spring boot整合Swagger2
2017-09-07 15:15
507 查看
Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成、描述、调用和可视化RESTful风格的 Web 服务。总体目标是使客户端和文件系统作为服务器以同样的速度来更新。文件的方法,参数和模型紧密集成到服务器端的代码,允许API来始终保持同步。Swagger 让部署管理和使用功能强大的API从未如此简单。
1.代码示例
1).在pom.xml文件中引入Swagger2
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
2).在Application同级目录下添加Swagger2的配置类
package com.example;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Config {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs")
.description("spring boot整合swagger2")
.termsOfServiceUrl("www.baidu.com")
.contact("牛头人")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
如上代码所示,通过 @Configuration 注解,让Spring来加载该类配置。再通过 @EnableSwagger2 注解来启用Swagger2。
通过 createRestApi 函数创建 Docket 的Bean之后, apiInfo() 用来创建该Api的基本信息(这些基本信息会展现在文档页面中)。 select() 函数返回一个 ApiSelectorBuilder 实例用来控制哪些接口暴露给Swagger来展现,本例采用指定扫描的包路径来定义,Swagger会扫描该包下所有Controller定义的API,并产生文档内容(除了被 @ApiIgnore 指定的请求)。 RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example")中com.example为controller的目录;
3).新建User实体类
package com.example.swagger2;
public class User {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
4).新建SwaggerDemoController类
package com.example.swagger2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponse;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponses;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/api")
@Api("SwaggerDemoController相关api")
public class SwaggerDemoController {
static Map<String, User> users = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, User>());
@ApiOperation(value="获取用户列表", notes="")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value={""}, method=RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> getUserList() {
List<User> r = new ArrayList<User>(users.values());
return r;
}
@ApiOperation(value="创建用户", notes="根据User对象创建用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value="", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String postUser(@RequestBody User user) {
users.put(user.getId(), user);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="获取用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来获取用户详细信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID",paramType="path", required = true, dataType = "String")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public User getUser(@PathVariable String id) {
System.out.println("id="+id);
return users.get(id);
}
@ApiOperation(value="更新用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来指定更新对象,并根据传过来的user信息来更新用户详细信息")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID",paramType="path", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
})
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(@PathVariable String id, @RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("id="+id);
User u = users.get(id);
u.setName(user.getName());
users.put(id, u);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="删除用户", notes="根据url的id来指定删除对象")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID",paramType="path", required = true, dataType = "String")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable String id) {
System.out.println("id="+id);
users.remove(id);
return "success";
}
}
说明:
@Api:用在类上,说明该类的作用
@ApiOperation:用在方法上,说明方法的作用
@ApiImplicitParams:用在方法上包含一组参数说明
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
header-->请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
query-->请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
path(用于restful接口)-->请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
body(不常用)
form(不常用)
name:参数名
dataType:参数类型
required:参数是否必须传
value:参数的意思
defaultValue:参数的默认值
@ApiResponses:用于表示一组响应
@ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
code:数字,例如400
message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好"
response:抛出异常的类
@ApiModel:描述一个Model的信息(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景,请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候)
@ApiModelProperty:描述一个model的属性
通过 @ApiOperation 注解来给API增加说明、通过 @ApiImplicitParams 、 @ApiImplicitParam 注解来给参数增加说明。
需要注意的是:

如果ApiImplicitParam中的phone的paramType是query的话,是无法注入到rest路径中的,而且如果是path的话,是不需要配置ApiImplicitParam的,即使配置了,其中的value="用户ID"也不会在swagger-ui展示出来。
具体其他的注解,查看:
https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-core/wiki/Annotations#apimodel
2.测试:
启动服务,浏览器输入"http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html"
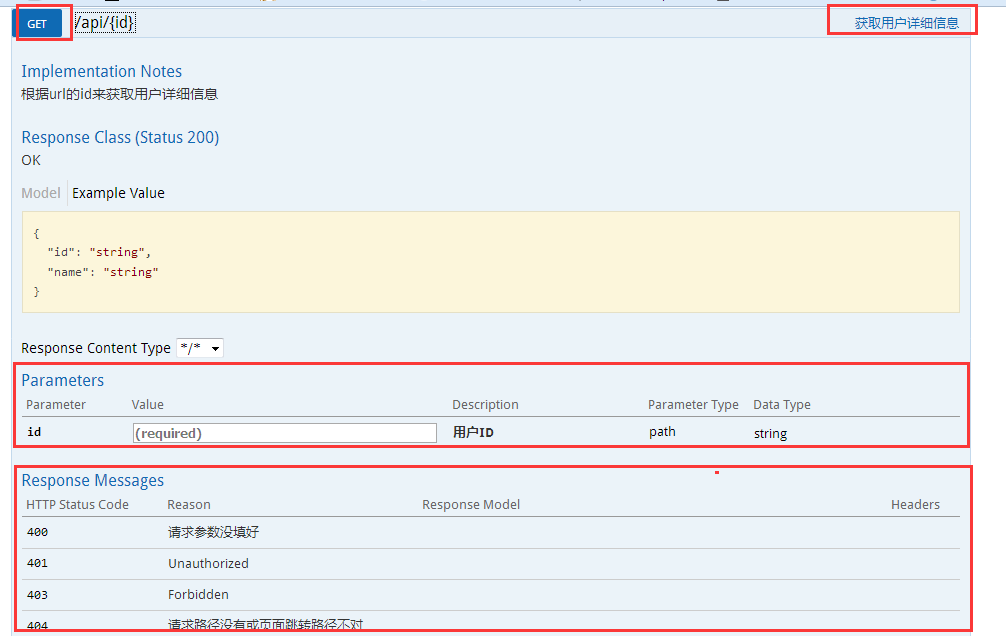
GET红框:method=RequestMethod.GET
右边红框:@ApiOperation
parameter红框:@ApiImplicitParams系列注解
response messages红框:@ApiResponses系列注解
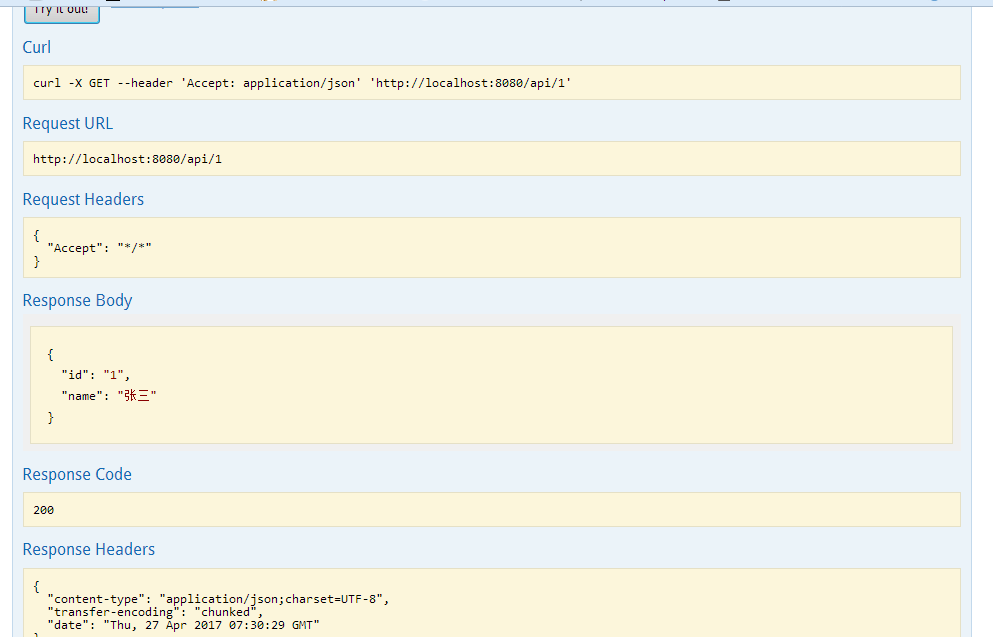
输入参数后,点击"try it out!",查看响应内容:
1.代码示例
1).在pom.xml文件中引入Swagger2
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
2).在Application同级目录下添加Swagger2的配置类
package com.example;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Config {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs")
.description("spring boot整合swagger2")
.termsOfServiceUrl("www.baidu.com")
.contact("牛头人")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
如上代码所示,通过 @Configuration 注解,让Spring来加载该类配置。再通过 @EnableSwagger2 注解来启用Swagger2。
通过 createRestApi 函数创建 Docket 的Bean之后, apiInfo() 用来创建该Api的基本信息(这些基本信息会展现在文档页面中)。 select() 函数返回一个 ApiSelectorBuilder 实例用来控制哪些接口暴露给Swagger来展现,本例采用指定扫描的包路径来定义,Swagger会扫描该包下所有Controller定义的API,并产生文档内容(除了被 @ApiIgnore 指定的请求)。 RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example")中com.example为controller的目录;
3).新建User实体类
package com.example.swagger2;
public class User {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
4).新建SwaggerDemoController类
package com.example.swagger2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponse;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponses;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/api")
@Api("SwaggerDemoController相关api")
public class SwaggerDemoController {
static Map<String, User> users = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, User>());
@ApiOperation(value="获取用户列表", notes="")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value={""}, method=RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> getUserList() {
List<User> r = new ArrayList<User>(users.values());
return r;
}
@ApiOperation(value="创建用户", notes="根据User对象创建用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value="", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String postUser(@RequestBody User user) {
users.put(user.getId(), user);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="获取用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来获取用户详细信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID",paramType="path", required = true, dataType = "String")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public User getUser(@PathVariable String id) {
System.out.println("id="+id);
return users.get(id);
}
@ApiOperation(value="更新用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来指定更新对象,并根据传过来的user信息来更新用户详细信息")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID",paramType="path", required = true, dataType = "String"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
})
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(@PathVariable String id, @RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("id="+id);
User u = users.get(id);
u.setName(user.getName());
users.put(id, u);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation(value="删除用户", notes="根据url的id来指定删除对象")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID",paramType="path", required = true, dataType = "String")
@ApiResponses({
@ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"),
@ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对")
})
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable String id) {
System.out.println("id="+id);
users.remove(id);
return "success";
}
}
说明:
@Api:用在类上,说明该类的作用
@ApiOperation:用在方法上,说明方法的作用
@ApiImplicitParams:用在方法上包含一组参数说明
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
header-->请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
query-->请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
path(用于restful接口)-->请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
body(不常用)
form(不常用)
name:参数名
dataType:参数类型
required:参数是否必须传
value:参数的意思
defaultValue:参数的默认值
@ApiResponses:用于表示一组响应
@ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
code:数字,例如400
message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好"
response:抛出异常的类
@ApiModel:描述一个Model的信息(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景,请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候)
@ApiModelProperty:描述一个model的属性
通过 @ApiOperation 注解来给API增加说明、通过 @ApiImplicitParams 、 @ApiImplicitParam 注解来给参数增加说明。
需要注意的是:

如果ApiImplicitParam中的phone的paramType是query的话,是无法注入到rest路径中的,而且如果是path的话,是不需要配置ApiImplicitParam的,即使配置了,其中的value="用户ID"也不会在swagger-ui展示出来。
具体其他的注解,查看:
https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-core/wiki/Annotations#apimodel
2.测试:
启动服务,浏览器输入"http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html"

GET红框:method=RequestMethod.GET
右边红框:@ApiOperation
parameter红框:@ApiImplicitParams系列注解
response messages红框:@ApiResponses系列注解
输入参数后,点击"try it out!",查看响应内容:

相关文章推荐
- spring boot整合Swagger2的示例代码
- SpringBoot整合Swagger2
- SpringBoot整合Swagger2
- Swagger(一) SpringBoot整合Swagger2简单的例子
- Spring Boot 整合Spring Security 和Swagger2 遇到的问题小结
- Swagger(一) SpringBoot整合Swagger2简单的例子
- SpringBoot实战之12 整合restful工具swagger2
- spring boot 整合Swagger2
- 个人推荐:SpringBoot整合Swagger2
- 2018 最新 spring boot 整合 swagger2 (swagger2 版本 2.8.0)
- SpringBoot(七):SpringBoot整合Swagger2
- SpringBoot整合Swagger2
- Spring Boot学习笔记 - 整合Swagger2自动生成RESTful API文档
- Spring Boot整合Swagger2
- SpringBoot(七):SpringBoot整合Swagger2
- Springboot整合swagger2项目的部署问题
- Swagger(一) SpringBoot整合Swagger2简单的例子
- Spring Boot 整合mybatis 与 swagger2
- Spring Boot整合Swagger2的完整步骤详解
- SpringBoot整合系列-整合Swagger2
