联合双边滤波器(joint bilateral filter) 代码及详细注释【OpenCV】
2016-10-19 11:52
561 查看
原理部分可以参看前一篇博客
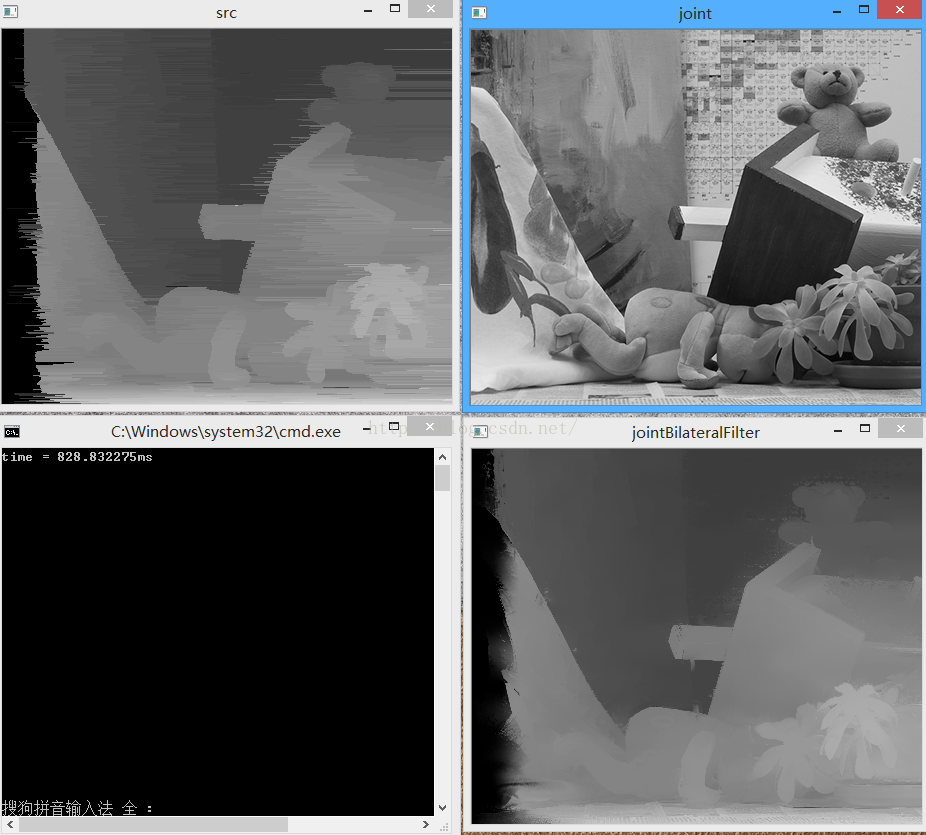
效果如图:
void jointBilateralFilter(const Mat &src, Mat &dst, int d, double sigma_color,
double sigma_space, Mat &joint = Mat(), int borderType =
BORDER_REPLICATE)
{
Size size = src.size();
if (dst.empty())
dst = Mat::zeros(src.size(), src.type());
CV_Assert(
(src.type() == CV_8UC1 || src.type() == CV_8UC3)
&& src.type() == dst.type() && src.size() == dst.size()
&& src.data != dst.data);
if (sigma_color <= 0)
sigma_color = 1;
if (sigma_space <= 0)
sigma_space = 1;
double gauss_color_coeff = -0.5 / (sigma_color * sigma_color);
double gauss_space_coeff = -0.5 / (sigma_space * sigma_space);
if (joint.empty())
src.copyTo(joint);
const int cn = src.channels();
const int cnj = joint.channels();
int radius;
if (d <= 0)
radius = cvRound(sigma_space * 1.5); // 根据 sigma_space 计算 radius
else
radius = d / 2;
radius = MAX(radius, 1);
d = radius * 2 + 1; // 重新计算 像素“矩形”邻域的直径d,确保是奇数
// 扩展 src 和 joint 长宽各2*radius
Mat jim;
Mat sim;
copyMakeBorder(joint, jim, radius, radius, radius, radius, borderType);
copyMakeBorder(src, sim, radius, radius, radius, radius, borderType);
// cnj: joint的通道数
vector<float> _color_weight(cnj * 256);
vector<float> _space_weight(d * d); // (2*radius + 1)^2
vector<int> _space_ofs_jnt(d * d);
vector<int> _space_ofs_src(d * d);
float *color_weight = &_color_weight[0];
float *space_weight = &_space_weight[0];
int *space_ofs_jnt = &_space_ofs_jnt[0];
int *space_ofs_src = &_space_ofs_src[0];
// initialize color-related bilateral filter coefficients
// 色差的高斯权重
for (int i = 0; i < 256 * cnj; i++)
color_weight[i] = (float) std::exp(i * i * gauss_color_coeff);
int maxk = 0; // 0 - (2*radius + 1)^2
// initialize space-related bilateral filter coefficients
for (int i = -radius; i <= radius; i++)
{
for (int j = -radius; j <= radius; j++)
{
double r = std::sqrt((double) i * i + (double) j * j);
if (r > radius)
continue;
space_weight[maxk] = (float) std::exp(r * r * gauss_space_coeff);
space_ofs_jnt[maxk] = (int) (i * jim.step + j * cnj); // joint 邻域内的相对坐标 (i, j)【偏移量】, 左上角为(-radius, -radius),右下角为(radius, radius)
space_ofs_src[maxk++] = (int) (i * sim.step + j * cn); // src 邻域内的相对坐标 (i, j)
}
}
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < size.height; i++)
{
const uchar *jptr = jim.data + (i + radius) * jim.step + radius * cnj; // &jim.ptr(i+radius)[radius]
const uchar *sptr = sim.data + (i + radius) * sim.step + radius * cn; // &sim.ptr(i+radius)[radius]
uchar *dptr = dst.data + i * dst.step; // dst.ptr(i)
// src 和 joint 通道数不同的四种情况
if (cn == 1 && cnj == 1)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size.width; j++)
{
float sum = 0, wsum = 0;
int val0 = jptr[j]; // jim.ptr(i + radius)[j + radius]
for (int k = 0; k < maxk; k++)
{
int val = jptr[j + space_ofs_src[k]]; // jim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[j + radius + offset_y]
int val2 = sptr[j + space_ofs_src[k]]; // sim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[j + radius + offset_y]
// 根据joint当前像素和邻域像素的 距离权重 和 色差权重,计算综合的权重
float w = space_weight[k]
* color_weight[std::abs(val - val0)];
sum += val2 * w; // 统计 src 邻域内的像素带权和
wsum += w; // 统计权重和
}
// overflow is not possible here => there is no need to use CV_CAST_8U
// 归一化 src 邻域内的像素带权和,并赋给 dst对应的像素
dptr[j] = (uchar) cvRound(sum / wsum);
}
}
else if (cn == 3 && cnj == 3)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size.width * 3; j += 3)
{
float sum_b = 0, sum_g = 0, sum_r = 0, wsum = 0;
int b0 = jptr[j], g0 = jptr[j + 1], r0 = jptr[j + 2]; // jim.ptr(i + radius)[j + radius][0...2]
for (int k = 0; k < maxk; k++)
{
const uchar *sptr_k = jptr + j + space_ofs_src[k];
const uchar *sptr_k2 = sptr + j + space_ofs_src[k];
int b = sptr_k[0], g = sptr_k[1], r = sptr_k[2]; // jim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[j + radius + offset_y][0...2]
float w = space_weight[k]
* color_weight[std::abs(b - b0) + std::abs(g - g0)
+ std::abs(r - r0)];
sum_b += sptr_k2[0] * w; // sim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[j + radius + offset_y][0...2]
sum_g += sptr_k2[1] * w;
sum_r += sptr_k2[2] * w;
wsum += w;
}
wsum = 1.f / wsum;
b0 = cvRound(sum_b * wsum);
g0 = cvRound(sum_g * wsum);
r0 = cvRound(sum_r * wsum);
dptr[j] = (uchar) b0;
dptr[j + 1] = (uchar) g0;
dptr[j + 2] = (uchar) r0;
}
}
else if (cn == 1 && cnj == 3)
{
for (int j = 0, l = 0; j < size.width * 3; j += 3, l++)
{
float sum_b = 0, wsum = 0;
int b0 = jptr[j], g0 = jptr[j + 1], r0 = jptr[j + 2]; // jim.ptr(i + radius)[j + radius][0...2]
for (int k = 0; k < maxk; k++)
{
int val = *(sptr + l + space_ofs_src[k]); // sim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[l + radius + offset_y]
const uchar *sptr_k = jptr + j + space_ofs_jnt[k];
int b = sptr_k[0], g = sptr_k[1], r = sptr_k[2]; // jim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[j + radius + offset_y][0...2]
float w = space_weight[k]
* color_weight[std::abs(b - b0) + std::abs(g - g0)
+ std::abs(r - r0)];
sum_b += val * w;
wsum += w;
}
wsum = 1.f / wsum;
b0 = cvRound(sum_b * wsum);
dptr[l] = (uchar) b0;
}
}
else if (cn == 3 && cnj == 1)
{
for (int j = 0, l = 0; j < size.width * 3; j += 3, l++)
{
float sum_b = 0, sum_g = 0, sum_r = 0, wsum = 0;
int val0 = jptr[l]; // jim.ptr(i + radius)[l + radius]
for (int k = 0; k < maxk; k++)
{
int val = jptr[l + space_ofs_jnt[k]]; // jim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[l + radius + offset_y]
const uchar *sptr_k = sptr + j + space_ofs_src[k]; // sim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[j + radius + offset_y]
float w = space_weight[k]
* color_weight[std::abs(val - val0)];
sum_b += sptr_k[0] * w; // sim.ptr(i + radius + offset_x)[j + radius + offset_y] [0...2]
sum_g += sptr_k[1] * w;
sum_r += sptr_k[2] * w;
wsum += w;
}
// overflow is not possible here => there is no need to use CV_CAST_8U
wsum = 1.f / wsum;
dptr[j] = (uchar) cvRound(sum_b * wsum);
dptr[j + 1] = (uchar) cvRound(sum_g * wsum);
dptr[j + 2] = (uchar) cvRound(sum_r * wsum);
}
}
}
}效果如图:

相关文章推荐
- 联合双边滤波器(joint bilateral filter)【OpenCV】
- opencv 之 icvCreateHidHaarClassifierCascade 分类器信息初始化函数部分详细代码注释。
- Coherence-Enhancing Shock Filters 代码及详细注释【OpenCV】
- 【VS开发】【图像处理】双边滤波器bilateral filter
- 泊松分布采样 (Poisson-Disk-Sample)代码及详细注释【OpenCV】
- 自适应直方图均衡(CLAHE) 代码及详细注释【OpenCV】
- opencv官方代码boost算法的详细注释
- L0 范数图像平滑(L0 Smooth) 代码及详细注释 【OpenCV】
- 用OpenCV的函数bilateralFilter做双边滤波~
- openCV实现多人脸检测,多眼部检测,完整代码和详细注释
- 彩色图像直方图均衡化及颜色直方图显示 opencv实现 完整代码及详细注释
- 彩色图像直方图均衡化及颜色直方图显示 opencv实现 完整代码及详细注释
- OpenCV中的DFT和iDFT的详细代码及注释
- 根据Merge Sort原理, 自己实现的归并排序算法+详细注释+代码(C#,C/C++) [分享]
- Win32 SDK窗口程序代码(含详细注释)
- 双边滤波器 OPENCV
- linux下创建守护进程(daemon process)代码-详细注释
- 初尝Linq,代码贴出来,有详细的注释
- asp.net画曲线图(折线图)代码 详细注释
- linux下创建守护进程(daemon process)代码-详细注释
