【java】【java8】Lambda、Stream、Function、Consumer、Predicate、Supplier
2017-04-16 23:58
786 查看
Lambda基本概念
示例代码:
person类
Stream基本概念
Stream是Java 8中引入的一个新的抽象层。使用流,您可以以类似于SQL语句的声明方式来处理数据。例如,以下SQL语句
SELECT max(salary),employee_id,employee_name FROM Employee
上述SQL表达式自动返回最高受薪雇员的详细信息,而不需要客户端做任何事情。在Java中使用集合框架,开发人员必须使用循环并进行重复检查。
另一个问题是效率;由于现在的电脑基本都是多核处理器,因此Java开发人员可以编写并行代码处理,但是往往会出错
为了解决这些问题,Java 8引入了流的概念,让开发人员以声明方式处理数据,并利用多核架构,而无需为其编写任何特定的代码。
(代码简洁+多核处理)
stream并不是某种数据结构,它只是数据源的一种视图。这里的数据源可以是一个数组,Java容器或I/O channel等。正因如此要得到一个stream通常不会手动创建,而是调用对应的工具方法,比如:
调用
调用
常见的stream接口继承关系如图:

图中4种stream接口继承自
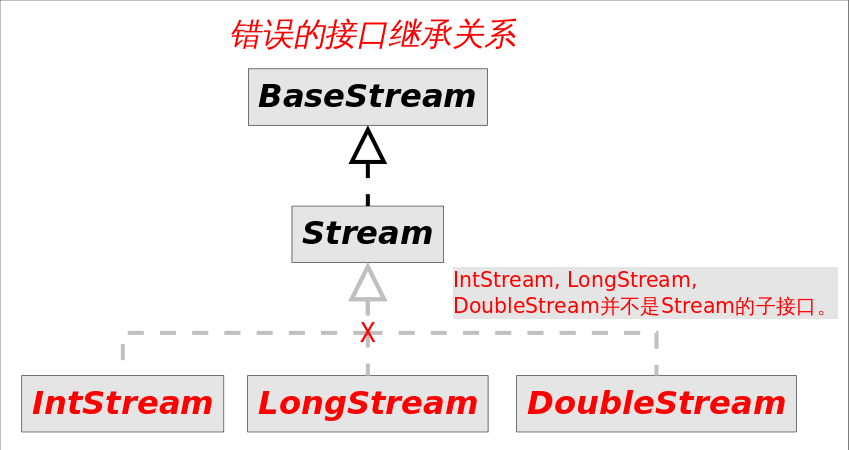
你可能会奇怪为什么不把
虽然大部分情况下stream是容器调用
无存储。stream不是一种数据结构,它只是某种数据源的一个视图,数据源可以是一个数组,Java容器或I/O channel等。
为函数式编程而生。对stream的任何修改都不会修改背后的数据源,比如对stream执行过滤操作并不会删除被过滤的元素,而是会产生一个不包含被过滤元素的新stream。(重新生成+副本)
惰式执行。stream上的操作并不会立即执行,只有等到用户真正需要结果的时候才会执行。(中间操作和结束操作)
可消费性。stream只能被“消费”一次,一旦遍历过就会失效,就像容器的迭代器那样,想要再次遍历必须重新生成。
count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();//filter里面是定义好的规则 其参数就是predicate
System.out.println("Empty Strings: " + count);
count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.length() == 3).count();
System.out.println("Strings of length 3: " + count);
每次使用都是重新调用stream()
对stream的操作分为为两类,中间操作(intermediate operations)和结束操作(terminal
operations),二者特点是:
中间操作总是会惰式执行,调用中间操作只会生成一个标记了该操作的新stream,仅此而已。
结束操作会触发实际计算,计算发生时会把所有中间操作积攒的操作以pipeline的方式执行,这样可以减少迭代次数。计算完成之后stream就会失效。下表汇总了
不要在结束操作后面再调用中间操作
示例代码:
Function源代码
实例代码
Predicate源代码
实例代码
Consumer源代码
实例代码
Supplier实例代码
参考资料: http://www.java2s.com/Tutorials/Java/Java_Lambda/index.htm http://blog.csdn.net/renfufei/article/details/24600507
A lambda expression is an unnamed function with parameters and a body.(匿名函数[参数+函数体])
The lambda expression body can be a block statement or an expression.(函数体可以是表达式或者是函数语句)
-> separates the parameters and the body.(分隔符)
语法规则:
(Parameters) -> { Body } (单个参数的时候左边括号也是可以省去的,Body可以没有花括号,那就成为了表达式)
注意点:
lambda表达式主体可能有局部变量语句。我们可以在lambda表达体中使用break,continue和return。 我们甚至可以从lambda表达体中抛出异常。
lambda表达式没有名称,因为它表示匿名内部类。
lambda表达式的返回类型由编译器推断。(隐式、显式)
lambda表达式不能像一个方法一样使用throws子句。
在通用功能界面中定义了lambda表达式不能通用。
举例:
(int x) -> x + 1 takes an int parameter and returns the parameter value incremented by 1.
(int x, int y) -> x + y takes two int parameters and returns the sum.
(String msg)->{System.out.println(msg);} takes a String parameter and prints it on the standard output.
msg->System.out.println(msg) takes a parameter and prints it on the standard output. It is identical to the code above.
() -> "hi" takes no parameters and returns a string.(例如BooleanSupplier)
(String str) -> str.length() takes a String parameter and returns its length.
示例代码一:
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyIntegerCalculator myIntegerCalculator = (Integer s1) -> s1 * 2;//接口方法具体实现 //s1的参数类型Integer可以不写 隐式 可以由javac通过上下文推导
System.out.println("1- Result x2 : " + myIntegerCalculator.calcIt(5));//10
}
}
interface MyIntegerCalculator {
public Integer calcIt(Integer s1);
}
示例代码二:
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
//注意参数类型
Processor stringProcessor = (String str) -> str.length();//实现接口方法
SecondProcessor secondProcessor = (String str) -> str.length();
//stringProcessor = secondProcessor; //compile error
String name = "stringProcessor";
int length = stringProcessor.getStringLength(name);
System.out.println(length);
String name2 = "secondProcessor2";
int length2 = secondProcessor.noName(name2);
System.out.println(length2);
}
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface Processor {
int getStringLength(String str);
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface SecondProcessor {
int noName(String str);
}
好处:简化代码
原来写法:为button添加按钮事件
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("hi");
}
});
lambda写法:
button.addActionListener(e->System.out.println("hi"))
解释:
Instead of passing in an inner class that implements an interface, we're passing in a block of code.
(不在需要匿名类去实现接口)
e is the name of a parameter,
-> separates the parameter from the body of the lambda expression.
In the lambda expression the parameter e is not declared with a type.
javac is inferring the type of e from its context, the signature of addActionListener.
(不要申明参数的类型 javac会根据上下文去自动获取相对应的类型)
We don't need to explicitly write out the type when it's obvious.
The lambda method parameters are still statically typed.示例代码:
package Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] atp = {"Rafael Nadal", "Novak Djokovic", "Stanislas Wawrinka", "David Ferrer", "Roger Federer", "Andy Murray", "Tomas Berdych", "Juan Martin Del Potro", "Richard Gasquet", "John Isner"};
List<String> players = Arrays.asList(atp);
// Old looping
for (String player : players) {
System.out.print(player + "; ");
}
System.out.println("");
/**
* default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (T t : this) {
action.accept(t);
}
}
* */
// Using lambda expression and functional operations
players.forEach((player) -> System.out.print(player + "; "));
System.out.println("");
// Using double colon operator in Java 8
players.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("");
// Using anonymous innerclass 实现匿名函数类的时候 如果参数列表中有参数 那么其就应该在使用lambda的时候就加上参数
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello world !");
}
}).start();
// Using lambda expression
new Thread(() -> System.out.println("Hello world !")).start();
// Using anonymous innerclass
Runnable race1 = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello world !");
}
};
// Using lambda expression
Runnable race2 = () -> System.out.println("Hello world !");
// Run em!
race1.run();
race2.run();
}
}package Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] players = {"Rafael Nadal", "Novak Djokovic", "Stanislas Wawrinka", "David Ferrer", "Roger Federer", "Andy Murray", "Tomas Berdych", "Juan Martin Del Potro", "Richard Gasquet", "John Isner"};
// Show the list of players
System.out.print("Show the list of players:\n");
Arrays.asList(players).forEach((player) -> System.out.println(player));
// Sort players by name using anonymous innerclass //Comparator是接口类型
Arrays.sort(players, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
return (s1.compareTo(s2));
}
});
// Sort players by name using lambda expression
Comparator<String> sortByName = (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.compareTo(s2));
Arrays.sort(players, sortByName);
// or this
Arrays.sort(players, (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.compareTo(s2)));
System.out.print("\nShow the list of players after sorting by name:\n");
Arrays.asList(players).forEach((player) -> System.out.println(player));
// Sort players by surname using anonymous innerclass
Arrays.sort(players, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
return (s1.substring(s1.indexOf(" ")).compareTo(s2.substring(s2.indexOf(" "))));
}
});
// Sort players by surname using lambda expression //根据姓开始字母顺序进行排序
Comparator<String> sortBySurname = (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.substring(s1.indexOf(" ")).compareTo(s2.substring(s2.indexOf(" "))));
Arrays.sort(players, sortBySurname);
// or this
Arrays.sort(players, (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.substring(s1.indexOf(" ")).compareTo(s2.substring(s2.indexOf(" ")))));
System.out.print("\nShow the list of players after sorting by surname:\n");
Arrays.asList(players).forEach((player) -> System.out.println(player));
// Sort players by name lenght using anonymous innerclass
Arrays.sort(players, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
return (s1.length() - s2.length());
}
});
// Sort players by name lenght using lambda expression
Comparator<String> sortByNameLenght = (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.length() - s2.length());
Arrays.sort(players, sortByNameLenght);
// or this
Arrays.sort(players, (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.length() - s2.length()));
System.out.print("\nShow the list of players after sorting by length:\n");
Arrays.asList(players).forEach((player) -> System.out.println(player));
// Sort players by last letter using anonymous innerclass
Arrays.sort(players, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
return (s1.charAt(s1.length() - 1) - s2.charAt(s2.length() - 1));
}
});
// Sort players by last letter using lambda expression
Comparator<String> sortByLastLetter = (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.charAt(s1.length() - 1) - s2.charAt(s2.length() - 1));
Arrays.sort(players, sortByLastLetter);
// or this
Arrays.sort(players, (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.charAt(s1.length() - 1) - s2.charAt(s2.length() - 1)));
System.out.print("\nShow the list of players after sorting by last letter:\n");
Arrays.asList(players).forEach((player) -> System.out.println(player));
}
}person类
package Test;
public class Person {
private String firstName, lastName, job, gender;
private int salary, age;
public Person(){}
public Person(String firstName, String lastName, String job, String gender, int age, int salary) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
this.job = job;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}package Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.IntSummaryStatistics;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.joining;
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toCollection;
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toList;
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toSet;
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> javaProgrammers = new ArrayList<Person>() {
{
add(new Person("Elsdon", "Jaycob", "Java programmer", "male", 43, 2000));
add(new Person("Tamsen", "Brittany", "Java programmer", "female", 23, 1500));
add(new Person("Floyd", "Donny", "Java programmer", "male", 33, 1800));
add(new Person("Sindy", "Jonie", "Java programmer", "female", 32, 1600));
add(new Person("Vere", "Hervey", "Java programmer", "male", 22, 1200));
add(new Person("Maude", "Jaimie", "Java programmer", "female", 27, 1900));
add(new Person("Shawn", "Randall", "Java programmer", "male", 30, 2300));
add(new Person("Jayden", "Corrina", "Java programmer", "female", 35, 1700));
add(new Person("Palmer", "Dene", "Java programmer", "male", 33, 2000));
add(new Person("Addison", "Pam", "Java programmer", "female", 34, 1300));
}
};
List<Person> phpProgrammers = new ArrayList<Person>() {
{
add(new Person("Jarrod", "Pace", "PHP programmer", "male", 34, 1550));
add(new Person("Clarette", "Cicely", "PHP programmer", "female", 23, 1200));
add(new Person("Victor", "Channing", "PHP programmer", "male", 32, 1600));
add(new Person("Tori", "Sheryl", "PHP programmer", "female", 21, 1000));
add(new Person("Osborne", "Shad", "PHP programmer", "male", 32, 1100));
add(new Person("Rosalind", "Layla", "PHP programmer", "female", 25, 1300));
add(new Person("Fraser", "Hewie", "PHP programmer", "male", 36, 1100));
add(new Person("Quinn", "Tamara", "PHP programmer", "female", 21, 1000));
add(new Person("Alvin", "Lance", "PHP programmer", "male", 38, 1600));
add(new Person("Evonne", "Shari", "PHP programmer", "female", 40, 1800));
}
};
// forEach examples
// Print programmers name
System.out.println("Print programmers names:");
javaProgrammers.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; ", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
phpProgrammers.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; ", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
// Increase salary by 5% to programmers
System.out.println("\n\nIncrease salary by 5% to programmers:");
Consumer<Person> giveRaise = e -> e.setSalary(e.getSalary() / 100 * 5 + e.getSalary());
javaProgrammers.forEach(giveRaise);
phpProgrammers.forEach(giveRaise);
javaProgrammers.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s earns now $%,d.%n", p.getFirstName(), p.getSalary()));
phpProgrammers.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s earns now $%,d.%n", p.getFirstName(), p.getSalary()));
// filter examples
// Print PHP programmers that earn more than $1,400
System.out.println("\nPHP programmers that earn more than $1,400:");
phpProgrammers.stream()
.filter((p) -> (p.getSalary() > 1400))
.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; ", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
// Define some filters 自定义过滤器
Predicate<Person> ageFilter = (p) -> (p.getAge() > 25);
Predicate<Person> salaryFilter = (p) -> (p.getSalary() > 1400);
Predicate<Person> genderFilter = (p) -> ("female".equals(p.getGender()));
System.out.println("\n\nFemale PHP programmers that earn more than $1,400 and are older than 24 years:");
phpProgrammers.stream()
.filter(ageFilter)
.filter(salaryFilter)
.filter(genderFilter)
.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; ", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
// Reuse filters
System.out.println("\n\nFemale Java programmers older than 24 years:");
javaProgrammers.stream()
.filter(ageFilter)
.filter(genderFilter)
.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; ", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
// limit examples
System.out.println("\n\nPrint first 3 Java programmers:");
javaProgrammers.stream()
.limit(3)
.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; ", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
System.out.println("\n\nPrint first 3 female Java programmers:");
javaProgrammers.stream()
.filter(genderFilter)
.limit(3)
.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; ", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
// sorted, collect, limit, min, max examples
System.out.println("\n\nSort and print first 5 Java programmers by name:");
List<Person> sortedJavaProgrammers = javaProgrammers
.stream()
.sorted((p, p2) -> (p.getFirstName().compareTo(p2.getFirstName())))
.limit(5)
.collect(toList());
sortedJavaProgrammers.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; %n", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
System.out.println("\nSort and print Java programmers by salary:");
sortedJavaProgrammers = javaProgrammers
.stream()
.sorted((p, p2) -> (p.getSalary() - p2.getSalary()))
.collect(toList());
sortedJavaProgrammers.forEach((p) -> System.out.printf("%s %s; %n", p.getFirstName(), p.getLastName()));
// min is faster than sorting and choosing the first
System.out.println("\nGet the lowest Java programmer salary:");
Person pers = javaProgrammers
.stream()
.min((p1, p2) -> (p1.getSalary() - p2.getSalary()))
.get();
System.out.printf("Name: %s %s; Salary: $%,d.", pers.getFirstName(), pers.getLastName(), pers.getSalary());
System.out.println("\nGet the highest Java programmer salary:");
Person person = javaProgrammers
.stream()
.max((p, p2) -> (p.getSalary() - p2.getSalary()))
.get();
System.out.printf("Name: %s %s; Salary: $%,d.", person.getFirstName(), person.getLastName(), person.getSalary());
// map, collect examples
System.out.println("\nGet PHP programmers first name to String:");
String phpDevelopers = phpProgrammers
.stream()
.map(Person::getFirstName)
.collect(joining(" ; ")); // this can be use as a token in further operations
System.out.println(phpDevelopers);
System.out.println("\nGet Java programmers first name to Set:");
Set<String> javaDevFirstName = javaProgrammers
.stream()
.map(Person::getFirstName)
.collect(toSet());
javaDevFirstName.stream().forEach((s) -> System.out.printf("%s ", s));;
System.out.println("\nGet Java programmers last name to TreeSet:");
TreeSet<String> javaDevLastName = javaProgrammers
.stream()
.map(Person::getLastName)
.collect(toCollection(TreeSet::new));
javaDevLastName.stream().forEach((s) -> System.out.printf("%s ", s));
int numProcessorsOrCores = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
System.out.printf("\n\nParallel version on %s-core machine:", numProcessorsOrCores);
// parrallel stream, sum examples
System.out.println("\nCalculate total money spent for paying Java programmers:");
int totalSalary = javaProgrammers
.parallelStream()
.mapToInt(p -> p.getSalary())
.sum();
System.out.printf("Money spent for paying Java programmers: $%,d %n", totalSalary);
//Get count, min, max, sum, and average for numbers
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
IntSummaryStatistics stats = numbers
.stream()
.mapToInt((x) -> x)
.summaryStatistics();
System.out.println("Highest number in List : " + stats.getMax());
System.out.println("Lowest number in List : " + stats.getMin());
System.out.println("Sum of all numbers : " + stats.getSum());
System.out.println("Average of all numbers : " + stats.getAverage());
}
}Stream基本概念
Stream是Java 8中引入的一个新的抽象层。使用流,您可以以类似于SQL语句的声明方式来处理数据。例如,以下SQL语句
SELECT max(salary),employee_id,employee_name FROM Employee
上述SQL表达式自动返回最高受薪雇员的详细信息,而不需要客户端做任何事情。在Java中使用集合框架,开发人员必须使用循环并进行重复检查。
另一个问题是效率;由于现在的电脑基本都是多核处理器,因此Java开发人员可以编写并行代码处理,但是往往会出错
为了解决这些问题,Java 8引入了流的概念,让开发人员以声明方式处理数据,并利用多核架构,而无需为其编写任何特定的代码。
(代码简洁+多核处理)
stream并不是某种数据结构,它只是数据源的一种视图。这里的数据源可以是一个数组,Java容器或I/O channel等。正因如此要得到一个stream通常不会手动创建,而是调用对应的工具方法,比如:
调用
Collection.stream()或者
Collection.parallelStream()方法
调用
Arrays.stream(T[] array)方法
常见的stream接口继承关系如图:

图中4种stream接口继承自
BaseStream,其中
IntStream, LongStream, DoubleStream对应三种基本类型(
int, long, double,注意不是包装类型),
Stream对应所有剩余类型的stream视图。为不同数据类型设置不同stream接口,可以1.提高性能,2.增加特定接口函数。

你可能会奇怪为什么不把
IntStream等设计成
Stream的子接口?毕竟这接口中的方法名大部分是一样的。答案是这些方法的名字虽然相同,但是返回类型不同,如果设计成父子接口关系,这些方法将不能共存,因为Java不允许只有返回类型不同的方法重载。
虽然大部分情况下stream是容器调用
Collection.stream()方法得到的,但stream和collections有以下不同:
无存储。stream不是一种数据结构,它只是某种数据源的一个视图,数据源可以是一个数组,Java容器或I/O channel等。
为函数式编程而生。对stream的任何修改都不会修改背后的数据源,比如对stream执行过滤操作并不会删除被过滤的元素,而是会产生一个不包含被过滤元素的新stream。(重新生成+副本)
惰式执行。stream上的操作并不会立即执行,只有等到用户真正需要结果的时候才会执行。(中间操作和结束操作)
可消费性。stream只能被“消费”一次,一旦遍历过就会失效,就像容器的迭代器那样,想要再次遍历必须重新生成。
count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();//filter里面是定义好的规则 其参数就是predicate
System.out.println("Empty Strings: " + count);
count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.length() == 3).count();
System.out.println("Strings of length 3: " + count);
每次使用都是重新调用stream()
对stream的操作分为为两类,中间操作(intermediate operations)和结束操作(terminal
operations),二者特点是:
中间操作总是会惰式执行,调用中间操作只会生成一个标记了该操作的新stream,仅此而已。
结束操作会触发实际计算,计算发生时会把所有中间操作积攒的操作以pipeline的方式执行,这样可以减少迭代次数。计算完成之后stream就会失效。下表汇总了
Stream接口的部分常见方法:
| 操作类型 | 接口方法 |
|---|---|
| 中间操作 | concat() distinct() filter() flatMap() limit() map() peek() skip() sorted() parallel() sequential() unordered() |
| 结束操作 | allMatch() anyMatch() collect() count() findAny() findFirst() forEach() forEachOrdered() max() min() noneMatch() reduce() toArray() |
示例代码:
package Java.Stream;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Java8Tester {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Using Java 7: ");
// Count empty strings
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd", "bbbb", "jkl");
System.out.println("List: " + strings);
long count = getCountEmptyStringUsingJava7(strings);
System.out.println("Empty Strings: " + count);
count = getCountLength3UsingJava7(strings);
System.out.println("Strings of length 3: " + count);
//Eliminate empty string
List<String> filtered = deleteEmptyStringsUsingJava7(strings);
System.out.println("Filtered List: " + filtered);
//Eliminate empty string and join using comma.
String mergedString = getMergedStringUsingJava7(strings, ", ");
System.out.println("Merged String: " + mergedString);
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 2, 2, 3, 7, 3, 5);
//get list of square of distinct numbers
List<Integer> squaresList = getSquares(numbers);
System.out.println("Squares List: " + squaresList);
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 13, 4, 15, 6, 17, 8, 19);
System.out.println("List: " + integers);
System.out.println("Highest number in List : " + getMax(integers));
System.out.println("Lowest number in List : " + getMin(integers));
System.out.println("Sum of all numbers : " + getSum(integers));
System.out.println("Average of all numbers : " + getAverage(integers));
System.out.println("Random Numbers: ");
//print ten random numbers
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(random.nextInt());
}
System.out.println("Using Java 8: ");
System.out.println("List: " + strings);
count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();//filter里面是定义好的规则 其参数就是predicate
System.out.println("Empty Strings: " + count);
count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.length() == 3).count();
System.out.println("Strings of length 3: " + count);
/**
* Collectors are used to combine the result of processing on the elements of a stream.
* Collectors can be used to return a list or a string(list和String都是可以的)
* */
filtered = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Filtered List: " + filtered);
mergedString = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
System.out.println("Merged String: " + mergedString);
/**
* The map method is used to map each element to its corresponding result
* key-value(结果)
* */
squaresList = numbers.stream().map(i -> i * i).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Squares List: " + squaresList);
System.out.println("List: " + integers);
/**
* With Java 8, statistics collectors are introduced to calculate all statistics when stream processing is being done.
* IntSummaryStatistics类中已经有最大值、最小值、数量、平均值等函数
* */
IntSummaryStatistics stats = integers.stream().mapToInt((x) -> x).summaryStatistics();
System.out.println("Highest number in List : " + stats.getMax());
System.out.println("Lowest number in List : " + stats.getMin());
System.out.println("Sum of all numbers : " + stats.getSum());
System.out.println("Average of all numbers : " + stats.getAverage());
System.out.println("Random Numbers: ");
/**
* Stream has provided a new method forEach to iterate each element of the stream.
* The following code segment shows how to print 10 random numbers using forEach.
* */
/**
* The limit method is used to reduce the size of the stream.
* */
/**
* The sorted method is used to sort the stream
* */
random.ints().limit(10).sorted().forEach(System.out::println);//返回的是10个已经排好顺序的伪随机int数
random.doubles().limit(10).forEachOrdered(System.out::println);//返回的是10个伪随机double数
/**
*
two methods to generate a Stream
stream() − Returns a sequential stream considering collection as its source.
parallelStream() − Returns a parallel Stream considering collection as its source.
* */
count = strings.parallelStream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();
System.out.println("Empty Strings: " + count);
}
//返回长度为0的字符串数量
private static int getCountEmptyStringUsingJava7(List<String> strings) {
int count = 0;
for (String string : strings) {
if (string.isEmpty()) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
//返回长度为3的字符串数量
private static int getCountLength3UsingJava7(List<String> strings) {
int count = 0;
for (String string : strings) {
if (string.length() == 3) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
//去除空字符串
private static List<String> deleteEmptyStringsUsingJava7(List<String> strings) {
List<String> filteredList = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String string : strings) {
if (!string.isEmpty()) {
filteredList.add(string);
}
}
return filteredList;
}
//加入分隔符
private static String getMergedStringUsingJava7(List<String> strings, String separator) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();//StringBuilder不是线程安全
for (String string : strings) {
if (!string.isEmpty()) {
stringBuilder.append(string);
stringBuilder.append(separator);
}
}
String mergedString = stringBuilder.toString();
return mergedString.substring(0, mergedString.length() - 2);
}
//平方
private static List<Integer> getSquares(List<Integer> numbers) {
List<Integer> squaresList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer number : numbers) {
Integer square = new Integer(number.intValue() * number.intValue());
if (!squaresList.contains(square)) {
squaresList.add(square);
}
}
return squaresList;
}
//获取最大值
private static int getMax(List<Integer> numbers) {
int max = numbers.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < numbers.size(); i++) {
Integer number = numbers.get(i);
if (number.intValue() > max) {
max = number.intValue();
}
}
return max;
}
//最小值
private static int getMin(List<Integer> numbers) {
int min = numbers.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < numbers.size(); i++) {
Integer number = numbers.get(i);
if (number.intValue() < min) {
min = number.intValue();
}
}
return min;
}
//和
private static int getSum(List numbers) {
int sum = (int) (numbers.get(0));
for (int i = 1; i < numbers.size(); i++) {
sum += (int) numbers.get(i);
}
return sum;
}
//平均值
private static int getAverage(List<Integer> numbers) {
return getSum(numbers) / numbers.size();
}
}Function源代码
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* Represents a function that accepts one argument and produces a result.
*
* <p>This is a functional interface whose functional method is apply(Object)
*
* @param <T> the type of the input to the function
* @param <R> the type of the result of the function
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
/**
* Applies this function to the given argument.
*
* @param t the function argument
* @return the function result
*/
R apply(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed function that first applies the {@code before}
* function to its input, and then applies this function to the result.
* If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to
* the caller of the composed function.
*
* @param <V> the type of input to the {@code before} function, and to the
* composed function
* @param before the function to apply before this function is applied
* @return a composed function that first applies the {@code before}
* function and then applies this function
* @throws NullPointerException if before is null
*
* @see #andThen(Function)
*/
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));
}
/**
* Returns a composed function that first applies this function to
* its input, and then applies the {@code after} function to the result.
* If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to
* the caller of the composed function.
*
* @param <V> the type of output of the {@code after} function, and of the
* composed function
* @param after the function to apply after this function is applied
* @return a composed function that first applies this function and then
* applies the {@code after} function
* @throws NullPointerException if after is null
*
* @see #compose(Function)
*/
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));
}
/**
* Returns a function that always returns its input argument.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input and output objects to the function
* @return a function that always returns its input argument
*/
static <T> Function<T, T> identity() {
return t -> t;
}
}实例代码
package Test.FCPS;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class testFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//简单的,只有一行
Function<String, String> function1 = (x) -> "test result1: " + x;
//标准的,有花括号, return, 分号.
Function<String, String> function2 = (x) -> {
return "after function1 "+" test result2: " + x;
};
Function<String, String> function3 = (x) -> {
return "before function2 "+" test result3: " + x;
};
System.out.println(function1.apply("98"));
System.out.println(function1.andThen(function2).apply("100"));//先执行function1 然后将其结果作为参数传递到function2中
System.out.println(function2.andThen(function1).apply("100"));
System.out.println(function2.compose(function3).apply("fun100"));//先执行function3 在执行function2
System.out.println(Function.identity());
}
}
/**
test result1: 98
after function1 test result2: test result1: 100
after function1 test result2: before function2 test result3: fun100
java.util.function.Function$$Lambda$6/558638686@448139f0
* */Predicate源代码
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* Represents a predicate (boolean-valued function) of one argument.
*
* This is afunctional interface whose functional method is test(Object).
*
* @param <T> the type of the input to the predicate
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate<T> {
/**
* Evaluates this predicate on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
* @return true if the input argument matches the predicate,otherwise false
*/
boolean test(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code false}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ANDed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) && other.test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate.
*
* @return a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate
*/
default Predicate<T> negate() {
return (t) -> !test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code true}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ORed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> or(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) || other.test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of arguments to the predicate
* @param targetRef the object reference with which to compare for equality,
* which may be {@code null}
* @return a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}
*/
static <T> Predicate<T> isEqual(Object targetRef) {
return (null == targetRef)
? Objects::isNull
: object -> targetRef.equals(object);
}
}实例代码
package Java.FCPS.PredicateStudy;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate<String> predicate=(s)->s.length()>5;
System.out.println(predicate.test("predicate"));
}
}package Java.FCPS.PredicateStudy;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
class Box {
private int weight = 0;
private String color = "";
public Box() {
}
public Box(int weight, String color) {
this.weight = weight;
this.color = color;
}
public Integer getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(Integer weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String toString() {
return "Apple{" + "color='" + color + '\'' + ", weight=" + weight + '}';
}
}
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Box> inventory = Arrays.asList(new Box(80, "green"), new Box(155, "green"), new Box(120, "red"));
//filter中的参数更好像是定义了一组规则 按照这个规则 然后predicate调用test函数
List<Box> greenApples = filter(inventory, Test02::isGreenApple);
System.out.println(greenApples);
List<Box> heavyApples = filter(inventory, Test02::isHeavyApple);
System.out.println(heavyApples);
List<Box> greenApples2 = filter(inventory, (Box a) -> "green".equals(a.getColor()));
System.out.println(greenApples2);
List<Box> heavyApples2 = filter(inventory, (Box a) -> a.getWeight() > 150);
System.out.println(heavyApples2);
List<Box> weirdApples = filter(inventory, (Box a) -> a.getWeight() < 80 || "brown".equals(a.getColor()));
System.out.println(weirdApples);
}
public static boolean isGreenApple(Box apple) {
return "green".equals(apple.getColor());
}
public static boolean isHeavyApple(Box apple) {
return apple.getWeight() > 150;
}
public static List<Box> filter(List<Box> inventory,
Predicate<Box> p) {
List<Box> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Box apple : inventory) {
if (p.test(apple)) {
result.add(apple);
}
}
return result;
}
}package Java.FCPS.PredicateStudy;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
class Student {
public int id;
public long gpa;
public String name;
Student(int id, long g, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.gpa = g;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + ":" + name + ": " + gpa;
}
}
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> employees = Arrays.asList(
new Student(1, 5, "John"),
new Student(2, 4, "Jane"),
new Student(3, 3, "Jack")
);
// with predicate
System.out.println(findStudents(employees, createCustomPredicateWith(4)));
// with function definition, both are same
Function<Double, Predicate<Student>> customFunction = threshold -> (e -> e.gpa > threshold);
System.out.println(findStudents(employees, customFunction.apply(4D)));
}
private static Predicate<Student> createCustomPredicateWith(double threshold) {
return e -> e.gpa >= threshold;
}
private static List<Student> findStudents(List<Student> employees, Predicate<Student> predicate) {
List<Student> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Student e : employees) {
if (predicate.test(e)) {
result.add(e);
}
}
return result;
}
}
/**
[1:John: 5, 2:Jane: 4]
[1:John: 5]
* */Consumer源代码
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* Represents an operation that accepts a single input argument and returns no
* result. Unlike most other functional interfaces, {@code Consumer} is expected
* to operate via side-effects.
*
* <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a>
* whose functional method is {@link #accept(Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input to the operation
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {
/**
* Performs this operation on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
*/
void accept(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either
* operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the
* composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception,
* the {@code after} operation will not be performed.
*
* @param after the operation to perform after this operation
* @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null
*/
default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); };
}
}实例代码
package Java.FCPS.ConsumerStudy;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Consumer<String> c = (x) -> System.out.println(x.toLowerCase());
c.accept("CONSUMER");
}
}package Java.FCPS.ConsumerStudy;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
//使用匿名函数形式
numbers.forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer integer) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
});
//使用Lambda
List<Integer> numbers2 = Arrays.asList(11, 21, 31, 41, 51, 61, 71, 81, 91, 110);
Consumer<List> consumer=(x)-> System.out.println(x);
consumer.accept(numbers2);
}
}package Java.FCPS.ConsumerStudy;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
class Student {
public int id;
public double gpa;
public String name;
public Student(){}
public Student(int id, long g, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.gpa = g;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + ":" + name + ": " + gpa;
}
}
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students = Arrays.asList(
new Student(1, 3, "John"),
new Student(2, 4, "Jane"),
new Student(3, 3,"Jack"));
Consumer<Student> raiser = e -> {
e.gpa = e.gpa * 1.1;
};
raiseStudents(students, System.out::println);
raiseStudents(students, raiser.andThen(System.out::println));//先执行raiser 然后再去执行输出操作
}
private static void raiseStudents(List<Student> employees,
Consumer<Student> fx) {
for (Student e : employees) {
fx.accept(e);
}
}
}Supplier实例代码
package Java.FCPS.Supplier;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Supplier<String> supplier=()->"Supplier";//定义了输出结果 因此没有必要重写toString()
System.out.println(supplier.get());
}
}package Java.FCPS.Supplier;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
class SunPower {
public SunPower() {
System.out.println("Sun Power initialized..");
}
}
public class Test02 {
public static SunPower produce(Supplier<SunPower> supp) {
return supp.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SunPower power = new SunPower();
SunPower p1 = produce(() -> power);//只会初始化一次 因此只会输出一个结果
SunPower p2 = produce(() -> power);
System.out.println("Check the same object? " + Objects.equals(p1, p2));
}
}
/**
* Sun Power initialized..
Check the same object? true
* */package Java.FCPS.Supplier;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
class Employee{
@Override
public String toString() {
return "A EMPLOYEE";
}
}
public class Test03 {
private static Employee employee(Supplier<Employee> supplier){
return supplier.get(); //在没有写构造函数的时候 就需要重写toString方法
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(employee(Employee::new));// A EMPLOYEE
}
}package Java.FCPS.Supplier;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
class Student {
public String name;
public double gpa;
public Student(){}
public Student(String name, double g) {
this.name = name;
this.gpa = g;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + ": " + gpa;
}
}
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Supplier<Student> studentGenerator = Test04::employeeMaker;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("#" + i + ": " + studentGenerator.get());
}
}
public static Student employeeMaker() {
return new Student("A",2);
}
}package Java.FCPS.Supplier;
import java.util.function.BooleanSupplier;
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BooleanSupplier bs = () -> true;//没有参数 但是有返回结果
System.out.println(bs.getAsBoolean());
int x = 0, y= 1;
bs = () -> x > y;
System.out.println(bs.getAsBoolean());
}
}参考资料: http://www.java2s.com/Tutorials/Java/Java_Lambda/index.htm http://blog.csdn.net/renfufei/article/details/24600507
相关文章推荐
- 学习笔记5:java 1.8 Predicate,Function,Supplier,Consumer,Comparator,Optional,Stream接口的使用
- Java 8中,Function,Consumer,Predicate,Supplier举例 ,以及CompletableFuture使用
- Java 8中,Function,Consumer,Predicate,Supplier举例
- 和Lambda表达式相关的Consumer、Function、Predicate 与 Supplier
- Java8的学习计划--lambda表达式的Function_predicate_consumer_bifunction
- java8 Function,Consumer,Predicate 接口
- Java8新特性学习-函数式编程(Stream/Function/Optional/Consumer)
- Java JVM(七):Function,Consumer,Predicate 接口
- Java JVM(七):Function,Consumer,Predicate 接口
- java.util.function 中的 Function、Predicate、Consumer
- java8函数式接口——Precidate、Consumer、Function、Supplier
- JAVA8 Function、Consumer、Predicate、Supplier接口
- java的lambda表达式、匿名类,Predicate接口,Consumer接口的应用
- JAVA8的新特性学习笔记-(lambda、stream)
- 在Java 8中对stream带有lambda表达式的操作进行调试
- JAVA8之lambda表达式详解,及stream中的lambda使用
- Java 8新特性:新语法方法引用和Lambda表达式及全新的Stream API
- Java 8新特性:新语法方法引用和Lambda表达式及全新的Stream API
- java8 Lambda 与 Stream
- Java8 Stream Lambda
