C语言之控制语句
2017-02-15 08:57
218 查看
转载 http://www.cnblogs.com/JCSU/articles/1306395.html
一、决策语句
1. if语句
(1) 一般形式
(2) 流程图和交通图
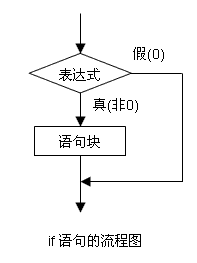
(3) 例子
2. if-else语句
(1) 一般形式
(2) 流程图和交通图
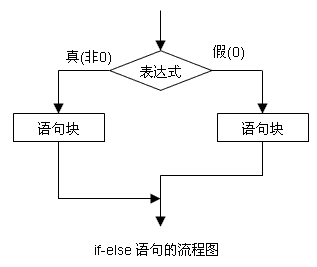

(3) 例子
#include <stdio.h>
main ()
{
int i;
scanf ("%ld",i);
if (i > 0)
{
printf ("That number was positive!");
}
else
{
printf ("That number was negative or zero!");
}
}
3. switch语句
(1) 一般形式
(2) 语句说明
对于switch条件语句,如果找到相同的结果值则执行case内的程序语句,当执行完case块后,并不会直接离开switch块,还是会住下继续执行其他case语句和default语句,这种情形称为“失败经过”(Falling Through)现象。
因此,每一道case语句最后,必须加上break语句来结束switch语句,才可以避免“失败经过”的情况。default语句可放在switch条件语句的任何位置,如果找不到吻合的结果值,最后会执行default语句,除非摆在最后时,才可以省略default语句内的break语句,否则还是必须加上break语句。
(3) 例子
二、循环语句
1. while语句
(1) 一般形式
(2) 流程图
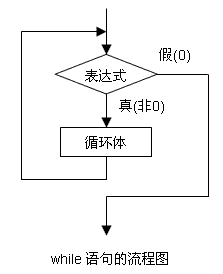
(3) 例子
2. do-while语句
(1) 一般形式
(2) 流程图
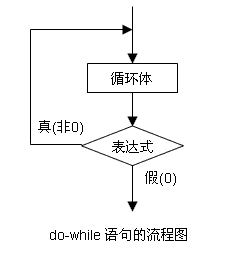
(3) 例子
/**********************************************/
/* */
/* do .. while demo */
/* */
/**********************************************/
/* print a string enclosed by quotes " " */
/* gets input from stdin i.e. keyboard */
/* skips anything outside the quotes */
#include <stdio.h>
/*************************************************/
/* Level 0 */
/*************************************************/
main ()
{
char ch,skipstring();
do
{
if ((ch = getchar()) == '"')
{
printf ("The string was:\n");
ch = skipstring();
}
}
while (ch != '\n')
{
}
}
/*************************************************/
/* Level 1 */
/*************************************************/
char skipstring () /* skip a string "" */
{
char ch;
do
{
ch = getchar();
putchar(ch);
if (ch == '\n')
{
printf ("\nString was not closed ");
printf ("before end of line\n");
break;
}
}
while (ch != '"')
{
}
return (ch);
}
3. for语句
(1) 一般形式
(2) 流程图
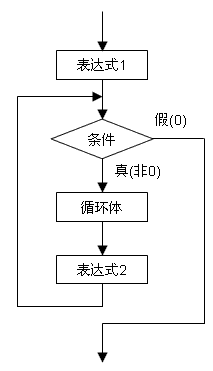
(3) 例子
/************************************************/
/* */
/* Prime Number Generator #1 */
/* */
/************************************************/
/* Check for prime number by raw number */
/* crunching. Try divid
4000
ing all numbers */
/* up to half the size of a given i, if */
/* remainder == 0 then not prime! */
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXINT 500
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
/*************************************************/
/* Level 0 */
/*************************************************/
main ()
{
int i;
for (i = 2; i <= MAXINT; i++)
{
if (prime(i))
{
printf ("%5d",i);
}
}
}
/*************************************************/
/* Level 1 */
/*************************************************/
prime (i) /* check for a prime number */
int i;
{
int j;
for (j = 2; j <= i/2; j++)
{
if (i % j == 0)
{
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
三、打断循环
1. break语句
(1) 说明
break语句的作用是跳出整个循环。如有嵌套的循环,则跳出最近的循环体。
(2) 例子
2. continue语句
(1) 说明
continue语句的作用是跳出一次循环,即忽略continue后面的其它语句,紧接着执行下一次循环。
(2) 例子
一、决策语句
1. if语句
(1) 一般形式
if (condition) statement;
or
if (condition)
{
compound statement
}(2) 流程图和交通图


(3) 例子
#include <stdio.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
main ()
{
int i;
if (TRUE)
{
printf ("This is always printed");
}
if (FALSE)
{
printf ("This is never printed");
}
}2. if-else语句
(1) 一般形式
if (condition) statement1; else statement2;
or
if (condition)
{
statements
}
else
{
statements
}(2) 流程图和交通图


(3) 例子
#include <stdio.h>
main ()
{
int i;
scanf ("%ld",i);
if (i > 0)
{
printf ("That number was positive!");
}
else
{
printf ("That number was negative or zero!");
}
}
3. switch语句
(1) 一般形式
switch (int or char expression)
{
case constant expression 1 : statement 1;
break; /* optional */
case constant expression 2 : statement 2;
break; /* optional */
case constant expression n : statement n;
break; /* optional */
default : default statement;
break;
}(2) 语句说明
对于switch条件语句,如果找到相同的结果值则执行case内的程序语句,当执行完case块后,并不会直接离开switch块,还是会住下继续执行其他case语句和default语句,这种情形称为“失败经过”(Falling Through)现象。
因此,每一道case语句最后,必须加上break语句来结束switch语句,才可以避免“失败经过”的情况。default语句可放在switch条件语句的任何位置,如果找不到吻合的结果值,最后会执行default语句,除非摆在最后时,才可以省略default语句内的break语句,否则还是必须加上break语句。
(3) 例子
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
switch(i)
{
default: printf("%d", i);
case 1: printf("%d", i); break;
case 2: printf("%d", i);
}
}
return 0;
}二、循环语句
1. while语句
(1) 一般形式
while (condition)
{
statements;
}(2) 流程图

(3) 例子
/* count all the spaces in an line of input */
#include <stdio.h>
main ()
{
char ch;
short count = 0;
printf ("Type in a line of text\n");
while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n')
{
if (ch == ' ')
{
count++;
}
}
printf ("Number of space = %d\n",count);
}2. do-while语句
(1) 一般形式
do
{
statements;
}
while (condition)(2) 流程图

(3) 例子
/**********************************************/
/* */
/* do .. while demo */
/* */
/**********************************************/
/* print a string enclosed by quotes " " */
/* gets input from stdin i.e. keyboard */
/* skips anything outside the quotes */
#include <stdio.h>
/*************************************************/
/* Level 0 */
/*************************************************/
main ()
{
char ch,skipstring();
do
{
if ((ch = getchar()) == '"')
{
printf ("The string was:\n");
ch = skipstring();
}
}
while (ch != '\n')
{
}
}
/*************************************************/
/* Level 1 */
/*************************************************/
char skipstring () /* skip a string "" */
{
char ch;
do
{
ch = getchar();
putchar(ch);
if (ch == '\n')
{
printf ("\nString was not closed ");
printf ("before end of line\n");
break;
}
}
while (ch != '"')
{
}
return (ch);
}
3. for语句
(1) 一般形式
for (expression1; condition; expression2)
{
}(2) 流程图

(3) 例子
/************************************************/
/* */
/* Prime Number Generator #1 */
/* */
/************************************************/
/* Check for prime number by raw number */
/* crunching. Try divid
4000
ing all numbers */
/* up to half the size of a given i, if */
/* remainder == 0 then not prime! */
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXINT 500
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
/*************************************************/
/* Level 0 */
/*************************************************/
main ()
{
int i;
for (i = 2; i <= MAXINT; i++)
{
if (prime(i))
{
printf ("%5d",i);
}
}
}
/*************************************************/
/* Level 1 */
/*************************************************/
prime (i) /* check for a prime number */
int i;
{
int j;
for (j = 2; j <= i/2; j++)
{
if (i % j == 0)
{
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
三、打断循环
1. break语句
(1) 说明
break语句的作用是跳出整个循环。如有嵌套的循环,则跳出最近的循环体。
(2) 例子
/* an expensive way of assigning i to be 12 would be: */
for (i = 1; i <= 20; i++)
{
if (i == 12)
{
break;
}
}
/* another way of making skipgarb() */
while (TRUE)
{
ch = getchar();
if (ch == '\n')
{
break;
}
}2. continue语句
(1) 说明
continue语句的作用是跳出一次循环,即忽略continue后面的其它语句,紧接着执行下一次循环。
(2) 例子
/* to avoid dividing by zero */
for (i = -10; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
continue;
}
printf ("%d", 20/i);
}
相关文章推荐
- C语言的9种控制语句
- C语言学习之控制语句
- 【C语言学习】《C Primer Plus》第6章 C控制语句:循环
- C语言-流程控制语句
- C语言学习十流程控制的学习之分支语句
- c语言控制语句对应的汇编语句代码
- [黑马程序员]09[C语言]循环控制语句部分学习笔记总结
- C语言的组成:32个关键词、9种控制语句、34种运算符
- 【C语言】C语言32个关键字简介和9种控制语句
- C语言学习之控制语句
- C语言的32个关键字和9种控制语句
- C语言流程控制语句的反汇编分析
- C语言的控制语句(4.23)
- C语言语句及流程控制
- C语言的32个关键字和9种控制语句
- C语言 流程控制语句
- C语言的控制语句
- 三 C语言流程控制语句
- 黑马程序员——C语言——循环控制语句
- Swift 中的switch 等控制语句与C语言 中区别
