【Java基础 五】---输入输出io流
2017-06-30 10:11
375 查看
今天来继续总结一下文件io流,这块儿内容是研一的时候学的,大概时间是2016年1月13日到2016年1月14日学的,现在有些忘记,还好之前的笔记还在,重新梳理一下吧。希望能快速上手。
首先io的意思就是输入输出嘛,主要包括内存,文件等地的输入输出。下边详细介绍。在介绍之前,先说一下java的编码吧。
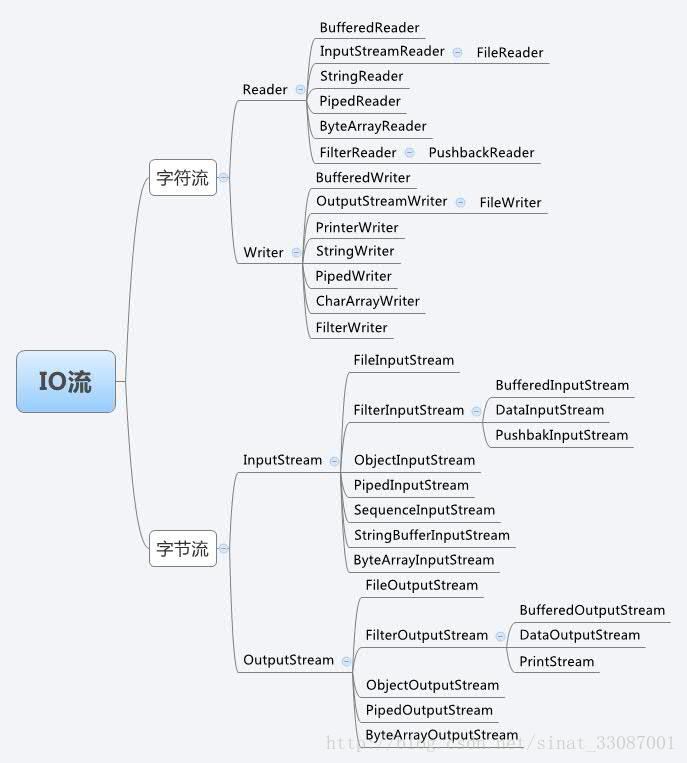
接下来是一张java的io类关系图
运行结果,中文汉字发生乱码
写入文件的是
因为转换了编码格式,所以看起来都是?
DataInputStream(ByteArrayInputStream)读出来=====ByteArrayInputStream(作为数据缓存区)
DataOutputStream数据输出流 将Java基本数据类型写入数据输出流中。并可以通过数据输入流DataInputStream将数据读入。ByteArrayInputStream类本身采用了适配器设计模式,它把字节数组类型转换为输入流类型,使得程序能够对字节数组进行读操作。
运行结果
重要总结 int,double等等数值类型的数据可以被读到程序里来,但是不能写到文件里,会乱码,所以有了object和data的应用。又因为int类型等数值类型可以直接转化为字符,字节类型,所以可以直接读取,汉字则不行,必须按照字符类型来读
读写类不一致也可以应用于同一个文件,因为是两个不同的管道,但复制文件的时候尽量一致,为了代码的美观高效
如果后续还需要补充就再补充第一次修改时间2017-6-30
首先io的意思就是输入输出嘛,主要包括内存,文件等地的输入输出。下边详细介绍。在介绍之前,先说一下java的编码吧。
编码和编码格式
编码
编码就是一个编号(数字)到字符的一种映射关系,就仅仅是一种一对一的映射而已,可以理解成一个很大的对应表格,java默认的字符集是Unicode(占两个字节byte,一个字节=8比特位bit,所以每个Unicode占用16比特位),所以对于char字符来说,一个英文单词‘c’和一个汉字‘和’一样,都占2个字节编码格式
编码格式 是用来序列化或存储编码中提到的那个“编号(数字)”的一种“格式”,包括gbk和utf-8gbk: 是指中国的中文字符,其它它包含了简体中文与繁体中文字符UTF-8: 它是一种全国家通过的一种编码。接下来是一张java的io类关系图

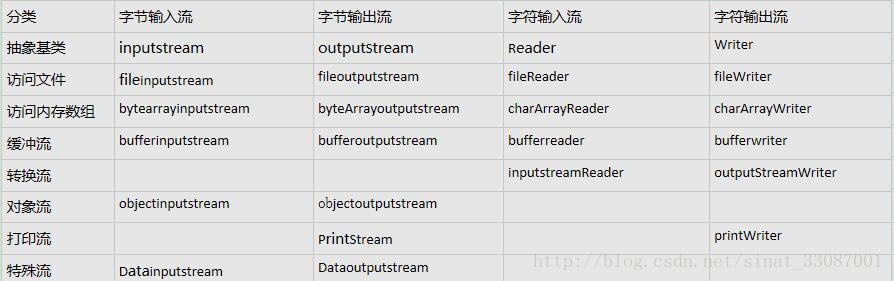
流的分类
依据方向
输入流/输出流 应该站在程序(控制台)的角度上,从文件到程序叫做输入流,从程序到文件叫输出流,读(输入)是读到为程序分配的内存空间中去啦,写(输出)是写到指定的文件中去了。依据数据单位
字节流/字符流 字节流:按照8位二进制读,字符流:按照2个8位二进制读,是2个字节utf-16依据功能不同
节点流/处理流 节点流:直接从特定数据源(文件,内存)读写数据。处理流:套在其它已存在流之上的,为程序提供更强大的读写功能文件io字节流
文件输入字节流
FileInputStreampublic static void main(String[] args) {
int b = 0;
FileInputStream in = null; //输入字节流
try {
in = new FileInputStream("g:\\TML\\TML.txt"); //创建一个管道,新建一个输入流(对接到指定文件)
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件");
System.exit(-1);
}
try {
long num=0;
while((b=in.read())!=-1){ //表示文件还没有读到结尾,读到结尾返回-1
System.out.println((char) b); //强制转化成字符读取出来,如果不加强转,输出的是一系列ASCII码对应每个字节
num++;
}
in.close(); //一定要记住,读完要关闭读
System.out.println("共读取了"+num+"个字节");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件读取错误");
System.exit(-1);
}
} //打印出来全是???,因为是一个字节一个字节往出读的,运行结果,中文汉字发生乱码
A DSFDFDF DFDF DFDFDFA ä¸ å›½
文件输出字节流
FileOutputStreampublic static void main(String[] args) {
int b = 0;
FileOutputStream out = null;
FileInputStream in = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream("g:\\TML\\TML.txt"); // 从文件里读数据
out = new FileOutputStream("g:\\TML\\ZYJ.txt"); // 往文件里写数据
int num = 0;
while ((b = in.read()) != -1) {
out.write(b); //写到指定文件中去
num++;
}
in.close();
out.close();
System.out.println("共复制了" + num + "个字节");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件复制错误");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("复制成功");
}输入字节流(buffer缓冲处理)
BufferedInputStreampublic static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
int c = 0;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("e:\\TML.txt");
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); //把字节流包装到buffer缓冲读入,减少对硬盘的损伤。
System.out.println((char)fis.read()); //读取第一个字符
System.out.println((char)bis.read()); //读取第二个字符
bis.mark(10); //要求在10个字符之内,这个mark应该保持有效,系统会保证buffer至少可以存储10个字符
for (int i = 0; i <= 10 && (c = bis.read()) != -1; i++) {
System.out.print((char)c + " ");
}
System.out.println();
bis.reset(); //回到标记的地方重新读入
for (int i = 0; i <= 10 && (c = bis.read()) != -1; i++) {
System.out.print((char)c + " ");
}
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}d e f g h i j k l m d f s f g h i j k l m d f s
文件io字符流
文件输入字符流
FileReaderpublic static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null; //注意,这里是fileReader
int c = 0;
try {
fr = new FileReader("g:\\TML\\TML.txt");
while ((c = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) c); //注意不要换行
}
fr.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("找不到指定文件");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件读取错误");
System.exit(-1);
}
}A DSFDFDF DFDF DFDFDFA 中 国
文件输出字符流
FileWriterpublic static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter fw = null;
int c = 0;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("g:\\TML\\MHW.txt");
for (c = 0; c < 200; c++) {
fw.write("支持茂神的点赞" + c+" ");
//只有字符流才能输出字符串,字节流只能输出字符
}
fw.close(); //切记,写完一定要关了,不关资源不释放,无法写入
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件读取错误");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("写入成功");
}复制文件小程序
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
int c = 0;
try {
fr = new FileReader("g:\\TML\\MHW.txt");
fw = new FileWriter("g:\\TML\\PXJ.TXT");
while ((c = fr.read()) != -1) {
fw.write((char) c);
} //代码的核心部分
fr.close();
fw.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("无法找到文件");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("无法复制文件");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("文件复制成功");
}输入输出字符流(buffer缓冲处理)
BufferedReader ——– BufferedWriterpublic static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("g:\\TML\\random.txt"));
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("g:\\TML\\random.txt"));
String s=null;
for(int i=1;i<20;i++){
s=String.valueOf(Math.random());
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.flush(); //一定要记得程序写完要冲刷
while((s=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(s);
}
bw.close();
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("文件写入成功");
}字节流与字符流
输入字节流转换字符流
InputStreamReader(字符流)——-BufferedReader(InputStreamReader)public static void main(String[] args) {
123e9
try {
System.out.println("请输入字符");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); //包装为buffer是为了按行读入
String s = null;
s = br.readLine();
while (s != null) {
if (s.equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) {
break; //阻塞
}
System.out.println("键盘输入内容为" + s);
s = br.readLine();
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}从键盘读入的是字节流,经过处理后变为字符流显示在控制台
输入字符流 转换为字节流
OutputStreamWriter(字符流)——FileOutputStream(是前者参数)public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("g:\\TML\\LSW.txt"));
osw.write("我是一个大帅哥你承不承认?"); //可以直接在文件里写字符
System.out.println(osw.getEncoding()); //得到字符编码
osw.close();
===============================================================
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(
"g:\\TML\\LSW.txt", true), "ISO8859_1"); //true代表在原文件基础之上添加,然后指定字符编码格式"ISO8859_1"包含所有的西欧语言latin1
osw.write("不得不承认你是");
System.out.println(osw.getEncoding());
osw.close(); //从这里可以看出没执行一次读写操作之后都要关了上一个
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}写入文件的是
我是一个大帅哥你承不承认? ???????
因为转换了编码格式,所以看起来都是?
从键盘写入文件
一定要用到转换流(把键盘输入的字节流转换为字符流)public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 给文件赋予名字
System.out.println("请输入要存储的文件名:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String filename = sc.next();
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("g:\\TML\\txtwenjian\\" + filename
+ ".txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
// 键盘输入字节流转换为字符流
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); // 包装为buffer是为了按行读入
String s =null;
System.out.println("请输入您的姓名和学号:");
while ((s=br.readLine()) != null) {
if (s.equals("quit")||s.equals("Quit")) {
break; // 阻塞
}
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("无法找到文件");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("无法读写文件");
System.exit(-1);
}数据流的输入输出(特殊流)
ByteArrayOutputStream(作为数据缓存区)—-DataOutputStream(ByteArrayOutputStream)写进去DataInputStream(ByteArrayInputStream)读出来=====ByteArrayInputStream(作为数据缓存区)
DataOutputStream数据输出流 将Java基本数据类型写入数据输出流中。并可以通过数据输入流DataInputStream将数据读入。ByteArrayInputStream类本身采用了适配器设计模式,它把字节数组类型转换为输入流类型,使得程序能够对字节数组进行读操作。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //把字节以数组形式包装
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos); //字节流改装成字符流
dos.writeDouble(Math.random()); //不需要string转换,直接可以写入
dos.writeBoolean(true);
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(
baos.toByteArray());
System.out.println(bais.available()); //显示写入了几个字节
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bais);
System.out.println(dis.readDouble()); // 先写入的先读出来
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
dos.close();
dis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}打印流
PrintStream (fileoutputstream)
public class testPrintstream {
public static void main(String[] args) { // 只有输入没有输出,最大的好处就是printstream可以自动编码,不用担心,outputstream不会。而且永远不会抛出异常,还会自动flush
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(
"g:\\TML\\txtwenjian\\print.txt"); // 先写个字节流
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(fos); // 套个处理流
if (ps != null) {
System.setOut(ps); // 重新设置输出位置为文件,如果以后输出的目标是文件的话还是用outputstream比较好,若要设置其它输出路径,用print比较好
}
int ln = 0;
for (char c = 0; c < 60000; c++) {
System.out.print(c + ""); //不用write方法也可以把内容写到文件里
if (ln++ >= 100) {
System.out.println();
ln = 0;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}PrintWriter
public class testPrintstream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
System.out.println("请您输入");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(
"g:\\TML\\txtwenjian\\printwriter.txt",true); //防止文件覆盖
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
String s = null;
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
if (s.equals("quit"))
break; //以后就用break,防止下一段执行不上输入的不需要再write,直接进入文件了
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase()); //键盘上显示
pw.println("————————————————");
pw.println(s.toUpperCase()); //把输入转到文件上并且改写为大写形式
pw.flush();
}
Date date=new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd-EEE HH:mm:dd");
pw.println("====" +sdf.format(date)+ "======");
//记录处理日志
pw.flush();
pw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}序列化流
ObjectOutputStream—ObjectInputStream—Serializablepublic class testObjectIO {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
T t = new T();
t.k = 8;
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(
"g:\\TML\\txtwenjian\\object.txt");
ObjectOutputStream ops = new ObjectOutputStream(fos); // object也是用来存储数据用的和data用法类似,但更加简便,一次性全部读写,不用管顺序
ops.writeObject(t); // 小心,这里是writeObject
ops.flush();
ops.close();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(
"g:\\TML\\txtwenjian\\object.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
T read = (T) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(read.i + " " + read.j + " " + read.d + " "
+ read.k);
}
}
class T implements Serializable { // Serializable序列化必须使用的接口,标记性接口,不需要重写
int i = 10;
int j = 9;
double d = 2.3;
transient int k = 15; // transient是透明的的意思,往硬盘上写的时候本值不予考虑,直接赋值0
}运行结果
10 9 2.3 0
文件的基本操作
File (该类不能进行文件读写)public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("g:\\TML\\txtwenjian");
System.out.println(file.getName()); //获取文件名
System.out.println(file.getParent()); //获取父类相对文件路径
System.out.println(file.getAbsoluteFile()); //获取绝对文件路径
System.out.println(file.getAbsoluteFile().getParent()); //获取父类绝对文件
File newFile = new File(System.currentTimeMillis() + "");
System.out.println("newfile对象是否存在:"+newFile.exists());
String[] filelist = file.list();
System.out.println("============当前路径下所有的文件和路径===============");//显示当前路径下所有文件和路径
for (String fileName : filelist) {
System.out.println(fileName);
}
}总结

重要总结 int,double等等数值类型的数据可以被读到程序里来,但是不能写到文件里,会乱码,所以有了object和data的应用。又因为int类型等数值类型可以直接转化为字符,字节类型,所以可以直接读取,汉字则不行,必须按照字符类型来读
读写类不一致也可以应用于同一个文件,因为是两个不同的管道,但复制文件的时候尽量一致,为了代码的美观高效
如果后续还需要补充就再补充第一次修改时间2017-6-30
相关文章推荐
- 黑马程序员--Java基础学习之IO流之字节流、字符流、读取写入文件、Copy文件、键盘输入输出、流操作的基本规律
- java基础知识记录--输入输出IO流 (摘自张孝祥整理java面试题)
- JAVA 基础IO流
- Java基础IO流的简单总结(转)
- Java基础20天--04--IO流
- java基础——输入输出流
- Java基础21天--05--IO流
- Java基础之IO流处理
- 黑马程序员---Java基础--19天(IO流之二)
- Java基础21天--01--IO流
- Java基础21天--03--IO流
- Java基础20天--03--IO流
- 【Java基础专题】IO与文件读写---Java的IO流架构
- Java基础19天--01--IO流
- 黑马程序员_java基础视频第18天_与系统交互的类及IO流
- Java基础20天--05--IO流
- Java基础:第十七讲 基本输入输出
- Java基础19天--03--IO流
- 黑马程序员—10、Java基础&IO流
- 黑马程序员---Java基础--18天(IO流之一)
