Java 学习系列:ConcurrentHashMap 的实现原理
2017-02-15 15:56
555 查看
在jdk并发包下面的ConcurrentHashMap类是一个支持多线程并发访问的集合类数据结构体; 支持多种方式的并发检索与更新操作. 包含containsKey, containsValue, remove, forEach等; 不允许null key与null value;
注: 此文基于jdk8环境
1 . 先看下ConcurrentHashMap的结构
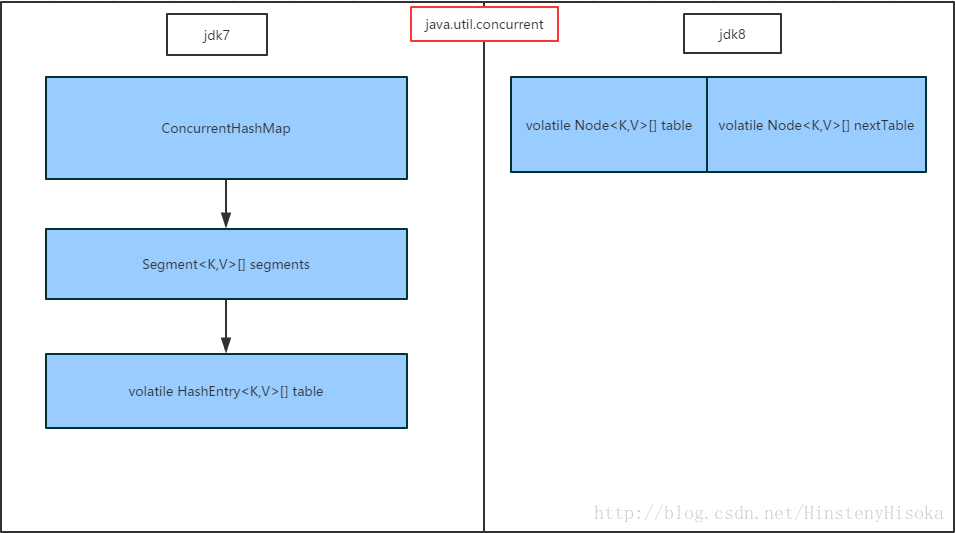
2 . 简述下对于并发控制的原理
1>. jdk7时, 采用分段锁机制首先根据key值hash定位要进行操作的segment[x], 然后对此段加锁, 再对hash值做一次hash散列定位到segment里面HashEntry[] 的哪一个节点, 再进行赋值替换操作, 在此期间包括扩容resize与原数据转移transfer;
2>.jdk8时, 取消了分段锁方式的数据结构, 还原成了类似于HashMap内部那样的纵向数组, 横向链表的方式, 但是第一步定位到纵向数组节点后, 就会对改节点进行加锁, 后续在操作该节点下的链表元素;
3 . ConcurrentHashMap的初始化
4 . 往ConcurrentHashMap put一个元素
5 . 从ConcurrentHashMap get一个元素
6 . ConcurrentHashMap 的扩容操作 resize
7 . 最后看下扩容大小数字算法
ps: 最后附个图说明下几种集合数据结构分别对多线程的支持情况
注: 此文基于jdk8环境
1 . 先看下ConcurrentHashMap的结构

2 . 简述下对于并发控制的原理
1>. jdk7时, 采用分段锁机制首先根据key值hash定位要进行操作的segment[x], 然后对此段加锁, 再对hash值做一次hash散列定位到segment里面HashEntry[] 的哪一个节点, 再进行赋值替换操作, 在此期间包括扩容resize与原数据转移transfer;
2>.jdk8时, 取消了分段锁方式的数据结构, 还原成了类似于HashMap内部那样的纵向数组, 横向链表的方式, 但是第一步定位到纵向数组节点后, 就会对改节点进行加锁, 后续在操作该节点下的链表元素;
3 . ConcurrentHashMap的初始化
/**
* 记录容器的容量大小,采用CAS方式更新
* Base counter value, used mainly when there is no contention,
* but also as a fallback during table initialization
* races. Updated via CAS.
*/
private transient volatile long baseCount;
/**
* 记录容器初始化或者扩容状态的标志量
* Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the
* table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization,
* else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise,
* when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon
* creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the
* next element count value upon which to resize the table.
*/
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
/**
* 仅仅创建一个空的map并设置容器大小, 后面第一次插入元素时才会真正进行节点创建
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size
* accommodating the specified number of elements without the need
* to dynamically resize.
*
* @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal
* sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}4 . 往ConcurrentHashMap put一个元素
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//散列下hash值, 让高位16位也参与hash运算以便hash分布的更散列
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();// 初始化容器
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
// 判断要添加的值落到了一个空的节点上, 所以直接插入进去即可
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
// 判断所命中节点处于转移状态中, 说明有其他线程正在操作此节点, 那就去帮助它进行数据转移
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
// 命中节点, 加锁该节点上的链表, 这一点和分段锁是比较像的, 但是更细化了, 相当于分段锁的数量变多了, 然后再进行后续操作
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
// 遍历链表查到合适位置并赋值
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
// 判断f是树, 进行树方式操作
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
// 判断链表长度大于7了, 随即把链表转化为树, 提高操作效率, 这一点和HashMap相通, 是jdk8的优化
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 容器元素总数加1, 此操作里包含了添加元素后的扩容, 扩充纵向数组大小
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}5 . 从ConcurrentHashMap get一个元素
/**
* 根据一个指定的key在map里面查找获取对应的value, 没找到时返回null
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());// 先散列定位对应的数组节点
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
// 刚好节点第一个元素hash值命中,直接比较对应key值
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
// 去查找树
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
// 去查找链表
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}6 . ConcurrentHashMap 的扩容操作 resize
/**
* Adds to count, and if table is too small and not already
* resizing, initiates transfer. If already resizing, helps
* perform transfer if work is available. Rechecks occupancy
* after a transfer to see if another resize is already needed
* because resizings are lagging additions.
*
* @param x the count to add
* @param check if <0, don't check resize, if <= 1 only check if uncontended
*/
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
//多线程CAS更新失败后执行
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
// 判断是否满足扩容条件
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
// 是否已经有线程在执行扩容操作了
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}7 . 最后看下扩容大小数字算法
/**
* 把所给整数扩增到比它大的最小的2的x次方的整数
* Returns a power of two table size for the given desired capacity.
* See Hackers Delight, sec 3.2
*/
private static final int tableSizeFor(int c) {
int n = c - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}ps: 最后附个图说明下几种集合数据结构分别对多线程的支持情况
| 集合类 | Key | Value | Super | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hashtable | 不允许为 null | 不允许为 null | Dictionary | 线程安全 |
| ConcurrentHashMap | 不允许为 null | 不允许为 null | AbstractMap | 分段锁技术 |
| TreeMap | 不允许为 null | 允许为 null | AbstractMap | 线程不安全 |
| HashMap | 允许为 null | 允许为 null | AbstractMap | 线程不安全 |
