java 将数据字典(父子结构)绑定成List集合
2017-08-22 09:55
465 查看
java 将数据字典(父子结构)绑定成List集合,以实现数据库同步功能
最近公司做了一个项目,其中有一个功能是将本地的数据库同步到远程服务器端,同步的过程不是本文章的重点,重点是在导入的过程中,涉及到一个数据字典类型的表,也就是带有父ID的表,即(父子表),这就对导入提出了新的要求:就是在导入新的表中时,必须先导入父表,再导入子表,如果多级的话,依次从顶级开始向下导入,领导和我说了一顿,什么while循环啊,递归啊,说实话,我知道他要表达的意思,可就是不会写,没办法上网找找,终于我看到了一偏文章:
Kaer_GG的文章,树形list(菜单树)递归遍历list对我帮助很大,好了,不费话,看看我的数据库结构:
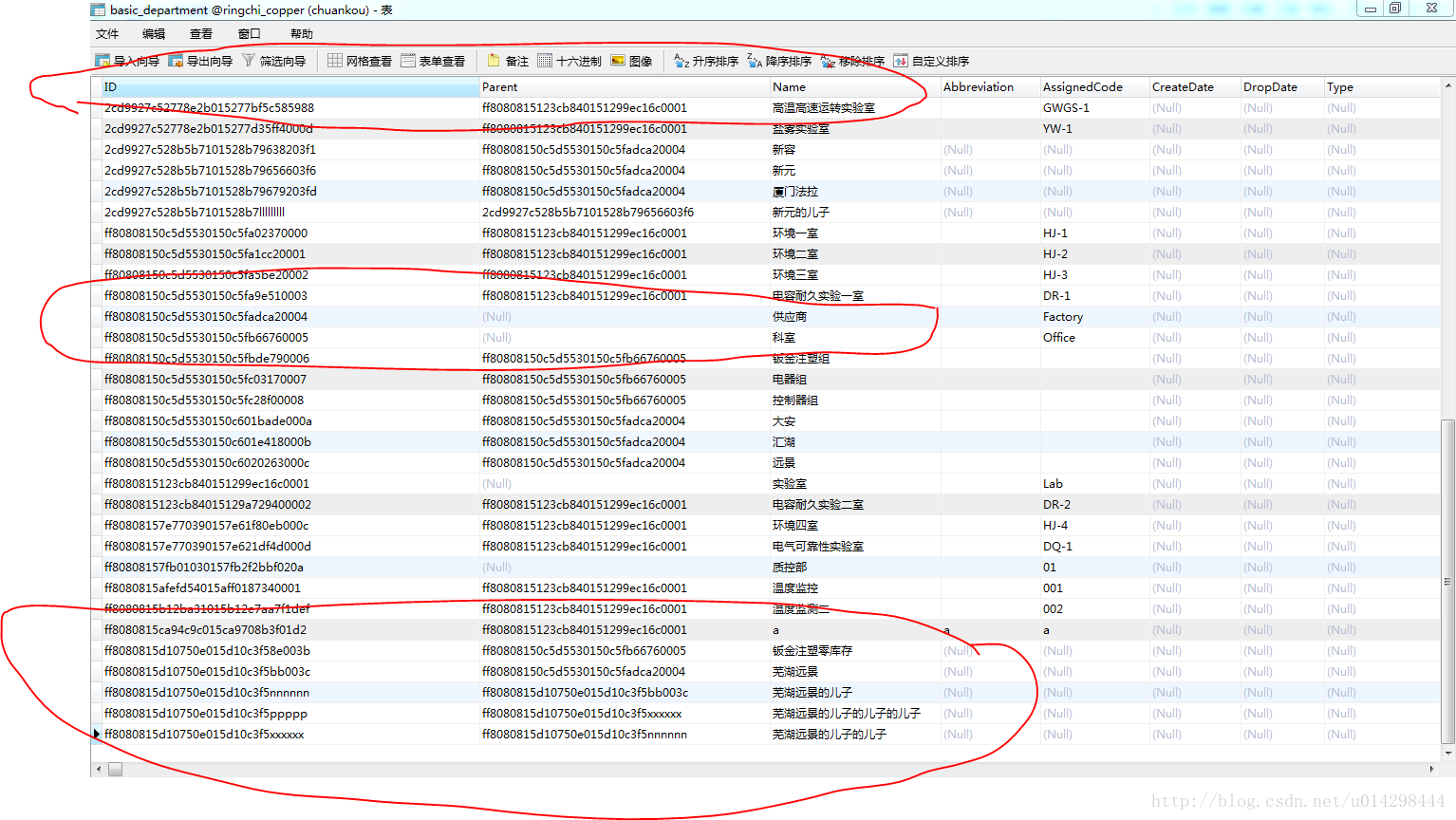
,好了,接下来把相对应的实体给大家看看
System.out.println(“新数据库”);
for (Department department : resultList) {
if (department.getParent()!=null) {
System.out.println(department.getId()+”\t”+department.getName()+”\t”+department.getParent().getName());
“`
好了,希望对大家有所帮助,对我自己也是个帮助!
最近公司做了一个项目,其中有一个功能是将本地的数据库同步到远程服务器端,同步的过程不是本文章的重点,重点是在导入的过程中,涉及到一个数据字典类型的表,也就是带有父ID的表,即(父子表),这就对导入提出了新的要求:就是在导入新的表中时,必须先导入父表,再导入子表,如果多级的话,依次从顶级开始向下导入,领导和我说了一顿,什么while循环啊,递归啊,说实话,我知道他要表达的意思,可就是不会写,没办法上网找找,终于我看到了一偏文章:
Kaer_GG的文章,树形list(菜单树)递归遍历list对我帮助很大,好了,不费话,看看我的数据库结构:

,好了,接下来把相对应的实体给大家看看
package com.ringchi.entity.department;
import com.ringchi.entity.NamedObject;
import com.ringchi.entity.NamedTreeObject;
import com.ringchi.entity.dictionary.Dictionary;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Temporal;
import javax.persistence.TemporalType;
import javax.persistence.Transient;
@Entity
@Table(name="basic_department")
public class Department extends NamedObject
implements NamedTreeObject
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3256440322035822899L;
private String assignedCode;
private String abbreviation;
private Dictionary type;
private Dictionary kind;
private Date createDate;
private Date dropDate;
private int sequence;
private String location;
private Department parent;
private Dictionary level;
private String levelCode;
public Department()
{
}
public Department(String id)
{
super(id);
}
public Department(String id, String name) {
super(id, name);
}
@Column(length=20)
public String getAbbreviation()
{
return this.abbreviation;
}
public void setAbbreviation(String abbreviation)
{
this.abbreviation = abbreviation;
}
@Column(length=20)
public String getAssignedCode() {
return this.assignedCode;
}
public void setAssignedCode(String assignedCode) {
this.assignedCode = assignedCode;
}
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
public Date getCreateDate()
{
return this.createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(Date createDate)
{
this.createDate = createDate;
}
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="Type")
public Dictionary getType()
{
return this.type;
}
public void setType(Dictionary type)
{
this.type = type;
}
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
public Date getDropDate()
{
return this.dropDate;
}
public void setDropDate(Date dropDate)
{
this.dropDate = dropDate;
}
public int getSequence()
{
return this.sequence;
}
public void setSequence(int sequence)
{
this.sequence = sequence;
}
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="Parent")
public Department getParent()
{
return this.parent;
}
public void setParent(Department parent)
{
this.parent = parent;
}
public String toString()
{
String result = getId() + ":" + getName() + "[";
if (getParent() != null) {
result = result + "{" + getParent().getId() + "} ";
}
result = result + "]";
return result;
}
@Transient
public NamedTreeObject getTreeParent() {
return getParent();
}
public void setTreeParent(NamedTreeObject parent) {
setParent((Department)parent);
}
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="Level")
public Dictionary getLevel() { return this.level; }
public void setLevel(Dictionary level)
{
this.level = level;
}
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="Kind")
public Dictionary getKind() { return this.kind; }
public void setKind(Dictionary kind)
{
this.kind = kind;
}
@Column(length=100)
public String getLocation() {
return this.location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
@Column(length=50)
public String getLevelCode()
{
return this.levelCode;
}
public void setLevelCode(String levelCode) {
this.levelCode = levelCode;
}
}
以上是实体部分,重点来了,如何将这些数据绑定成List集合呢?看代码
//先查找原数据库
List<Department> equips = theDMO.getObjects("FROM Department");
System.out.println("原数据库");
for (Department department : equips) {
System.out.println(department);
}
//我们来看看打印的结果:

可以看到原来的数据库是无序的,此时要是导入的话,肯定出错,下面看具体的转换过程List<Department> resultList=new ArrayList<Department>();
for (Department department : equips) {
if (department.getParent()==null) {//父级菜单开始添加
resultList.add(department);
if (ifChilds(equips, department.getId())) {//存在子集
List<Department> childs = new ArrayList<>();
childs = getChildList(equips,department.getId(),childs);
resultList.addAll(childs);
}
}
}//判断是否存在子集
private static boolean ifChilds(List<Department> list,String pId) {
boolean flag = false;
for (Department department : list) {
if (department.getParent()!=null) {
if (department.getParent().getId().equals(pId)) {
flag=true;
break;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
//获取父id下的子集合
private static List<Department> getChildList(List<Department> list,String pId,List<Department> reList) {
for (Department department : list) {
if (department.getParent()!=null) {
if (department.getParent().getId().equals(pId)) {//查询下级菜单
reList.add(department);
if (ifChilds(list, department.getId())) {
getChildList(list, department.getId(), reList);
}
}
}
}
return reList;
}
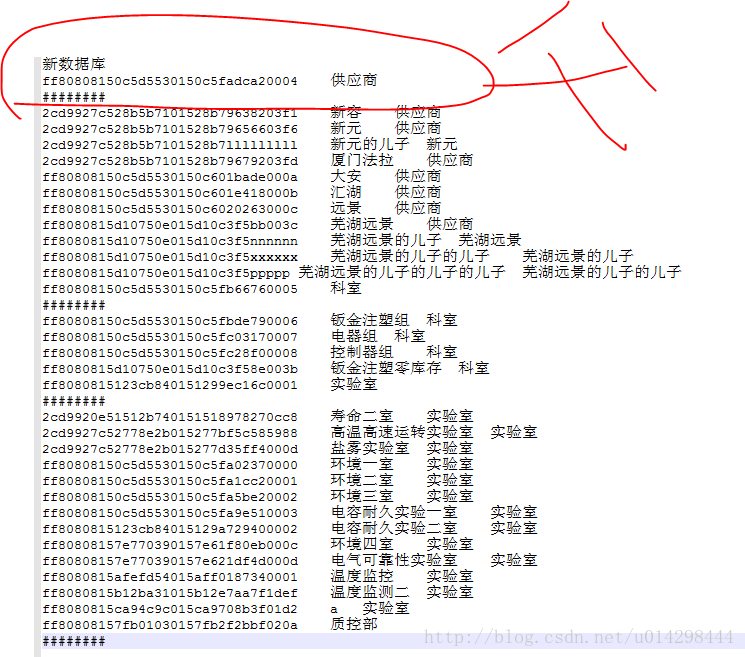
现在看看转换后的情况吧:System.out.println(“新数据库”);
for (Department department : resultList) {
if (department.getParent()!=null) {
System.out.println(department.getId()+”\t”+department.getName()+”\t”+department.getParent().getName());
}else {
System.out.println(department.getId()+"\t"+department.getName());
System.out.println("########");
}
}“`

好了,希望对大家有所帮助,对我自己也是个帮助!
相关文章推荐
- java 将数据字典(父子结构)绑定成List集合(第二种写法)
- java学习日记_79:集合框架之数据结构的讲解和引出List子类的特点
- python基础数据结构——列表(list), 元祖(tuple), 字典(dict), 字符串(string), 集合(set) 介绍及相互转换
- JAVA基础学习之String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder、基本数据类型的使用、整形进制转换、集合Collection、Vector、ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet、TreeSet等(3)
- Java使用LinkedList模拟一个堆栈或者队列数据结构
- Tree结构数据拆分成List集合算法
- java中去除List集合中重复数据的方法
- 再论JAVA中核心数据结构——List
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记36:List练习之键盘录入多个数据在控制台输出最大值
- java读取csv数据到list缓存,并对list集合分组统计结果
- java集合list中的数据按照多个属性分组
- Java数据结构笔记4——LinkedList
- Java 实践——JTabel 绑定 List 数据
- java容器--List集合中的体系结构分析(一)
- java后台 jstl输出数据库表中的一组数据&&jstl输出数据库表中的所有数据并放在List集合
- Java大课堂:常用数据结构二(List)
- java用数据库获取的list数据构造hashmap树结构
- springMVC中复杂嵌套对象、List等集合类型数据绑定
- java获取list集合转换成json数据
- Java:集合,对列表(List)中的数据(整型、字符串、日期等)进行排序(正序、倒序)的方法;字符串按照整型排序的方法
