c++运算符重载string类
2017-09-20 09:52
337 查看
一、 运算符重载的规则
运算符重载规则如下:
①、 C++中的运算符除了少数几个之外,全部可以重载,而且只能重载C++中已有的运算符。
②、 重载之后运算符的优先级和结合性都不会改变。
③、 运算符重载是针对新类型数据的实际需要,对原有运算符进行适当的改造。一般来说,重载的功能应当与原有功能相类似,不能改变原运算符的操作对象个数,同时至少要有一个操作对象是自定义类型。
不能重载的运算符只有五个,它们是:成员运算符“.”、指针运算符“*”、作用域运算符“::”、“sizeof”、条件运算符“?:”。
运算符重载形式有两种,重载为类的成员函数和重载为类的友元函数。
运算符重载为类的成员函数的一般语法形式为:
函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表)
{
函数体;
}
运算符重载为类的友元函数的一般语法形式为:
friend 函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表)
{
函数体;
}
其中,函数类型就是运算结果类型;operator是定义运算符重载函数的关键字;运算符是重载的运算符名称。
当运算符重载为类的成员函数时,函数的参数个数比原来的操作个数要少一个;当重载为类的友元函数时,参数个数与原操作数个数相同。原因是重载为类的成员函数时,如果某个对象使用重载了的成员函数,自身的数据可以直接访问,就不需要再放在参数表中进行传递,少了的操作数就是该对象本身。而重载为友元函数时,友元函数对某个对象的数据进行操作,就必须通过该对象的名称来进行,因此使用到的参数都要进行传递,操作数的个数就不会有变化。
运算符重载的主要优点就是允许改变使用于系统内部的运算符的操作方式,以适应用户自定义类型的类似运算。
二、 运算符重载为成员函数
对于双目运算符B,如果要重载B为类的成员函数,使之能够实现表达式oprd1 B oprd2,其中oprd1为类A的对象,则应当把B重载为A类的成员函数,该函数只有一个形参,形参的类型是oprd2所属的类型。经过重载后
4000
,表达式oprd1 B oprd2 就相当于函数调用oprd1.operator B(oprd2).
对于前置单目运算符U,如“-”(负号)等,如果要重载U为类的成员函数,用来实现表达式U oprd,其中oprd为A类的对象,则U应当重载为A类的成员函数,函数没有形参。经过重载之后,表达式U oprd相当于函数调用oprd.operator U().
对于后置运算符“++”和“- -”,如果要将它们重载为类的成员函数,用来实现表达式oprd++或oprd--,其中oprd为A类的对象,那么运算符就应当重载为A类的成员函数,这时函数要带有一个整型形参。重载之后,表达式oprd++和oprd—就想当于函数调用oprd.operator++(0)和oprd.operator—(0);
运算符重载就是赋予已有的运算符多重含义。通过重新定义运算符,使它能够用于特定类的对象执行特定的功能,这便增强了C++语言的扩充能力。
1. 运算符重载的作用:
运算符重载允许C/C++的运算符在用户定义类型(类)上拥有一个用户定义的意义。
关于string类大概可以重写的运算符如下:
MyString.h
#ifndef __MYSTRING_H__
#define __MYSTRING_H__
#include <iostream>
class MyString
{
// 重载 << 操作符
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out, MyString &str);
// 重载 >> 操作符
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, MyString &str);
public:
MyString(); // 无参构造
MyString(const char *s); // 有参构造
MyString(int len, char data = 0); // 有参构造
MyString(const MyString &s); // 拷贝构造
~MyString(); // 析构函数
// 重载=、[]操作符
public:
MyString& operator=(const char *s); // 普通字符串赋值
MyString& operator=(const MyString &s); // 类对象之间赋值
char & operator[](int index);
// 重载 + 运算符
public:
MyString& operator+(const char *str);
MyString& operator+(const MyString &s);
MyString& operator+=(const char *str);
MyString& operator+=(const MyString &s);
// 重载 == !=
public:
bool operator==(const char *str) const;
bool operator==(const MyString &str) const;
bool operator!=(const char *str) const;
bool operator!=(const MyString &str) const;
// 重载 < >
public:
bool operator>(const char *str) const;
bool operator>(const MyString &str) const;
bool operator<(const char *str) const;
bool operator<(const MyString &str) const;
public:
const char *c_str()
{
return m_p;
}
char *c_str2()
{
return m_p;
}
int leng()
{
return m_len;
}
private:
int m_len; // 字符串长度
char *m_p; // 字符串数据
};
#endif // __MYSTRING_H__
MyString.cpp
#include "MyString.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, MyString &str)
{
out << str.m_p;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, MyString &str)
{
in >> str.m_p;
return in;
}
MyString::MyString()
{
m_len = 0;
m_p = new char[m_len+1];
m_p[0] = '\0';
}
MyString::MyString(const char *s)
{
m_len = strlen(s);
m_p = new char[m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,s);
}
MyString::MyString(int len, char data)
{
m_len = len;
m_p = new char[m_len+1];
memset(m_p,data,m_len);
m_p[len] = 0;
}
MyString::MyString(const MyString &s)
{
m_len = s.m_len;
m_p = new char[m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,s.m_p);
}
MyString::~MyString()
{
if (m_p != NULL)
{
delete []m_p;
m_p = NULL;
}
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(const char *s)
{
if (m_p != NULL)
{
delete []m_p;
m_p = NULL;
}
m_len = strlen(s);
m_p = new char [m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,s);
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(const MyString &s)
{
if(this == &s)
return *this;
if (m_p != NULL)
{
delete []m_p;
m_p = NULL;
}
m_len = s.m_len;
m_p = new char [m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,s.m_p);
return *this;
}
char & MyString::operator[](int index)
{
return m_p[index];
}
MyString& MyString::operator+(const char *str)
{
char *tmp = m_p;
m_len = strlen(m_p) + strlen(str);
m_p = new char [m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,tmp);
strcat(m_p,str);
delete []tmp;
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator+(const MyString &s)
{
*this = *this + s.m_p;
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator+=(const char *str)
{
char *tmp = m_p;
m_len = strlen(m_p) + strlen(str);
m_p = new char [m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,tmp);
strcat(m_p,str);
delete []tmp;
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator+=(const MyString &s)
{
*this = *this + s.m_p;
return *this;
}
bool MyString::operator==(const char *str) const
{
if (m_len != strlen(str))
return false;
for(int i=0;i<m_len;i++)
{
if(m_p[i] != str[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool MyString::operator==(const MyString &str) const
{
if (m_len != str.m_len)
return false;
for(int i=0;i<m_len;i++)
{
if(m_p[i] != str.m_p[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool MyString::operator!=(const char *str) const
{
return !(*this == str);
}
bool MyString::operator!=(const MyString &str) const
{
return !(*this == str);
}
bool MyString::operator>(const char *str) const
{
if(strcmp(m_p,str)==1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyString::operator>(const MyString &str) const
{
if(strcmp(m_p,str.m_p)==1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyString::operator<(const char *str) const
{
if(strcmp(m_p,str)==-1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyString::operator<(const MyString &str) const
{
if(strcmp(m_p,str.m_p)==-1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
main.cpp
#include "MyString.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
MyString s1;
MyString s2 = "hello";
MyString s3("world");
MyString s4(10);
MyString s5(5,'a');
MyString s6 = s3;
printf("s1:%s,%d\n",s1.c_str2(),s1.leng());
printf("s2:%s,%d\n",s2.c_str2(),s2.leng());
printf("s3:%s,%d\n",s3.c_str2(),s3.leng());
printf("s4:%s,%d\n",s4.c_str2(),s4.leng());
printf("s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
printf("s6:%s,%d\n",s6.c_str2(),s6.leng());
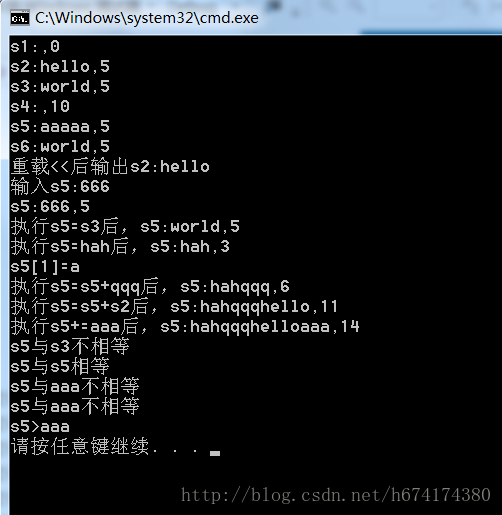
cout<<"重载<<后输出s2:";
cout<< s2.c_str2()<<endl;
cout <<"输入s5:";
cin >> s5;
printf("s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
s5 = s3;
printf("执行s5=s3后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
s5 = "hah";
printf("执行s5=hah后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
printf("s5[1]=%c\n",s5[1]);
s5 = s5 + "qqq";
printf("执行s5=s5+qqq后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
s5 = s5 + s2;
printf("执行s5=s5+s2后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
s5 += "aaa";
printf("执行s5+=aaa后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
if(s5 == s3)
printf("s5与s3相等\n");
else
printf("s5与s3不相等\n");
if(s5 == s5)
printf("s5与s5相等\n");
else
printf("s5与s5不相等\n");
if(s5 == "aaa")
printf("s5与aaa相等\n");
else
printf("s5与aaa不相等\n");
if(s5 != "aaa")
printf("s5与aaa不相等\n");
else
printf("s5与aaa相等\n");
if(s5 > "aaa")
printf("s5>aaa\n");
else
printf("s5<aaa\n");
return 0;
}
运算符重载规则如下:
①、 C++中的运算符除了少数几个之外,全部可以重载,而且只能重载C++中已有的运算符。
②、 重载之后运算符的优先级和结合性都不会改变。
③、 运算符重载是针对新类型数据的实际需要,对原有运算符进行适当的改造。一般来说,重载的功能应当与原有功能相类似,不能改变原运算符的操作对象个数,同时至少要有一个操作对象是自定义类型。
不能重载的运算符只有五个,它们是:成员运算符“.”、指针运算符“*”、作用域运算符“::”、“sizeof”、条件运算符“?:”。
运算符重载形式有两种,重载为类的成员函数和重载为类的友元函数。
运算符重载为类的成员函数的一般语法形式为:
函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表)
{
函数体;
}
运算符重载为类的友元函数的一般语法形式为:
friend 函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表)
{
函数体;
}
其中,函数类型就是运算结果类型;operator是定义运算符重载函数的关键字;运算符是重载的运算符名称。
当运算符重载为类的成员函数时,函数的参数个数比原来的操作个数要少一个;当重载为类的友元函数时,参数个数与原操作数个数相同。原因是重载为类的成员函数时,如果某个对象使用重载了的成员函数,自身的数据可以直接访问,就不需要再放在参数表中进行传递,少了的操作数就是该对象本身。而重载为友元函数时,友元函数对某个对象的数据进行操作,就必须通过该对象的名称来进行,因此使用到的参数都要进行传递,操作数的个数就不会有变化。
运算符重载的主要优点就是允许改变使用于系统内部的运算符的操作方式,以适应用户自定义类型的类似运算。
二、 运算符重载为成员函数
对于双目运算符B,如果要重载B为类的成员函数,使之能够实现表达式oprd1 B oprd2,其中oprd1为类A的对象,则应当把B重载为A类的成员函数,该函数只有一个形参,形参的类型是oprd2所属的类型。经过重载后
4000
,表达式oprd1 B oprd2 就相当于函数调用oprd1.operator B(oprd2).
对于前置单目运算符U,如“-”(负号)等,如果要重载U为类的成员函数,用来实现表达式U oprd,其中oprd为A类的对象,则U应当重载为A类的成员函数,函数没有形参。经过重载之后,表达式U oprd相当于函数调用oprd.operator U().
对于后置运算符“++”和“- -”,如果要将它们重载为类的成员函数,用来实现表达式oprd++或oprd--,其中oprd为A类的对象,那么运算符就应当重载为A类的成员函数,这时函数要带有一个整型形参。重载之后,表达式oprd++和oprd—就想当于函数调用oprd.operator++(0)和oprd.operator—(0);
运算符重载就是赋予已有的运算符多重含义。通过重新定义运算符,使它能够用于特定类的对象执行特定的功能,这便增强了C++语言的扩充能力。
1. 运算符重载的作用:
运算符重载允许C/C++的运算符在用户定义类型(类)上拥有一个用户定义的意义。
关于string类大概可以重写的运算符如下:

MyString.h
#ifndef __MYSTRING_H__
#define __MYSTRING_H__
#include <iostream>
class MyString
{
// 重载 << 操作符
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out, MyString &str);
// 重载 >> 操作符
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, MyString &str);
public:
MyString(); // 无参构造
MyString(const char *s); // 有参构造
MyString(int len, char data = 0); // 有参构造
MyString(const MyString &s); // 拷贝构造
~MyString(); // 析构函数
// 重载=、[]操作符
public:
MyString& operator=(const char *s); // 普通字符串赋值
MyString& operator=(const MyString &s); // 类对象之间赋值
char & operator[](int index);
// 重载 + 运算符
public:
MyString& operator+(const char *str);
MyString& operator+(const MyString &s);
MyString& operator+=(const char *str);
MyString& operator+=(const MyString &s);
// 重载 == !=
public:
bool operator==(const char *str) const;
bool operator==(const MyString &str) const;
bool operator!=(const char *str) const;
bool operator!=(const MyString &str) const;
// 重载 < >
public:
bool operator>(const char *str) const;
bool operator>(const MyString &str) const;
bool operator<(const char *str) const;
bool operator<(const MyString &str) const;
public:
const char *c_str()
{
return m_p;
}
char *c_str2()
{
return m_p;
}
int leng()
{
return m_len;
}
private:
int m_len; // 字符串长度
char *m_p; // 字符串数据
};
#endif // __MYSTRING_H__
MyString.cpp
#include "MyString.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, MyString &str)
{
out << str.m_p;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, MyString &str)
{
in >> str.m_p;
return in;
}
MyString::MyString()
{
m_len = 0;
m_p = new char[m_len+1];
m_p[0] = '\0';
}
MyString::MyString(const char *s)
{
m_len = strlen(s);
m_p = new char[m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,s);
}
MyString::MyString(int len, char data)
{
m_len = len;
m_p = new char[m_len+1];
memset(m_p,data,m_len);
m_p[len] = 0;
}
MyString::MyString(const MyString &s)
{
m_len = s.m_len;
m_p = new char[m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,s.m_p);
}
MyString::~MyString()
{
if (m_p != NULL)
{
delete []m_p;
m_p = NULL;
}
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(const char *s)
{
if (m_p != NULL)
{
delete []m_p;
m_p = NULL;
}
m_len = strlen(s);
m_p = new char [m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,s);
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(const MyString &s)
{
if(this == &s)
return *this;
if (m_p != NULL)
{
delete []m_p;
m_p = NULL;
}
m_len = s.m_len;
m_p = new char [m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,s.m_p);
return *this;
}
char & MyString::operator[](int index)
{
return m_p[index];
}
MyString& MyString::operator+(const char *str)
{
char *tmp = m_p;
m_len = strlen(m_p) + strlen(str);
m_p = new char [m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,tmp);
strcat(m_p,str);
delete []tmp;
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator+(const MyString &s)
{
*this = *this + s.m_p;
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator+=(const char *str)
{
char *tmp = m_p;
m_len = strlen(m_p) + strlen(str);
m_p = new char [m_len+1];
strcpy(m_p,tmp);
strcat(m_p,str);
delete []tmp;
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator+=(const MyString &s)
{
*this = *this + s.m_p;
return *this;
}
bool MyString::operator==(const char *str) const
{
if (m_len != strlen(str))
return false;
for(int i=0;i<m_len;i++)
{
if(m_p[i] != str[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool MyString::operator==(const MyString &str) const
{
if (m_len != str.m_len)
return false;
for(int i=0;i<m_len;i++)
{
if(m_p[i] != str.m_p[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool MyString::operator!=(const char *str) const
{
return !(*this == str);
}
bool MyString::operator!=(const MyString &str) const
{
return !(*this == str);
}
bool MyString::operator>(const char *str) const
{
if(strcmp(m_p,str)==1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyString::operator>(const MyString &str) const
{
if(strcmp(m_p,str.m_p)==1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyString::operator<(const char *str) const
{
if(strcmp(m_p,str)==-1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyString::operator<(const MyString &str) const
{
if(strcmp(m_p,str.m_p)==-1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
main.cpp
#include "MyString.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
MyString s1;
MyString s2 = "hello";
MyString s3("world");
MyString s4(10);
MyString s5(5,'a');
MyString s6 = s3;
printf("s1:%s,%d\n",s1.c_str2(),s1.leng());
printf("s2:%s,%d\n",s2.c_str2(),s2.leng());
printf("s3:%s,%d\n",s3.c_str2(),s3.leng());
printf("s4:%s,%d\n",s4.c_str2(),s4.leng());
printf("s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
printf("s6:%s,%d\n",s6.c_str2(),s6.leng());
cout<<"重载<<后输出s2:";
cout<< s2.c_str2()<<endl;
cout <<"输入s5:";
cin >> s5;
printf("s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
s5 = s3;
printf("执行s5=s3后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
s5 = "hah";
printf("执行s5=hah后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
printf("s5[1]=%c\n",s5[1]);
s5 = s5 + "qqq";
printf("执行s5=s5+qqq后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
s5 = s5 + s2;
printf("执行s5=s5+s2后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
s5 += "aaa";
printf("执行s5+=aaa后,s5:%s,%d\n",s5.c_str2(),s5.leng());
if(s5 == s3)
printf("s5与s3相等\n");
else
printf("s5与s3不相等\n");
if(s5 == s5)
printf("s5与s5相等\n");
else
printf("s5与s5不相等\n");
if(s5 == "aaa")
printf("s5与aaa相等\n");
else
printf("s5与aaa不相等\n");
if(s5 != "aaa")
printf("s5与aaa不相等\n");
else
printf("s5与aaa相等\n");
if(s5 > "aaa")
printf("s5>aaa\n");
else
printf("s5<aaa\n");
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 从零开始学C++之运算符重载(三):完善String类([]、 +、 += 运算符重载)、>>和<<运算符重载
- 【C++】String类中的运算符重载
- C++:运算符重载、string类重写、数据类型转换、->操作符重载、virtual继承、virtual函数、typeid
- C++面试题,自己实现String类的构造函数,拷贝构造函数,赋值操作符,append,replace,+运算符重载等
- 从零开始学C++之运算符重载(三):完善String类([]、 +、 += 运算符重载)、>>和<<运算符重载
- C++:运算符重载、string类重写、数据类型转换、->操作符重载、virtual继承、virtual函数、typeid
- 手写C++中string类(编译时多态:运算符重载)
- 【C++】String类中的运算符重载
- 从零开始学C++之运算符重载(三):完善String类([]、 +、 += 运算符重载)、>>和<<运算符重载
- C++ 简易string类实现(六)-真正的写时复制
- 从String类中看C++当中的深拷贝与浅拷贝解
- 【C++】运算符重载
- 2012/2/7 《C++ Primer Plus》第十六章:string类和标准模板库 学习笔记
- C/C++编程细节(三)——类、继承、模板、运算符重载
- C++ 将String类作为包含类
- C++的运算符重载
- C++面试题(二)——自己实现一个String类
- C++ 运算符重载
- C++面试中string类的一种正确简明的写法
- c++中string类字符串和c中char*/char[]型型字符串的区别
