Qt 学习之路 2(66):访问网络(2)
2017-10-05 21:14
295 查看
上一章我们了解了
现在我们先来研究下 OpenWeatherMap
的相关 API。之所以选择 OpenWeatherMap,主要是因为这个网站提供了简洁的 API 接口,非常适合示例程序,并且其开发也不需要额外申请 App ID。OpenWeatherMap 的 API 可以选择返回 JSON 或者 XML,这里我们选择使用 JSON 格式。在进行查询时,OpenWeatherMap 支持使用城市名、地理经纬度以及城市 ID,为简单起见,我们选择使用城市名。我们先来看一个例子:http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=Beijing,cn&mode=json&units=metric&lang=zh_cn。下面是这个链接的参数分析:
点击链接,服务器返回一个 JSON 字符串(此时你应该能够使用浏览器看到这个字符串):
我们从这里找到 JSON 各个字段的含义。现在我们关心的是:时间(dt);气温(temp);气压(pressure);湿度(humidity)和天气状况(weather)。基于此,我们设计了
setter 和 getter 函数,这里不再把源代码写出来。值得说明的是最后两个全局函数:
我们重写了
这两个函数虽然比较长,但是很简单,这里不再赘述。
下面我们来看主窗口:
正如前面所说的,这里依然使用了 d 指针模式。头文件没有什么可说的。
我们将
接下来我们来看
由于使用了 Qt5,我们选择新的连接语法。第一个
服务器返回的
选择我们可以运行下程序了:
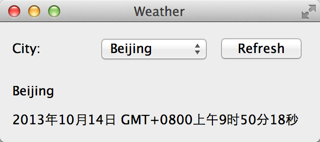
博客源地址:https://www.devbean.net/2013/10/qt-study-road-2-access-network-2/
NetWorker类的简单实现。不仅如此,我们还提到了几个 C++ 开发时常用的设计模式。这些在接下来得代码中依然会用到。
现在我们先来研究下 OpenWeatherMap
的相关 API。之所以选择 OpenWeatherMap,主要是因为这个网站提供了简洁的 API 接口,非常适合示例程序,并且其开发也不需要额外申请 App ID。OpenWeatherMap 的 API 可以选择返回 JSON 或者 XML,这里我们选择使用 JSON 格式。在进行查询时,OpenWeatherMap 支持使用城市名、地理经纬度以及城市 ID,为简单起见,我们选择使用城市名。我们先来看一个例子:http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=Beijing,cn&mode=json&units=metric&lang=zh_cn。下面是这个链接的参数分析:
| 参数名字 | 传入值 | 说明 |
| q | Beijing,cn | 查询中国北京的天气 |
| mode | json | 返回格式为 JSON |
| units | metric | 返回单位为公制 |
| lang | zh_cn | 返回语言为中文 |
| 1 | {"coord":{"lon":116.397232,"lat":39.907501},"sys":{"country":"CN","sunrise":1381530122,"sunset":1381570774},"weather":[{"id":800,"main":"Clear","description":"晴","icon":"01d"}],"base":"gdps stations","main":{"temp":20,"pressure":1016,"humidity":34,"temp_min":20,"temp_max":20},"wind":{"speed":2,"deg":50},"clouds":{"all":0},"dt":1381566600,"id":1816670,"name":"Beijing","cod":200} |
WeatherInfo类,用于封装服务器返回的信息:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 | class WeatherDetail { public: WeatherDetail(); ~WeatherDetail(); QString desc() const; void setDesc(const QString &desc); QString icon() const; void setIcon(const QString &icon); private: class Private; friend class Private; Private *d; }; class WeatherInfo { public: WeatherInfo(); ~WeatherInfo(); QString cityName() const; void setCityName(const QString &cityName); quint32 id() const; void setId(quint32 id); QDateTime dateTime() const; void setDateTime(const QDateTime &dateTime); float temperature() const; void setTemperature(float temperature); float humidity() const; void setHumidity(float humidity); float pressure() const; void setPressure(float pressure); QList<WeatherDetail *> details() const; void setDetails(const QList<WeatherDetail *> details); private: class Private; friend class Private; Private *d; }; QDebug operator <<(QDebug dbg, const WeatherDetail &w); QDebug operator <<(QDebug dbg, const WeatherInfo &w); |
WeatherInfo和
WeatherDetail两个类相互合作存储我们所需要的数据。由于是数据类,所以只有单纯的
setter 和 getter 函数,这里不再把源代码写出来。值得说明的是最后两个全局函数:
| 12 | QDebug operator <<(QDebug dbg, const WeatherDetail &w);QDebug operator <<(QDebug dbg, const WeatherInfo &w); |
<<运算符,以便能够使用类似
qDebug() << weatherInfo;这样的语句进行调试。它的实现是这样的:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | QDebug operator <<(QDebug dbg, const WeatherDetail &w) { dbg.nospace() << "(" << "Description: " << w.desc() << "; " << "Icon: " << w.icon() << ")"; return dbg.space(); } QDebug operator <<(QDebug dbg, const WeatherInfo &w) { dbg.nospace() << "(" << "id: " << w.id() << "; " << "City name: " << w.cityName() << "; " << "Date time: " << w.dateTime().toString(Qt::DefaultLocaleLongDate) << ": " << endl << "Temperature: " << w.temperature() << ", " << "Pressure: " << w.pressure() << ", " << "Humidity: " << w.humidity() << endl << "Details: ["; foreach (WeatherDetail *detail, w.details()) { dbg.nospace() << "( Description: " << detail->desc() << ", " << "Icon: " << detail->icon() << "), "; } dbg.nospace() << "] )"; return dbg.space(); } |
下面我们来看主窗口:
| 123456789101112 | class MainWindow : public QMainWindow{ Q_OBJECTpublic: MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0); ~MainWindow(); private: class Private; friend class Private; Private *d;}; |
MainWindow::Private的实现依旧简单:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | class MainWindow::Private { public: Private() { netWorker = NetWorker::instance(); } void fetchWeather(const QString &cityName) const { netWorker->get(QString("http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=%1&mode=json&units=metric&lang=zh_cn").arg(cityName)); } NetWorker *netWorker; }; |
MainWindow所需要的
NetWorker作为
MainWindow::Private的一个成员变量。
MainWindow::Private提供了一个
fetchWeather()函数。由于
NetWorker提供的函数都是相当底层的,为了提供业务级别的处理,我们将这样的函数封装在
MainWindow::Private中。当然,你也可以在
NetWorker中直接提供类似的函数,这取决于你的系统分层设计。
| 12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152535455565758596061626364656667686970717273747576 | MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : QMainWindow(parent), d(new MainWindow::Private){ QComboBox *cityList = new QComboBox(this); cityList->addItem(tr("Beijing"), QLatin1String("Beijing,cn")); cityList->addItem(tr("Shanghai"), QLatin1String("Shanghai,cn")); cityList->addItem(tr("Nanjing"), QLatin1String("Nanjing,cn")); QLabel *cityLabel = new QLabel(tr("City: "), this); QPushButton *refreshButton = new QPushButton(tr("Refresh"), this); QHBoxLayout *cityListLayout = new QHBoxLayout; cityListLayout->setDirection(QBoxLayout::LeftToRight); cityListLayout->addWidget(cityLabel); cityListLayout->addWidget(cityList); cityListLayout->addWidget(refreshButton); QVBoxLayout *weatherLayout = new QVBoxLayout; weatherLayout->setDirection(QBoxLayout::TopToBottom); QLabel *cityNameLabel = new QLabel(this); weatherLayout->addWidget(cityNameLabel); QLabel *dateTimeLabel = new QLabel(this); weatherLayout->addWidget(dateTimeLabel); QWidget *mainWidget = new QWidget(this); QVBoxLayout *mainLayout = new QVBoxLayout(mainWidget); mainLayout->addLayout(cityListLayout); mainLayout->addLayout(weatherLayout); setCentralWidget(mainWidget); resize(320, 120); setWindowTitle(tr("Weather")); connect(d->netWorker, &NetWorker::finished, [=] (QNetworkReply *reply) { qDebug() << reply; QJsonParseError error; QJsonDocument jsonDocument = QJsonDocument::fromJson(reply->readAll(), &error); if (error.error == QJsonParseError::NoError) { if (!(jsonDocument.isNull() || jsonDocument.isEmpty()) && jsonDocument.isObject()) { QVariantMap data = jsonDocument.toVariant().toMap(); WeatherInfo weather; weather.setCityName(data[QLatin1String("name")].toString()); QDateTime dateTime; dateTime.setTime_t(data[QLatin1String("dt")].toLongLong()); weather.setDateTime(dateTime); QVariantMap main = data[QLatin1String("main")].toMap(); weather.setTemperature(main[QLatin1String("temp")].toFloat()); weather.setPressure(main[QLatin1String("pressure")].toFloat()); weather.setHumidity(main[QLatin1String("humidity")].toFloat()); QVariantList detailList = data[QLatin1String("weather")].toList(); QList<WeatherDetail *> details; foreach (QVariant w, detailList) { QVariantMap wm = w.toMap(); WeatherDetail *detail = new WeatherDetail; detail->setDesc(wm[QLatin1String("description")].toString()); detail->setIcon(wm[QLatin1String("icon")].toString()); details.append(detail); } weather.setDetails(details); cityNameLabel->setText(weather.cityName()); dateTimeLabel->setText(weather.dateTime().toString(Qt::DefaultLocaleLongDate)); } } else { QMessageBox::critical(this, tr("Error"), error.errorString()); } reply->deleteLater(); }); connect(refreshButton, &QPushButton::clicked, [=] () { d->fetchWeather(cityList->itemData(cityList->currentIndex()).toString()); });} MainWindow::~MainWindow(){ delete d; d = 0;} |
MainWindow的构造函数和析构函数。构造函数虽然很长但是并不复杂,主要是对界面的构建。我们这里略过这些界面的代码,直接看两个信号槽的连接。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | connect(d->netWorker, &NetWorker::finished, [=] (QNetworkReply *reply) { QJsonParseError error; QJsonDocument jsonDocument = QJsonDocument::fromJson(reply->readAll(), &error); if (error.error == QJsonParseError::NoError) { if (!(jsonDocument.isNull() || jsonDocument.isEmpty()) && jsonDocument.isObject()) { QVariantMap data = jsonDocument.toVariant().toMap(); WeatherInfo weather; weather.setCityName(data[QLatin1String("name")].toString()); QDateTime dateTime; dateTime.setTime_t(data[QLatin1String("dt")].toLongLong()); weather.setDateTime(dateTime); QVariantMap main = data[QLatin1String("main")].toMap(); weather.setTemperature(main[QLatin1String("temp")].toFloat()); weather.setPressure(main[QLatin1String("pressure")].toFloat()); weather.setHumidity(main[QLatin1String("humidity")].toFloat()); QVariantList detailList = data[QLatin1String("weather")].toList(); QList<WeatherDetail *> details; foreach (QVariant w, detailList) { QVariantMap wm = w.toMap(); WeatherDetail *detail = new WeatherDetail; detail->setDesc(wm[QLatin1String("description")].toString()); detail->setIcon(wm[QLatin1String("icon")].toString()); details.append(detail); } weather.setDetails(details); cityNameLabel->setText(weather.cityName()); dateTimeLabel->setText(weather.dateTime().toString(Qt::DefaultLocaleLongDate)); } } else { QMessageBox::critical(this, tr("Error"), error.errorString()); } reply->deleteLater(); }); connect(refreshButton, &QPushButton::clicked, [=] () { d->fetchWeather(cityList->itemData(cityList->currentIndex()).toString()); }); |
connect()函数中,我们按照 API 文档中描述的那样对服务器返回的 JSON 字符串进行解析,然后将数据填充到一个
WeatherInfo的对象。然后操作界面的两个控件显示数据。值得注意的是函数的最后一行,
reply->deleteLater();。当网络请求结束时,delete
服务器返回的
QNetworkReply对象是用户的责任。用户需要选择一个恰当的时机进行 delete 操作。但是,我们不能直接在
finiahed()信号对应的槽函数中调用
delete运算符。相反,我们需要使用
deleteLater()函数,正如前面代码中显示的那样。第二个槽函数则相对简单,仅仅是重新获取新的数据。
选择我们可以运行下程序了:

博客源地址:https://www.devbean.net/2013/10/qt-study-road-2-access-network-2/
相关文章推荐
- Qt 学习之路 2(68):访问网络(4)
- Qt 学习之路 :访问网络(4)
- Qt 学习之路 2(65):访问网络(1)
- Qt 学习之路 2(67):访问网络(3)
- Qt学习之路之ODBC访问SQLserver数据库
- Linux学习第七单元-访问网络文件共享服务
- 我的LINUX学习之路之十二之批量网络安装不同版本Linux之基础篇
- Qt学习之路(5):组件布局
- Qt5 OpenGL学习之路1
- netty框架学习之路(一)—— Java网络IO模型
- Qt 学习之路 2(62):保存 XML
- Qt 学习之路 2(11):布局管理器
- Qt学习之路-简易画板2(自由涂鸦)
- Qt 学习之路 2(17):文件对话框
- 网络安全学习之路
- 计算机网络学习之路01--概念详解
- Qt学习之路之菜单打开网页
- qt 学习之路2
- Qt 学习之路:存储容器
- Qt 学习之路:线程和 QObject
