Spring Cloud Sleuth使用简介
2017-05-04 16:46
543 查看
spring-Cloud
Spring Cloud为开发者提供了在分布式系统(如配置管理、服务发现、断路器、智能路由、微代理、控制总线、一次性Token、全局锁、决策竞选、分布式会话和集群状态)操作的开发工具。使用SpringCloud开发者可以快速实现上述这些模式。
SpringCloud Sleuth
Distributed tracing for Spring Cloud applications, compatiblewith Zipkin, HTrace and log-based(e.g. ELK)tracing.
Spring-Cloud-Sleuth是Spring Cloud的组成部分之一,为SpringCloud应用实现了一种分布式追踪解决方案,其兼容了Zipkin,
HTrace和log-based追踪
术语(Terminology)
Span:基本工作单元,例如,在一个新建的span中发送一个RPC等同于发送一个回应请求给RPC,span通过一个64位ID唯一标识,trace以另一个64位ID表示,span还有其他数据信息,比如摘要、时间戳事件、关键值注释(tags)、span的ID、以及进度ID(通常是IP地址)
span在不断的启动和停止,同时记录了时间信息,当你创建了一个span,你必须在未来的某个时刻停止它。
Trace:一系列spans组成的一个树状结构,例如,如果你正在跑一个分布式大数据工程,你可能需要创建一个trace。
Annotation:用来及时记录一个事件的存在,一些核心annotations用来定义一个请求的开始和结束
cs - Client Sent -客户端发起一个请求,这个annotion描述了这个span的开始
sr - Server Received -服务端获得请求并准备开始处理它,如果将其sr减去cs时间戳便可得到网络延迟
ss - Server Sent -注解表明请求处理的完成(当请求返回客户端),如果ss减去sr时间戳便可得到服务端需要的处理请求时间
cr - Client Received -表明span的结束,客户端成功接收到服务端的回复,如果cr减去cs时间戳便可得到客户端从服务端获取回复的所有所需时间
将Span和Trace在一个系统中使用Zipkin注解的过程图形化:

每个颜色的注解表明一个span(总计7个spans,从A到G),如果在注解中有这样的信息:
Trace Id = X
Span Id = D
Client Sent
这就表明当前span将Trace-Id设置为X,将Span-Id设置为D,同时它还表明了ClientSent事件。
spans 的parent/child关系图形化:

目的(Purpose)
基于Zipkin的分布式追踪
总计11个spans,如果在Zipkin中查看traces将看到如下图:

但如果你选取一个特殊的trace你将看到8个spans:

在展示Span和Trace图形化的图片中有20个颜色标签,Zipkin又是如何接收10个spans的呢?
2个span A标签表明span的开始和结束,接近结束时一个单独的span发送给Zipkin
4个span B标签实际上是一个有4个注解的单独span,然而这个span是由两个分离的实例组成的,一个由
service 1发出,一个由service 2发出,因此实际上两个span实例是发送到Zipkin并在那合并
2个span C标签表明span的开始和结束,接近结束时一个单独的span发送给Zipkin
4个span D标签实际上是一个有4个注解的单独span,然而这个span是由两个分离的实例组成的,一个由
service 2发出,一个由service 3发出,因此实际上两个span实例是发送到Zipkin并在那合并
2个span E标签表明span的开始和结束,接近结束时一个单独的span发送给Zipkin
4个span F标签实际上是一个有4个注解的单独span,然而这个span是由两个分离的实例组成的,一个由
service 2发出,一个由service 4发出,因此实际上两个span实例是发送到Zipkin并在那合并
2个span G标签表明span的开始和结束,接近结束时一个单独的span发送给Zipkin
因此1个span来自A,2个span来自B,1个span来自C,2个span来自D,1个span来自E,2个span来自F,1个来自G,总计10个spans。
Zipkin中的依赖图:

Log相关
当使用trace id为2485ec27856c56f4抓取这四个应用的log时,会获得如下输出:
如果你使用log集合工具例如Kibana、Splunk等,你可以看到事件的发生信息,Kibana的例子如下:
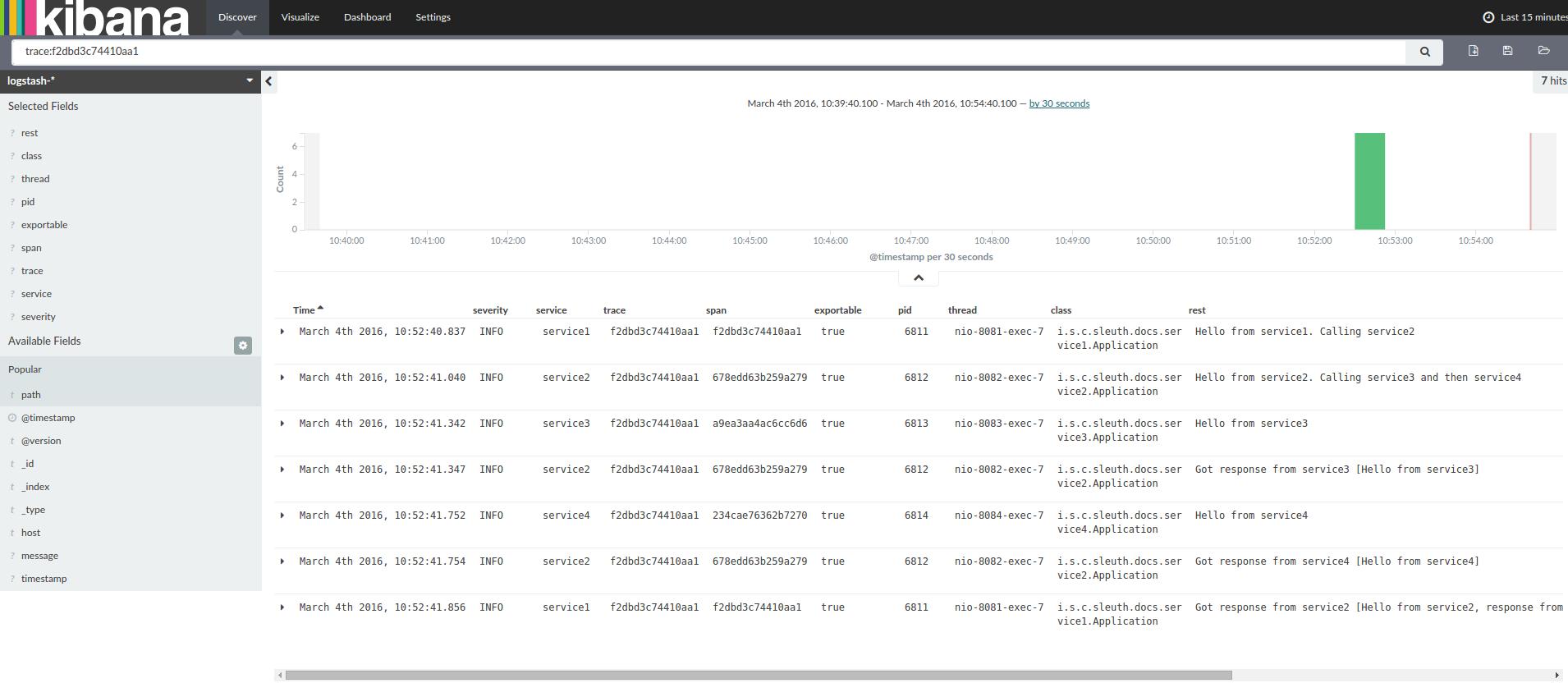
以下是Logstash的Grok模式:
JSON Logback with Logstash
为了方便获取Logstash,通常保存log在JSON文件中而不是text文件中,配置方法如下:
依赖建立
确保Logback在classpath中(ch.qos.logback:logback-core)
增加LogstashLogback编码 - version 4.6的例子:net.logstash.logback:logstash-logback-encoder:4.6
Logback建立
以下是一个Logback配置的例子:
使用JSON格式记录应用信息到build/${spring.application.name}.json文件
有两个添加注释源- console和标准log文件
与之前章节使用相同的log模式
添加进工程
仅Sleuth(log收集)
如果仅需要Spring Cloud Sleuth而不需要Zipkin集成,只需要增加spring-cloud-starter-sleuth模块到你工程中
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
通过HTTP使用基于Zipkin的Sleuth
如果你需要Sleuth和Zipkin,只需要添加spring-cloud-starter-zipkin依赖
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-zipkin
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-zipkin
通过Spring Cloud Stream使用Sleuth+Zipkin
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-sleuth-stream
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
添加一个binder(e.g.Rabbit binder)来告诉Spring Cloud Stream应该绑定什么
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-sleuth-stream
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
添加一个binder(e.g.Rabbit binder)来告诉Spring Cloud Stream应该绑定什么
Spring Cloud Sleuth Stream Zipkin Collector
启动一个Spring Cloud Sleuth Stream Zipkin收集器只需要添加spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin-stream依赖
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin-stream
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
添加一个binder(e.g.Rabbit binder)来告诉Spring Cloud Stream应该绑定什么
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin-stream
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
添加一个binder(e.g.Rabbit binder)来告诉Spring Cloud Stream应该绑定什么
之后只需要在你的主类中添加@EnableZipkinStreamServer注解
特点(Features)
添加trace和spanid到Slf4J MDC,然后就可以从一个给定的trace或span中提取所有的log,例如
注意MDC中的[appname,traceId,spanId,exportable]:
spanId - the id of a specific operation that took place
appname - the name of the application that logged the span
traceId - the id of the latency graph that contains the span
exportable - whether the log should be exported to Zipkin or not. Whenwould you like the span not to be exportable? In the case in which you want towrap some operation in a
Span and have it written to the logs only.
在通常的分布式追踪数据模型上提供一种抽象模型:traces、spans(生成一个DAG)、annotations、key-value
annotations。基于HTrace是较为宽松的,但Zipkin(Dapper)更具兼容性
Sleuth记录时间信息来帮助延迟分析,使用Sleuth可以精确找到应用中延迟的原因,Sleuth不会log太多,因此不会导致你的应用挂掉
propagatesstructural data about your call-graph in-band, and the rest out-of-band
includesopinionated instrumentation of layers such as HTTP
includessampling policy to manage volume
canreport to a Zipkin system for query and visualization
使用Spring应用装备出入口点(servletfilter、async endpoints、rest
template、scheduled actions、messagechannels、zuul
filters、feign client)
Sleuth包含默认逻辑通过http或messaging boundaries来加入一个trace,例如,http传播通过Zipkin-compatiblerequest
headers工作,这个传播逻辑定义和定制是通过SpanInjector和SpanExtractor实现提供简单的接受或放弃span
度量(metrics)
如果依赖了spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin,应用将生成并收集Zipkin-compatible traces,一般会通过HTTP将这些traces发送给一个本地Zipkin服务器(port
9411),使用spring.zipkin.baseUrl来配置服务的地址
如果依赖了spring-cloud-sleuth-stream,应用将通过Spring Cloud Stream生成并收集traces,应用自动成为tracer消息的生产者,这些消息会通过你的中间件分发(e.g.
RabbitMQ,Apache Kafka,Redis)
抽样(Samling)
在分布式追踪时,数据量可能会非常大,因此抽样就变得非常重要(通常不需要导出所有的spans以得到事件发生原貌),Spring
Cloud Sleuth有一个Sampler战略,即用户可以控制抽样算法,Samplers不会停止正在生成的span
id(相关的),但他们会阻止tags和events附加和输出,默认战略是当一个span处于活跃状态会继续trace,但新的span会一直处于不输出状态,如果所有应用都使用这个sampler,你会在logs中看到traces,但不会出现在任何远程仓库。测试状态资源都是充足的,并且你只使用logs的话他就是你需要的全部(e.g.一个ELK集合),如果输出span数据到Zipkin或Spring
Cloud Stream,有AlwaysSampler输出所有数据和PercentageBasedSampler采样spans确定的一部分。
通过创建一个bean定义就可以新建一个sampler
Instrumentation
Spring Cloud Sleuth自动装配所有Spring应用,因此你不用做任何事来让他工作,装配是使用一系列技术添加的,例如对于一个servlet
web应用我们使用一个Filter,对于SpringIntegration我们使用ChannelInterceptors。
用户可以使用span tags定制关键字,为了限制span数据量,一般一个HTTP请求只会被少数元数据标记,例如status
code、host以及URL,用户可以通过配置spring.sleuth.keys.http.headers(一系列头名称)添加request
headers。
Span生命周期
通过Trace接口的方式可以在Span上进行如下操作:
start -当打开一个span时,其名字被指定且开始时间戳被记录
close - span已经结束(span的结束时间已被记录)并且如果span是输出的,他将是Zipkin合适的收集项,span在当前线程也将被移除
continue - span的一个新实例将被创建,然而他将是正是正在运行的span的一个复制体
detach - span不会停止或关闭,他只会被从当前线程中移除
create with explicit parent -建立一个新的span并设置一个明确的parent给他
新建和关闭spans
使用Tracer接口可以手动新建spans
在例子中我们可以看到如何新建一个span实例,假设在当前线程中已经有一个span,那么新建的线程将会是这个线程的parent。
持续(Continuing)spans
有时你不想要新建一个span但你又想持续使用,这种情况的例子可能如下(当然实际依赖于使用情况):
AOP -如果在实际应用前已经有一个span新建可用,那么就不需要新建一个span
Hystrix -对于当前处理流程而言,执行Hystrix操作是最为合理的一部分,实际上只有技术实现细节的话,不必将他作为分离的部分反映在tracing中
span的持续实例等同于正在运行的:
可以使用Tracer接口延续一个span
使用明确的parent新建spans
如果你想新建一个span并且提供一个明确的parent给他,假设span的parent在一个thread中,而你想在另一个thread中新建span,Tracer接口的startSpan命令就是你需要的。
命名spans
为span命名是很重要的工作,span名称必须描述了一个操作名称,名称必须要简明(e.g.不包括标识符)。
Since there is a lot of instrumentation going on some of thespan names will be artificial like:
· controller-method-name when received by a Controller with a methodnameconrollerMethodName
· async for asynchronous operations done via wrappedCallable andRunnable
· @Scheduled annotated methods will return the simple nameof the class
Fortunately, for the asynchronous processing you can provideexplicit naming.
@SpanName注解
可以使用@SpanName注解明确命名span
在这种情况下,使用下面的方式便命名一个span为calculateTax
toString()方法
为Runnable或Callable建立分离的classes是非常少见的,一般建立这些classes的匿名实例,你不能注解这些classes除非override,如果没有@SpanName注解,我们将会检查class是否使用传统的toString()方法实现
执行这些代码将新建一个名为calculateTax的span:
定制化
使用SpanInjector和SpanExtractor你可以定制化span的新建和传播。
当前有两种built-in方法来在进程间传递tracing信息:
通过SpringIntegration
通过HTTP
span id是从Zipkin-compatible(B3)头中提取的(不论Message或HTTP头),以此来开始或加入一个存在的trace,trace信息被注入到输出请求中,这样后面的步骤就可以提取他。
Spring Integration
对于Spring Integration,存在beans负责span从Message的创建和使用tracing信息装配MessageBuilder。
用户可以使用自己的实现来override他,或者添加@Primary注解到你的bean定义
HTTP
对于HTTP,存在beans负责span从HttpServletRequest的创建和使用tracing信息装配HttpServletResponse。
用户可以使用自己的实现来override他,或者添加@Primary注解到你的bean定义
例子
对比传统的兼容Zipkin,tracingHTTP头名有以下格式
traceid - correlationId
spanid - mySpanId
以下是一个SpanExtractor的例子
以下SpanInjector将被建立
并且你可以这样注册他们
SpringData as Messages
可以通过Spring Cloud Stream来积累和发送span数据,配置时需要包含spring-cloud-sleuth-streamjar为依赖且增加一个Channel
Binder实现方式(e.g. spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit对应RabbitMQ或spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafka对应Kafka),使用payload格式Spans将自动把你的app变为一个信息生产者
Zipkin Consumer
有一种特殊而又便利的注解方式,即为span数据建立一个信息消费者,并将他推到一个Zipkin SpanStrore中
这种应用将通过Spring Cloud Stream Binder监听不论何种方式传输的span数据(e.g.包括spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit对应RabbitMQ,和对应Redis和Kafka的类似starter存在),如果添加以下UI依赖
你将启动一个Zipkin server应用,他将通过端口9411访问UI和api。
默认SpanStore是in-memory的(适合于demos且启动迅速),你可以添加MySQL和spring-boot-starter-jdbc到你的系统环境并通过配置激活JDBC
SpanStore。例如:
定制消费者
使用spring-cloud-sleuth-stream且绑定SleuthSink可以很方便的实现定制消费者。例子:
度量(Metrics)
当前Spring Cloud Sleuth记录非常简单的spans metrics,使用Spring
Boot的metrics support来计算接收丢弃的span数量,当有span发送给Zipkin时,接收span的数量就会增加,如果有错误发生,丢弃span数量就会增加。
Integrations
Runable和Callable
如果你要将你的逻辑包裹在Runable或Callable中,足够将这些classes放到他们的Sleuth代表中。
Runnable的例子:
Callable的例子:
这种方式你可以保证一个新的Span在每次执行时新建和关闭。
Hystrix
传统并发策略
我们以将所有的Callable实例置入到他们的Sleuth代表-TraceCallable的方式来记录一个传统的HystrixConcurrencyStrategy,策略的打开或延续一个span取决于在Hystrix操作被调用前tracing是否在工作,为了使传统Hystrix并发策略无效可以设置spring.sleuth.hystrix.strategy.enable为false。
手动操作设置
假设你有以下HystrixCommand:
为了传递tracing信息你必须将同样的逻辑置于HystrixCommand的Sleuth版本中,也就是TraceCommand:
RxJava
我们记录了一个典型的RxJavaSchedulersHook,他将所有Action0实例置入到他们的Sleuth代表-TraceAction中,hook打开或延续一个span取决于Action被安排前tracing是否已经在工作,为了使RxJavaSchedulersHook无效可设置spring.sleuth.rxjava.schedulers.hook.enabled为false。
You can define a list of regular expressions for thread names,for which you don’twant a Span to be created. Just provide a comma separated list
of regularexpressions in the spring.sleuth.rxjava.schedulers.ignoredthreads property.
HTTP integration
将spring.sleuth.web.enabled配置值设置为false可以使这章中的特征方法无效
HTTP Filter
通过TraceFilter,所有抽样输入的请求都会归结到span的创建,span的名称为"http+请求发送的路径",例如,如果请求发送到/foo/bar,名称即为http:/foo/bar,你可以配置通过spring.sleuth.web.skipPattern,那些URIs将被过滤掉,如果你在环境中添加了ManagementServerProperties,你的contextPath值会附加到过滤配置上。
HandlerIntercepter
由于需要span名称的精确,我们使用一个TraceHandlerInterceptor来置入一个存在的HandlerInterceptor或直接添加到存在的HandlerInterceptors列表中,TraceHandlerInterceptor添加一个特殊的请求属性给HttpServletRequest,如果TraceFilter没有看到属性,他会建立一个"fallback"span,这是一个建立在服务端的附加的span,此时trace在UI中可以正确的显示。
HTTP client integration
同步RestTemplate
我们注入一个RestTemplate拦截器来保证所有的tracing信息被发送到请求端,每当一个请求被生成,一个新的span将被创建,他会在接收应答后关闭,为了限制同步RestTemplate只需要设置spring.sleuth.web.client.enabled为false。
异步RestTemplate
传统的instrumentation是通过发送接收请求来建立关闭span的,你可以通过注册你的bean来定制ClientHttpRequestFactory和AsyncClientHttpRequestFactory,记得使用tracing
compatible实现方式(e.g.不要忘记将ThreadPoolTaskScheduler置入一个TraceAsyncListenableTaskExecutor),传统请求工厂例子如下:
通过设置spring.sleuth.web.async.client.enabled为false可以限制AsyncRestTemplate,使默认的TraceAsyncClientHttpRequestFactoryWrapper无效可以设置spring.sleuth.web.async.client.factory.enabled为false,如果你不想创建AsyncRestClient,设置spring.sleuth.web.async.client.template.enabled为false。
Feign
默认Spring Cloud Sleuth通过TraceFeignClientAutoConfiguration提供feign的集成,你可以设置spring.sleuth.feign.enabled为false来使他无效,如果这样设置那么所有feign相关的装配都无法发生。
通过FeignBeanPostProcessor feign装配的部分结束,可以设置spring.sleuth.feign.processor.enabled为false来是他无效化,如果你这样设置,Spring
Cloud Sleuth将不会装配任何你的传统feign组件,所有默认装配保持原有状态。
异步通信
@Async注解方法
在Spring Cloud Sleuth中,我们装配异步关联组件以使得tracing信息可以在threads间传递,你可以通过设置spring.sleuth.async.enabled值为false来使其无效化。
如果你使用@Async来注解你的方法,我们将自动建立一个新的span:
span名称将是注解方法名
span将被标注为方法类名和方法名
@Scheduled注解方法
在Spring Cloud Sleuth中,我们装配scheduled执行方法以使得tracing信息可以在threads间传递,你可以通过设置spring.sleuth.scheduled.enabled值为false来使其无效化。
如果你使用@Scheduled来注解你的方法,我们将自建立一个新的span:
span名称将是注解方法名
span将被标注为方法类名和方法名
如果在一些@Scheduled注解类中你想跳过span新建过程,可以设置spring.sleuth.scheduled.skipPattern为一个指定的表达式,这将匹配@Scheduled注解类的完整描述名称。
Executor, ExecutorServiceand ScheduledExecutorService
我们提供了LazyTraceExecutor,TraceableExecutorService和TraceableScheduledExecutorService。每当一个新的任务被提交、调用或scheduled时,这些实现会建立新的spans。
以下是当使用CompletableFuture时如何用TraceableExecutorService传递tracing信息:
消息传递
Spring Cloud Sleuth集成了Spring Integration。他会建立span来发布或订阅事件,设置spring.sleuth.integration.enabled为false可以使Spring
Integration无效。
Spring Cloud Sleuth到1.0.4版本前都是使用消息传递时发送无效tracing头,这些头和在HTTP(包含
- )发送的名称时一样的,为了在1.0.4版本的向后兼容目的,我们开始发送所有有效和无效的头,请更新到1.0.4,因为在Spring
Cloud Sleuth 1.1中我们将会移除对分离头的支持。
从1.0.4后可以明确设置spring.sleuth.integration.patterns模式来提供你想要包含的tracing信道名称,默认所有的信道已被包含在内。
Zuul
我们注册Zuul过滤器来传播tracing信息(请求头使用tracing数据填满),可以设置spring.sleuth.zuul.enabled为false来关闭Zuul服务。
Moreinformation
https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-sleuth/#_example
参考http://blog.csdn.net/u010257992/article/details/52474639
Spring Cloud为开发者提供了在分布式系统(如配置管理、服务发现、断路器、智能路由、微代理、控制总线、一次性Token、全局锁、决策竞选、分布式会话和集群状态)操作的开发工具。使用SpringCloud开发者可以快速实现上述这些模式。
SpringCloud Sleuth
Distributed tracing for Spring Cloud applications, compatiblewith Zipkin, HTrace and log-based(e.g. ELK)tracing.
Spring-Cloud-Sleuth是Spring Cloud的组成部分之一,为SpringCloud应用实现了一种分布式追踪解决方案,其兼容了Zipkin,
HTrace和log-based追踪
术语(Terminology)
Span:基本工作单元,例如,在一个新建的span中发送一个RPC等同于发送一个回应请求给RPC,span通过一个64位ID唯一标识,trace以另一个64位ID表示,span还有其他数据信息,比如摘要、时间戳事件、关键值注释(tags)、span的ID、以及进度ID(通常是IP地址)
span在不断的启动和停止,同时记录了时间信息,当你创建了一个span,你必须在未来的某个时刻停止它。
Trace:一系列spans组成的一个树状结构,例如,如果你正在跑一个分布式大数据工程,你可能需要创建一个trace。
Annotation:用来及时记录一个事件的存在,一些核心annotations用来定义一个请求的开始和结束
cs - Client Sent -客户端发起一个请求,这个annotion描述了这个span的开始
sr - Server Received -服务端获得请求并准备开始处理它,如果将其sr减去cs时间戳便可得到网络延迟
ss - Server Sent -注解表明请求处理的完成(当请求返回客户端),如果ss减去sr时间戳便可得到服务端需要的处理请求时间
cr - Client Received -表明span的结束,客户端成功接收到服务端的回复,如果cr减去cs时间戳便可得到客户端从服务端获取回复的所有所需时间
将Span和Trace在一个系统中使用Zipkin注解的过程图形化:

每个颜色的注解表明一个span(总计7个spans,从A到G),如果在注解中有这样的信息:
Trace Id = X
Span Id = D
Client Sent
这就表明当前span将Trace-Id设置为X,将Span-Id设置为D,同时它还表明了ClientSent事件。
spans 的parent/child关系图形化:

目的(Purpose)
基于Zipkin的分布式追踪
总计11个spans,如果在Zipkin中查看traces将看到如下图:

但如果你选取一个特殊的trace你将看到8个spans:

| 当选取一个特殊trace时你会看到合并的spans,这意味着如果有两个spans使用客户端接收发送/服务端接收发送注解发送至Zipkin时,他们将表现为一个单独的span |
2个span A标签表明span的开始和结束,接近结束时一个单独的span发送给Zipkin
4个span B标签实际上是一个有4个注解的单独span,然而这个span是由两个分离的实例组成的,一个由
service 1发出,一个由service 2发出,因此实际上两个span实例是发送到Zipkin并在那合并
2个span C标签表明span的开始和结束,接近结束时一个单独的span发送给Zipkin
4个span D标签实际上是一个有4个注解的单独span,然而这个span是由两个分离的实例组成的,一个由
service 2发出,一个由service 3发出,因此实际上两个span实例是发送到Zipkin并在那合并
2个span E标签表明span的开始和结束,接近结束时一个单独的span发送给Zipkin
4个span F标签实际上是一个有4个注解的单独span,然而这个span是由两个分离的实例组成的,一个由
service 2发出,一个由service 4发出,因此实际上两个span实例是发送到Zipkin并在那合并
2个span G标签表明span的开始和结束,接近结束时一个单独的span发送给Zipkin
因此1个span来自A,2个span来自B,1个span来自C,2个span来自D,1个span来自E,2个span来自F,1个来自G,总计10个spans。
Zipkin中的依赖图:

Log相关
当使用trace id为2485ec27856c56f4抓取这四个应用的log时,会获得如下输出:
| service1.log:2016-02-26 11:15:47.561 INFO [service1,2485ec27856c56f4,2485ec27856c56f4,true] 68058 --- [nio-8081-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service1.Application : Hello from service1. Calling service2 service2.log:2016-02-26 11:15:47.710 INFO [service2,2485ec27856c56f4,9aa10ee6fbde75fa,true] 68059 --- [nio-8082-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service2.Application : Hello from service2. Calling service3 and then service4 service3.log:2016-02-26 11:15:47.895 INFO [service3,2485ec27856c56f4,1210be13194bfe5,true] 68060 --- [nio-8083-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service3.Application : Hello from service3 service2.log:2016-02-26 11:15:47.924 INFO [service2,2485ec27856c56f4,9aa10ee6fbde75fa,true] 68059 --- [nio-8082-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service2.Application : Got response from service3 [Hello from service3] service4.log:2016-02-26 11:15:48.134 INFO [service4,2485ec27856c56f4,1b1845262ffba49d,true] 68061 --- [nio-8084-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service4.Application : Hello from service4 service2.log:2016-02-26 11:15:48.156 INFO [service2,2485ec27856c56f4,9aa10ee6fbde75fa,true] 68059 --- [nio-8082-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service2.Application : Got response from service4 [Hello from service4] service1.log:2016-02-26 11:15:48.182 INFO [service1,2485ec27856c56f4,2485ec27856c56f4,true] 68058 --- [nio-8081-exec-1] i.s.c.sleuth.docs.service1.Application : Got response from service2 [Hello from service2, response from service3 [Hello from service3] and from service4 [Hello from service4]] |

以下是Logstash的Grok模式:
| filter { # pattern matching logback pattern grok { match => { "message" => "%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:timestamp}\s+%{LOGLEVEL:severity}\s+ \s+%{DATA:pid}---\s+ \s+%{DATA:class}\s+:\s+%{GREEDYDATA:rest}" } } } |
JSON Logback with Logstash
为了方便获取Logstash,通常保存log在JSON文件中而不是text文件中,配置方法如下:
依赖建立
确保Logback在classpath中(ch.qos.logback:logback-core)
增加LogstashLogback编码 - version 4.6的例子:net.logstash.logback:logstash-logback-encoder:4.6
Logback建立
以下是一个Logback配置的例子:
使用JSON格式记录应用信息到build/${spring.application.name}.json文件
有两个添加注释源- console和标准log文件
与之前章节使用相同的log模式
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <configuration> <include resource="org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/defaults.xml"/> <springProperty scope="context" name="springAppName" source="spring.application.name"/> <!-- Example for logging into the build folder of your project --> <property name="LOG_FILE" value="${BUILD_FOLDER:-build}/${springAppName}"/> <property name="CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN" value="%clr(%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}){faint} %clr(${LOG_LEVEL_PATTERN:-%5p}) %clr([${springAppName:-},%X{X-B3-TraceId:-},%X{X-B3-SpanId:-},%X{X-Span-Export:-}]){yellow} %clr(${PID:- }){magenta} %clr(---){faint} %clr([%15.15t]){faint} %clr(%-40.40logger{39}){cyan} %clr(:){faint} %m%n${LOG_EXCEPTION_CONVERSION_WORD:-%wEx}"/> <!-- Appender to log to console --> <appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter"> <!-- Minimum logging level to be presented in the console logs--> <level>INFO</level> </filter> <encoder> <pattern>${CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN}</pattern> <charset>utf8</charset> </encoder> </appender> <!-- Appender to log to file --> <appender name="flatfile" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <file>${LOG_FILE}</file> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <fileNamePattern>${LOG_FILE}.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.gz</fileNamePattern> <maxHistory>7</maxHistory> </rollingPolicy> <encoder> <pattern>${CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN}</pattern> <charset>utf8</charset> </encoder> </appender> <!-- Appender to log to file in a JSON format --> <appender name="logstash" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <file>${LOG_FILE}.json</file> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <fileNamePattern>${LOG_FILE}.json.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.gz</fileNamePattern> <maxHistory>7</maxHistory> </rollingPolicy> <encoder class="net.logstash.logback.encoder.LoggingEventCompositeJsonEncoder"> <providers> <timestamp> <timeZone>UTC</timeZone> </timestamp> <pattern> <pattern> { "severity": "%level", "service": "${springAppName:-}", "trace": "%X{X-B3-TraceId:-}", "span": "%X{X-B3-SpanId:-}", "exportable": "%X{X-Span-Export:-}", "pid": "${PID:-}", "thread": "%thread", "class": "%logger{40}", "rest": "%message" } </pattern> </pattern> </providers> </encoder> </appender> <root level="INFO"> <!--<appender-ref ref="console"/>--> <appender-ref ref="logstash"/> <!--<appender-ref ref="flatfile"/>--> </root> </configuration> |
添加进工程
仅Sleuth(log收集)
如果仅需要Spring Cloud Sleuth而不需要Zipkin集成,只需要增加spring-cloud-starter-sleuth模块到你工程中
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
| <dependencyManagement> (1) <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Brixton.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependency> (2) <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId> </dependency> |
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
| dependencyManagement { (1) imports { mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:Brixton.RELEASE" } } dependencies { (2) compile "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-sleuth" } |
通过HTTP使用基于Zipkin的Sleuth
如果你需要Sleuth和Zipkin,只需要添加spring-cloud-starter-zipkin依赖
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-zipkin
| <dependencyManagement> (1) <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Brixton.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependency> (2) <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId> </dependency> |
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-zipkin
| dependencyManagement { (1) imports { mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:Brixton.RELEASE" } } dependencies { (2) compile "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-zipkin" } |
通过Spring Cloud Stream使用Sleuth+Zipkin
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-sleuth-stream
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
添加一个binder(e.g.Rabbit binder)来告诉Spring Cloud Stream应该绑定什么
| <dependencyManagement> (1) <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Brixton.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependency> (2) <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-sleuth-stream</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> (3) <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- EXAMPLE FOR RABBIT BINDING --> <dependency> (4) <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit</artifactId> </dependency> |
添加依赖到spring-cloud-sleuth-stream
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
添加一个binder(e.g.Rabbit binder)来告诉Spring Cloud Stream应该绑定什么
| dependencyManagement { (1) imports { mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:Brixton.RELEASE" } } dependencies { compile "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-sleuth-stream" (2) compile "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-sleuth" (3) // Example for Rabbit binding compile "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit" (4) } |
Spring Cloud Sleuth Stream Zipkin Collector
启动一个Spring Cloud Sleuth Stream Zipkin收集器只需要添加spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin-stream依赖
为了不手动添加版本号,更好的方式是通过Spring BOM添加dependencymanagement
添加依赖到spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin-stream
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
添加一个binder(e.g.Rabbit binder)来告诉Spring Cloud Stream应该绑定什么
| <dependencyManagement> (1) <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Brixton.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependency> (2) <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin-stream</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> (3) <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- EXAMPLE FOR RABBIT BINDING --> <dependency> (4) <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit</artifactId> </dependency> |
添加依赖到spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin-stream
添加依赖到spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
添加一个binder(e.g.Rabbit binder)来告诉Spring Cloud Stream应该绑定什么
| dependencyManagement { (1) imports { mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:Brixton.RELEASE" } } dependencies { compile "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin-stream" (2) compile "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-sleuth" (3) // Example for Rabbit binding compile "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit" (4) } |
| package example; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.sleuth.zipkin.stream.EnableZipkinStreamServer; @SpringBootApplication @EnableZipkinStreamServer public class ZipkinStreamServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { SpringApplication.run(ZipkinStreamServerApplication.class, args); } } |
特点(Features)
添加trace和spanid到Slf4J MDC,然后就可以从一个给定的trace或span中提取所有的log,例如
| 2016-02-02 15:30:57.902 INFO [bar,6bfd228dc00d216b,6bfd228dc00d216b,false] 23030 --- [nio-8081-exec-3] ... 2016-02-02 15:30:58.372 ERROR [bar,6bfd228dc00d216b,6bfd228dc00d216b,false] 23030 --- [nio-8081-exec-3] ... 2016-02-02 15:31:01.936 INFO [bar,46ab0d418373cbc9,46ab0d418373cbc9,false] 23030 --- [nio-8081-exec-4] ... |
spanId - the id of a specific operation that took place
appname - the name of the application that logged the span
traceId - the id of the latency graph that contains the span
exportable - whether the log should be exported to Zipkin or not. Whenwould you like the span not to be exportable? In the case in which you want towrap some operation in a
Span and have it written to the logs only.
在通常的分布式追踪数据模型上提供一种抽象模型:traces、spans(生成一个DAG)、annotations、key-value
annotations。基于HTrace是较为宽松的,但Zipkin(Dapper)更具兼容性
Sleuth记录时间信息来帮助延迟分析,使用Sleuth可以精确找到应用中延迟的原因,Sleuth不会log太多,因此不会导致你的应用挂掉
propagatesstructural data about your call-graph in-band, and the rest out-of-band
includesopinionated instrumentation of layers such as HTTP
includessampling policy to manage volume
canreport to a Zipkin system for query and visualization
使用Spring应用装备出入口点(servletfilter、async endpoints、rest
template、scheduled actions、messagechannels、zuul
filters、feign client)
Sleuth包含默认逻辑通过http或messaging boundaries来加入一个trace,例如,http传播通过Zipkin-compatiblerequest
headers工作,这个传播逻辑定义和定制是通过SpanInjector和SpanExtractor实现提供简单的接受或放弃span
度量(metrics)
如果依赖了spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin,应用将生成并收集Zipkin-compatible traces,一般会通过HTTP将这些traces发送给一个本地Zipkin服务器(port
9411),使用spring.zipkin.baseUrl来配置服务的地址
如果依赖了spring-cloud-sleuth-stream,应用将通过Spring Cloud Stream生成并收集traces,应用自动成为tracer消息的生产者,这些消息会通过你的中间件分发(e.g.
RabbitMQ,Apache Kafka,Redis)
| 如果使用Zipkin或Stream,使用spring.sleuth.sampler.percentage配置输出spans的百分比(默认10%),不然你可能会认为Sleuth没有工作,因为他省略了一些spans |
| SLF4J MDC一直处于工作状态,logback用户可以在logs中立刻看到trace和span id,其他logging系统不得不配置他们自己的模式以得到相同的结果,默认logging.pattern.level设置为%clr(%5p) %clr([${spring.application.name:},%X{X-B3-TraceId:-},%X{X-B3-SpanId:-},%X{X-Span-Export:-}]){yellow}(对于logback用户,这是一种Spring Boot特征),这意味着如果你没有使用SLF4J这个模式将不会自动适用 |
在分布式追踪时,数据量可能会非常大,因此抽样就变得非常重要(通常不需要导出所有的spans以得到事件发生原貌),Spring
Cloud Sleuth有一个Sampler战略,即用户可以控制抽样算法,Samplers不会停止正在生成的span
id(相关的),但他们会阻止tags和events附加和输出,默认战略是当一个span处于活跃状态会继续trace,但新的span会一直处于不输出状态,如果所有应用都使用这个sampler,你会在logs中看到traces,但不会出现在任何远程仓库。测试状态资源都是充足的,并且你只使用logs的话他就是你需要的全部(e.g.一个ELK集合),如果输出span数据到Zipkin或Spring
Cloud Stream,有AlwaysSampler输出所有数据和PercentageBasedSampler采样spans确定的一部分。
| 如果使用spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin或spring-cloud-sleuth-stream,PercentageBasedSampler是默认的,你可以使用spring.sleuth.sampler.percentage配置输出 |
| @Bean public Sampler defaultSampler() { return new AlwaysSampler(); } |
Instrumentation
Spring Cloud Sleuth自动装配所有Spring应用,因此你不用做任何事来让他工作,装配是使用一系列技术添加的,例如对于一个servlet
web应用我们使用一个Filter,对于SpringIntegration我们使用ChannelInterceptors。
用户可以使用span tags定制关键字,为了限制span数据量,一般一个HTTP请求只会被少数元数据标记,例如status
code、host以及URL,用户可以通过配置spring.sleuth.keys.http.headers(一系列头名称)添加request
headers。
| tags仅在Sampler允许其被收集和输出时工作(默认情况其不工作,因此不会有在不配置的情况下收集过多数据的意外危险出现) |
Span生命周期
通过Trace接口的方式可以在Span上进行如下操作:
start -当打开一个span时,其名字被指定且开始时间戳被记录
close - span已经结束(span的结束时间已被记录)并且如果span是输出的,他将是Zipkin合适的收集项,span在当前线程也将被移除
continue - span的一个新实例将被创建,然而他将是正是正在运行的span的一个复制体
detach - span不会停止或关闭,他只会被从当前线程中移除
create with explicit parent -建立一个新的span并设置一个明确的parent给他
新建和关闭spans
使用Tracer接口可以手动新建spans
| // Start a span. If there was a span present in this thread it will become // the `newSpan`'s parent. Span newSpan = this.tracer.createSpan("calculateTax"); try { // ... // You can tag a span this.tracer.addTag("taxValue", taxValue); // ... // You can log an event on a span newSpan.logEvent("taxCalculated"); } finally { // Once done remember to close the span. This will allow collecting // the span to send it to Zipkin this.tracer.close(newSpan); } |
| 新建span后要记得清除他!如果你想要将一个span发送给Zipkin,不要忘记关闭他。 |
有时你不想要新建一个span但你又想持续使用,这种情况的例子可能如下(当然实际依赖于使用情况):
AOP -如果在实际应用前已经有一个span新建可用,那么就不需要新建一个span
Hystrix -对于当前处理流程而言,执行Hystrix操作是最为合理的一部分,实际上只有技术实现细节的话,不必将他作为分离的部分反映在tracing中
span的持续实例等同于正在运行的:
| Span continuedSpan = this.tracer.continueSpan(spanToContinue); assertThat(continuedSpan).isEqualTo(spanToContinue); |
| // let's assume that we're in a thread Y and we've received // the `initialSpan` from thread X Span continuedSpan = this.tracer.continueSpan(initialSpan); try { // ... // You can tag a span this.tracer.addTag("taxValue", taxValue); // ... // You can log an event on a span continuedSpan.logEvent("taxCalculated"); } finally { // Once done remember to detach the span. That way you'll // safely remove it from the current thread without closing it this.tracer.detach(continuedSpan); } |
| 新建一个span后记得清除他!如果有些工作在一个线程(e.g. thread X)中已经结束并且他在等待另外的线程(e.g. Y,Z)结束时,不要忘记分离span,在线程Y,Z中的spans在他们工作结束时也应被分离,结果收集完成时thread X中的span应该被关闭 |
使用明确的parent新建spans
如果你想新建一个span并且提供一个明确的parent给他,假设span的parent在一个thread中,而你想在另一个thread中新建span,Tracer接口的startSpan命令就是你需要的。
| // let's assume that we're in a thread Y and we've received // the `initialSpan` from thread X. `initialSpan` will be the parent // of the `newSpan` Span newSpan = this.tracer.createSpan("calculateCommission", initialSpan); try { // ... // You can tag a span this.tracer.addTag("commissionValue", commissionValue); // ... // You can log an event on a span newSpan.logEvent("commissionCalculated"); } finally { // Once done remember to close the span. This will allow collecting // the span to send it to Zipkin. The tags and events set on the // newSpan will not be present on the parent this.tracer.close(newSpan); } |
| 记得在新建这样的span后关闭他,否则你在你的log中看到大量的相关warning,更糟糕的是你的span不会正常关闭,这样的话就无法被Zipkin收集 |
命名spans
为span命名是很重要的工作,span名称必须描述了一个操作名称,名称必须要简明(e.g.不包括标识符)。
Since there is a lot of instrumentation going on some of thespan names will be artificial like:
· controller-method-name when received by a Controller with a methodnameconrollerMethodName
· async for asynchronous operations done via wrappedCallable andRunnable
· @Scheduled annotated methods will return the simple nameof the class
Fortunately, for the asynchronous processing you can provideexplicit naming.
@SpanName注解
可以使用@SpanName注解明确命名span
| @SpanName("calculateTax") class TaxCountingRunnable implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { // perform logic } } |
| Runnable runnable = new TraceRunnable(tracer, spanNamer, new TaxCountingRunnable()); Future<?> future = executorService.submit(runnable); // ... some additional logic ... future.get(); |
toString()方法
为Runnable或Callable建立分离的classes是非常少见的,一般建立这些classes的匿名实例,你不能注解这些classes除非override,如果没有@SpanName注解,我们将会检查class是否使用传统的toString()方法实现
执行这些代码将新建一个名为calculateTax的span:
| Runnable runnable = new TraceRunnable(tracer, spanNamer, new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // perform logic } @Override public String toString() { return "calculateTax"; } }); Future<?> future = executorService.submit(runnable); // ... some additional logic ... future.get(); |
定制化
使用SpanInjector和SpanExtractor你可以定制化span的新建和传播。
当前有两种built-in方法来在进程间传递tracing信息:
通过SpringIntegration
通过HTTP
span id是从Zipkin-compatible(B3)头中提取的(不论Message或HTTP头),以此来开始或加入一个存在的trace,trace信息被注入到输出请求中,这样后面的步骤就可以提取他。
Spring Integration
对于Spring Integration,存在beans负责span从Message的创建和使用tracing信息装配MessageBuilder。
| @Bean public SpanExtractor<Message> messagingSpanExtractor() { ... } @Bean public SpanInjector<MessageBuilder> messagingSpanInjector() { ... } |
HTTP
对于HTTP,存在beans负责span从HttpServletRequest的创建和使用tracing信息装配HttpServletResponse。
| @Bean public SpanExtractor<HttpServletRequest> httpServletRequestSpanExtractor() { ... } @Bean public SpanInjector<HttpServletResponse> httpServletResponseSpanInjector() { ... } |
例子
对比传统的兼容Zipkin,tracingHTTP头名有以下格式
traceid - correlationId
spanid - mySpanId
以下是一个SpanExtractor的例子
| static class CustomHttpServletRequestSpanExtractor implements SpanExtractor<HttpServletRequest> { @Override public Span joinTrace(HttpServletRequest carrier) { long traceId = Span.hexToId(carrier.getHeader("correlationId")); long spanId = Span.hexToId(carrier.getHeader("mySpanId")); // extract all necessary headers Span.SpanBuilder builder = Span.builder().traceId(traceId).spanId(spanId); // build rest of the Span return builder.build(); } } |
| static class CustomHttpServletResponseSpanInjector implements SpanInjector<HttpServletResponse> { @Override public void inject(Span span, HttpServletResponse carrier) { carrier.addHeader("correlationId", Span.idToHex(span.getTraceId())); carrier.addHeader("mySpanId", Span.idToHex(span.getSpanId())); // inject the rest of Span values to the header } } |
| @Bean @Primary SpanExtractor<HttpServletRequest> customHttpServletRequestSpanExtractor() { return new CustomHttpServletRequestSpanExtractor(); } @Bean @Primary SpanInjector<HttpServletResponse> customHttpServletResponseSpanInjector() { return new CustomHttpServletResponseSpanInjector(); } |
SpringData as Messages
可以通过Spring Cloud Stream来积累和发送span数据,配置时需要包含spring-cloud-sleuth-streamjar为依赖且增加一个Channel
Binder实现方式(e.g. spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit对应RabbitMQ或spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafka对应Kafka),使用payload格式Spans将自动把你的app变为一个信息生产者
Zipkin Consumer
有一种特殊而又便利的注解方式,即为span数据建立一个信息消费者,并将他推到一个Zipkin SpanStrore中
| @SpringBootApplication @EnableZipkinStreamServer public class Consumer { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Consumer.class, args); } } |
| <groupId>io.zipkin.Java</groupId> <artifactId>zipkin-autoconfigure-ui</artifactId> |
默认SpanStore是in-memory的(适合于demos且启动迅速),你可以添加MySQL和spring-boot-starter-jdbc到你的系统环境并通过配置激活JDBC
SpanStore。例如:
| spring: rabbitmq: host: ${RABBIT_HOST:localhost} datasource: schema: classpath:/mysql.sql url: jdbc:mysql://${MYSQL_HOST:localhost}/test username: root password: root # Switch this on to create the schema on startup: initialize: true continueOnError: true sleuth: enabled: false zipkin: storage: type: mysql |
| @EnableZipkinStreamServer也使用@EnableZipkinServer注解,因此进程也会显示标准Zipkin服务终端以通过HTTP收集span,且可以通过Zipkin Web UI查询 |
定制消费者
使用spring-cloud-sleuth-stream且绑定SleuthSink可以很方便的实现定制消费者。例子:
| @EnableBinding(SleuthSink.class) @SpringBootApplication(exclude = SleuthStreamAutoConfiguration.class) @MessageEndpoint public class Consumer { @ServiceActivator(inputChannel = SleuthSink.INPUT) public void sink(Spans input) throws Exception { // ... process spans } } |
| 上述的消费者应用明确排除SleuthStreamAutoConfiguration,因此他不会给自己发消息,但这是可选的(你可能想要trace请求到消费者app) |
度量(Metrics)
当前Spring Cloud Sleuth记录非常简单的spans metrics,使用Spring
Boot的metrics support来计算接收丢弃的span数量,当有span发送给Zipkin时,接收span的数量就会增加,如果有错误发生,丢弃span数量就会增加。
Integrations
Runable和Callable
如果你要将你的逻辑包裹在Runable或Callable中,足够将这些classes放到他们的Sleuth代表中。
Runnable的例子:
| Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // do some work } @Override public String toString() { return "spanNameFromToStringMethod"; } }; // Manual `TraceRunnable` creation with explicit "calculateTax" Span name Runnable traceRunnable = new TraceRunnable(tracer, spanNamer, runnable, "calculateTax"); // Wrapping `Runnable` with `Tracer`. The Span name will be taken either from the // `@SpanName` annotation or from `toString` method Runnable traceRunnableFromTracer = tracer.wrap(runnable); |
| Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { return someLogic(); } @Override public String toString() { return "spanNameFromToStringMethod"; } }; // Manual `TraceCallable` creation with explicit "calculateTax" Span name Callable<String> traceCallable = new TraceCallable<>(tracer, spanNamer, callable, "calculateTax"); // Wrapping `Callable` with `Tracer`. The Span name will be taken either from the // `@SpanName` annotation or from `toString` method Callable<String> traceCallableFromTracer = tracer.wrap(callable); |
Hystrix
传统并发策略
我们以将所有的Callable实例置入到他们的Sleuth代表-TraceCallable的方式来记录一个传统的HystrixConcurrencyStrategy,策略的打开或延续一个span取决于在Hystrix操作被调用前tracing是否在工作,为了使传统Hystrix并发策略无效可以设置spring.sleuth.hystrix.strategy.enable为false。
手动操作设置
假设你有以下HystrixCommand:
| HystrixCommand<String> hystrixCommand = new HystrixCommand<String>(setter) { @Override protected String run() throws Exception { return someLogic(); } }; |
| TraceCommand<String> traceCommand = new TraceCommand<String>(tracer, traceKeys, setter) { @Override public String doRun() throws Exception { return someLogic(); } }; |
我们记录了一个典型的RxJavaSchedulersHook,他将所有Action0实例置入到他们的Sleuth代表-TraceAction中,hook打开或延续一个span取决于Action被安排前tracing是否已经在工作,为了使RxJavaSchedulersHook无效可设置spring.sleuth.rxjava.schedulers.hook.enabled为false。
You can define a list of regular expressions for thread names,for which you don’twant a Span to be created. Just provide a comma separated list
of regularexpressions in the spring.sleuth.rxjava.schedulers.ignoredthreads property.
HTTP integration
将spring.sleuth.web.enabled配置值设置为false可以使这章中的特征方法无效
HTTP Filter
通过TraceFilter,所有抽样输入的请求都会归结到span的创建,span的名称为"http+请求发送的路径",例如,如果请求发送到/foo/bar,名称即为http:/foo/bar,你可以配置通过spring.sleuth.web.skipPattern,那些URIs将被过滤掉,如果你在环境中添加了ManagementServerProperties,你的contextPath值会附加到过滤配置上。
HandlerIntercepter
由于需要span名称的精确,我们使用一个TraceHandlerInterceptor来置入一个存在的HandlerInterceptor或直接添加到存在的HandlerInterceptors列表中,TraceHandlerInterceptor添加一个特殊的请求属性给HttpServletRequest,如果TraceFilter没有看到属性,他会建立一个"fallback"span,这是一个建立在服务端的附加的span,此时trace在UI中可以正确的显示。
HTTP client integration
同步RestTemplate
我们注入一个RestTemplate拦截器来保证所有的tracing信息被发送到请求端,每当一个请求被生成,一个新的span将被创建,他会在接收应答后关闭,为了限制同步RestTemplate只需要设置spring.sleuth.web.client.enabled为false。
| 你必须注册一个RestTemplate为bean以使得拦截器可以注入,如果你使用一个新的关键字建立一个RestTemplate实例,instrumentation将无法工作 |
传统的instrumentation是通过发送接收请求来建立关闭span的,你可以通过注册你的bean来定制ClientHttpRequestFactory和AsyncClientHttpRequestFactory,记得使用tracing
compatible实现方式(e.g.不要忘记将ThreadPoolTaskScheduler置入一个TraceAsyncListenableTaskExecutor),传统请求工厂例子如下:
| Unresolved directive in spring-cloud-sleuth.adoc - include::../../../../spring-cloud-sleuth-core/src/test/java/org/springframework/cloud/sleuth/instrument/web/client/TraceWebAsyncClientAutoConfigurationTest.java[tags=async_template_factories,indent=0] |
Feign
默认Spring Cloud Sleuth通过TraceFeignClientAutoConfiguration提供feign的集成,你可以设置spring.sleuth.feign.enabled为false来使他无效,如果这样设置那么所有feign相关的装配都无法发生。
通过FeignBeanPostProcessor feign装配的部分结束,可以设置spring.sleuth.feign.processor.enabled为false来是他无效化,如果你这样设置,Spring
Cloud Sleuth将不会装配任何你的传统feign组件,所有默认装配保持原有状态。
异步通信
@Async注解方法
在Spring Cloud Sleuth中,我们装配异步关联组件以使得tracing信息可以在threads间传递,你可以通过设置spring.sleuth.async.enabled值为false来使其无效化。
如果你使用@Async来注解你的方法,我们将自动建立一个新的span:
span名称将是注解方法名
span将被标注为方法类名和方法名
@Scheduled注解方法
在Spring Cloud Sleuth中,我们装配scheduled执行方法以使得tracing信息可以在threads间传递,你可以通过设置spring.sleuth.scheduled.enabled值为false来使其无效化。
如果你使用@Scheduled来注解你的方法,我们将自建立一个新的span:
span名称将是注解方法名
span将被标注为方法类名和方法名
如果在一些@Scheduled注解类中你想跳过span新建过程,可以设置spring.sleuth.scheduled.skipPattern为一个指定的表达式,这将匹配@Scheduled注解类的完整描述名称。
Executor, ExecutorServiceand ScheduledExecutorService
我们提供了LazyTraceExecutor,TraceableExecutorService和TraceableScheduledExecutorService。每当一个新的任务被提交、调用或scheduled时,这些实现会建立新的spans。
以下是当使用CompletableFuture时如何用TraceableExecutorService传递tracing信息:
| CompletableFuture<Long> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // perform some logic return 1_000_000L; }, new TraceableExecutorService(executorService, // 'calculateTax' explicitly names the span - this param is optional tracer, traceKeys, spanNamer, "calculateTax")); |
Spring Cloud Sleuth集成了Spring Integration。他会建立span来发布或订阅事件,设置spring.sleuth.integration.enabled为false可以使Spring
Integration无效。
Spring Cloud Sleuth到1.0.4版本前都是使用消息传递时发送无效tracing头,这些头和在HTTP(包含
- )发送的名称时一样的,为了在1.0.4版本的向后兼容目的,我们开始发送所有有效和无效的头,请更新到1.0.4,因为在Spring
Cloud Sleuth 1.1中我们将会移除对分离头的支持。
从1.0.4后可以明确设置spring.sleuth.integration.patterns模式来提供你想要包含的tracing信道名称,默认所有的信道已被包含在内。
Zuul
我们注册Zuul过滤器来传播tracing信息(请求头使用tracing数据填满),可以设置spring.sleuth.zuul.enabled为false来关闭Zuul服务。
Moreinformation
https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-sleuth/#_example
参考http://blog.csdn.net/u010257992/article/details/52474639
相关文章推荐
- Spring Cloud Sleuth使用简介
- Spring Cloud Sleuth使用简介
- Api Gateway Zuul简介及SpringCloud中的使用
- springcloud(十二):使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin进行分布式链路跟踪
- springcloud(十二):使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin进行分布式链路跟踪
- Spring Cloud Sleuth Zipkin 升级使用
- 使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin进行分布式链路跟踪
- Spring Cloud Config - RSA简介以及使用RSA加密配置文件
- Ribbon 框架简介及搭建(没有与SpringCloud整合,独立使用)
- Spring Cloud Config - RSA简介以及使用RSA加密配置文件
- Spring Cloud Sleuth Zipkin 升级使用
- Ribbon 框架简介及搭建(没有与SpringCloud整合,独立使用)
- Spring Cloud Edgware新特性之九:Sleuth使用MQ方式整合Zipkin
- SpringCLoud实战微服务之——微服务简介以及入门使用
- SpringCloud Sleuth 使用
- 使用Spring Cloud Sleuth实现链路监控
- Spring Cloud Config RSA简介及使用RSA加密配置文件的方法
- 使用Spring Cloud Sleuth实现链路监控
- SpringCloud 分布式配置中心Cloud Config使用
- springCloud feign使用/优化总结
