C++二叉树遍历总结\100. Same Tree
2017-02-15 14:45
218 查看
理论学习
概念介绍
遍历图解
遍历算法
代码实践
实现模板
Same Tree
题目描述
代码实现
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/c602273091/article/details/55195284
前序就是访问结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前。
中序就是访问结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中,一般是遍历左边子树以后。
后序就是访问结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。
这里可以参考【1】中,对数据结构做了一个整理。
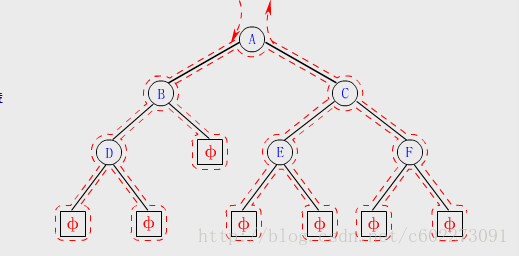
图中每个节点经过了3次。
先序为: A B D C E F
中序为: D B A E C F
后序为: D B E F C A
PS:(1) 在搜索路线中,若访问结点均是第一次经过结点时进行的,则是前序遍历;若访问结点均是在第二次(或第三次)经过结点时进行的,则是中序遍历(或后序遍历)。只要将搜索路线上所有在第一次、第二次和第三次经过的结点分别列表,即可分别得到该二叉树的前序序列、中序序列和后序序列。
(2) 上述三种序列都是线性序列,有且仅有一个开始结点和一个终端结点,其余结点都有且仅有一个前趋结点和一个后继结点。为了区别于树形结构中前趋(即双亲)结点和后继(即孩子)结点的概念,对上述三种线性序列,要在某结点的前趋和后继之前冠以其遍历次序名称。上图所示的二叉树中结点C,其前序前趋结点是D,前序后继结点是E;中序前趋结点是E,中序后继结点是F;后序前趋结点是F,后序后继结点是A。但是就该树的逻辑结构而言,C的前趋结点是A,后继结点是E和F。
二叉树建立过程可以看:【2】
(1)遍历左子树;
(2)访问根结点;
(3)遍历右子树。
2.先序遍历的递归算法定义:若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
(1) 访问根结点;
(2) 遍历左子树;
(3) 遍历右子树。
3.后序遍历得递归算法定义:若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
(1)遍历左子树;
(2)遍历右子树;
(3)访问根结点。
对于这个详细的图解,可以看【8】。
前序遍历:
中序遍历:
后序遍历:
非递归的前序:
非递归的中序:
非递归的后序:
在【5】中,作者提出了更加简单的二叉树实现,推荐看看。
在【6】中,作者提出了二叉树先中后序遍历(递归&非递归)算法、层次遍历(正序&逆序&锯齿形)非递归算法、二叉树深度算法、结点总数算法。
还有一些应用,比如搜索:二叉树的查找【7】
统计节点的个数:
比较两个数是否相同:
【1】数据结构整理:http://student.zjzk.cn/course_ware/data_structure/web/shu/shu6.3.1.htm
【2】二叉树建立动画过程:http://student.zjzk.cn/course_ware/data_structure/web/flashhtml/erchashujianli.htm
【3】建立二叉树:http://blog.csdn.net/pony_maggie/article/details/38390513
【4】二叉树的三种遍历方法:http://blog.csdn.net/presidentpresident/article/details/7549170
【5】二叉树各种方法总结:http://www.jianshu.com/p/49c8cfd07410
【6】二叉树各种遍历方法:http://www.cnblogs.com/yfsmooth/p/4671903.html
【7】二叉树的很多应用:http://blog.csdn.net/fansongy/article/details/6798278/
【8】二叉树详细图解:http://www.cnblogs.com/yc_sunniwell/archive/2010/06/27/1766233.html
概念介绍
遍历图解
遍历算法
代码实践
实现模板
Same Tree
题目描述
代码实现
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/c602273091/article/details/55195284
理论学习
概念介绍
二叉树的遍历分成前序、中序、后序遍历。前序就是访问结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前。
中序就是访问结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中,一般是遍历左边子树以后。
后序就是访问结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。
这里可以参考【1】中,对数据结构做了一个整理。
遍历图解

图中每个节点经过了3次。
先序为: A B D C E F
中序为: D B A E C F
后序为: D B E F C A
PS:(1) 在搜索路线中,若访问结点均是第一次经过结点时进行的,则是前序遍历;若访问结点均是在第二次(或第三次)经过结点时进行的,则是中序遍历(或后序遍历)。只要将搜索路线上所有在第一次、第二次和第三次经过的结点分别列表,即可分别得到该二叉树的前序序列、中序序列和后序序列。
(2) 上述三种序列都是线性序列,有且仅有一个开始结点和一个终端结点,其余结点都有且仅有一个前趋结点和一个后继结点。为了区别于树形结构中前趋(即双亲)结点和后继(即孩子)结点的概念,对上述三种线性序列,要在某结点的前趋和后继之前冠以其遍历次序名称。上图所示的二叉树中结点C,其前序前趋结点是D,前序后继结点是E;中序前趋结点是E,中序后继结点是F;后序前趋结点是F,后序后继结点是A。但是就该树的逻辑结构而言,C的前趋结点是A,后继结点是E和F。
二叉树建立过程可以看:【2】
// 假设虚结点输入时以空格字符表示,相应的构造算法为:
void CreateBinTree (BinTree *T) {
//构造二叉链表。T是指向根指针的指针,故修改*T就修改了实参(根指针)本身
char ch;
if((ch=getchar())=='') *T=NULL; //读人空格,将相应指针置空
else{ //读人非空格
*T=(BinTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BinTNode)); //生成结点
(*T)->data=ch;
CreateBinTree(&(*T)->lchild); //构造左子树
CreateBinTree(&(*T)->rchild); //构造右子树
}
}遍历算法
1.中序遍历的递归算法定义:若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:(1)遍历左子树;
(2)访问根结点;
(3)遍历右子树。
2.先序遍历的递归算法定义:若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
(1) 访问根结点;
(2) 遍历左子树;
(3) 遍历右子树。
3.后序遍历得递归算法定义:若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
(1)遍历左子树;
(2)遍历右子树;
(3)访问根结点。
对于这个详细的图解,可以看【8】。
代码实践
参考【3】【4】中的代码建立二叉树。实现模板
在【5】里,作者总结了一套很好的二叉树遍历的模板。以下为摘录部分。前序遍历:
//前序遍历
void preorder(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &path)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
path.push_back(root->val);
preorder(root->left, path);
preorder(root->right, path);
}
}中序遍历:
//中序遍历
void inorder(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &path)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
inorder(root->left, path);
path.push_back(root->val);
inorder(root->right, path);
}
}后序遍历:
//后续遍历
void postorder(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &path)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
postorder(root->left, path);
postorder(root->right, path);
path.push_back(root->val);
}
}非递归的前序:
//非递归前序遍历
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &path)
{
stack<TreeNode *> s;
TreeNode *p = root;
while(p != NULL || !s.empty())
{
while(p != NULL)
{
path.push_back(p->val);
s.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
if(!s.empty())
{
p = s.top();
s.pop();
p = p->right;
}
}
}非递归的中序:
//非递归中序遍历
void inorderTraversal(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &path)
{
stack<TreeNode *> s;
TreeNode *p = root;
while(p != NULL || !s.empty())
{
while(p != NULL)
{
s.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
if(!s.empty())
{
p = s.top();
path.push_back(p->val);
s.pop();
p = p->right;
}
}
}非递归的后序:
//非递归后序遍历-迭代
void postorderTraversal(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &path)
{
stack<TempNode *> s;
TreeNode *p = root;
TempNode *temp;
while(p != NULL || !s.empty())
{
while(p != NULL) //沿左子树一直往下搜索,直至出现没有左子树的结点
{
TreeNode *tempNode = new TreeNode;
tempNode->btnode = p;
tempNode->isFirst = true;
s.push(tempNode);
p = p->left;
}
if(!s.empty())
{
temp = s.top();
s.pop();
if(temp->isFirst == true) //表示是第一次出现在栈顶
{
temp->isFirst = false;
s.push(temp);
p = temp->btnode->right;
}
else //第二次出现在栈顶
{
path.push_back(temp->btnode->val);
p = NULL;
}
}
}
}在【5】中,作者提出了更加简单的二叉树实现,推荐看看。
在【6】中,作者提出了二叉树先中后序遍历(递归&非递归)算法、层次遍历(正序&逆序&锯齿形)非递归算法、二叉树深度算法、结点总数算法。
还有一些应用,比如搜索:二叉树的查找【7】
bintree search_tree(bintree t,datatype x){
if(!t){
return NULL;
}
if(t->data == x){
return t;
}else{
if(!search_tree(t->lchild,x)){
return search_tree(t->rchild,x);
}
return t;
}
}统计节点的个数:
int count_tree(bintree t){
if(t){
return (count_tree(t->lchild)+count_tree(t->rchild)+1);
}
return 0;
}比较两个数是否相同:
int is_equal(bintree t1,bintree t2){
if(!t1 && !t2){ //都为空就相等
return 1;
}
if(t1 && t2 && t1->data == t2->data){ //有一个为空或数据不同就不判断了
if(is_equal(t1->lchild,t2->lchild))
if(is_equal(t1->rchild,t2->rchild)){
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}100. Same Tree
题目描述
Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are equal or not. Two binary trees are considered equal if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same value.
代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2) {
if(!t1 && !t2){ //都为空就相等
return true;
}
if(t1 && t2 && t1->val == t2->val){ //有一个为空或数据不同就不判断了
if(isSameTree(t1->left,t2->left))
if(isSameTree(t1->right,t2->right)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};【1】数据结构整理:http://student.zjzk.cn/course_ware/data_structure/web/shu/shu6.3.1.htm
【2】二叉树建立动画过程:http://student.zjzk.cn/course_ware/data_structure/web/flashhtml/erchashujianli.htm
【3】建立二叉树:http://blog.csdn.net/pony_maggie/article/details/38390513
【4】二叉树的三种遍历方法:http://blog.csdn.net/presidentpresident/article/details/7549170
【5】二叉树各种方法总结:http://www.jianshu.com/p/49c8cfd07410
【6】二叉树各种遍历方法:http://www.cnblogs.com/yfsmooth/p/4671903.html
【7】二叉树的很多应用:http://blog.csdn.net/fansongy/article/details/6798278/
【8】二叉树详细图解:http://www.cnblogs.com/yc_sunniwell/archive/2010/06/27/1766233.html
相关文章推荐
- LeetCode 100. Same Tree (C++)
- leecode 解题总结:100. Same Tree
- LeetCode 100. Same Tree(C++版)
- c++总结系列(一)---动态库dll中使用资源
- C++代码优化方法总结
- c++学习总结系列--序言
- C++ young 程序库——y_binary_search_tree_base.hpp、y_red_black_tree_base.hpp 和 y_red_black_tree.hpp
- 偶总结的FORTRAN/C/C++混合编程,大家有兴趣就看看吧
- (补课)borland c++ bulder的文件操作总结-1
- C++总结
- C++技术总结
- JAVA与C++::关于JNI中文字符串操作问题总结
- C++代码优化方法总结
- C和C++的区别总结
- C++代码优化方法总结
- c++总结系列(-)----动态库(dll)
- (补课)borland c++ bulder的文件操作总结-4
- 对c++的const指针定义的一句话总结
- C/C++语言基础知识总结
- C++面试的一些总结
