从零开始学C++之RTTI、dynamic_cast、typeid、类与类之间的关系uml
2016-10-26 09:05
459 查看
一、RTTI
Run-time type information (RTTI) is a mechanism that allows the type of an object to be determined during program execution.
There are three main C++ language elements to run-time type information:
The dynamic_cast operator.
Used for conversion of polymorphic types.
The typeid operator.
Used for identifying the exact type of an object.
The type_info class.
Used to hold the type information returned by the typeid operator.
The result of typeid is a const type_info&. The value is a reference to a type_info object that represents either the type-id or the type of the expression, depending on which form of typeid is used.
为了支持RTTI,为每一个多态类创建一个type_info 对象(静态数据区),并把其地址保存到vtable中的固定位置(一般为第一个位置)(取决于具体编译器实现,标准并没有规定)。
如上所述,dynamic_cast 和 typeid 操作符 都可以实现运行时类型识别。其中使用dynamic_cast 时需要开启运行时类型信息,在项目-》属性-》C/C++-》语言-》启用运行时类型信息。在使用typeid时需要注意的是返回的是type_info 对象的引用,且type_info 类的拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符都声明为私有,故不能这样写: type_info tf = typeid(Circle);
二、类与类之间的关系
Unified Modeling Language (UML)又称统一建模语言或标准建模语言,是始于1997年一个OMG标准,它是一个支持模型化和软件系统开发的图形化语言。
1、继承(泛化)Generalization
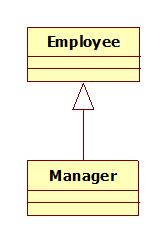
Manager 继承自Employee.
2、关联 Association,单向关联 DirectedAssociation
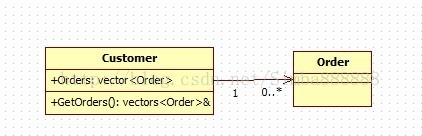
Order 作为Customer 的成员,如vector orders ;
3、聚合 Aggregation
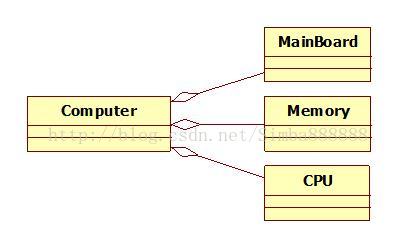
当A释放时,不负责B的释放,也许B是被共享的。
4、组合 Composition

当Company 释放时要负责Department 的释放,Department 不是共享的。
5、依赖 Dependency
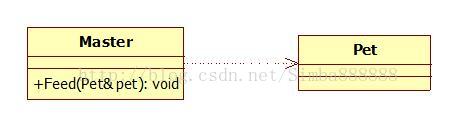
类A依赖于B:
从语义上来上是A use B,偶然的,临时的
B作为A的成员函数参数
B作为A的成员函数的局部变量
A的成员函数调用B的静态方法
比较5种关系:
继承体现的是类与类之间的纵向关系,其他4种体现的是类与类之间的横向关系。
关联强弱
依赖<关联<聚合<组合
继承(A is B)
关联、聚合、组合(A has B)
依赖(A use B)
参考:
C++ primer 第四版
Effective C++ 3rd
C++编程规范
转载自http://blog.csdn.net/jnu_simba/article/details/9320275
Run-time type information (RTTI) is a mechanism that allows the type of an object to be determined during program execution.
There are three main C++ language elements to run-time type information:
The dynamic_cast operator.
Used for conversion of polymorphic types.
The typeid operator.
Used for identifying the exact type of an object.
The type_info class.
Used to hold the type information returned by the typeid operator.
class type_info {
public:
virtual ~type_info();
bool operator==(const type_info& rhs) const;
bool operator!=(const type_info& rhs) const;
int before(const type_info& rhs) const;
const char* name() const;
const char* raw_name() const;
private:
void *_m_data;
char _m_d_name[1];
type_info(const type_info& rhs);
type_info& operator=(const type_info& rhs);
static const char _Name_base(const type_info *,__type_info_node* __ptype_info_node);
};The result of typeid is a const type_info&. The value is a reference to a type_info object that represents either the type-id or the type of the expression, depending on which form of typeid is used.
为了支持RTTI,为每一个多态类创建一个type_info 对象(静态数据区),并把其地址保存到vtable中的固定位置(一般为第一个位置)(取决于具体编译器实现,标准并没有规定)。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
public:
virtual void Draw() = 0;
virtual ~Shape() {}
};
class Circle : public Shape
{
public:
void Draw()
{
cout << "Circle Draw ..." << endl;
}
};
class Square : public Shape
{
public:
void Draw()
{
cout << "Square Draw ..." << endl;
}
};
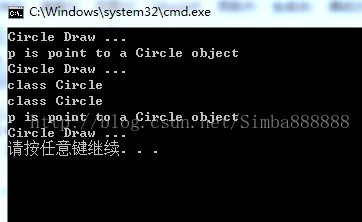
int main(void)
{
Shape *p;
Circle c;
p = &c;
p->Draw();
//使用dynamic_cast 的条件
//1、开启运行时类型信息;2、应用在具有多态关系的继承体系上;
if (dynamic_cast<Circle *>(p))
{
cout << "p is point to a Circle object" << endl;
Circle *cp = dynamic_cast<Circle *>(p); // 安全向下转型
cp->Draw(); //效率没有 p->Draw(); 高
}
else if (dynamic_cast<Square *>(p))
{
cout << "p is point to a Square object" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "p is point to a Other object" << endl;
}
cout << typeid(*p).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(Circle).name() << endl;
if (typeid(Circle).name() == typeid(*p).name())
{
cout << "p is point to a Circle object" << endl;
((Circle *)p)->Draw();
}
else if (typeid(Square).name() == typeid(*p).name())
{
cout << "p is point to a Circle object" << endl;
((Square *)p)->Draw();
}
else
{
cout << "p is point to a Other object" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
如上所述,dynamic_cast 和 typeid 操作符 都可以实现运行时类型识别。其中使用dynamic_cast 时需要开启运行时类型信息,在项目-》属性-》C/C++-》语言-》启用运行时类型信息。在使用typeid时需要注意的是返回的是type_info 对象的引用,且type_info 类的拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符都声明为私有,故不能这样写: type_info tf = typeid(Circle);
二、类与类之间的关系
Unified Modeling Language (UML)又称统一建模语言或标准建模语言,是始于1997年一个OMG标准,它是一个支持模型化和软件系统开发的图形化语言。
1、继承(泛化)Generalization

Manager 继承自Employee.
2、关联 Association,单向关联 DirectedAssociation

Order 作为Customer 的成员,如vector orders ;
3、聚合 Aggregation

class B
class A
{
public:
B* b_;
};当A释放时,不负责B的释放,也许B是被共享的。
4、组合 Composition

当Company 释放时要负责Department 的释放,Department 不是共享的。
5、依赖 Dependency

类A依赖于B:
从语义上来上是A use B,偶然的,临时的
B作为A的成员函数参数
B作为A的成员函数的局部变量
A的成员函数调用B的静态方法
比较5种关系:
继承体现的是类与类之间的纵向关系,其他4种体现的是类与类之间的横向关系。
关联强弱
依赖<关联<聚合<组合
继承(A is B)
关联、聚合、组合(A has B)
依赖(A use B)
参考:
C++ primer 第四版
Effective C++ 3rd
C++编程规范
转载自http://blog.csdn.net/jnu_simba/article/details/9320275
相关文章推荐
- 从零开始学C++之RTTI、dynamic_cast、typeid、类与类之间的关系uml
- 从零开始学C++之RTTI、dynamic_cast、typeid、类与类之间的关系uml
- 从零开始学C++之RTTI、dynamic_cast、typeid、类与类之间的关系uml
- RTTI、dynamic_cast、typeid、类与类之间的关系uml
- 【C++专题】virtual函数实现的多态、RTTI(dynamic_cast,typeid)、vtable中类型信息
- c++ 38 RTTI ,dynamic_cast ,typeid
- C++学习之多态篇(运行时类型识别--RTTI(typeid和dynamic_cast))
- C++的RTTI(dynamic_cast与typeid)
- C++ 运行时类型识别RTTI typeid<->dynamic_cast
- 标准c++的类型转换符之间的区别(static_cast,dynamic_cast,const_cast,reinterpret_cast)(转载)
- c\c++复习基础要点15----c++运行时类型识别 dynamic_cast typeid type_info
- typeid 与 dynamic_cast(C++学习)
- 浅议 Dynamic_cast 和 RTTI与虚函数表的关系
- C++中的RTTI与dynamic_cast<> static_cast<>
- C++ 使用dynamic_cast进行downcast时常会出现的问题 [RTTI]
- C++的RTTI和dynamic_cast
- typeidRTTI.cpp;dynamic_cast<Derive22&>(b2);
- (转)RTTI特性小究(dynamic_cast转换操作符和typeid操作符)
- 三十三、RTTI(runtime type information)、dynamic_cast运算符、typeid运算符、type_info
- RTTI(dynamic_cast与typeid)
