C语言代码复习笔记:第二章
2017-06-21 09:55
274 查看
输出星星
默认情况下, C++函数按照值传递参数, 这就意味着函数中定义的形参是新的变量, C函数通过通过使用拷贝, 保护了原始数据的完整性;
虽然C语言数组名就是一个地址指针, 但是它们仍然还是按照值传递的;
如果参数是数组的话, 默认传递的是数组的复制品:
输出为:
如果参数为数组,接收的参数设置为指针, 修改指针即会修改原来的数组:
从一堆数组中找出指定的的数字:
静态变量, 静态变量
输出:
如果声明了静态变量, 那么这个变量就会和函数挂钩, 相对于函数的属性, 静态变量只会初始化一次
数字后面不同的后缀,说明了不同的类型;
查看二进制数字包含1的进制位:
如果数据太大, 超出了能够存储的大小, 计算结果会出现问题, 尴尬😅:
又是精度问题, 使用小树会导致计算结果有误差:
统计用户输入数字的个数:
以上的代码经过优化以后, 变成这样:
如果直接使用双引号""声明字符串, 那么字符串的最后默认会被添加一个0,作为结束标记;
字符整理成大写:
字符串整理成大写:
还数组和指针:
使用指针会比使用字符串数组更加灵活:
指针数组 相对于 标准的数组, 更灵活, 而且存放的空间会更小:
如果是标准的数组, 需要给一个固定的长度, 但是使用指针数组的话, 并不会出现多余的数据, 图示:
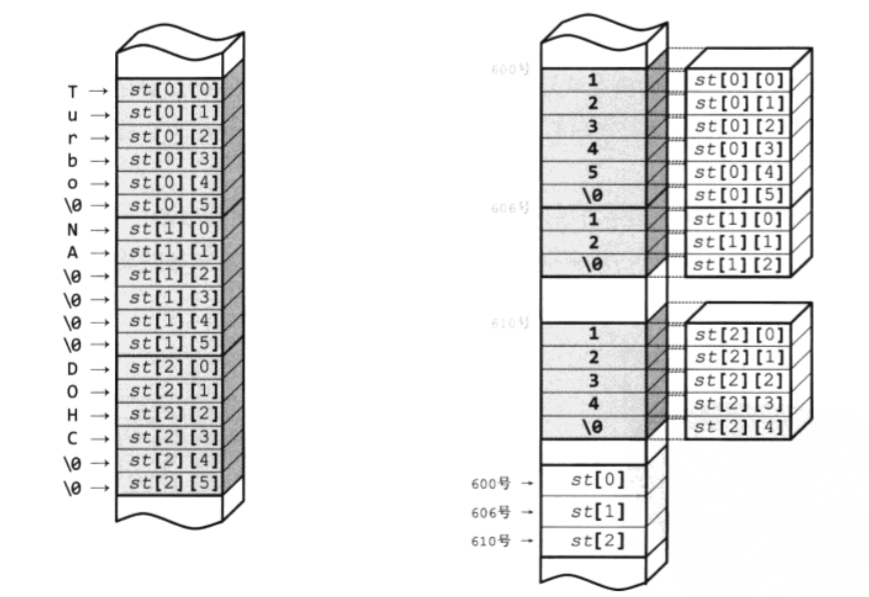
调用函数的时候, 如果直接把结构体作为参数, 其实传递的时候结构体的副本,( 这个和js有点区别, js中对象就是是指针) 如果在函数中修改结构体, 要注意必须传递指针, 数组传递的也是副本, (除非你传递指针或者引用), 这个要注意:
以上的代码中, 我们定义了stu这个结构体, 但是 使用了比较多的的代码:
通过使用typedef, 可以进行简化:
文件读取操作的代码, 创建一个文件对象, 然后读区copy.cpp文件,通过putchar输出到控制台:
通过描述符打开文件, 区别于fopen和FILE句柄:
文件写入并查看:
给文件的固定位置添加数据, lseek :
获取文件的状态 stat的结构为:
创建结构:
厦门点燃未来网络科技有限公司, 是厦门最好的微信应用, 小程序, 微信网站, 公众号开发公司
EOF
#include <stdio.h>
void printStart( int num ) {
while(num-->0) {
printf("*");
};
}
int main() {
int n = 20, i;
for(i=0; i<n; i++) {
printStart(i);
printf("\n");
}
printStart(4);
return 0;
}默认情况下, C++函数按照值传递参数, 这就意味着函数中定义的形参是新的变量, C函数通过通过使用拷贝, 保护了原始数据的完整性;
虽然C语言数组名就是一个地址指针, 但是它们仍然还是按照值传递的;
如果参数是数组的话, 默认传递的是数组的复制品:
#include <stdio.h>
void change(int array[2]) {
array[0] = 2;
}
int main() {
int arr[2] = {1,2};
printf("arr的第一个值是:%d\n", arr[0]);
change(arr);
printf("arr的第一个值是:%d\n", arr[0]);
return 0;
}输出为:
arr的第一个值是:1 arr的第一个值是:2
如果参数为数组,接收的参数设置为指针, 修改指针即会修改原来的数组:
#include <stdio.h>
void change(int *p) {
p[0] = 2;
}
int main() {
int arr[2] = {1,2};
printf("arr的第一个值是:%d\n", arr[0]);
change(arr);
printf("arr的第一个值是:%d\n", arr[0]);
return 0;
}从一堆数组中找出指定的的数字:
#include <stdio.h>
#define NUMBER 5
int search(int *p, int n) {
int index = 0;
printf("string\n");
while(true) {
if(*(p+index) == n) {
return index+1;
}
printf("%d\n", *p);
index++;
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
int arr[NUMBER] = {0};
int num;
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<NUMBER; i++) {
printf("输入索引为%d的值\n", i);
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
printf("输入需要查找的数字\n");
scanf("%d", &num);
int index = search(arr, num);
printf("找到的索引为%d", index);
return 0;
}静态变量, 静态变量
#include <stdio.h>
int foo = 0;
void func() {
static int sx = 0;
foo++;
sx++;
printf("%d--%d\n", foo, sx);
}
int main() {
func();
func();
func();
func();
return 0;
}输出:
1--1 2--2 3--3 4--4
如果声明了静态变量, 那么这个变量就会和函数挂钩, 相对于函数的属性, 静态变量只会初始化一次
数字后面不同的后缀,说明了不同的类型;
1u:unsigned int 1l:long 1ll: long long 1UL:unsigned long 0.5f:float
查看二进制数字包含1的进制位:
#include <stdio.h>
int count_bit(unsigned x) {
int count = 0;
while(x) {
if(x & 1U) count++;
x >>= 1;
}
return count;
}
int main() {
unsigned bits = 3;
int length = count_bit(bits);
printf("length is %d\n", length);
return 0;
}如果数据太大, 超出了能够存储的大小, 计算结果会出现问题, 尴尬😅:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("int 的位数 是 %d\n", sizeof(int));
int x = 4294967296-1;
int y = 333333;
x += y;
printf("result is %d\n", x);//输出 : result is 333332
return 0;
}又是精度问题, 使用小树会导致计算结果有误差:
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
float i;
for(i=0.0; i<1.0; i+=0.01) {
printf("%f", i);
}
return 0;
}统计用户输入数字的个数:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int count = 0;
int arr[5] = {0};
while( true ) {
printf("请输入数字0-4\n");
char c = getchar();
switch( c ) {
case '0':
arr[0]++;
break;
case '1':
arr[1]++;
break;
case '2':
arr[2]++;
break;
case '3':
arr[3]++;
break;
case '4':
arr[4]++;
break;
}
printf("统计位数: \n 0 : %d \n 1 : %d \n 2 : %d \n 3 : %d \n 4 : %d \n", arr[0], arr[1], arr[2], arr[3], arr[4]);
}
return 0;
}以上的代码经过优化以后, 变成这样:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int count = 0;
int arr[5] = {0};
while( true ) {
printf("请输入数字0-4\n");
char c = getchar();
if( c >= '0' && c <= '4') {
printf("%d\n",c);
int i = c;
arr[i-48]++;
}
printf("统计位数: \n 0 : %d \n 1 : %d \n 2 : %d \n 3 : %d \n 4 : %d \n", arr[0], arr[1], arr[2], arr[3], arr[4]);
}
return 0;
}如果直接使用双引号""声明字符串, 那么字符串的最后默认会被添加一个0,作为结束标记;
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[] = "ABCD";
char str1[] = {'A','B','C','D'};
printf("%s ==>> %d \n", str, sizeof(str)); //长度为5
printf("%s ==>> %d \n", str1, sizeof(str1)); //长度为4, 少了一个结束位, 必须自己给上
return 0;
}字符整理成大写:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main() {
while(true) {
char ch = getchar();
if(ch == EOF) {
break;
}
printf("%c",toupper(ch));
}
return 0;
}字符串整理成大写:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void up(char str[]){
int i = 0;
while(str[i]) {
str[i] = toupper(str[i]);
i++;
}
}
int main() {
char str[10];
while(true) {
scanf("%s",str);
printf("you enter => %s\n", str);
up(str);
printf("to uppper => %s\n", str);
}
return 0;
}还数组和指针:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int data[] = {22,33,44,55,66};
int *p = data;
// int *p = &data[0]; 这样写也行, 因为数组中对一个数据的地址就是数组的地址;
int i;
for( i = 0; i < 5; i++ ) {
printf("i = %d ==> %d\n", i, data[i]);
printf("i = %d ==> %d\n", i, p[i]);
printf("i = %d ==> %d\n", i, *(p+i));
}
return 0;
}使用指针会比使用字符串数组更加灵活:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
//char arr[] = "ABC";
//arr = "EDG"; //此法是不行的,arr其实是一个地址,必须这么干:strcpy(arr,"EDG");
//但是指针可以修改
char *p = "ABC";
p = "EDG";
printf("%s\n\n", p);
return 0;
}指针数组 相对于 标准的数组, 更灵活, 而且存放的空间会更小:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int data[] = {22,33,44,55,66};
int *p = data;
// int *p = &data[0]; 这样写也行, 因为数组中对一个数据的地址就是数组的地址;
int i;
for( i = 0; i < 5; i++ ) {
printf("i = %d ==> %d\n", i, data[i]);
printf("i = %d ==> %d\n", i, *(p+i));
}
return 0;
}如果是标准的数组, 需要给一个固定的长度, 但是使用指针数组的话, 并不会出现多余的数据, 图示:

调用函数的时候, 如果直接把结构体作为参数, 其实传递的时候结构体的副本,( 这个和js有点区别, js中对象就是是指针) 如果在函数中修改结构体, 要注意必须传递指针, 数组传递的也是副本, (除非你传递指针或者引用), 这个要注意:
#include <stdio.h>
struct student{
char name[10];
int age;
};
void showAge(struct student *s) {
printf("%d\n",s->age);
}
int main() {
struct student stu = {"abc", 10};
printf("%s\n", stu.name);
showAge(&stu);
return 0;
}以上的代码中, 我们定义了stu这个结构体, 但是 使用了比较多的的代码:
student struct stu
通过使用typedef, 可以进行简化:
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct {
char name[10];
int age;
} student;
void showAge(student *s) {
printf("%d\n",s->age);
}
int main() {
student stu = {"abc", 10};
printf("%s\n", stu.name);
showAge(&stu);
return 0;
}文件读取操作的代码, 创建一个文件对象, 然后读区copy.cpp文件,通过putchar输出到控制台:
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
FILE *f;
int c;
f = fopen("copy.cpp","r");
if(f == NULL) {
printf("error\n");
}else{
while( (c=fgetc(f) )!=EOF ) {
//printf("%c",c);
putchar(c);
}
printf("open\n");
fclose(f);
}
return 0;
}通过描述符打开文件, 区别于fopen和FILE句柄:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <memory.h>
int main() {
int fd = -1;
char filename[] = "fileopen.cpp";
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
if( -1 == fd ) {
printf("error\n");
}else{
printf("fd is %d\n", fd);
}
int size = -1;
char buffer[80];
while(size) {
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
size = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
//printf("%s",buffer);
for(int i=0 ; i<size; i++) {
printf("%c",buffer[i]);
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}文件写入并查看:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <memory.h>
int main() {
int fd = -1;
char filename[] = "test.txt";
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
if( -1 == fd ) {
printf("error\n");
}else{
printf("fd is %d\n", fd);
}
//write
char str[] = "12345";
write(fd, str, sizeof(str));
//read
int size = -1;
char buffer[10];
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);
while(size) {
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
size = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
for(int i=0 ; i<size; i++) {
printf("%c",buffer[i]);
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}给文件的固定位置添加数据, lseek :
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int fd = -1, i;
char buf1[] = "123456";
char buf2[] = "abcdefg";
char filename[] = "hole.txt";
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR|O_CREAT, S_IRWXU);
if(fd == -1) {
printf("error\n");
return 0;
}
int size = write(fd, buf1, sizeof(buf1));
//set offset
off_t offset = lseek(fd, 32, SEEK_SET);
if( -1 == offset ) {
printf("error\n");
return 0;
}
write(fd, buf2, sizeof(buf2));
close(fd);
return 0;
}获取文件的状态 stat的结构为:
struct stat {
mode_t st_mode; //文件对应的模式,文件,目录等
ino_t st_ino; //inode节点号
dev_t st_dev; //设备号码
dev_t st_rdev; //特殊设备号码
nlink_t st_nlink; //文件的连接数
uid_t st_uid; //文件所有者
gid_t st_gid; //文件所有者对应的组
off_t st_size; //普通文件,对应的文件字节数
time_t st_atime; //文件最后被访问的时间
time_t st_mtime; //文件内容最后被修改的时间
time_t st_ctime; //文件状态改变时间
blksize_t st_blksize; //文件内容对应的块大小
blkcnt_t st_blocks; //伟建内容对应的块数量
};创建结构:
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
struct stat st;
if(-1==stat("test.txt",&st))
{
printf("get file status failure\n");
return -1;
}
printf("此文件的大小:%d\n",st.st_size);
printf("此文件的租后修改时间:%d\n",st.st_mtime);
printf("此文件的节点:%d\n",st.st_ino);
printf("此文件的保护模式:%d\n",st.st_mode);
}厦门点燃未来网络科技有限公司, 是厦门最好的微信应用, 小程序, 微信网站, 公众号开发公司
EOF
相关文章推荐
- C语言复习笔记三:三种程序结构记习题总结(1)
- c语言复习笔记(1)--从HelloWorld说起
- 2014年软考程序员-常考知识点复习笔记【第二章】
- Linux高级编程复习笔记 第二章 映射虚拟内存 mmap gcc 静态库 动态库
- effective C++ 第二章复习笔记
- 代码大全2笔记-第二章-隐喻
- 自学笔记-C语言复习2015年7月1日
- C语言复习笔记(二)
- 学习C语言和创建你自己编程语言在1000代码以内——第二章环境
- 自学笔记—C语言复习2015年6月23日
- c语言复习笔记(2)--标准库中的I/O
- c语言复习笔记——sizeof()
- c语言复习笔记--指针定义
- C语言复习笔记(三)
- 【C/C++】C语言复习笔记-17种小算法-解决实际问题
- 2011年计算机软考网络管理员复习笔记第二章
- C语言复习串讲课堂笔记
- C语言复习笔记--static 全局变量和普通全局变量
- C++ Primer复习和学习笔记 第二章 变量和基本类型
- 自学笔记-C语言复习2015年6月25日
