JAVA8新特性[第四季]-强大的Stream API
2017-08-23 09:07
393 查看
Java8中有两大最为重要的改变。第一个是 Lambda 表达式 ;另外一 个则是 Stream API(java.util.stream.*)。
Stream 是 Java8 中处理集合的关键抽象概念,它可以指定你希望对 集合进行的操作,可以执行非常复杂的查找、过滤和映射数据等操作。
使用Stream API 对集合数据进行操作,就类似于使用 SQL 执行的数 据库查询。也可以使用 Stream API 来并行执行操作。简而言之, Stream API 供了一种高效且易于使用的处理数据的方式。
流(Stream) 到底是什么呢?
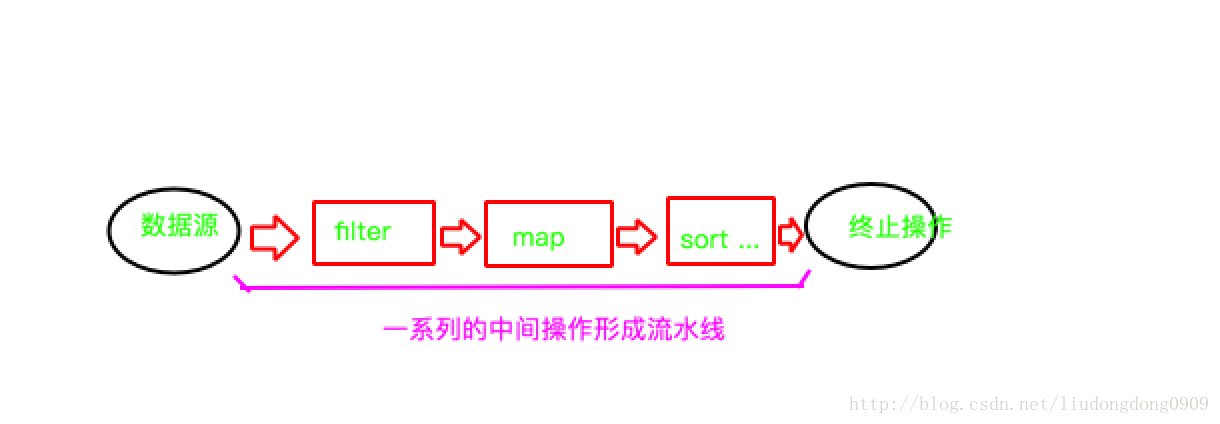
是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合、数组等)所生成的元素序列。
集合讲的是数据,流讲的是计算!
注意:
1. Stream自己不会存储元素。
2. Stream不会改变原对象。相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stream。
3. Stream操作是延迟执行。这意味着他们会等到需要结果的时候才执行。
一个数据源(如:集合或数组),获取一个流
一个中间操作链,对数据源的数据进行处理。
一个终止操作,执行中间操作链,并产生结果。
Java8 中的 Collection 接口被扩展, 供了两个获取流的方法:
1. default Stream< E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流
2. default Stream< E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流
案例:
2
3
1
2
3
[/code]
通过 Arrays中的静态方法 stream() 创建数据源 。
static < T> Stream< T> stream(T[] array): 返回一个流
重载形式,能够处理对应基本类型的数组:
1. public static IntStream stream(int[] array)
2. public static LongStream stream(long[] array)
3. public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array)
案例:
2
1
2
[/code]
可以使用静态方法 Stream.of(), 通过显示值 创建一个流。它可以接收任意数量的参数。
public static< T> Stream< T> of(T… values) : 返回一个流
案例:
1
[/code]
可以使用静态方法 Stream.iterate() 和 Stream.generate(), 创建无限流。
1. 迭代:public static< T> Stream< T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator< T> f)
2. 生成:public static< T> Stream< T> generate(Supplier< T> s)
案例:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
[/code]
多个 中间操作 可以连接起来形成一个流水线,除非流水 线上触发终止操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何的处理! 而在终止操作时一次性全部处理,称为“惰性求值”。
案例:
定义一个集合: Employee 重写 hashcode , equals — 去重时使用
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行操作:
1.内部迭代 - 迭代操作由Stream API 完成操作
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
2.外部迭代
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
[/code]
3.中间操作 - 截断流
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
[/code]
执行结果:
2
1
2
[/code]
4.中间操作 - 跳过
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
1
2
3
[/code]
5.中间操作 - 筛选去重
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
[/code]
案例:
1.map操作
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
2.flatMap操作
先定义一个 filterCharacter(String str) 方法:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行测试代码:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[/code]
案例:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
终止操作会从流的流水线生成结果。其结果可以是任何不是流的值,例如:List、Integer,甚至是 void 。
案例:
1.匹配
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
[/code]
2.第一个元素 、 任意一个元素
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
1
2
3
[/code]
3.统计总个数、 最大、 最小值
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
[/code]
备注:map 和 reduce 的连接通常称为 map-reduce 模式,因 Google 用它 来进行网络搜索而出名。
案例:
1.求和
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行结果:
1
[/code]
2.计算次数
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
1
2
3
[/code]
案例:
1.收集
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
2.收集统计
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
3.收集-分组
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[/code]
4.收集-多级分组
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
执行结果:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[/code]
Collector 接口中方法的实现决定了如何对流执行收集操作(如收 集到 List、Set、Map)。但是 Collectors 实用类 供了很多静态 方法,可以方便地创建常见收集器实例,具体方法与实例如下表:
相关源码地址:https://github.com/liudongdong0909/java8/tree/master/java8-Lambda/src/com/donggua
Stream 是 Java8 中处理集合的关键抽象概念,它可以指定你希望对 集合进行的操作,可以执行非常复杂的查找、过滤和映射数据等操作。
使用Stream API 对集合数据进行操作,就类似于使用 SQL 执行的数 据库查询。也可以使用 Stream API 来并行执行操作。简而言之, Stream API 供了一种高效且易于使用的处理数据的方式。
一、什么是 Stream
流(Stream) 到底是什么呢?是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合、数组等)所生成的元素序列。
集合讲的是数据,流讲的是计算!
注意:
1. Stream自己不会存储元素。
2. Stream不会改变原对象。相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stream。
3. Stream操作是延迟执行。这意味着他们会等到需要结果的时候才执行。
二、Stream操作的三个步骤
2.1 第一步:创建stream
一个数据源(如:集合或数组),获取一个流
2.2 第二步:中间操作
一个中间操作链,对数据源的数据进行处理。
2.3 第三步:终止操作(终端操作)
一个终止操作,执行中间操作链,并产生结果。
三、创建Stream的四种方式
3.1 第一种方式:通过 Collection 系列集合提供的方法 stream() 或者 parallelStream()
Java8 中的 Collection 接口被扩展, 供了两个获取流的方法:1. default Stream< E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流
2. default Stream< E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流
案例:
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>(); Stream<Employee> stream = list.stream(); Stream<Employee> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();1
2
3
1
2
3
[/code]
3.2 第二种方式:由数组创建流
通过 Arrays中的静态方法 stream() 创建数据源 。static < T> Stream< T> stream(T[] array): 返回一个流
重载形式,能够处理对应基本类型的数组:
1. public static IntStream stream(int[] array)
2. public static LongStream stream(long[] array)
3. public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array)
案例:
Integer[] num = new Integer[23]; Stream<Integer> stream1 = Arrays.stream(num);1
2
1
2
[/code]
3.3 第三种方式:由值创建流
可以使用静态方法 Stream.of(), 通过显示值 创建一个流。它可以接收任意数量的参数。public static< T> Stream< T> of(T… values) : 返回一个流
案例:
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.of(1, 5, 7);1
1
[/code]
3.4 第四种方式:由函数创建流,创建无限流。
可以使用静态方法 Stream.iterate() 和 Stream.generate(), 创建无限流。1. 迭代:public static< T> Stream< T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator< T> f)
2. 生成:public static< T> Stream< T> generate(Supplier< T> s)
案例:
// 迭代
Stream<Integer> stream3 = Stream.iterate(0, (x) -> x + 2).limit(2);
stream3.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------");
// 生成
Stream<Double> stream4 = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(4);
stream4.forEach(System.out::println);12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[/code]
执行结果:
0 2 ------------- 0.8009341328264229 0.3393727316726045 0.16402941830797657 0.189839641538307121
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
[/code]
四、Stream的中间操作
多个 中间操作 可以连接起来形成一个流水线,除非流水 线上触发终止操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何的处理! 而在终止操作时一次性全部处理,称为“惰性求值”。
4.1 筛选与切片
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| filter(Predicate p) | 接收 Lambda , 从流中排除某些元素。 |
| distinct() | 筛选,通过流所生成元素的 hashCode() 和 equals() 去 除重复元素 |
| limit(long maxSize) | 截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量 |
| skip(long n) | 跳过元素,返回一个扔掉了前 n 个元素的流。若流中元素 不足 n 个,则返回一个空流。与 limit(n) 互补 |
定义一个集合: Employee 重写 hashcode , equals — 去重时使用
List<Employee> emps = Arrays.asList( new Employee(101, "林青霞", 28, 9889.99), new Employee(102, "东方不败", 29, 4329.85), new Employee(103, "周星驰", 40, 1233.88), new Employee(104, "大圣", 500, 5000.44), new Employee(105, "张无忌", 15, 3000.09), new Employee(102, "东方不败", 29, 4329.85) );1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行操作:
1.内部迭代 - 迭代操作由Stream API 完成操作
@Test
public void test2() {
// 中间操作不会做任何处理
Stream<Employee> stream = emps.stream()
.filter((e) -> {
System.out.println("惰性求值");
return e.getAge() < 30;
});
System.out.println("--------------------");
// 终止操作,一次性执行全部功能, 称为 "惰性求值"
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
执行结果:
--------------------
惰性求值
Employee{id=101, name='林青霞', age=28, salary=9889.99, status=null}
惰性求值
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null}
惰性求值
惰性求值
惰性求值
Employee{id=105, name='张无忌', age=15, salary=3000.09, status=null}
惰性求值
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
2.外部迭代
@Test
public void test3() {
Iterator<Employee> iterator = emps.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行结果:
Employee{id=101, name='林青霞', age=28, salary=9889.99, status=null}
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null}
Employee{id=103, name='周星驰', age=40, salary=1233.88, status=null}
Employee{id=104, name='大圣', age=500, salary=5000.44, status=null}
Employee{id=105, name='张无忌', age=15, salary=3000.09, status=null}
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null}12
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
[/code]
3.中间操作 - 截断流
@Test
public void test4() {
emps.stream()
.filter(employee -> employee.getAge() < 30) // 过滤年龄小于30的人
.limit(1) // 截取一个
.forEach(System.out::println);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
[/code]
执行结果:
Employee{id=101, name='林青霞', age=28, salary=9889.99, status=null}12
1
2
[/code]
4.中间操作 - 跳过
@Test
public void test5() {
emps.stream()
.filter(employee -> employee.getAge() < 30)
.skip(2)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行结果:
Employee{id=105, name='张无忌', age=15, salary=3000.09, status=null}
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null}12
3
1
2
3
[/code]
5.中间操作 - 筛选去重
@Test
public void test6() {
emps.stream()
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}12
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
[/code]
执行结果:
Employee{id=101, name='林青霞', age=28, salary=9889.99, status=null}Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null}
Employee{id=103, name='周星驰', age=40, salary=1233.88, status=null}
Employee{id=104, name='大圣', age=500, salary=5000.44, status=null}
Employee{id=105, name='张无忌', age=15, salary=3000.09, status=null}12
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
[/code]
4.2 映射
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| map(Function f) | 接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元 素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。 |
| mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction f) | 接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元 素上,产生一个新的 DoubleStream。 |
| mapToInt(ToIntFunction f) | 接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元 素上,产生一个新的 IntStream。 |
| mapToLong(ToLongFunction f) | 接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元 素上,产生一个新的 LongStream。 |
| flatMap(Function f) | 接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流 |
1.map操作
@Test
public void test7() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa", "java", "ccc", "java8", "hello world");
list.stream()
.map((x) -> x.toUpperCase())
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------");
emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getAge)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
执行结果:
AAA JAVA CCC JAVA8 HELLO WORLD ------------- 28 29 40 500 15 291
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[/code]
2.flatMap操作
先定义一个 filterCharacter(String str) 方法:
private static Stream<Character> filterCharacter(String str) {
List<Character> characters = new ArrayList<>();
for (Character character : str.toCharArray()) {
characters.add(character);
}
return characters.stream();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行测试代码:
@Test
public void test8() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa", "hello world");
Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream = list.stream()
.map(LambdaStramAPI::filterCharacter);
streamStream.forEach((s) -> {
s.forEach((c) -> System.out.println(c + ""));
System.out.println();
});
System.out.println("----------------------");
list.stream()
.flatMap(LambdaStramAPI::filterCharacter)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
执行结果:
a a a h e l l o w o r l d ---------------------- a a a h e l l o w o r l d1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[/code]
4.3 排序
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| sorted() | 产生一个新流,其中按自然顺序排序 |
| sorted(Comparator comp) | 产生一个新流,其中按比较器顺序排序 |
@Test
public void test9() {
emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.sorted()
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-----------------");
emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getAge)
.sorted(Integer::compare)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[/code]
执行结果:
1233.88 3000.09 4329.85 4329.85 5000.44 9889.99 ----------------- 15 28 29 29 40 5001
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
五、 Stream的终止操作
终止操作会从流的流水线生成结果。其结果可以是任何不是流的值,例如:List、Integer,甚至是 void 。
5.1 查找与匹配
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| allMatch(Predicate p) | 检查是否匹配所有元素 |
| anyMatch(Predicate p) | 检查是否至少匹配一个元素 |
| noneMatch(Predicate p) | 检查是否没有匹配所有元素 |
| findFirst() | 返回第一个元素 |
| findAny() | 返回当前流中的任意元素 |
| count() | 返回流中元素总数 |
| max(Comparator c) | 返回流中最大值 |
| min(Comparator c) | 返回流中最小值 |
| forEach(Consumer c) | 内部迭代(使用 Collection 接口需要用户去做迭 代,称为外部迭代。相反,Stream API 使用内部 迭代——它帮你把迭代做了) |
1.匹配
@Test
public void test10() {
boolean allMatch = emps.stream()
.allMatch((employee -> employee.getName().equals("林青霞")));
System.out.println(allMatch);
System.out.println("-----------------");
boolean anyMatch = emps.stream()
.anyMatch(employee -> employee.getName().equals("林青霞"));
System.out.println(anyMatch);
System.out.println("-----------------");
boolean noneMatch = emps.stream()
.noneMatch(employee -> employee.getName().equals("林青霞"));
System.out.println(noneMatch);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
执行结果:
false ----------------- true ----------------- false1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
[/code]
2.第一个元素 、 任意一个元素
@Test
public void test12() {
Optional<String> first = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.sorted()
.findFirst(); // 获取第一个元素
System.out.println(first.get());
System.out.println("-----------------");
Optional<Employee> findAny = emps.parallelStream()
.filter(employee -> employee.getName().equals("林青霞"))
.findAny(); //任意一个元素
System.out.println(findAny.get());
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
[/code]
执行结果:
东方不败
-----------------
Employee{id=101, name='林青霞', age=28, salary=9889.99, status=null}12
3
1
2
3
[/code]
3.统计总个数、 最大、 最小值
// 注意: 流一旦执行终止操作后, 就不能在重复使用
@Test
public void test13() {
Stream<Employee> stream = emps.stream();
long count = stream.count();
System.out.println(count);
System.out.println("-----------------");
Optional<Double> doubleOptional = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.max(Double::compare); //最大值
System.out.println(doubleOptional.get());
System.out.println("-----------------");
Optional<Employee> employeeOptional = emps.stream()
.min((x, y) -> Double.compare(x.getSalary(), y.getSalary())); // 最小值
System.out.println(employeeOptional.get());
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
[/code]
执行结果:
6
-----------------
9889.99
-----------------
Employee{id=103, name='周星驰', age=40, salary=1233.88, status=null}12
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
[/code]
5.2 归约
备注:map 和 reduce 的连接通常称为 map-reduce 模式,因 Google 用它 来进行网络搜索而出名。| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| reduce(T iden, BinaryOperator b) | 可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。 返回 T |
| reduce(BinaryOperator b) | 可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。 返回 Optional< T> |
1.求和
@Test
public void test14() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
Integer sum = list.stream()
.reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println(sum);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[/code]
执行结果:
551
1
[/code]
2.计算次数
@Test
public void test15() {
Optional<Double> doubleOptional = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.reduce(Double::max);
System.out.println(doubleOptional);
System.out.println("-----------------");
//查看 东方不败 出现的次数 -- 【此处还有点毛病】
Optional<Integer> sumOptional = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.flatMap(LambdaStramAPI::filterCharacter)
.map((c) -> {
if (c.equals("东")) return 1;
else return 0;
}).reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println(sumOptional.get());
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[/code]
执行结果:
Optional[9889.99] ----------------- 01
2
3
1
2
3
[/code]
5.3 收集
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| collect(Collector c) | 将流转换为其他形式。接收一个 Collector接口的 实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法 |
1.收集
@Test
public void test16(){
List<String> collect = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
collect.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------------");
Set<String> set = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
set.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------------");
HashSet<String> hashSet = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[/code]
执行结果:
林青霞 东方不败 周星驰 大圣 张无忌 东方不败 ------------------- 周星驰 林青霞 大圣 东方不败 张无忌 ------------------- 周星驰 林青霞 大圣 东方不败 张无忌1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[/code]
2.收集统计
// 收集统计
@Test
public void test17(){
// 统计总个数
Long count = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(count);
System.out.println("-------------------");
// 求平均值
Double avg = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(avg);
System.out.println("-------------------");
// 求和
Double sum = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(sum);
System.out.println("-------------------");
//求最大值
Optional<Employee> max = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.maxBy((x, y) -> Double.compare(x.getSalary(), y.getSalary())));
System.out.println(max.get());
System.out.println("-------------------");
//求最小值
Optional<Double> min = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getSalary)
.collect(Collectors.minBy(Double::compare));
System.out.println(min.get());
System.out.println("-------------------");
//统计分析
DoubleSummaryStatistics doubleSummaryStatistics = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(doubleSummaryStatistics.getAverage());
System.out.println("-------------------");
//拼接
String join = emps.stream()
.map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining(",", "--", "--"));
System.out.println(join);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
[/code]
执行结果:
61
-------------------
4630.683333333333
-------------------
27784.1
-------------------
Employee{id=101, name='林青霞', age=28, salary=9889.99, status=null}-------------------
1233.88
-------------------
4630.683333333333
-------------------
--林青霞,东方不败,周星驰,大圣,张无忌,东方不败--
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[/code]
3.收集-分组
// 分组
@Test
public void test18(){
Map<String, List<Employee>> group = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getName));
System.out.println(group);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
[/code]
执行结果:
{
周星驰=[Employee{id=103, name='周星驰', age=40, salary=1233.88, status=null}],
林青霞=[Employee{id=101, name='林青霞', age=28, salary=9889.99, status=null}],
大圣=[Employee{id=104, name='大圣', age=500, salary=5000.44, status=null}],
东方不败=[
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null},
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null}
],
张无忌=[Employee{id=105, name='张无忌', age=15, salary=3000.09, status=null}]}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[/code]
4.收集-多级分组
// 多级分组
@Test
public void test19(){
Map<String, Map<String, List<Employee>>> group = emps.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getName, Collectors.groupingBy((e) -> {
if (e.getAge() < 30) return "青年";
else if (e.getAge() < 50) return "中年";
else return "老年";
})));
System.out.println(group);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[/code]
执行结果:
{周星驰={中年=[Employee{id=103, name='周星驰', age=40, salary=1233.88, status=null}]},
林青霞={青年=[Employee{id=101, name='林青霞', age=28, salary=9889.99, status=null}]},
大圣={老年=[Employee{id=104, name='大圣', age=500, salary=5000.44, status=null}]},
东方不败={青年=[
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null},
Employee{id=102, name='东方不败', age=29, salary=4329.85, status=null}
]},
张无忌={青年=[Employee{id=105, name='张无忌', age=15, salary=3000.09, status=null}]}}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[/code]
Collector 接口中方法的实现决定了如何对流执行收集操作(如收 集到 List、Set、Map)。但是 Collectors 实用类 供了很多静态 方法,可以方便地创建常见收集器实例,具体方法与实例如下表:
| 方法 | 返回类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| toList | List<T> | 把流中元素收集到List |
| List<Employee> emps= list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList()); | ||
| toSet | Set<T> | 把流中元素收集到Set |
| Set<Employee> emps= list.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet()); | ||
| toCollection | Collection<T> | 把流中元素收集到创建的集合 |
| Collection<Employee>emps=list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)); | ||
| counting | Long | 计算流中元素的个数 |
| long count = list.stream().collect(Collectors.counting()); | ||
| summingInt | Integer | 对流中元素的整数属性求和 |
| inttotal=list.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Employee::getSalary)); | ||
| averagingInt | Double | 计算流中元素Integer属性的平均 值 |
| doubleavg= list.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Employee::getSalary)); | ||
| summarizingInt | IntSummaryStatistics | 收集流中Integer属性的统计值。 如:平均值 |
| IntSummaryStatisticsiss= list.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Employee::getSalary)); | ||
| joining | String | 连接流中每个字符串 |
| String str= list.stream().map(Employee::getName).collect(Collectors.joining()); | ||
| maxBy | Optional<T> | 根据比较器选择最大值 |
| Optional<Emp>max= list.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy(comparingInt(Employee::getSalary))); | ||
| minBy | Optional<T> | 根据比较器选择最小值 |
| Optional<Emp> min = list.stream().collect(Collectors.minBy(comparingInt(Employee::getSalary))); | ||
| reducing | 归约产生的类型 | 从一个作为累加器的初始值 开始,利用BinaryOperator与 流中元素逐个结合,从而归 约成单个值 |
| inttotal=list.stream().collect(Collectors.reducing(0, Employee::getSalar, Integer::sum)); | ||
| collectingAndThen | 转换函数返回的类型 | 包裹另一个收集器,对其结 果转换函数 |
| inthow= list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), List::size)); | ||
| groupingBy | Map<K, List<T>> | 根据某属性值对流分组,属 性为K,结果为V |
| Map<Emp.Status, List<Emp>> map= list.stream() .collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getStatus)); | ||
| partitioningBy | Map<Boolean, List<T>> | 根据true或false进行分区 |
| Map<Boolean,List<Emp>>vd= list.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(Employee::getManage)); |
相关文章推荐
- JAVA8新特性[第四季]-强大的Stream API
- Java8新特性(二)——强大的Stream API
- Java 8新特性(Lambda,Stream API)
- Java 9 新特性! 看过才知道强大
- JAVA8新特性(四)——Stream API
- Java 8 新特性——Stream API
- Java 8新特性:全新的Stream API
- Java 8新特性:全新的Stream API和lambda表达式
- java8新特性回顾(二)---stream api
- 强大的JAVA剖析器JProfiler v10.0发布,新增多个显示特性|附下载
- java8新特性源码解析
- Java 10的10个新特性,将彻底改变你写代码的方式!
- java面向对象三大特性之封装
- C++和java技术特性对比
- 【java高级特性之反射】Field类和Constructor类的使用
- javaSE_07Java中类和对象-封装特性
- 【Java并发编程】:并发新特性—Lock锁和条件变量
- Java 8 新特性概述
- JAVA高级特性总结
- Spring 4支持的Java 8新特性一览
