the root of all deployed JAR files.
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader#CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX
*/
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
通过2个接口的源码对比,我们发现ResourceLoader提供 classpath下单资源文件的载入,而ResourcePatternResolver提供了多资源文件的载入。
ResourcePatternResolver有一个实现类:PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver,那我们直奔主题,查看PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver的getResources()
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

public Resource[]
getResources(String locationPattern)throws IOException
{
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location
pattern must not be null");
//是否以classpath*开头
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX))
{
//是否包含?或者*
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length())))
{
// a class path resource
pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// all class path resources
with the given name
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// Only look for a pattern
after a prefix here
// (to not get fooled by a
pattern symbol in a strange prefix).
int prefixEnd
= locationPattern.indexOf(":") +1;
//是否包含?或者*
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd)))
{
// a file pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// a single resource with
the given name
return new Resource[]
{getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
//是否以classpath*开头
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {
//是否包含?或者*
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {
// a class path resource pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// all class path resources with the given name
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// Only look for a pattern after a prefix here
// (to not get fooled by a pattern symbol in a strange prefix).
int prefixEnd = locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1;
//是否包含?或者*
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
// a file pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// a single resource with the given name
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
由此我们可以看出在加载配置文件时,以是否是以classpath*开头分为2大类处理场景,每大类在又根据路径中是否包括通配符分为2小类进行处理,
处理的流程图如下:

从上图看,整个加载资源的场景有三条处理流程
以classpath*开头,但路径不包含通配符的
让我们来看看findAllClassPathResources是怎么处理的
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

protected Resource[]
findAllClassPathResources(String location)throws IOException
{
String path = location;
if (path.startsWith("/"))
{
path = path.substring(1);
}
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = getClassLoader().getResources(path);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements())
{
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
String path = location;
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = getClassLoader().getResources(path);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
我们可以看到,最关键的一句代码是:Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = getClassLoader().getResources(path);
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

public ClassLoader
getClassLoader() {
return getResourceLoader().getClassLoader();
}
public ResourceLoader
getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
//默认情况下
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver()
{
this.resourceLoader
= new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return getResourceLoader().getClassLoader();
}
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
//默认情况下
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
其实上面这3个方法不是最关键的,之所以贴出来,是让大家清楚整个调用链,其实这种情况最关键的代码在于ClassLoader的getResources()方法。那么我们同样跟进去,看看源码
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

public Enumeration<URL>
getResources(String name)throws IOException
{
Enumeration[] tmp = new Enumeration[2];
if (parent
!= null) {
tmp[0]
= parent.getResources(name);
} else {
tmp[0]
= getBootstrapResources(name);
}
tmp[1]
= findResources(name);
return new CompoundEnumeration(tmp);
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public Enumeration<URL> getResources(String name) throws IOException {
Enumeration[] tmp = new Enumeration[2];
if (parent != null) {
tmp[0] = parent.getResources(name);
} else {
tmp[0] = getBootstrapResources(name);
}
tmp[1] = findResources(name);
return new CompoundEnumeration(tmp);
}
是不是一目了然了?当前类加载器,如果存在父加载器,则向上迭代获取资源, 因此能加到jar包里面的资源文件。
不以classpath*开头,且路径不包含通配符的
处理逻辑如下
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

return new Resource[]
{getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
[java] view
plain copy
print?
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
上面我们已经贴过getResourceLoader()的逻辑了, 即默认是DefaultResourceLoader(),那我们进去看看getResouce()的实现
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

public Resource
getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must
not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX))
{
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()),
getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location
as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException
ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource
path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
其实很简单,如果以classpath开头,则创建为一个ClassPathResource,否则则试图以URL的方式加载资源,创建一个UrlResource.
路径包含通配符的
这种情况是最复杂的,涉及到层层递归,那我把加了注释的代码发出来大家看一下,其实主要的思想就是
1.先获取目录,加载目录里面的所有资源
2.在所有资源里面进行查找匹配,找出我们需要的资源
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

protected Resource[]
findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern)throws IOException
{
//拿到能确定的目录,即拿到不包括通配符的能确定的路径 比如classpath*:/aaa/bbb/spring-*.xml
则返回classpath*:/aaa/bbb/ //如果是classpath*:/aaa/*/spring-*.xml,则返回 classpath*:/aaa/
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
//得到spring-*.xml
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
//递归加载所有的根目录资源,要注意的是递归的时候又得考虑classpath,与classpath*的情况,而且还得考虑根路径中是否又包含通配符,参考上面那张流程图
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
//将根目录所有资源中所有匹配我们需要的资源(如spring-*)加载result中
for (Resource
rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
if (isJarResource(rootDirResource))
{
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
else if (rootDirResource.getURL().getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS))
{
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirResource, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
{
logger.debug("Resolved location
pattern [" + locationPattern +"] to resources " +
result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
//拿到能确定的目录,即拿到不包括通配符的能确定的路径 比如classpath*:/aaa/bbb/spring-*.xml 则返回classpath*:/aaa/bbb/ //如果是classpath*:/aaa/*/spring-*.xml,则返回 classpath*:/aaa/
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
//得到spring-*.xml
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
//递归加载所有的根目录资源,要注意的是递归的时候又得考虑classpath,与classpath*的情况,而且还得考虑根路径中是否又包含通配符,参考上面那张流程图
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
//将根目录所有资源中所有匹配我们需要的资源(如spring-*)加载result中
for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
if (isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
else if (rootDirResource.getURL().getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirResource, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
值得注解一下的是determineRootDir()方法的作用,是确定根目录,这个根目录必须是一个能确定的路径,不会包含通配符。如果classpath*:aa/bb*/spring-*.xml,得到的将是classpath*:aa/ 可以看下他的源码
[java] view
plaincopyprint?

protected String
determineRootDir(String location) {
int prefixEnd
= location.indexOf(":") +1;
int rootDirEnd
= location.length();
while (rootDirEnd
> prefixEnd && getPathMatcher().isPattern(location.substring(prefixEnd, rootDirEnd))) {
rootDirEnd = location.lastIndexOf('/',
rootDirEnd -2) + 1;
}
if (rootDirEnd
== 0) {
rootDirEnd = prefixEnd;
}
return location.substring(0,
rootDirEnd);
}
[java] view
plain copy
print?
protected String determineRootDir(String location) {
int prefixEnd = location.indexOf(":") + 1;
int rootDirEnd = location.length();
while (rootDirEnd > prefixEnd && getPathMatcher().isPattern(location.substring(prefixEnd, rootDirEnd))) {
rootDirEnd = location.lastIndexOf('/', rootDirEnd - 2) + 1;
}
if (rootDirEnd == 0) {
rootDirEnd = prefixEnd;
}
return location.substring(0, rootDirEnd);
}
分析到这,结合测试我们可以总结一下:
1.无论是classpath还是classpath*都可以加载整个classpath下(包括jar包里面)的资源文件。
2.classpath只会返回第一个匹配的资源,查找路径是优先在项目中存在资源文件,再查找jar包。
3.文件名字包含通配符资源(如果spring-*.xml,spring*.xml), 如果根目录为"", classpath加载不到任何资源, 而classpath*则可以加载到classpath中可以匹配的目录中的资源,但是不能加载到jar包中的资源
第1,2点比较好表理解,大家可以自行测试,第三点表述有点绕,举个例,现在有资源文件结构如下:

classpath:notice*.txt 加载不到资源
classpath*:notice*.txt 加载到resource根目录下notice.txt
classpath:META-INF/notice*.txt 加载到META-INF下的一个资源(classpath是加载到匹配的第一个资源,就算删除classpath下的notice.txt,他仍然可以
加载jar包中的notice.txt)
classpath:META-*/notice*.txt 加载不到任何资源
classpath*:META-INF/notice*.txt 加载到classpath以及所有jar包中META-INF目录下以notice开头的txt文件
classpath*:META-*/notice*.txt 只能加载到classpath下 META-INF目录的notice.txt
相关文章推荐
- 关于Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析
- 关于Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析
- 资源——关于Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析(五)
- 关于Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析
- 关于Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析
- 关于Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析
- Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析
- Spring加载classpath与classpath*的过程剖析
- 关于Spring加载classpath与classpath*
- Spring资源文件加载时classpath和classpath*的区别
- Spring的classpath与classpath*通配符加载配置文件
- spring加载classpath与classpath*的区别别
- Spring : Spring加载配置文件classpath、classpath*、file解析
- Spring加载配置文件时 classpath* 和 classpath的区别
- 请慎用spring-ClassPathXmlApplicationContext手动加载spring配置文件
- spring中classpath和classpath*的配置区别
- Spring配置中的classpath和classpath*的区别
- Spring中classpath和classpath*的问题
- java.Spring加载resource时classpath*:与classpath:的区别
- [Spring实战系列] - No.11 Spring项目中的classpath和classpath*问题
