C++ 数据结构链表的实现代码
2017-01-18 12:31
387 查看
C++ 链表
之前一直没怎么在意C++中的链表,但是突然一下子让自己写,就老是出错。没办法,决定好好恶补一下该方面的知识,也为今后的数据结构打下个良好的基础,于是我总结出以下几点,有些地方可能不正确,还望大家不吝赐教,旨在共同进步。总结:
1、链表List的基本单元是节点Node,因此想要操作方便,就必须为每一步打好基础,Node的基本结构如下:class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node(int da = 0, Node *p = NULL) {
this->data = da;
this->next = p;
}
};我们可以看出,Node的成员变量一共有两个,都是public,因为我们要对这两个变量进行操作,所以不能是private类型的。然后是一个构造函数,第二个参数默认值为NULL,也就是说如果我们创建新节点时只指定第一个参数,而不写第二个参数,那么它默认的就是NULL,以这种方式可以更灵活的使用Node,个人建议这么使用哦。
2、第二步就是创建我们的链表了,同样我们这里先给出链表的代码,再进行一一的解释。
class List{
private:
Node *head,*tail;
int position;
public:
List(){head=tail=NULL;};
~List(){delete head;delete tail;};
void print();
void Insert(int da=0);
void Delete(int da=0);
void Search(int da=0);
};我们这里面有两个数据类型,一个是Node。另一个是指代节点位置的成员变量(起不到什么作用,且不去管它吧)。使用head和tail来命名便是为了见名知意,使操作更加准确。然后是重要的六个函数,各自的功能不言而喻咯,其实最重要的是在每一个函数中我们都默认能操作head和tail两个成员变量,这样能简化我们的参数列表,使得函数更加优雅。
下面是我的一个单链表的实现,包含创建链表,插入值,删除特定的值,查找特定值得在链表中的位置。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int da = 0, Node *p = NULL) { this->data = da; this->next = p; } };
class List {
private:
Node *head, *tail;
int position;
public:
List() { head = tail = NULL; };
~List() {
delete head;
delete tail;
};
void print();
void Insert(int da = 0);
void Delete(int da = 0);
void Search(int da = 0);
int getValueAt(int position);
void setValueAt(int position, int da);
};
int List::getValueAt(int position) {
Node *p = head;
if (p == NULL) {
cout << "The List is Empty!" << endl;
} else {
int posi = 0;
while (p != NULL && posi != position) {
posi++;
p = p->next;
}
if (p == NULL) {
cout << "There is no value of this position in this List!" << endl;
} else {
cout << "In this Position,the value is" << p->data << endl;
}
}
return p->data;
}
void List::setValueAt(int position, int da) {
Node *p = head;
if (p == NULL) {
cout << "The List is Empty!" << endl;
} else {
int posi = 0;
while (p != NULL && posi != position) {
posi++;
p = p->next;
}
if (p == NULL) {
cout << "There is No Position in this List!" << endl;
} else {
p->data = da;
cout << "The Value in this position has been Updated!" << endl;
}
}
}
void List::Search(int da) {
Node *p = head;
if (p == NULL) {
cout << "Sorry, The List is Empty!" << endl;
return;
}
int count = 0;
while (p != NULL && p->data != da) {
p = p->next;
count++;
}
cout << "the value you want to search is at position %d" << count << endl;
}
void List::Delete(int da) {
Node *p = head, *q = head;
if (p == NULL) {
cout << "Sorry, The List is Empty!" << endl;
return;
}
while (p != NULL && p->data != da) {
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
q->next = p->next;
cout << "The Deletion Operation had been finished!" << endl;
}
void List::Insert(int da) {
if (head == NULL) {
head = tail = new Node(da);
head->next = NULL;
tail->next = NULL;
} else {
Node *p = new Node(da);
tail->next = p;
tail = p;
tail->next = NULL;
}
}
void List::print() {
Node *p = head;
while (p != NULL) {
cout << p->data << " \a";
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
List l1;
l1.Insert(1);
l1.Insert(2);
l1.Insert(3);
l1.Insert(4);
l1.Insert(5);
l1.Insert(6);
l1.Insert(7);
l1.print();
l1.Search(4);
l1.Delete(6);
l1.print();
l1.getValueAt(3);
l1.setValueAt(3, 9);
l1.print();
cout << "The End!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
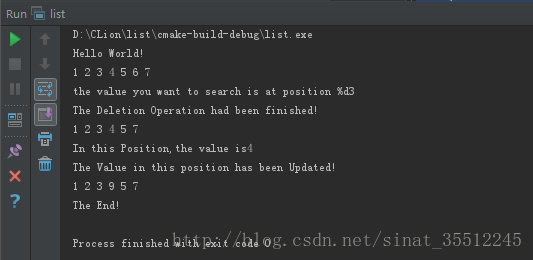
相关文章推荐
- [C++]数据结构:有序链表SortedChain的基本实现与操作
- 数据结构_队列_用链表动态建立释放节点实现队列各种操作_C++实现
- C++实现数据结构四 单循环链表
- 【数据结构】用C++实现单循环链表的各种操作(包括头删,尾删,插入,逆序,摧毁,清空等等)
- C++实现数据结构中的单链表
- 数据结构学习系列二-链表的C++实现
- 【C++数据结构学习笔记---线性表】用单链表实现线性表
- C/C++基本数据结构:链表的基本使用和实现
- 严版数据结构 第29页 单链表 C++实现
- 通讯录实现代码 C++ 链表
- 数据结构_链表_稀疏多项式求值_C++实现
- C++类模板 实现双向循环链表的基本算法 《数据结构》(C++版 北京科海)中摘抄
- 数据结构_串_用链表做存储结构实现KMP算法_C++实现
- C++数据结构--单向循环链表(实现头插法,尾插法)
- 用单链表实现一元多项式相加 C++代码
- 数据结构_链表_多项式求导_C++实现
- 线索链表的实现 C++代码实现
- 用一段代码实现一个链表倒序(C++实现)
- C++链表AT&T代码,通过Ubuntu实现生成(Linux内核分析笔记)
- 数据结构 链表的lua实现 仿照C++中list 实现
