Spring4深入理解01----Bean配置
2016-11-18 17:34
232 查看
参考代码下载github:https://github.com/changwensir/java-ee/tree/master/spring4
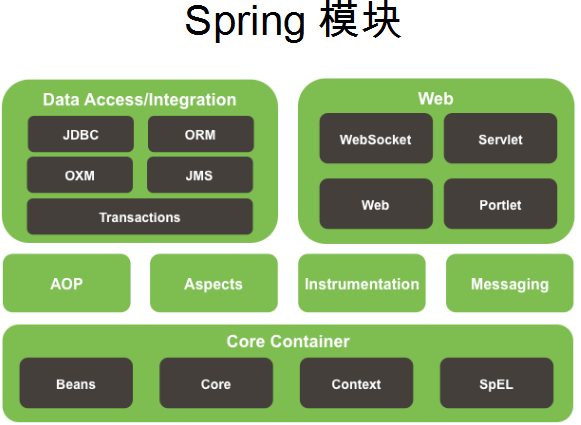
Spring是什么?
Spring 是一个开源框架.
Spring 为简化企业级应用开发而生.
使用 Spring 可以使简单的 JavaBean 实现以前只有 EJB 才能实现的功能.
Spring 是一个 IOC(DI) 和 AOP 容器框架.
具体描述 Spring:
--轻量级:Spring 是非侵入性的 - 基于 Spring 开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于
Spring 的API
--依赖注入(DI --- dependency injection、IOC)
--面向切面编程(AOP --- aspect oriented programming)
--容器: Spring 是一个容器, 因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期
--框架: Spring 实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用. 在 Spring
中可以使用 XML 和 Java 注解组合这些对象
--一站式:在 IOC 和 AOP 的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库
(实际上 Spring 自身也提供了展现层的 SpringMVC 和 持久层的 Spring JDBC)
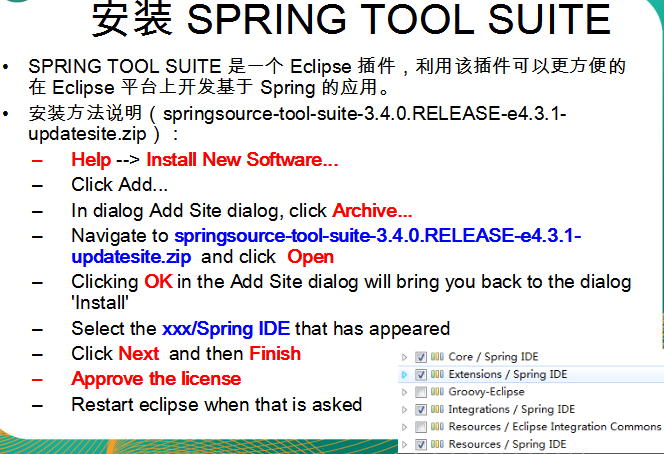
只要后面是Spring IDE就行了
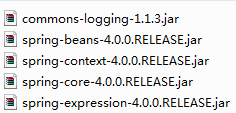
把以下 jar 包加入到工程的 classpath 下:
Spring 的配置文件: 一个典型的 Spring 项目需要创建一个或多个 Bean 配置文件, 这些配置文件用于在 Spring IOC 容器里配置 Bean. Bean 的配置文件可以放在 classpath 下, 也可以放在其它目录下
IOC(Inversion of Control):其思想是反转资源获取的方向. 传统的资源查找方式要求组件向容器发起请求查找资源. 作为回应, 容器适时的返回资源. 而应用了 IOC 之后, 则是容器主动地将资源推送给它所管理的组件, 组件所要做的仅是选择一种合适的方式来接受资源. 这种行为也被称为查找的被动形式
DI(Dependency Injection) — IOC 的另一种表述方式:即组件以一些预先定义好的方式(例如: setter 方法)接受来自如容器的资源注入. 相对于 IOC 而言,这种表述更直接
配置 bean
--配置形式:基于 XML 文件的方式;基于注解的方式
--Bean 的配置方式:通过全类名(反射)、通过工厂方法(静态工厂方法 & 实例工厂方法)、FactoryBean
--IOC 容器 BeanFactory & ApplicationContext 概述
--依赖注入的方式:属性注入;构造器注入
--注入属性值细节
--自动转配
--bean 之间的关系:继承;依赖
--bean 的作用域:singleton;prototype;WEB 环境作用域
--使用外部属性文件
--spEL
--IOC 容器中 Bean 的生命周期
--Spring 4.x 新特性:泛型依赖注入
在 IOC 容器中必须是唯一的
若 id 没有指定,Spring 自动将权限定性类名作为 Bean 的名字
id 可以指定多个名字,名字之间可用逗号、分号、或空格分隔
1-1-1.IOC 容器
在 Spring IOC 容器读取 Bean 配置创建 Bean 实例之前, 必须对它进行实例化. 只有在容器实例化后, 才可以从 IOC 容器里获取 Bean 实例并使用.
Spring 提供了两种类型的 IOC 容器实现.
--BeanFactory: IOC 容器的基本实现.
--ApplicationContext: 提供了更多的高级特性. 是 BeanFactory 的子接口.
--BeanFactory 是 Spring 框架的基础设施,面向 Spring 本身;ApplicationContext 面向使用 Spring 框架的开发者,几乎所有的应用场合都直接使用 ApplicationContext 而非底层的 BeanFactory
--无论使用何种方式, 配置文件时相同的.
ApplicationContext
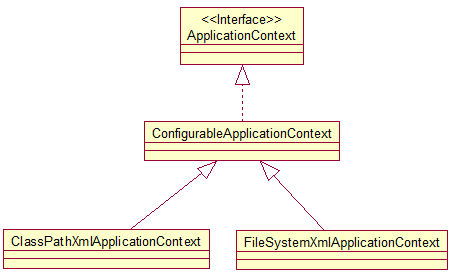
ApplicationContext 的主要实现类:
--ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从 类路径下加载配置文件
--FileSystemXmlApplicationContext: 从文件系统中加载配置文件
ConfigurableApplicationContext 扩展于 ApplicationContext,新增加两个主要方法:refresh() 和 close(), 让 ApplicationContext 具有启动、刷新和关闭上下文的能力
ApplicationContext 在初始化上下文时就实例化所有单例的 Bean。
WebApplicationContext 是专门为 WEB 应用而准备的,它允许从相对于 WEB 根目录的路径中完成初始化工作
1-1-2.依赖注入的方式
Spring 支持 3 种依赖注入的方式
--属性注入
--构造器注入
--工厂方法注入(很少使用,不推荐)
1).属性注入
属性注入即通过 setter 方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象
属性注入使用 <property> 元素, 使用 name 属性指定 Bean 的属性名称,value 属性或 <value> 子节点指定属性值
属性注入是实际应用中最常用的注入方式
在applicationContext.xml
通过构造方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了 Bean 实例在实例化后就可以使用。
构造器注入在 <constructor-arg> 元素里声明属性, <constructor-arg> 中没有 name 属性
基本数据类型及其封装类、String 等类型都可以采取字面值注入的方式
若字面值中包含特殊字符,可以使用 <![CDATA[]]> 把字面值包裹起来。
3).注入属性值细节
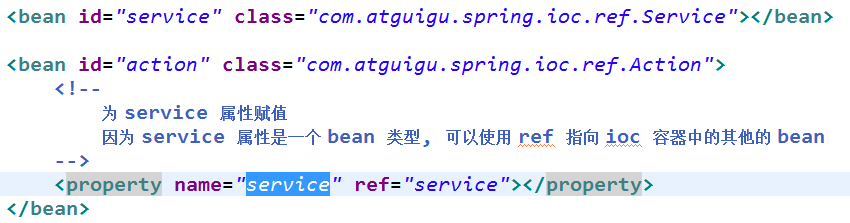
引用其它 Bean
组成应用程序的 Bean 经常需要相互协作以完成应用程序的功能. 要使 Bean 能够相互访问,
就必须在 Bean 配置文件中指定对 Bean 的引用
在 Bean 的配置文件中, 可以通过 <ref> 元素或 ref 属性为 Bean
的属性或构造器参数指定对 Bean 的引用.
也可以在属性或构造器里包含 Bean 的声明, 这样的 Bean 称为内部 Bean
内部Bean
--当 Bean 实例仅仅给一个特定的属性使用时, 可以将其声明为内部 Bean. 内部
Bean 声明直接包含在 <property> 或 <constructor-arg> 元素里, 不需要设置任何 id 或 name 属性
--内部 Bean 不能使用在任何其他地方
注入参数详解:null 值和级联属性
--可以使用专用的 <null/> 元素标签为 Bean 的字符串或其它对象类型的属性注入 null 值,意义不大
--和 Struts、Hiberante 等框架一样,Spring 支持级联属性的配置,例如在xml文件里设置Car.price
Spring是什么?
Spring 是一个开源框架.
Spring 为简化企业级应用开发而生.
使用 Spring 可以使简单的 JavaBean 实现以前只有 EJB 才能实现的功能.
Spring 是一个 IOC(DI) 和 AOP 容器框架.
具体描述 Spring:
--轻量级:Spring 是非侵入性的 - 基于 Spring 开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于
Spring 的API
--依赖注入(DI --- dependency injection、IOC)
--面向切面编程(AOP --- aspect oriented programming)
--容器: Spring 是一个容器, 因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期
--框架: Spring 实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用. 在 Spring
中可以使用 XML 和 Java 注解组合这些对象
--一站式:在 IOC 和 AOP 的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库
(实际上 Spring 自身也提供了展现层的 SpringMVC 和 持久层的 Spring JDBC)


只要后面是Spring IDE就行了
把以下 jar 包加入到工程的 classpath 下:

Spring 的配置文件: 一个典型的 Spring 项目需要创建一个或多个 Bean 配置文件, 这些配置文件用于在 Spring IOC 容器里配置 Bean. Bean 的配置文件可以放在 classpath 下, 也可以放在其它目录下
一、IOC 和 DI
IOC(Inversion of Control):其思想是反转资源获取的方向. 传统的资源查找方式要求组件向容器发起请求查找资源. 作为回应, 容器适时的返回资源. 而应用了 IOC 之后, 则是容器主动地将资源推送给它所管理的组件, 组件所要做的仅是选择一种合适的方式来接受资源. 这种行为也被称为查找的被动形式DI(Dependency Injection) — IOC 的另一种表述方式:即组件以一些预先定义好的方式(例如: setter 方法)接受来自如容器的资源注入. 相对于 IOC 而言,这种表述更直接
配置 bean
--配置形式:基于 XML 文件的方式;基于注解的方式
--Bean 的配置方式:通过全类名(反射)、通过工厂方法(静态工厂方法 & 实例工厂方法)、FactoryBean
--IOC 容器 BeanFactory & ApplicationContext 概述
--依赖注入的方式:属性注入;构造器注入
--注入属性值细节
--自动转配
--bean 之间的关系:继承;依赖
--bean 的作用域:singleton;prototype;WEB 环境作用域
--使用外部属性文件
--spEL
--IOC 容器中 Bean 的生命周期
--Spring 4.x 新特性:泛型依赖注入
1-1.基于 XML 文件的方式配置 bean
public class HelloWorldBean {
private String user;
public HelloWorldBean() {
System.out.println("HelloWorldBean's constructor...");
}
// 如果这里修改为setUser2,刚applicationContext.xml修改为property name="user2"
public void setUser(String user) {
System.out.println("setUser:" + user);
this.user = user;
}
public HelloWorldBean(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("Hello: " + user);
}
}applicationContext.xml的关键内容如下:<!-- 通过全类名配置一个 bean, class:bean的全类名!,是Spring通过反射的方式在IOC容器中创建Bean(对象), 所有Bean一定要有无参的构造器!!! id:标识容器中的Bean,id是唯一的,建议用类名小写 property name:对应setter方法(public void setUser(String user) value:就是setter赋的值)--> <bean id="helloWorld" class="Spring4_IOC.bean.HelloWorldBean"> <property name="user" value="Tom"/> </bean>id:Bean 的名称。
在 IOC 容器中必须是唯一的
若 id 没有指定,Spring 自动将权限定性类名作为 Bean 的名字
id 可以指定多个名字,名字之间可用逗号、分号、或空格分隔
@Test
public void testHelloWorld() {
// 前两行可以用Spring来实现
// HelloWorldBean helloWorldBean = new HelloWorldBean();
// helloWorldBean.setUser("Tom");
// helloWorldBean.hello();
//1. 创建 Spring 的 IOC 容器(ApplicationContext代表Spring 的 IOC 容器)
//创建的时候会先调用无参构造器,同时会调用 setter方法对属性赋值!!
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Spring4_IOC/applicationContext.xml");
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//2. 从 IOC 容器中的id获取 bean 的实例,如果为“helloWorld2”,则bean id="helloWorld2"
HelloWorldBean helloWorldBean = (HelloWorldBean) ctx.getBean("helloWorld");
//根据类型来获取 bean 的实例: 要求在 IOC 容器中只有一个与之类型匹配的 bean, 若有多个则会抛出异常.
//一般情况下, 该方法可用, 因为一般情况下, 在一个 IOC 容器中一个类型对应的 bean 也只有一个.
// HelloWorldBean helloWorld1 = ctx.getBean(HelloWorldBean.class);
//3. 使用 bean
helloWorldBean.hello();
}| HelloWorldBean's constructor... setUser:Tom ------------------------------ Hello: Tom |
在 Spring IOC 容器读取 Bean 配置创建 Bean 实例之前, 必须对它进行实例化. 只有在容器实例化后, 才可以从 IOC 容器里获取 Bean 实例并使用.
Spring 提供了两种类型的 IOC 容器实现.
--BeanFactory: IOC 容器的基本实现.
--ApplicationContext: 提供了更多的高级特性. 是 BeanFactory 的子接口.
--BeanFactory 是 Spring 框架的基础设施,面向 Spring 本身;ApplicationContext 面向使用 Spring 框架的开发者,几乎所有的应用场合都直接使用 ApplicationContext 而非底层的 BeanFactory
--无论使用何种方式, 配置文件时相同的.
ApplicationContext

ApplicationContext 的主要实现类:
--ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从 类路径下加载配置文件
--FileSystemXmlApplicationContext: 从文件系统中加载配置文件
ConfigurableApplicationContext 扩展于 ApplicationContext,新增加两个主要方法:refresh() 和 close(), 让 ApplicationContext 具有启动、刷新和关闭上下文的能力
ApplicationContext 在初始化上下文时就实例化所有单例的 Bean。
WebApplicationContext 是专门为 WEB 应用而准备的,它允许从相对于 WEB 根目录的路径中完成初始化工作
1-1-2.依赖注入的方式
Spring 支持 3 种依赖注入的方式
--属性注入
--构造器注入
--工厂方法注入(很少使用,不推荐)
1).属性注入
属性注入即通过 setter 方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象
属性注入使用 <property> 元素, 使用 name 属性指定 Bean 的属性名称,value 属性或 <value> 子节点指定属性值
属性注入是实际应用中最常用的注入方式
在applicationContext.xml
<!-- Spring 支持 3 种依赖注入的方式 属性注入(最常用) 构造器注入 工厂方法注入(很少使用,不推荐)--> <bean id="helloWorld2" class="Spring4_IOC.bean.HelloWorldBean"> <!-- 为属性赋值 --> <!-- 通过属性注入: 通过 setter 方法注入属性值 如setUser() --> <property name="user" value="Tom2"/> </bean> <!-- 通过构造器注入属性值 --> <bean id="helloWorld3" class="Spring4_IOC.bean.HelloWorldBean"> <!-- 要求: 在 Bean 中必须有对应的构造器.(public HelloWorldBean(String user)) --> <constructor-arg value="Mike"/> </bean>2).构造方法注入
通过构造方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了 Bean 实例在实例化后就可以使用。
构造器注入在 <constructor-arg> 元素里声明属性, <constructor-arg> 中没有 name 属性
public class Car {
private String company;
private String brand;
private int maxSpeed;
private float price;
public Car() {
}
public Car(String brand, float price) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public CarCycle(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
this.price = price;
}
//省去get,set方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CarCycle [company=" + company + ", brand=" + brand + ", maxSpeed="
+ maxSpeed + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}<!-- 默认是按顺序配置的(个数), 若一个 bean 有多个构造器, 则还需要通过参数的类型来配置,如car2 --> <!-- 可以根据 index 和 value 进行更加精确的定位. (了解) --> <bean name="car" class="Spring4_IOC.bean.Car"> <constructor-arg value="KUGA" index="0"/> <constructor-arg value="ChangAnFord" index="1"/> <constructor-arg value="250000" type="float"/> </bean> <bean id="car2" class="Spring4_IOC.bean.Car"> <!--最好设置参数类型--> <constructor-arg value="ChangAnMazda" type="java.lang.String"/> <!-- 若字面值中包含特殊字符, 则可以使用 CDATA 来进行赋值. (了解) --> <constructor-arg value="ShangHai" type="java.lang.String"/> <!--value里的字符为<ShangHai> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String"> <value><![CDATA[<ShangHai>]]></value> </constructor-arg>--> <constructor-arg value="180" type="int"/> <!-- 上面也可以用这个代替 <constructor-arg type="int"> <value>180</value> </constructor-arg>--> <!-- 测试null,没有什么意义,因为属性本来就是null。<null/>的专有标记 <constructor-arg ><null/> </constructor-arg> --> </bean>字面值:可用字符串表示的值,可以通过 <value> 元素标签或 value 属性进行注入。
基本数据类型及其封装类、String 等类型都可以采取字面值注入的方式
若字面值中包含特殊字符,可以使用 <![CDATA[]]> 把字面值包裹起来。
/***********
* Bean 的配置方式:-、通过全类名(反射);二、通过工厂方法(静态工厂方法 & 实例工厂方法);三、FactoryBean
*
* 配置Bean:配置方式:通过全类名(反射)***************/
//测试依赖注入
@Test
public void testDependencyInjection() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Spring4_IOC/applicationContext.xml");
Car car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car");
System.out.println("1-->"+car);
//测试car里有多个构造器,如何配置IOC
Car car2 = (Car) ctx.getBean("car2");
System.out.println("2-->"+car2);
}| 1-->CarCycle [company=KUGA, brand=ChangAnFord, maxSpeed=0, price=250000.0] 2-->CarCycle [company=ChangAnMazda, brand=ShangHai, maxSpeed=180, price=0.0] |
引用其它 Bean
组成应用程序的 Bean 经常需要相互协作以完成应用程序的功能. 要使 Bean 能够相互访问,
就必须在 Bean 配置文件中指定对 Bean 的引用
在 Bean 的配置文件中, 可以通过 <ref> 元素或 ref 属性为 Bean
的属性或构造器参数指定对 Bean 的引用.
也可以在属性或构造器里包含 Bean 的声明, 这样的 Bean 称为内部 Bean
<bean id="person" class="Spring4_IOC.bean.Person"> <property name="name" value="changwen"/> <property name="age" value="24"/> <!-- 可以使用property的ref 属于建立bean之间的引用关系。--> <property name="car" ref="car2"/> <!-- 也可以这么写 <property name="car"> <ref bean="car2"/> </property> --> <!-- 还能用内部bean,这个bean不能被外部引用,只能在内部使用 <property name="car"> <bean class="Spring4_IOC.bean.CarCycle"> <constructor-arg value="KUGA" type="java.lang.String"/> <constructor-arg value="ChangAnFord" type="java.lang.String"/> <constructor-arg value="180" type="int"/> </bean> </property> --> </bean>

内部Bean
--当 Bean 实例仅仅给一个特定的属性使用时, 可以将其声明为内部 Bean. 内部
Bean 声明直接包含在 <property> 或 <constructor-arg> 元素里, 不需要设置任何 id 或 name 属性
--内部 Bean 不能使用在任何其他地方
注入参数详解:null 值和级联属性
--可以使用专用的 <null/> 元素标签为 Bean 的字符串或其它对象类型的属性注入 null 值,意义不大
--和 Struts、Hiberante 等框架一样,Spring 支持级联属性的配置,例如在xml文件里设置Car.price
相关文章推荐
- Spring4深入理解01----Bean配置(依赖注入和控制反转的区别)
- Spring4深入理解01----Bean配置(依赖注入和控制反转的区别)
- Spring4深入理解01----Bean配置(依赖注入和控制反转的区别)
- Spring4深入理解IOC&DI04----Bean配置方式(全类名,工厂方法,FactoryBean),配置形式(基于XML和注解),泛型依赖注入
- Spring4深入理解----事务(声明式事务和xml配置事务,事务传播属性,事务其他属性(隔离级别&回滚&只读&过期))
- Spring4深入理解IOC&DI02----Bean配置--自动装配、bean之间的继承与依赖、使用外部属性文件
- 7.10.2: 深入理解依赖关系配置---注入其他Bean的Field值
- Spring4深入理解AOP02----AOP简介,AspectJ,AOP基于注解和XML配置(5种通知,切面优先级)
- Spring4深入理解----事务(声明式事务和xml配置事务,事务传播属性,事务其他属性(隔离级别&回滚&只读&过期))
- Spring4深入理解IOC&DI03----Bean配置--SpEL,IOC 容器中 Bean 的生命周期
- 7.10.3: 深入理解依赖关系配置---注入其他bean的方法返回值
- 7.10.1: 深入理解依赖关系配置---注入其他Bean的属性值
- 深入理解软件包的配置、编译与安装【转】
- 【转】C RunTime Library 暨 深入理解编译选项的含义 - 01
- <jsp:useBean />及相关动作深入理解
- [转]深入理解软件包的配置、编译与安装
- 深入理解软件包的配置、编译与安装
- make makefile 深入理解软件包的配置、编译与安装
- 深入理解 GNU GRUB - 01
- 深入理解软件包的配置、编译与安装[转]
