Java文本读写
2016-12-04 09:44
399 查看
1、我们一般以行的方式来读取文本文件的
下面是用例: BufferedReader/BufferedWriter
读:

写:
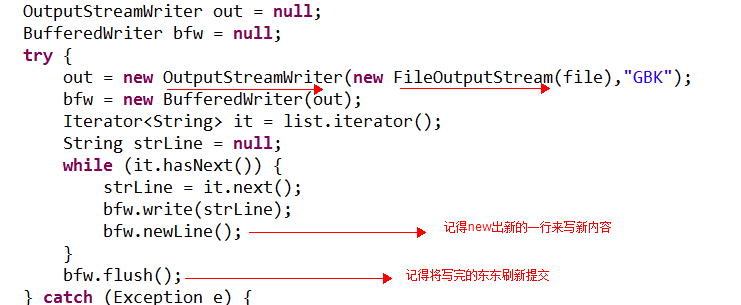
out = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file),”GBK”);
bfw = new BufferWriter(out);
源文件中的编码方式为UTF-8,输出时也为UTF-8,结果输出乱码,问题出在FileReader读取文件的
程中,FileReader继承了InputStreamReader,但并没有实现父类中带字符集参数的构造函数。
所以FileReader只能按系统默认的字符集来解码,然后在UTF-8 -> GBK -> UTF-8的过程中编码出现损
失,造成结果不能还原最初的字符。
原因明确了,这个问题解决起来并不困难,用InputStreamReader代替FileReader,
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName),”UTF-8”);
这样读取文件就会直接用UTF-8解码,不用再做编码转换。
例如:
读:
/**
* 将文本中的数据解析到ArrayList中
* @param fileName 文件名:全路径
* @return 解析后的List数据集
*/
public static ArrayList fileData2List(String fileName) {
BufferedReader bfr = null;
InputStreamReader in = null;
String encoding = “GBK”;
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
try {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (file.isFile() && file.exists()) {
in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), encoding);
bfr = new BufferedReader(in);
String line = null;
while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) {
if(!StringUtils.isBlank(line))
arrayList.add(line);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return arrayList;
}
下面是用例: BufferedReader/BufferedWriter
读:

写:

out = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file),”GBK”);
bfw = new BufferWriter(out);
源文件中的编码方式为UTF-8,输出时也为UTF-8,结果输出乱码,问题出在FileReader读取文件的
程中,FileReader继承了InputStreamReader,但并没有实现父类中带字符集参数的构造函数。
所以FileReader只能按系统默认的字符集来解码,然后在UTF-8 -> GBK -> UTF-8的过程中编码出现损
失,造成结果不能还原最初的字符。
原因明确了,这个问题解决起来并不困难,用InputStreamReader代替FileReader,
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName),”UTF-8”);
这样读取文件就会直接用UTF-8解码,不用再做编码转换。
例如:
读:
/**
* 将文本中的数据解析到ArrayList中
* @param fileName 文件名:全路径
* @return 解析后的List数据集
*/
public static ArrayList fileData2List(String fileName) {
BufferedReader bfr = null;
InputStreamReader in = null;
String encoding = “GBK”;
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
try {
File file = new File(fileName);
if (file.isFile() && file.exists()) {
in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), encoding);
bfr = new BufferedReader(in);
String line = null;
while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) {
if(!StringUtils.isBlank(line))
arrayList.add(line);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return arrayList;
}
相关文章推荐
- java对世界各个时区(TimeZone)的通用转换处理方法(转载)
- java-注解annotation
- java-模拟tomcat服务器
- java-用HttpURLConnection发送Http请求.
- java-WEB中的监听器Lisener
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- Debian 7.x 安装Oracle JAVA
- springmvc实现url路由功能
- spring boot 配置 druid/** * 配置druid * Created by adam on 4/11/16. */ @Configuration public class D
- api接口rsa加密
- 介绍一款信息管理系统的开源框架---jeecg
- 聚类算法之kmeans算法java版本
- java实现 PageRank算法
- PropertyChangeListener简单理解
